Aerosol Optical Properties and Associated Direct Radiative Forcing over the Yangtze River Basin during 2001–2015
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Satellite and Ground Data
2.2. Methodology
2.2.1. Validation between CARSNET and MODIS (DB) AODs
2.2.2. Calculation of Instantaneous ADRE
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Validation of MODIS (DB) AOD versus CARSNET AOD
3.2. Spatiotemporal Distributions of Aerosol Optical Properties
3.2.1. Temporal Variation of Regional Average
3.2.2. Spatial Patterns of Temporal Variation of AOD
3.2.3. Frequency Distribution of Temporal Variation
3.3. Spatiotemporal Distribution of IADRE
3.3.1. Temporal Distribution of IADRE
3.3.2. Spatial Patterns of IADRE
3.3.3. Temporal Distribution of IADRE Efficiency
4. Uncertainty Analysis
5. Summary and Conclusions
- High correlation coefficients between MODIS (DB) and CARSNET AOD550 were observed at Chengdu (0.82), Changde (0.70) and Dongtan (0.82), which provided possibility and confidence to estimate aerosol optical and radiative properties over YRB using MODIS (DB) aerosol retrievals.
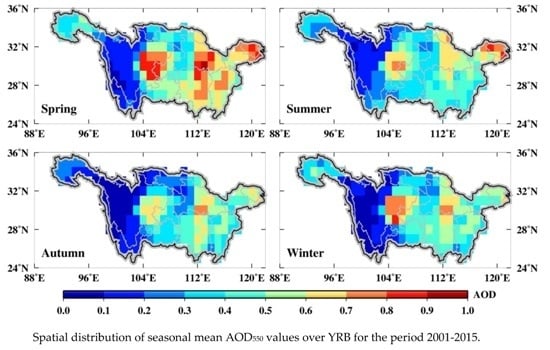
- The 15-year averaged AOD550, AE470–660 and WVC values were 0.49, 1.42 and 2.13 cm, respectively. High AOD550 values generally appeared in spring and summer due to long-distance dust transport from North China and the local biomass burning, while low AOD550 values were observed in winter and autumn as a result of dry and windy weather conditions. Seasonal AE470–660 values were all larger than 1.0 with the minimum (1.33 ± 0.36) in spring, indicating the dominance of fine-mode particles over YRB. Spatially, high AOD550 values (>0.6) were observed over the midstream and downstream regions of YRB and Sichuan Basin because of intensive industrial and urban activities, while low AOD550 values (<0.3) were in high mountains over the upstream region of YRB.
- Approximately 92% of the AOD550 values were less than 1.0; there was a wide distribution of AOD550 in the range 0.1–2.3 in summer, probably due to the variety of aerosol sources. The frequency analyses indicated 90% of the AE470–660 values to be higher than 1.0, and about 71% of the WVC values were in the range of 0.2–3 cm, and 64% of the WVC values were around 3–6 cm in summer.
- The IADRE values were generally higher in spring (−40.01 ± 8.30 Wm−2) and summer (−40.71 ± 6.86 Wm−2), and lower in autumn (−32.52 ± 6.52 Wm−2) and winter (−29.19 ± 7.04 Wm−2). The spatial distribution of IADRE over each 1° × 1° grid is in agreement with AOD550 over the Sichuan Basin and the midstream region of YRB. However, large aerosol loadings (AOD550 > 0.6) over the YRD did not transfer into high IADRE values (<−30 Wm−2).
- The total uncertainty of IADRE was estimated to be ±1.8 Wm−2, from the calculation of Fclr, CERES radiances unfiltered, conversion of CERES TOA radiances to fluxes and cloud contamination.
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. Climate Change 2013—The Physical Science Basis: Working Group I Contribution to the Fifth Assessment Report of the IPCC, Climate Change 2013; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Patadia, F.; Gupta, P.; Christopher, S.A. First observational estimates of global clear sky shortwave aerosol direct radiative effect over land. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2008, 35, 228–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patadia, F.; Gupta, P.; Christopher, S.A.; Reid, J.S. A Multisensor satellite-based assessment of biomass burning aerosol radiative impact over Amazonia. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2008, 113, 1113–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christopher, S.A.; Zhang, J. Shortwave Aerosol Radiative Forcing from MODIS and CERES observations over the oceans. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2002, 29, 6:1–6:4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christopher, S.A.; Zhang, J. Cloud-free shortwave aerosol radiative effect over oceans: Strategies for identifying anthropogenic forcing from Terra satellite measurements. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2004, 31, 169–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levy, R.C.; Remer, L.A.; Kleidman, R.G.; Mattoo, S.; Ichoku, C.; Kahn, R.; Eck, T.F. Global evaluation of the Collection 5 MODIS dark-target aerosol products over land. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2010, 10, 10399–10420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Levy, R.C.; Mattoo, S.; Munchak, L.A.; Remer, L.A.; Sayer, A.M.; Patadia, F.; Hsu, N.C. The Collection 6 MODIS aerosol products over land and ocean. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2013, 6, 2989–3034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Q.; Li, C.; Geng, F.; Lei, Y.; Li, Y. Study on long-term aerosol distribution over the land of East China using MODIS data. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2012, 12, 304–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Mao, J.; Lau, K.H.A.; Chen, J.C.; Yuan, Z.; Liu, X.; Liu, G. Characteristics of distribution and seasonal variation of aerosol optical depth in eastern China with MODIS products. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2003, 48, 2488–2495. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, P.; Cao, X.; Zhang, L.; Sun, N.; Sun, L.; Logan, T.; Huang, Z. Aerosol vertical distribution and optical properties over China from long-term satellite and ground-based remote sensing. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2017, 17, 2509–2523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pathak, B.; Kalita, G.; Bhuyan, K.; Bhuyan, P.K.; Moorthy, K.K. Aerosol temporal characteristics and its impact on shortwave radiative forcing at a location in the northeast of India. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2010, 115, 5548–5554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jose, S.; Gharai, B.; Niranjan, K.; Rao, P.V.N. Investigation on seasonal variations of aerosol properties and its influence on radiative effect over an urban location in central India. Atmos. Environ. 2016, 133, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Zhu, J.; Che, H.; Xia, X.; Zhang, R. Column-integrated aerosol optical properties and direct radiative forcing based on sun photometer measurements at a semi-arid rural site in Northeast China. Atmos. Res. 2015, 157, 56–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, X.; Che, H.; Zhu, J.; Chen, H.; Cong, Z.; Deng, X.; Liu, Q. Ground-based remote sensing of aerosol climatology in China: Aerosol optical properties, direct radiative effect and its parameterization. Atmos. Environ. 2015, 124, 243–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, N.; Kumar, K.R.; Yu, X.; Yin, Y. Column-integrated aerosol optical properties and direct radiative forcing over the urban-industrial megacity Nanjing in the Yangtze River Delta, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 17535–17552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, X.; Lü, R.; Kumar, K.R.; Ma, J.; Zhang, Q.; Jiang, Y.; Li, M. Dust aerosol properties and radiative forcing observed in spring during 2001–2014 over urban Beijing, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 15432–15442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sena, E.T.; Artaxo, P.; Correia, A.L. Spatial variability of the direct radiative forcing of biomass burning aerosols and the effects of land use change in Amazonia. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2013, 13, 1261–1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, N.; Christopher, S.A. Satellite and surface-based remote sensing of Southeast Asian aerosols and their radiative effects. Atmos. Res. 2013, 122, 544–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, N.; Christopher, S.A. Clear sky direct radiative effects of aerosols over Southeast Asia based on satellite observations and radiative transfer calculations. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 152, 333–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswas, J.; Pathak, B.; Patadia, F.; Bhuyan, P.K.; Gogoi, M.M.; Babu, S.S. Satellite-retrieved direct radiative forcing of aerosols over North-East India and adjoining areas: Climatology and impact assessment. Int. J. Climatol. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Remer, L.A.; Kaufman, Y.J. Aerosol direct radiative effect at the top of the atmosphere over cloud free ocean derived from four years of MODIS data. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2006, 6, 237–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundström, A.M.; Arola, A.; Kolmonen, P.; Xue, Y.; de Leeuw, G.; Kulmala, M. On the use of satellite remote sensing based approach for determining aerosol direct radiative effect over land: A case study over China. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2015, 15, 505–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badarinath, K.V.S.; Kharol, S.K.; Kaskaoutis, D.G.; Kambezidis, H.D. Case study of a dust storm over Hyderabad area, India: Its impact on solar radiation using satellite data and ground measurements. Sci. Total Environ. 2007, 384, 316–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Badarinath, K.V.S.; Kharol, S.K.; Krishna Prasad, V.; Kaskaoutis, D.G.; Kambezidis, H.D. Variation in aerosol properties over Hyderabad, India during intense cyclonic conditions. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2008, 29, 4575–4597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badarinath, K.V.S.; Kharol, S.K.; Sharma, A.R.; Ramaswamy, V.; Kaskaoutis, D.G.; Kambezidis, H.D. Investigations of an intense aerosol loading during 2007 cyclone SIDR—A study using satellite data and ground measurements over Indian region. Atmos. Environ. 2009, 43, 3708–3716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalapureddy, M.C.R.; Kaskaoutis, D.G.; Ernest Raj, P.; Devara, P.C.S.; Kambezidis, H.D.; Kosmopoulos, P.G.; Nastos, P.T. Identification of aerosol type over the Arabian Sea in the premonsoon season during the Integrated Campaign for Aerosols, Gases and Radiation Budget (ICARB). J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2009, 114, D17203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaskaoutis, D.G.; Badarinath, K.V.S.; Kharol, S.K.; Sharma, A.R.; Kambezidis, H.D. Variations in the aerosol optical properties and types over the tropical urban site of Hyderabad, India. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2009, 114, 2191–2196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badarinath, K.V.S.; Kharol, S.K.; Kaskaoutis, D.G.; Sharma, A.R.; Ramaswamy, V.; Kambezidis, H.D. Long-range transport of dust aerosols over the Arabian Sea and Indian region—A case study using satellite data and ground-based measurements. Glob. Planet. Chang. 2010, 72, 164–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kharol, S.K.; Badarinath, K.V.S.; Sharma, A.R.; Kaskaoutis, D.G.; Kambezidis, H.D. Multiyear analysis of Terra/Aqua MODIS aerosol optical depth and ground observations over tropical urban region of Hyderabad, India. Atmos. Environ. 2011, 45, 1532–1542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaskaoutis, D.; Kosmopoulos, P.; Kambezidis, H.; Nastos, P. Aerosol climatology and discrimination of different types over Athens, Greece, based on MODIS data. Atmos. Environ. 2007, 41, 7315–7329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kambezidis, H.D.; Kaskaoutis, D.G. Aerosol climatology over four AERONET sites: An overview. Atmos. Environ. 2008, 42, 1892–1906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaskaoutis, D.G.; Kalapureddy, M.C.R.; Devara, P.C.S.; Kosmopoulos, P.G.; Nastos, P.T.; Krishna Moorthy, K.; Kambezidis, H.D. Spatiotemporal aerosol optical characteristics over the Arabian Sea during the pre monsoon season. Atmos. Chem. Phys. Discuss. 2009, 9, 22223–22269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaskaoutis, D.; Nastos, P.; Kosmopoulos, P.; Kambezidis, H. The combined use of satellite data, air-mass trajectories and model applications for monitoring dust transport over Athens, Greece. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2010, 31, 5089–5109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, R.; Che, H.Z.; Chen, Q.L.; Tao, J.; Wang, Y.Q.; Sun, J.Y.; Zhang, X.Y. Study of Aerosol Optical Properties Based on Ground Measurements over Sichuan Basin, China. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2014, 14, 905–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Gong, W.; Xia, X.; Zhu, J.; Li, J.; Zhu, Z. Long-term observations of aerosol optical properties at Wuhan, an urban site in Central China. Atmos. Environ. 2015, 101, 94–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Cong, Z.; Wang, Y.; Xin, J.; Wan, X.; Pan, Y.; Wang, Y. Background aerosol over the Himalayas and Tibetan Plateau: Observed characteristics of aerosol mass loading. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2017, 17, 449–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Song, C.; Zhang, K.; Cheng, X.; Band, L.E.; Zhang, Q. Effects of land use/land cover and climate changes on terrestrial net primary productivity in the Yangtze River Basin, China, from 2001 to 2010. J. Geophys. Res. Biogeosci. 2014, 119, 1092–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Che, H.; Zhang, X.Y.; Xia, X.; Goloub, P.; Holben, B.; Zhao, H.; Damiri, B. Ground-based aerosol climatology of China: Aerosol optical depths from the China Aerosol Remote Sensing Network (CARSNET) 2002–2013. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2015, 15, 7619–7652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, L.; Che, H.; Geng, F.; Xia, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, C.; Guo, J. Aerosol optical properties based on ground measurements over the Chinese Yangtze Delta Region. Atmos. Environ. 2010, 44, 2587–2596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Che, H.; Shi, G.; Uchiyama, A.; Yamazaki, A.; Chen, H.; Goloub, P.; Zhang, X. Intercomparison between aerosol optical properties by a PREDE skyradiometer and CIMEL sunphotometer over Beijing, China. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2008, 8, 3199–3214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Remer, L.A.; Kleidman, R.G.; Levy, R.C.; Kaufman, Y.J.; Tanré, D.; Mattoo, S.; Martins, J.V.; Ichoku, C.; Koren, I.; Yu, H.; et al. Global aerosol climatology from the MODIS satellite sensors. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2008, 113, 752–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, N.C.; Jeong, M.J.; Bettenhausen, C.; Sayer, A.M.; Hansell, R.; Seftor, C.S.; Huang, J.; Tsay, S.C. Enhanced Deep Blue aerosol retrieval algorithm: The second generation. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2013, 118, 9296–9315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ichoku, C.; Chu, D.A.; Mattoo, S.; Kaufman, Y.J.; Remer, L.A.; Tanré, D.; Holben, B.N. A spatio-temporal approach for global validation and analysis of MODIS aerosol product. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2002, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christopher, S.A. Satellite remote sensing methods for estimating clear Sky shortwave Top of atmosphere fluxes used for aerosol studies over the global oceans. Remote Sens. Environ. 2011, 115, 3002–3006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loeb, N.G.; Kato, S.; Loukachine, K.; Manalo-Smith, N.; Doelling, D.R. Angular distribution models for top-of-atmosphere radiative flux estimation from the Clouds and the Earth’s Radiant Energy System instrument on the Terra satellite. Part II: Validation. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2007, 24, 564–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Xin, J.; Yin, Y.; Wang, L.; Wang, Y. The Variations and Trends of MODIS C5 & C6 Products’ Errors in the Recent Decade over the Background and Urban Areas of North China. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 754. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Xiong, X.; Qu, J.J.; Che, H. Validation of MODIS aerosol optical depth product over China using CARSNET measurements. Atmos. Environ. 2011, 45, 5970–5978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boiyo, R.; Kumar, K.R.; Zhao, T.; Bao, Y. Climatological analysis of aerosol optical properties over East Africa observed from space-borne sensors during 2001–2015. Atmos. Environ. 2017, 152, 298–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Gong, W.; Singh, R.P.; Xia, X.; Che, H.; Zhang, M.; Lin, H. Aerosol optical properties over Mount Song, a rural site in central China. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2015, 15, 2051–2064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.; Wu, H.; Qin, J.; Lin, C.; Tang, W.; Chen, Y. Recent climate changes over the Tibetan Plateau and their impacts on energy and water cycle: A review. Glob. Planet. Chang. 2014, 112, 79–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Zhu, B.; Fan, S.; Yin, Y.; Bu, X. Ground-based observation of aerosol optical properties in Lanzhou, China. J. Environ. Sci. 2009, 21, 1519–1524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Minnis, P.; Yi, Y.; Tang, Q.; Wang, X.; Hu, Y.; Winker, D. Summer dust aerosols detected from CALIPSO over the Tibetan Plateau. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2007, 34, 529–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Huang, J.; Zhao, C.; Qian, Y.; Leung, L.R.; Yang, B. Modeling the transport and radiative forcing of Taklimakan dust over the Tibetan Plateau: A case study in the summer of 2006. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2013, 118, 797–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Liu, J.; Zhou, X.; Sparrow, M.; Ma, M.; Sun, Z.; Jiang, W. Validation of the MODIS global land surface albedo product using ground measurements in a semidesert region on the Tibetan Plateau. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2004, 109, D05107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.J.; Lee, S.C.; Chow, J.C.; Watson, J.G.; Ho, K.F.; Zhang, R.J.; Zou, S.C. Spatial and seasonal distributions of carbonaceous aerosols over China. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2007, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penner, J.E.; Charlson, R.J.; Schwartz, S.E.; Hales, J.M.; Laulainen, N.S.; Travis, L.; Radke, L.F. Quantifying and minimizing uncertainty of climate forcing by anthropogenic aerosols. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 1994, 75, 375–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Chen, Y.; Niu, Y.; Salazar, G.; Gon, W. Analysis of Atmospheric Turbidity in Clear Skies at Wuhan, Central China. J. Earth Sci. 2017, 28, 729–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Ma, Y.; Gong, W.; Wang, L.; Xia, X.; Che, H.; Hu, B.; Liu, B. Aerosol radiative effect in UV, VIS, NIR, and SW spectra under haze and high-humidity urban conditions. Atmos. Environ. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]















| Sensor | Product | Level | Parameter | Spatial Resolution | Temporal Resolution | Temporal Coverage | Application |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CARSNET | - | 1.5 | AOD | - | Daily | 2007–2011 | Validation of MODIS AOD and CARSNET AOD |
| MODIS | MOD04 | 2.0 | AOD (DB) | 10 km | Daily | 2007–2011 | |
| MODIS | MOD08 | 3.0 | AOD, AE WVC | 1° | Monthly | 2001–2015 | Analysis of aerosol optical properties |
| CERES | SSF | 2.0 | AOD, SW Flux | 20 km | Instantaneous | 2001–2015 | Estimation of aerosol direct radiative effect |
| Month | IADRE (Wm−2) | Year | IADRE (Wm−2) |
|---|---|---|---|
| January | −27.74 ± 8.51 | 2001 | −46.65 ± 11.32 |
| February | −36.74 ± 8.75 | 2002 | −41.35 ± 9.56 |
| March | −39.42 ± 8.70 | 2003 | −42.50 ± 7.22 |
| April | −41.95 ± 6.38 | 2004 | −42.22 ± 7.80 |
| May | −38.96 ± 11.07 | 2005 | −48.76 ± 8.08 |
| June | −41.87 ± 8.70 | 2006 | −33.06 ± 10.93 |
| July | −39.98 ± 6.68 | 2007 | −32.75 ± 7.81 |
| August | −40.19 ± 9.86 | 2008 | −31.89 ± 7.73 |
| September | −36.98 ± 7.02 | 2009 | −33.12 ± 8.20 |
| October | −32.41 ± 9.60 | 2010 | −31.59 ± 8.13 |
| November | −28.18 ± 7.58 | 2011 | −30.96 ± 5.20 |
| December | −24.76 ± 7.33 | 2012 | −29.98 ± 4.79 |
| Spring | −40.01 ± 8.30 | 2013 | −27.99 ± 6.12 |
| Summer | −40.71 ± 6.86 | 2014 | −30.20 ± 7.61 |
| Autumn | −32.52 ± 6.52 | 2015 | −31.13 ± 5.82 |
| Winter | −29.19 ± 7.04 | Annual | −35.60 ± 6.71 |
| Reference | Study Area | Data/Time Coverage | Method | AOD550 | Fclr (Wm−2) | Faero (Wm−2) | IADRE (Wm−2) | IADRE Efficiency (Wm−2τ−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Jhuma Biswas et al. [20] | Northeast India | CERES-SSF-XTPK-Aqua July 2002–December 2013 | Satellite-retrieved | 0.09~0.67 | 131~270 | 150~340 | −4.43~−70.66 (seasonal) | −19.9~−435.97 (seasonal) |
| Feng and Christopher [19] | Southeast Asia | CERES-SSF-Terra 2001–2010 | Satellite-retrieved | 0.24 ± 0.04 (land) | 150.0 ± 8.6 (land) | 160.9 ± 2.6 (land) | −12.8 ± 2.1 (land) | −32.9 ± 9.6 (land) |
| Sundström et al. [22] | East China | CERES-SSF-Terra March–October 2009 | Satellite-retrieved | N/A | N/A | N/A | −8.8 | N/A |
| Kang et al. [15] | Nanjing China | AERONET/OMI September 2007–August 2008 | Model-simulated | 0.95 ± 0.41 (500 nm) | N/A | N/A | −21.85~33.85 | −26.05~−45.46 |
| Xia et al. [14] | YRD China | Sunphotometer ground-based data | Model-simulated | 0.04~0.74 | N/A | N/A | −16~−37 | −48~−59 |
| Yu et al. [16] | Beijing China | AERONET | Model-simulated | 1.2 (dust) 0.7 (non) (440 nm) | N/A | N/A | −66~−116 (dust day) −13~−23 (non-dust) | −33~−50 (dust day) −15~−27 (non-dust) |
| This study | Yangtze River China | CERES-SSF-Terra 2001–2015 | Satellite-retrieved | 0.39 ± 0.48 | 151.59 ± 3.76 | 192.31 ± 11.39 | −35.60 ± 6.71 | −65.18 ± 7.79 |
| Reference | Source of Uncertainty in IADRE | Uncertainty in IADRE (Wm−2) |
|---|---|---|
| Loeb et al. [45] | Calibration of CERES radiances | ±0.4 |
| CERES radiances unfiltering | ±0.4 | |
| Patadia et al. [2] | Conversion of CERES TOA radiances to fluxes | ±0.4 |
| Feng et al. [18] | Cloud contamination | ±0.5 |
| This study | Estimation of the Fclr caused by linear regression | ±1.6 |
| This study | Total uncertainty | ±1.8 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
He, L.; Wang, L.; Lin, A.; Zhang, M.; Bilal, M.; Tao, M. Aerosol Optical Properties and Associated Direct Radiative Forcing over the Yangtze River Basin during 2001–2015. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 746. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs9070746
He L, Wang L, Lin A, Zhang M, Bilal M, Tao M. Aerosol Optical Properties and Associated Direct Radiative Forcing over the Yangtze River Basin during 2001–2015. Remote Sensing. 2017; 9(7):746. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs9070746
Chicago/Turabian StyleHe, Lijie, Lunche Wang, Aiwen Lin, Ming Zhang, Muhammad Bilal, and Minghui Tao. 2017. "Aerosol Optical Properties and Associated Direct Radiative Forcing over the Yangtze River Basin during 2001–2015" Remote Sensing 9, no. 7: 746. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs9070746
APA StyleHe, L., Wang, L., Lin, A., Zhang, M., Bilal, M., & Tao, M. (2017). Aerosol Optical Properties and Associated Direct Radiative Forcing over the Yangtze River Basin during 2001–2015. Remote Sensing, 9(7), 746. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs9070746