Similarity and Error Intercomparison of the GPM and Its Predecessor-TRMM Multisatellite Precipitation Analysis Using the Best Available Hourly Gauge Network over the Tibetan Plateau
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
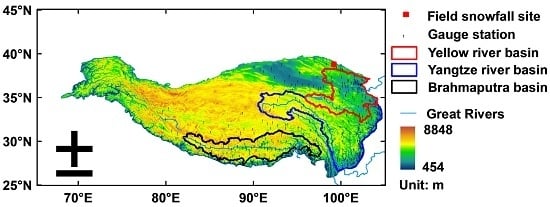
2.1. Study Region
2.2. Satellite Retrievals and Gauge Data
2.3. Evaluation Indicators
3. Results
3.1. Similarity of Spatial Rainfall Patterns
3.2. Pixel-Scale Error Intercomparison
3.3. Basin-Scale Error Intercomparison
3.4. Elevation Impact Analyses
3.5. Latitude Impact Analyses
3.6. Snowfall Regime Analyses
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
- (1)
- Overall, IMERG and 3B42V7 show similar rainfall patterns across the TP, with a decreasing trend from the southeast to the northwest. However, IMERG performs better, with slightly higher correlation and lower bias than 3B42V7 at the three-hourly scale, although both datasets show similar spatial patterns for all assessment indicators.
- (2)
- As elevations increase, there is no obvious difference in CC between IMERG and 3B42V7. However, IMERG shows slightly lower POD for elevations above 4200 m and significantly smaller FAR for elevations below 3000 m. In addition, higher consistency is detected from the IMERG products for light rainfall than 3B42V7 estimates.
- (3)
- The latitudinal rainfall gradients of the Indian monsoon dynamics are successfully detected by the two satellite estimates. In particular, the relatively light rain from the early and end Indian monsoon moisture surge events is often not observed by the sparse gauges over the TP.
- (4)
- Over high and complex TP regions, this study provides the very first understanding of GPM at the hourly scale and confirms the desired results that the GPM-era Day-1 Level-3 products perform at least equally well, often times better for light and solid precipitation at high elevations, than the TRMM V7 mature products.
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CC | Correlation Coefficients |
| CMA | China Meteorological Administration |
| CMORPH | Climate Prediction Center (CPC) MORPHing Technique |
| CREST | Coupled Routing and Excess STorage |
| DPR | Dual-frequency Precipitation Radar |
| FAR | False Alarm Ratio |
| GMI | GPM Microwave Imager |
| IDW | Inverse Distance Weighting |
| IFOV | Instantaneous Field Of View |
| IMERG | Integrated Multi-satellitE Retrievals for the GPM mission |
| GPCC | Global Precipitation Climatology Center |
| GPM | Global Precipitation Measurement |
| GPROF | Goddard Profiling Algorithm |
| PERSIANN | Precipitation Estimation from Remotely Sensed Information using Artificial Neural Networks |
| PERSIANN-CCS | PERSIANN-Cloud Classification System |
| POD | Probability Of Detection |
| RB | Relative Bias |
| RMSE | Root Mean Square Error |
| RT | Real Time |
| SD | Standard Deviation |
| TP | Tibetan Plateau |
| TRMM | Tropical Rainfall Measuring Mission |
| TMPR | TRMM Multi-satellite Precipitation Analysis |
| VIC | Variable Infiltration Capacity |
References
- Tong, K.; Su, F.; Yang, D.; Zhang, L.; Hao, Z. Tibetan Plateau precipitation as depicted by gauge observations, reanalysis and satellite retrievals. Int. J. Climatol. 2014, 34, 265–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, D.; Farhan, S. Precipitation bias variability versus various gauges under different climatic conditions over the Third Pole Environment (TPE) region. Int. J. Climatol. 2015, 35, 1201–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinku, T.; Ceccato, P.; Connor, S. Challenges of satellite rainfall estimation over mountainous and arid parts of east Africa. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2011, 32, 5965–5979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorooshian, S.; Kouchak, A.; Arkin, P.; Eylander, J.; Foufoula, E.; Harmon, R.; Hendrickx, J.; Imam, B.; Kuligowski, R.; Skahill, B.; et al. Advancing the remote sensing of precipitation. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2011, 92, 1271–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Peters-Lidard, C. A global map of uncertainties in satellite-based precipitation measurements. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2010, 14, 139–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, A.; Kakar, R.; Neeck, S.; Azarbarzin, A.; Kummerow, C.; Kojima, M.; Oki, R.; Nakamura, K.; Iguchi, T. The Global Precipitation Measurement Mission. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2014, 95, 701–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Z.; Liu, X.; Zhang, X.; Chung, C. Using a geographic information system to improve special sensor microwave imager (SSM/I) precipitation estimates over the Tibetan Plateau. J. Geophys. Res. 2004, 109, D03110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Z.; Zhang, X.; Liu, X.; Colella, M.; Chen, X. An assessment of the biases of satellite rainfall estimates over the Tibetan Plateau and correction methods based on topographic analysis. J. Hydrometeorol. 2008, 9, 301–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Liu, M. Evaluation of high-resolution satellite precipitation products using rain gauge observations over the Tibetan Plateau. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2013, 17, 837–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Xiong, A.; Hong, Y.; Yu, J.; Pan, Y.; Chen, Z.; Saharia, M. Uncertainty analysis of five satellite-based precipitation products and evaluation of three optimally merged multi-algorithm products over the Tibetan Plateau. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2014, 35, 6843–6858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, K.; Su, F.; Yang, D.; Hao, Z. Evaluation of satellite precipitation retrievals and their potential utilities in hydrologic modeling over the Tibetan Plateau. J. Hydrol. 2014, 519, 423–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Hong, Y.; Cao, Q.; Gourley, J.J.; Kirstetter, P.; Yong, B.; Tian, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Shen, Y.; Hu, J.; et al. Similarity and difference of the two successive V6 and V7 TRMM multisatellite precipitation analysis performance over China. J. Geophys. Res. 2013, 118, 13060–13074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, B.; Yang, D.; Ding, Y.; Han, T.; Koike, T. A bias-corrected precipitation climatology for China. J. Hydrometeorol. 2004, 5, 1147–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, Q.; Kang, S.; Ren, G.; Fraedrich, K.; Pepin, N.; Yan, Y.; Ma, L. Observed changes in snow depth and number of snow days in the eastern and central Tibetan Plateau. Clim. Res. 2011, 46, 171–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Xiong, A.; Wang, Y.; Xie, P. Performance of high-resolution satellite precipitation products over China. J. Geophys. Res. 2010, 115, D02114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, J. China: The third pole. Nat. News 2008, 454, 393–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, T.; Thompson, L.; Yang, W.; Yu, W.; Gao, Y.; Guo, X.; Yang, X.; Duan, K.; Zhao, H.; Xu, B.; et al. Different glacier status with atmospheric circulations in Tibetan Plateau and surroundings. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2012, 2, 663–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huffman, G.; Bolvin, D.; Braithwaite, D.; Hsu, K.; Joyce, R.; Xie, P. NASA Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) Integrated Multi-Satellie Retrievals for GPM (IMERG); Algorithm Theoretical Basis Document, Version 4.4; NASA: Greenbelt, MD, USA, 2014; p. 30. [Google Scholar]
- GPM Data Downloads. Available online: http://pmm.nasa.gov/data-access/downloads/gpm (accessed on 28 March 2016).
- Joyce, R.; Xie, P.; Janowiak, J. Kalman filter–based CMORPH. J. Hydrometeorol. 2011, 12, 1547–1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, Y.; Gochis, D.; Cheng, J.; Hsu, K.; Sorooshian, S. Evaluation of PERSIANN-CCS rainfall measurement using the NAME event rain gauge network. J. Hydrometeorol. 2007, 8, 469–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huffman, G.; Bolvin, D.; Nelkin, E.; Wolff, D.; Adler, R.; Gu, G.; Hong, Y.; Bowman, K.; Stocker, E. The TRMM Multisatellite Precipitation Analysis (TMPA): Quasi-global, multiyear, combined-sensor precipitation estimates at fine scales. J. Hydrometeorol. 2007, 8, 38–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habib, E.; Henschke, A.; Adler, R. Evaluation of TMPA satellite-based research and real-time rainfall estimates during six tropical-related heavy rainfall events over Louisiana, USA. Atmos. Res. 2009, 94, 373–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yong, B.; Hong, Y.; Ren, L.; Gourley, J.; Huffman, G.; Chen, X.; Wang, W.; Khan, S. Assessment of evolving TRMM-based multisatellite real-time precipitation estimation methods and their impacts on hydrologic precipitation in a high latitude basin. J. Geophys. Res. 2012, 117, D09108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Liu, S.; Mo, X.; Peng, B.; Qiu, J.; Li, M.; Liu, C.; Wang, Z.; Bauer-Gottwein, P. Evaluation of remotely sensed precipitation and its performance for streamflow simulations in basins of the southeast Tibetan Plateau. J. Hydrometeorol. 2015, 16, 2577–2594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Z.; Zhao, P.; Zhang, Q. Quality control procedures for hourly precipitation data from automatic weather stations in China. Meteorol. Mon. 2010, 36, 123–132. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Shen, Y.; Zhao, P.; Pan, Y.; Yu, J. A high spatiotemporal gauge-satellite merged precipitation analysis over China. J. Geophys. Res. 2014, 119, 3063–3075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.; Liu, J.; Kang, E.; Yang, Y.; Han, C.; Liu, Z.; Song, Y.; Qing, W.; Zhu, P. Precipitation measurement intercomparison in the Qilian Mountains, north-eastern Tibetan Plateau. Cryosphere 2015, 9, 1995–2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebert, E.; Janowiak, J.; Kidd, C. Comparison of near-real-time precipitation estimates from satellite observations and numerical models. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2007, 88, 47–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Peters-Lidard, C.; Eylander, J.; Joyce, R.; Huffman, G.; Adler, R.; Hsu, K.; Turk, F.; Garcia, M.; Zeng, J. Component analysis of errors in satellite-based precipitation estimates. J. Geophys. Res. 2009, 114, D24101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, M.; Peters-Lidard, C.; Goodrich, D. Spatial interpolation of precipitation in a dense gauge network for monsoon storm events in the southwestern United States. Water Resour. Res. 2008, 44, W05S13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yong, B.; Ren, L.; Hong, Y.; Wang, J.; Gourley, J.; Jiang, S.; Chen, X.; Wang, W. Hydrologic evaluation of multisatellite precipitation analysis standard precipitation products in basins beyond its inclined latitude band: A case study in Laohahe basin, China. Water Resour. Res. 2010, 46, W07542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bajracharya, S.; Palash, W.; Shrestha, M.; Khadgi, V.; Duo, C.; Das, P.; Dorji, C. Systematic evaluation of satellite-based rainfall products over the Brahmaputra basin for hydrologic applications. Adv. Meteorol. 2015, 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, G.; Zeng, Z.; Guo, X.; Long, D.; Yong, B.; Hong, Y. Statistical and hydrological comparison between IMERG and TMPA products over a mid-latitude basin: Is GPM a good successor for TRMM. J. Hydrometeorol. 2016, 17, 121–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandwell, D. Biharmonic spline interpolation of GEOS-3 and SEASAT altimeter data. Geophys. Res. Lett. 1987, 14, 139–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Dai, Y. Characteristics of Northwest China rainfall intensity in recent 50 years. Chin. J. Atmos. Sci. 2008, 33, 923–935. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Gochis, D.; Jimenez, A.; Watts, C.; Garatuza-Payan, J.; Shuttleworth, W. Analysis of 2002 and 2003 warm-season precipitation from the North American Monsoon Experiment event rain gauge network. Mon. Weather Rev. 2004, 132, 2938–2953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, X.; Hong, Y.; Limaye, A.S.; Gourley, J.J.; Huffman, G.J.; Khan, S.I.; Dorji, C.; Chen, S. Statistical and hydrological evaluation of TRMM-based Multi-satellite Precipitation Analysis over the Wangchu Basin of Bhutan: Are the latest satellite precipitation products 3B42V7 ready for use in ungauged basins? J. Hydrol. 2013, 499, 91–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, F.; Gao, H.; Huffman, G.J.; Lettenmaier, D.P. Potential utility of the real-time TMPA-RT precipitation estimates in streamflow prediction. J. Hydrometeorol. 2011, 12, 444–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Z.; Tong, K.; Liu, X.; Zhang, L. Capability of TMPA products to simulate streamflow in upper Yellow and Yangtze River basins on Tibetan Plateau. Water Sci. Eng. 2014, 7, 237–249. [Google Scholar]
- Yong, B.; Liu, D.; Gourley, J.; Tian, Y.; Huffman, G.; Ren, L.; Hong, Y. Global view of real-time TRMM Multisatellite precipitation analysis: Implications for its successor Global Precipitation Measurement mission. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2015, 96, 283–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinku, T.; Chidzambwa, S.; Ceccato, P.; Connor, S.; Ropelewski, C. Validation of high-resolution satellite rainfall products over complex terrain in Africa. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2008, 29, 4097–4110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shige, S.; Kida, S.; Ashiwake, H.; Kubota, T.; Aonashi, K. Improvement of TMI rain retrievals in mountainous areas. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 2013, 52, 242–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behrangi, A.; Andreadis, K.; Fisher, J.B.; Turk, F.J.; Granger, S.; Painter, T.; Das, N. Satellite-based precipitation estimation and its application for streamflow prediction over mountainous western U.S. basins. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 2014, 53, 2823–2842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, T.; Masson-Delmotte, V.; Gao, J.; Yu, W.; Yang, X.; Risi, C.; Sturm, C.; Werner, M.; Zhao, H.; He, Y.; et al. A review of climatic controls on δ18O in precipitation over the Tibetan Plateau: Observations and simulations. Rev. Geophys. 2013, 51, 525–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]










| CC | RMSE (mm) | RB (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hourly | IMERG | 0.32 | 2.94 | 30.6 |
| 3-Hourly | IMERG | 0.45 | 3.26 | 28.1 |
| 3B42V7 | 0.42 | 3.47 | 48.6 |
| Minimum (%) | Mean (%) | Maximum (%) | SD (%) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Yellow River | hourly | IMERG | −40.5 | 4.4 | 236.2 | 28.7 |
| 3-hourly | IMERG | −40.3 | 3.7 | 149.0 | 26.1 | |
| 3B42V7 | −33.1 | 5.8 | 192.9 | 24.2 | ||
| Yangtze River | hourly | IMERG | −46.9 | 12.0 | 118.2 | 21.7 |
| 3-hourly | IMERG | −46.8 | 10.8 | 118.2 | 20.4 | |
| 3B42V7 | −35.4 | 13.8 | 129.3 | 19.4 | ||
| Brahmaputra | hourly | IMERG | −77.8 | 35.6 | 422.6 | 49.9 |
| 3-hourly | IMERG | −77.7 | 35.6 | 410.8 | 49.5 | |
| 3B42V7 | −41.0 | 92.6 | 340.3 | 59.6 |
| Date | IMERG (mm) | Field Snowfall | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Total Precipitation | Snowfall | Observation (mm) | |
| 1 April 2014 | 0.2 | 0.2 | 2.4 |
| 10 October 2014 | 18.1 | 11.0 | 9.4 |
| 11 October 2014 | 2.0 | 2.0 | 6.3 |
| 30 October 2014 | 1.1 | 1.1 | 1.7 |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ma, Y.; Tang, G.; Long, D.; Yong, B.; Zhong, L.; Wan, W.; Hong, Y. Similarity and Error Intercomparison of the GPM and Its Predecessor-TRMM Multisatellite Precipitation Analysis Using the Best Available Hourly Gauge Network over the Tibetan Plateau. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 569. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs8070569
Ma Y, Tang G, Long D, Yong B, Zhong L, Wan W, Hong Y. Similarity and Error Intercomparison of the GPM and Its Predecessor-TRMM Multisatellite Precipitation Analysis Using the Best Available Hourly Gauge Network over the Tibetan Plateau. Remote Sensing. 2016; 8(7):569. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs8070569
Chicago/Turabian StyleMa, Yingzhao, Guoqiang Tang, Di Long, Bin Yong, Lingzhi Zhong, Wei Wan, and Yang Hong. 2016. "Similarity and Error Intercomparison of the GPM and Its Predecessor-TRMM Multisatellite Precipitation Analysis Using the Best Available Hourly Gauge Network over the Tibetan Plateau" Remote Sensing 8, no. 7: 569. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs8070569
APA StyleMa, Y., Tang, G., Long, D., Yong, B., Zhong, L., Wan, W., & Hong, Y. (2016). Similarity and Error Intercomparison of the GPM and Its Predecessor-TRMM Multisatellite Precipitation Analysis Using the Best Available Hourly Gauge Network over the Tibetan Plateau. Remote Sensing, 8(7), 569. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs8070569