Cloud and Snow Discrimination for CCD Images of HJ-1A/B Constellation Based on Spectral Signature and Spatio-Temporal Context
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Study Area and Data
2.1. Study Area
2.2. HJ-1A/B Overview

2.3. Image Pre-Processing
2.3.1. Geometric Correction
2.3.2. Radiometric Calibration
2.3.3. HJ-1A/B CCD Time Series Stack
3. Methodology

3.1. Initial Spectral Test for Cloud and Snow
3.2. Separate Clouds from Snow Using the Temporal Context
3.2.1. Compositing for the Monthly Cloud-Free Reference Images

3.2.2. Post-Processing for the Composites

3.2.3. Cloud and Snow Discrimination by the Reference Images

3.3. Separate Clouds from Snow Using the Synthesize Spatial Context
3.3.1. Theoretical Basis
3.3.2. RCM Implement for Cloud and Snow Discrimination

3.4. Accuracy Assessment
4. Results and Analysis
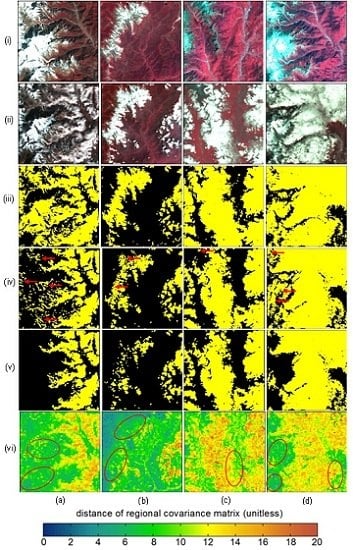
4.1. Mask Results



4.2. Performance of Each Stage for the Cloud and Snow Discrimination

4.3. Pixel Accuracy Assessment



5. Discussions
5.1. The Effectiveness of the Temporal Contextual Information for Cloud and Snow Discrimination
5.2. The Usefulness of Spatial Contextual Information for Cloud and Snow Discrimination
5.3. Error Sources of the Proposed Method
5.4. Applicability of the Developed Methods in the Future
6. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhu, Z.; Woodcock, C.E. Object-based cloud and cloud shadow detection in Landsat imagery. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 118, 83–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, A.; Jiang, J.; Bian, J.; Deng, W. Combining the matter element model with the associated function of probability transformation for multi-source remote sensing data classification in mountainous regions. ISPRS J. Photogramm. 2012, 67, 80–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.Q.; Coward, S.N.; Masek, J.G.; Thomas, N.; Zhu, Z.L.; Vogelmann, J.E. An automated approach for reconstructing recent forest disturbance history using dense Landsat time series stacks. Remote Sens. Environ. 2010, 114, 183–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, J.C.; Wulder, M.A.; Hobart, G.W.; Luther, J.E.; Hermosilla, T.; Griffiths, P.; Coops, N.C.; Hall, R.J.; Hostert, P.; Dyk, A.; et al. Pixel-based image compositing for large-area dense time series applications and science. Can. J. Remote Sens. 2014, 40, 192–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, D.P.; Ju, J.C.; Kline, K.; Scaramuzza, P.L.; Kovalskyy, V.; Hansen, M.; Loveland, T.R.; Vermote, E.; Zhang, C.S. Web-Enabled Landsat Data (WELD): Landsat ETM plus composited mosaics of the conterminous United States. Remote Sens. Environ. 2010, 114, 35–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baret, F.; Hagolle, O.; Geiger, B.; Bicheron, P.; Miras, B.; Huc, M.; Berthelot, B.; Niño, F.; Weiss, M.; Samain, O. Lai, fapar and fcover cyclopes global products derived from vegetation: Part 1: Principles of the algorithm. Remote Sens. Environ. 2007, 110, 275–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, A.; Huang, C.; Sun, G.; Shi, H.; Toney, C.; Zhu, Z.L.; Rollins, M.; Goward, S.; Masek, J. Modeling the height of young forests regenerating from recent disturbances in Mississippi using Landsat and ICEsat data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2011, 115, 1837–1849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyapustin, A.; Wang, Y.; Frey, R. An automatic cloud mask algorithm based on time series of MODIS measurements. J. Geophys. Res.-Atmos. 2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Woodcock, C.E. Automated cloud, cloud shadow, and snow detection in multitemporal Landsat data: An algorithm designed specifically for monitoring land cover change. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 152, 217–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Wang, S.; Woodcock, C.E. Improvement and expansion of the fmask algorithm: Cloud, cloud shadow, and snow detection for Landsats 4–7, 8, and Sentinel 2 images. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 159, 269–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Platnick, S.; King, M.D.; Ackerman, S.A.; Menzel, W.P.; Baum, B.A.; Riedi, J.C.; Frey, R.A. The MODIS cloud products: Algorithms and examples from terra. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2003, 41, 459–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovalskyy, V.; Roy, D. A one year Landsat 8 conterminous United States study of cirrus and non-cirrus clouds. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 564–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, H.F.; Li, H.F.; Qian, Y.; Zhang, L.P.; Yuan, Q.Q. An effective thin cloud removal procedure for visible remote sensing images. ISPRS J. Photogramm. 2014, 96, 224–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amato, U.; Antomadis, A.; Cuomo, V.; Cutillo, L.; Franzese, M.; Murino, L.; Serio, C. Statistical cloud detection from SEVIRI multispectral images. Remote Sens. Environ. 2008, 112, 750–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, M.C.; Roy, D.P.; Lindquist, E.; Adusei, B.; Justice, C.O.; Altstatt, A. A method for integrating MODIS and Landsat data for systematic monitoring of forest cover and change in the Congo basin. Remote Sens. Environ. 2008, 112, 2495–2513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.Q.; Thomas, N.; Goward, S.N.; Masek, J.G.; Zhu, Z.L.; Townshend, J.R.G.; Vogelmann, J.E. Automated masking of cloud and cloud shadow for forest change analysis using Landsat images. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2010, 31, 5449–5464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Woodcock, C.E.; Olofsson, P. Continuous monitoring of forest disturbance using all available Landsat imagery. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 122, 75–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dozier, J. Spectral signature of alpine snow cover from the Landsat Thematic Mapper. Remote Sens. Environ. 1989, 28, 9–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, D.K.; Riggs, G.A.; Salomonson, V.V. Development of methods for mapping global snow cover using moderate resolution imaging spectroradiometer data. Remote Sens. Environ. 1995, 54, 127–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, H.; Bindschadler, R. Cloud detection in Landsat imagery of ice sheets using shadow matching technique and automatic normalized difference snow index threshold value decision. Remote Sens. Environ. 2004, 91, 237–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vermote, E.; Saleous, N. Ledaps Surface Reflectance Product Description. 2007. Avaiable online: https://dwrgis.water.ca.gov/documents/269784/4654504/LEDAPS+Surface+Reflectance+Product+Description.pdf (accessed on 27 September 2015). [Google Scholar]
- Masek, J.G.; Vermote, E.F.; Saleous, N.E.; Wolfe, R.; Hall, F.G.; Huemmrich, K.F.; Gao, F.; Kutler, J.; Lim, T.K. A land surface reflectance dataset for north America, 1990–2000. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2006, 3, 68–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagolle, O.; Huc, M.; Pascual, D.V.; Dedieu, G. A multi-temporal method for cloud detection, applied to Formosat-2, Venmus, Landsat and Sentinel-2 images. Remote Sens. Environ. 2010, 114, 1747–1755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Goodwin, N.R.; Collett, L.J.; Denham, R.J.; Flood, N.; Tindall, D. Cloud and cloud shadow screening across queensland, australia: An automated method for Landsat TM/ETM Plus time series. Remote Sens. Environ. 2013, 134, 50–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tseng, D.C.; Tseng, H.T.; Chien, C.L. Automatic cloud removal from multitemporal SPOT images. Appl. Math. Comput. 2008, 205, 584–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tso, B.; Olsen, R.C. A contextual classification scheme based on MRF model with improved parameter estimation and multiscale fuzzy line process. Remote Sens. Environ. 2005, 97, 127–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, D.S.; Kelly, M.; Gong, P. A spatial-temporal approach to monitoring forest disease spread using multi-temporal high spatial resolution imagery. Remote Sens. Environ. 2006, 101, 167–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.-H.; Kuo, B.-C.; Lin, C.-T.; Huang, C.-S. A spatial–contextual support vector machine for remotely sensed image classification. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2012, 50, 784–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, G.P. On the mean accuracy of statistical pattern recognizers. IEEE Trans. Inform. Theory 1968, 14, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Dong, L.; Xiao, H.; Xu, M. A cloud image detection method based on SVM vector machine. Neurocomputing 2015, 169, 34–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasquez, R.E.; Manian, V.B. Texture-based cloud detection in MODIS images. Proc. SPIE 2003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Xiao, P.; Feng, X.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Z.; Jiang, L. Support vector machine-based decision tree for snow cover extraction in mountain areas using high spatial resolution remote sensing image. J. Appl. Remote Sens. 2014, 8, 084698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Racoviteanu, A.; Williams, M.W. Decision tree and texture analysis for mapping debris-covered glaciers in the Kangchenjunga area, eastern Himalaya. Remote Sens. 2012, 4, 3078–3109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Townshend, J.R.G.; Justice, C.O. Selecting the spatial-resolution of satellite sensors required for global monitoring of land transformations. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1988, 9, 187–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Chen, Y.; Wu, Y.; Shi, P.; She, J.; Zhou, P. Temporal-spatial variation and controls of soil respiration in different primary succession stages on glacier forehead in Gongga Mountain, China. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e42354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; He, Y.; Pang, H.; Yang, X.; Jia, W.; Zhang, N.; Wang, X.; Ning, B.; Yuan, L.; Song, B. Source of major anions and cations of snowpacks in Hailuogou No. 1 glacier, Mt. Gongga and Baishui No. 1 glacier, Mt. Yulong. J. Geogr. Sci. 2008, 18, 115–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Wu, C.; Li, Q.; Li, J. Chinese HJ-1A/B satellites and data characteristics. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2010, 53, 51–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Cui, T.W.; Qiu, Z.F.; Lin, C.S. A three-band semi-analytical model for deriving total suspended sediment concentration from HJ-1A/CCD data in turbid coastal waters. ISPRS J. Photogramm. 2014, 93, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, S.L.; Wu, B.F.; Yan, N.N.; Wang, H. Water body mapping method with HJ-1A/B satellite imagery. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. 2011, 13, 428–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- China Centre for Resources Satellite Data and Application. Avialable online: Http://www.Cresda.Com/site2/satellite/7117.Shtml (accessed on 27 September 2015).
- Bian, J.; Li, A.; Jin, H.; Lei, G.; Huang, C.; Li, M. Auto-registration and orthorecification algorithm for the time series HJ-1A/B CCD images. J. Mt. Sci.-Engl. 2013, 10, 754–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutman, G.; Huang, C.Q.; Chander, G.; Noojipady, P.; Masek, J.G. Assessment of the NASA-USGS Global Land Survey (GLS) datasets. Remote Sens. Environ. 2013, 134, 249–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolfe, R.E.; Nishihama, M.; Fleig, A.J.; Kuyper, J.A.; Roy, D.P.; Storey, J.C.; Patt, F.S. Achieving sub-pixel geolocation accuracy in support of MODIS land science. Remote Sens. Environ. 2002, 83, 31–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Chen, X.; Tian, L.; Feng, L. Tracking radiometric responsivity of optical sensors without on-board calibration systems-case of the Chinese HJ-1A/B CCD sensors. Opt. Express 2015, 23, 1829–1847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Z.; Li, A.; Bian, J.; Huang, C. An improved DDV method to retrieve AOT for HJ CCD image in typical mountainous areas. Spectrosc. Spect. Anal. 2015, 35, 1479–1487. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Bian, J.; Li, A.; Wang, Q.; Huang, C. Development of dense time series 30-m image products from the Chinese HJ-1A/B constellation: A case study in zoige plateau, china. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 16647–16671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez-Chova, L.; Camps-Valls, G.; Calpe-Maravilla, J.; Guanter, L.; Moreno, J. Cloud-screening algorithm for ENVISAT/MERIS multispectral images. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2007, 45, 4105–4118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Guindon, B.; Cihlar, J. An image transform to characterize and compensate for spatial variations in thin cloud contamination of Landsat images. Remote Sens. Environ. 2002, 82, 173–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goward, S.N.; Turner, S.; Dye, D.G.; Liang, S. The University-of-Maryland improved global vegetation index product. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1994, 15, 3365–3395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holben, B.N. Characteristics of maximum-value composite images from temporal AVHRR data. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1986, 7, 1417–1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, D.P. The impact of misregistration upon composited wide field of view satellite data and implications for change detection. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote 2000, 38, 2017–2032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, S.; Zhong, B.; Fang, H. Improved estimation of aerosol optical depth from MODIS imagery over land surfaces. Remote Sens. Environ. 2006, 104, 416–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Trishchenko, A.P.; Khlopenkov, K.V. Developing clear-sky, cloud and cloud shadow mask for producing clear-sky composites at 250-meter spatial resolution for the seven MODIS land bands over canada and north America. Remote Sens. Environ. 2008, 112, 4167–4185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flood, N. Seasonal composite Landsat TM/ETM+ images using the Medoid (a multi-dimensional median). Remote Sens. 2013, 5, 6481–6500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, J.H.; Li, A.N.; Song, M.Q.; Ma, L.Q.; Jiang, J.G. Reconstructing ndvi time-series data set of modis based on the Savitzky-Golay filter. J. Remote Sens. 2010, 14, 725–741. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.; Jonsson, P.; Tamura, M.; Gu, Z.H.; Matsushita, B.; Eklundh, L. A simple method for reconstructing a high-quality NDVI time-series data set based on the Savitzky-Golay filter. Remote Sens. Environ. 2004, 91, 332–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savitzky, A.; Golay, M.J.E. Smoothing and differentiation of data by simplified least squares procedure. Anal. Chem. 1964, 36, 1627–1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.Y.; Yuan, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Shi, C.M. Non-rigid object tracking in complex scenes. Pattern Recogn. Lett. 2009, 30, 98–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.G.; Liu, H.H.; Li, X.L. Target tracking for mobile robot platforms via object matching and background anti-matching. Robot. Auton. Syst. 2010, 58, 1197–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuzel, O.; Porikli, F.; Meer, P. Region covariance: A fast descriptor for detection and classification. Lect. Notes Comput. Sci. 2006, 3952, 589–600. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.H.; Liu, H.W. A hierarchical ship detection scheme for high-resolution SAR images. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2012, 50, 4173–4184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Förstner, W.; Moonen, B. A metric for covariance matrices. In Geodesy—The Challenge of the 3rd Millennium; Grafarend, W.E., Krumm, F.W., Schwarze, V.S., Eds.; Springer-Verlag: Berlin, Germany; Heidelberg, Germany, 2003; pp. 299–309. [Google Scholar]
- Haralick, R.M.; Shanmuga, K.; Dinstein, I. Textural features for image classification. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. 1973, SMC-3, 610–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powers, D.M. Evaluation: From precision, recall and f-measure to ROC, informedness, markedness and correlation. J. Mach. Learn. Technol. 2011, 2, 37–63. [Google Scholar]
- Derrien, M.; le Gléau, H. Improvement of cloud detection near sunrise and sunset by temporal-differencing and region-growing techniques with real-time SEVIRI. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2010, 31, 1765–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.P.; Huang, X.; Huang, B.; Li, P.X. A pixel shape index coupled with spectral information for classification of high spatial resolution remotely sensed imagery. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2006, 44, 2950–2961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fauvel, M.; Benediktsson, J.A.; Chanussot, J.; Sveinsson, J.R. Spectral and spatial classification of hyperspectral data using SVMS and morphological profiles. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2008, 46, 3804–3814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Zhang, L.; Li, P. A multiscale feature fusion approach for classification of very high resolution satellite imagery based on wavelet transform. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2008, 29, 5923–5941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.F.; Zhang, L.P.; Shen, H.F.; Li, P.X. A variational gradient-based fusion method for visible and SWIR imagery. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 2012, 78, 947–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drusch, M.; del Bello, U.; Carlier, S.; Colin, O.; Fernandez, V.; Gascon, F.; Hoersch, B.; Isola, C.; Laberinti, P.; Martimort, P.; et al. Sentinel-2: ESA’s optical high-resolution mission for GMES operational services. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 120, 25–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons by Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bian, J.; Li, A.; Liu, Q.; Huang, C. Cloud and Snow Discrimination for CCD Images of HJ-1A/B Constellation Based on Spectral Signature and Spatio-Temporal Context. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 31. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs8010031
Bian J, Li A, Liu Q, Huang C. Cloud and Snow Discrimination for CCD Images of HJ-1A/B Constellation Based on Spectral Signature and Spatio-Temporal Context. Remote Sensing. 2016; 8(1):31. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs8010031
Chicago/Turabian StyleBian, Jinhu, Ainong Li, Qiannan Liu, and Chengquan Huang. 2016. "Cloud and Snow Discrimination for CCD Images of HJ-1A/B Constellation Based on Spectral Signature and Spatio-Temporal Context" Remote Sensing 8, no. 1: 31. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs8010031
APA StyleBian, J., Li, A., Liu, Q., & Huang, C. (2016). Cloud and Snow Discrimination for CCD Images of HJ-1A/B Constellation Based on Spectral Signature and Spatio-Temporal Context. Remote Sensing, 8(1), 31. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs8010031