CloudSat-Based Assessment of GPM Microwave Imager Snowfall Observation Capabilities
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methodology: GMI-CPR Dataset Description
3. Results
3.1. Case Studies
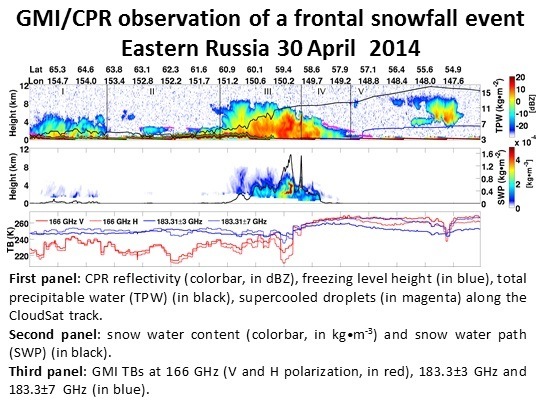
3.1.1. Case 1: Intense Snowfall Event on 30 April 2014
3.1.2. Case 2: Orographic Precipitation Event on 14 December 2014
3.1.3. Case 3: Synoptic Snowfall Event over the Labrador Sea 27 March 2014
3.2. Analysis of the 166 GHz Channel Capabilities for Snowfall Detection
3.2.1. Regression Tree Analysis of 166 GHz ∆TB
3.2.2. Analysis of 166 GHz ∆TB and TB Sensitivity to CPR Snowfall
3.2.3. Impact of Supercooled Droplets on 166 GHz TB and ∆TB
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions and Future Work
- A snowfall case study analysis;
- A regression tree statistical analysis applied to the entire GMI-CPR snowfall dataset illustrating 166 GHz ∆TB polarization signal variability related to various parameters and associated snowfall detection efficacy applications; and
- A 166 GHz ∆TB, TB, and snow water path relationship analysis for various surface types and highlighting supercooled water layer effects.
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Skofronick-Jackson, G.; Johnson, B.T. Surface and atmospheric contributions to passive microwave brightness temperatures for falling snow events. J. Geophys. Res. 2011, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, Y.; Wang, N.-Y.; Ferraro, R.; Rudlosky, S. Quantifying the Snowfall Detection Performance of the GPM Microwave Imager Channels over Land. J. Hydrometeorol. 2017, 18, 729–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulie, M.S.; Bennartz, R.; Greenwald, T.J.; Chen, Y.; Weng, F. Uncertainties in Microwave Properties of Frozen Precipitation: Implications for Remote Sensing and Data Assimilation. J. Atmos. Sci. 2010, 67, 3471–3487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prigent, C.; Aires, F.; Rossow, W.B. Land Surface Microwave Emissivities over the Globe for a Decade. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2006, 87, 1573–1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turk, F.J.; Haddad, Z.S.; You, Y. Principal Components of Multifrequency Microwave Land Surface Emissivities. Part I: Estimation under Clear and Precipitating Conditions. J. Hydrometeorol. 2014, 15, 3–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kongoli, C.; Meng, H.; Dong, J.; Ferraro, R. A snowfall detection algorithm over land utilizing high-frequency passive microwave measurements-Application to ATMS: A Snowfall Detection Algorithm over Land. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2015, 120, 1918–1932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G. Deriving snow cloud characteristics from CloudSat observations. J. Geophys. Res. 2008, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulie, M.S.; Bennartz, R. Utilizing Spaceborne Radars to Retrieve Dry Snowfall. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 2009, 48, 2564–2580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulie, M.S.; Milani, L.; Wood, N.B.; Tushaus, S.A.; Bennartz, R.; L’Ecuyer, T.S. A Shallow Cumuliform Snowfall Census Using Spaceborne Radar. J. Hydrometeorol. 2016, 17, 1261–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spencer, R.W.; Goodman, H.M.; Hood, R.E. Precipitation Retrieval over Land and Ocean with the SSM/I: Identification and Characteristics of the Scattering Signal. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 1989, 6, 254–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennartz, R.; Petty, G.W. The Sensitivity of Microwave Remote Sensing Observations of Precipitation to Ice Particle Size Distributions. J. Appl. Meteorol. 2001, 40, 345–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petty, G.W. Physical retrievals of over-ocean rain rate from multichannel microwave imagery. Part I: Theoretical characteristics of normalized polarization and scattering indices. Meteorol. Atmos. Phys. 1994, 54, 79–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, K.-S.; Olson, W.S.; Johnson, B.T.; Grecu, M.; Tian, L.; Clune, T.L.; van Aartsen, B.H.; Heymsfield, A.J.; Liao, L.; Meneghini, R. The Microwave Radiative Properties of Falling Snow Derived from Nonspherical Ice Particle Models. Part I: An Extensive Database of Simulated Pristine Crystals and Aggregate Particles, and Their Scattering Properties. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 2016, 55, 691–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olson, W.S.; Tian, L.; Grecu, M.; Kuo, K.-S.; Johnson, B.T.; Heymsfield, A.J.; Bansemer, A.; Heymsfield, G.M.; Wang, J.R.; Meneghini, R. The Microwave Radiative Properties of Falling Snow Derived from Nonspherical Ice Particle Models. Part II: Initial Testing Using Radar, Radiometer and In Situ Observations. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 2016, 55, 709–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skofronick-Jackson, G.M.; Kim, M.-J.; Weinman, J.A.; Chang, D.-E. A physical model to determine snowfall over land by microwave radiometry. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2004, 42, 1047–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennartz, R.; Bauer, P. Sensitivity of microwave radiances at 85–183 GHz to precipitating ice particles. Radio Sci. 2003, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Michele, S.; Bauer, P. Passive microwave radiometer channel selection based on cloud and precipitation information content. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2006, 132, 1299–1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebtehaj, A.M.; Kummerow, C.D. Microwave retrievals of terrestrial precipitation over snow-covered surfaces: A lesson from the GPM satellite. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2017, 44, 6154–6162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kneifel, S.; Löhnert, U.; Battaglia, A.; Crewell, S.; Siebler, D. Snow scattering signals in ground-based passive microwave radiometer measurements. J. Geophys. Res. 2010, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xie, X.; Löhnert, U.; Kneifel, S.; Crewell, S. Snow particle orientation observed by ground-based microwave radiometry. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2012, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kongoli, C.; Pellegrino, P.; Ferraro, R.R.; Grody, N.C.; Meng, H. A new snowfall detection algorithm over land using measurements from the Advanced Microwave Sounding Unit (AMSU). Geophys. Res. Lett. 2003, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surussavadee, C.; Staelin, D.H. Satellite Retrievals of Arctic and Equatorial Rain and Snowfall Rates Using Millimeter Wavelengths. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2009, 47, 3697–3707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noh, Y.-J.; Liu, G.; Jones, A.S.; Vonder Haar, T.H. Toward snowfall retrieval over land by combining satellite and in situ measurements. J. Geophys. Res. 2009, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kummerow, C.D.; Randel, D.L.; Kulie, M.; Wang, N.-Y.; Ferraro, R.; Joseph Munchak, S.; Petkovic, V. The Evolution of the Goddard Profiling Algorithm to a Fully Parametric Scheme. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2015, 32, 2265–2280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, J.; Wu, D.L. Microphysical properties of frozen particles inferred from Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) Microwave Imager (GMI) polarimetric measurements. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2017, 17, 2741–2757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boening, C.; Lebsock, M.; Landerer, F.; Stephens, G. Snowfall-driven mass change on the East Antarctic ice sheet. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2012, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behrangi, A.; Christensen, M.; Richardson, M.; Lebsock, M.; Stephens, G.; Huffman, G.J.; Bolvin, D.; Adler, R.F.; Gardner, A.; Lambrigtsen, B.; et al. Status of high-latitude precipitation estimates from observations and reanalyses. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2016, 121, 4468–4486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casella, D.; Panegrossi, G.; Sanò, P.; Marra, A.C.; Dietrich, S.; Johnson, B.T.; Kulie, M.S. Evaluation of the GPM-DPR snowfall detection capability: Comparison with CloudSat-CPR. Atmos. Res. 2017, 197, 64–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- L’Ecuyer, T.S.; Jiang, J.H. Touring the atmosphere aboard the A-Train. Phys. Today 2010, 63, 36–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palerme, C.; Kay, J.E.; Genthon, C.; L’Ecuyer, T.; Wood, N.B.; Claud, C. How much snow falls on the Antarctic ice sheet? Cryosphere 2014, 8, 1577–1587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, G.; Seo, E.-K.; Fu, Y. Liquid water in snowing clouds: Implications for satellite remote sensing of snowfall. Atmos. Res. 2013, 131, 60–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milani, L.; Kulie, M.S.; Casella, D.; Dietrich, S.; L’Ecuyer, T.S.; Panegrossi, G.; Porcù, F.; Sanò, P.; Wood, N.B. CloudSat Snowfall Estimates over Antarctica and the Southern Ocean: An Assessment of Independent Retrieval Methodologies and Multi-Year Snowfall Analysis. Atmos. Res. 2017. under review. [Google Scholar]
- Turk, F.J. CloudSat-GPM Coincidence Dataset. 2016. Available online: https://pmm.nasa.gov/sites/default/files/document_files/CSATGPM_COIN_ATBD.pdf (accessed on 4 December 2017).
- Grecu, M.; Olson, W.S.; Munchak, S.J.; Ringerud, S.; Liao, L.; Haddad, Z.; Kelley, B.L.; McLaughlin, S.F. The GPM Combined Algorithm. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2016, 33, 2225–2245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iguchi, T.; Seto, S.; Meneghini, R.; Yoshida, N.; Awaka, J.; Kubota, T. GPM/DPR Level-2 Algorithm Theoretical Basis Document. 2016. Available online: http://www.eorc.jaxa.jp/GPM/doc/algorithm/ATBD_DPR_2015_whole_2a.pdf (accessed on 4 December 2017).
- Wood, N.B.; L’Ecuyer, T.S.; Bliven, F.L.; Stephens, G.L. Characterization of video disdrometer uncertainties and impacts on estimates of snowfall rate and radar reflectivity. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2013, 6, 3635–3648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, N.B.; L’Ecuyer, T.S.; Heymsfield, A.J.; Stephens, G.L.; Hudak, D.R.; Rodriguez, P. Estimating snow microphysical properties using collocated multisensor observations. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2014, 119, 8941–8961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiley, M.J.; Kulie, M.S.; Bennartz, R. Uncertainty analysis for CloudSat snowfall retrievals. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 2011, 50, 399–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Hong, Y.; Kulie, M.; Behrangi, A.; Stepanian, P.M.; Cao, Q.; You, Y.; Zhang, J.; Hu, J.; Zhang, X. Comparison of snowfall estimates from the NASA CloudSat Cloud Profiling Radar and NOAA/NSSL Multi-Radar Multi-Sensor System. J. Hydrol. 2016, 3644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delanoë, J.; Hogan, R.J. A variational scheme for retrieving ice cloud properties from combined radar, lidar, and infrared radiometer. J. Geophys. Res. 2008, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delanoë, J.; Hogan, R.J. Combined CloudSat-CALIPSO-MODIS retrievals of the properties of ice clouds. J. Geophys. Res. 2010, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, D.K.; Riggs, G.A.; Salomonson, V.V.; DiGirolamo, N.E.; Bayr, K.J. MODIS snow-cover products. Remote Sens. Environ. 2002, 83, 181–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spreen, G.; Kaleschke, L.; Heygster, G. Sea ice remote sensing using AMSR-E 89-GHz channels. J. Geophys. Res. 2008, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Seo, E.-K. Detecting snowfall over land by satellite high-frequency microwave observations: The lack of scattering signature and a statistical approach. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2013, 118, 1376–1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breiman, L.; Friedman, J.H.; Olshen, R.A.; Stone, C.J. Classification and Regression Trees; Chapman & Hall/CRC: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1984; p. 368. [Google Scholar]
- Therneau, T.M.; Atkinson, E.J. An Introduction to Recursive Partitioning Using the Rpart Routines; Mayo Clinic: Rochester, MN, USA, 1997; p. 452. [Google Scholar]
- Ceccaldi, M.; Delanoë, J.; Hogan, R.J.; Pounder, N.L.; Protat, A.; Pelon, J. From CloudSat-CALIPSO to EarthCare: Evolution of the DARDAR cloud classification and its comparison to airborne radar-lidar observations. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2013, 118, 7962–7981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NASA Precipitation Processing System. 2017. Available online: ftp://arthurhou.pps.eosdis.nasa.gov (accessed on 12 October 2017).
- CloudSat Product Website. 2017. Available online: ftp.cloudsat.cira.colostate.edu (accessed on 12 October 2017).
- DARDAR Product Website. 2016. Available online: http://www.icare.univ-lille1.fr/projects/dardar (accessed on 12 October 2017).
- AMSR2 Sea Ice Dataset. 2017. Available online: https://seaice.uni-bremen.de/sea-ice-concentration/ (accessed on 12 October 2017).









| Source | Sensor/Model | Product | Main Variables |
|---|---|---|---|
| GPM | GMI | 1C-R V5A | Brightness temperatures (TBs) (K) |
| GPM | GMI | GPROF V4 and V5 | Surface precipitation rate (mm·h−1) Liquid fraction (V4) (%) Frozen precipitation rate (V5) (mm·h−1) |
| CloudSat | CPR | 2C-SNOW-PROFILE V4 | Equivalent radar reflectivity factor (Z) (dBZ) Snow water content (SWC) (kg·m−3) Surface snowfall rate (mm·h−1) |
| CloudSat | CPR | 2C-PRECIP-COLUMN V4 | Surface precipitation rate (mm·h−1) Liquid fraction (%) |
| CloudSat | CPR | 2B-CLOUD-CLASS V4 | Surface type Cloud type |
| CloudSat | ECMWF | ECMWF-AUX V4 | 2 m temperature (T2m) (K) Surface pressure (hPa) Total precipitable water (TPW) (kg·m−2) |
| Icare/University of Lille 1 | CALIPSO/CPR | DARDAR | Ice water content (IWC) (kg·m−3) Phase/microphysics classes |
| University of Bremen | AMSR2 | ASI | Daily sea-ice concentration (%) |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Panegrossi, G.; Rysman, J.-F.; Casella, D.; Marra, A.C.; Sanò, P.; Kulie, M.S. CloudSat-Based Assessment of GPM Microwave Imager Snowfall Observation Capabilities. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 1263. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs9121263
Panegrossi G, Rysman J-F, Casella D, Marra AC, Sanò P, Kulie MS. CloudSat-Based Assessment of GPM Microwave Imager Snowfall Observation Capabilities. Remote Sensing. 2017; 9(12):1263. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs9121263
Chicago/Turabian StylePanegrossi, Giulia, Jean-François Rysman, Daniele Casella, Anna Cinzia Marra, Paolo Sanò, and Mark S. Kulie. 2017. "CloudSat-Based Assessment of GPM Microwave Imager Snowfall Observation Capabilities" Remote Sensing 9, no. 12: 1263. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs9121263
APA StylePanegrossi, G., Rysman, J.-F., Casella, D., Marra, A. C., Sanò, P., & Kulie, M. S. (2017). CloudSat-Based Assessment of GPM Microwave Imager Snowfall Observation Capabilities. Remote Sensing, 9(12), 1263. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs9121263