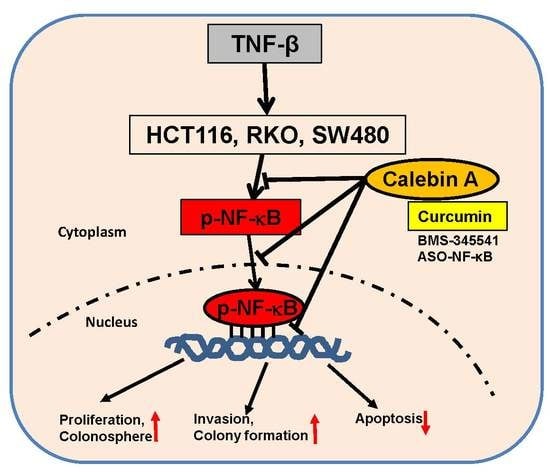
Evidence That Calebin A, a Component of Curcuma Longa Suppresses NF-κB Mediated Proliferation, Invasion and Metastasis of Human Colorectal Cancer Induced by TNF-β (Lymphotoxin)
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Lines
2.2. Reagents and Antibodies
2.3. Experimental Setup
2.4. Three-Dimensional Cell Culture
2.5. Transfection with Antisense Oligonucleotides
2.6. Cell Vitality Assay
2.7. Proliferation and Migration Assay
2.8. Transmission Electron-Microscopy
2.9. Immunofluorescence Imaging
2.10. Western Blot Analysis
2.11. Statistical Evaluation
3. Results
3.1. Calebin A Suppressed TNF-β-Promoted Proliferation in Different CRC Cells
3.2. Calebin A Significantly Supresses TNF-β-Promoted Colonosphere Formation, Invasion and Stimulates Apoptosis of CRC Cells
3.3. Calebin A, Similar to Curcumin and Specific IKK Inhibitor BMS-345541, Blocks TNF-β-Promoted Nuclear Translocation of p65-NF-κB to the Cell Nucleus in Different CRC Cell Lines
3.4. Calebin A Supresses TNF-β-Promoted p65-NF-κB Activation Time-Dependently in All Three CRC Cell Lines
3.5. Calebin A Specifically Suppresses TNF-β-Induced p65-NF-κB Activation, Similar to Curcumin, ASO-NF-κB or BMS-345541 in CRC Cells
3.6. Calebin A Suppresses TNF-β-Promoted p65-NF-κB Activation and NF-κB-Dependent Gene Products Involved in Metastasis, Migration and Apoptosis of CRC Cells
3.7. Calebin A Disrupts the Interaction of p65-NF-κB to DNA and DTT Suppresses this Binding
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Araghi, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jenkins, M.; Brierley, J.; Morris, E.; Bray, F.; Arnold, M. Global Trends in Colorectal Cancer Mortality: Projections to the Year 2035. Int. J. Cancer 2019, 144, 2992–3000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Fedewa, S.A.; Ahnen, D.J.; Meester, R.G.S.; Barzi, A.; Jemal, A. Colorectal Cancer Statistics, 2017. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2017, 67, 177–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van der Jeught, K.; Xu, H.C.; Li, Y.J.; Lu, X.B.; Ji, G. Drug Resistance and New Therapies in Colorectal Cancer. World J. Gastroenterol. 2018, 24, 3834–3848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sethi, G.; Shanmugam, M.K.; Ramachandran, L.; Kumar, A.P.; Tergaonkar, V. Multifaceted Link between Cancer and Inflammation. Biosci. Rep. 2012, 32, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, S.C.; Kunnumakkara, A.B.; Aggarwal, S.; Aggarwal, B.B. Inflammation, a Double-Edge Sword for Cancer and Other Age-Related Diseases. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 2160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aggarwal, B.B.; Shishodia, S.; Sandur, S.K.; Pandey, M.K.; Sethi, G. Inflammation and Cancer: How Hot Is the Link? Biochem. Pharmacol. 2006, 72, 1605–1621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colombo, F.; Zambrano, S.; Agresti, A. Nf-Kappab, the Importance of Being Dynamic: Role and Insights in Cancer. Biomedicines 2018, 6, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, L.; Tan, S.; Zhou, Y.; Lin, J.; Wang, H.; Oyang, L.; Tian, Y.; Liu, L.; Su, M.; Wang, H.; et al. Role of the Nfkappab-Signaling Pathway in Cancer. Onco Targets Ther. 2018, 11, 2063–2073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kearns, J.D.; Basak, S.; Werner, S.L.; Huang, C.S.; Hoffmann, A. Ikappabepsilon Provides Negative Feedback to Control Nf-Kappab Oscillations, Signaling Dynamics, and Inflammatory Gene Expression. J. Cell Biol. 2006, 173, 659–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karin, M. Nuclear Factor-Kappab in Cancer Development and Progression. Nature 2006, 441, 431–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, J.; Gohda, J.; Akiyama, T.; Semba, K. Nf-Kappab Activation in Development and Progression of Cancer. Cancer Sci. 2007, 98, 268–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buhrmann, C.; Yazdi, M.; Popper, B.; Shayan, P.; Goel, A.; Aggarwal, B.B.; Shakibaei, M. Resveratrol Chemosensitizes Tnf-Beta-Induced Survival of 5-Fu-Treated Colorectal Cancer Cells. Nutrients 2018, 10, 888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buhrmann, C.; Yazdi, M.; Popper, B.; Shayan, P.; Goel, A.; Aggarwal, B.B.; Shakibaei, M. Evidence that Tnf-Beta Induces Proliferation in Colorectal Cancer Cells and Resveratrol Can Down-Modulate It. Exp. Biol. Med. 2019, 244, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aggarwal, B.B.; Kohr, W.J.; Hass, P.E.; Moffat, B.; Spencer, S.A.; Henzel, W.J.; Bringman, T.S.; Nedwin, G.E.; Goeddel, D.V.; Harkins, R.N. Human Tumor Necrosis Factor. Production, Purification, and Characterization. J. Biol. Chem. 1985, 260, 2345–2354. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Aggarwal, B.B.; Moffat, B.; Harkins, R.N. Human Lymphotoxin. Production by a Lymphoblastoid Cell Line, Purification, and Initial Characterization. J. Biol. Chem. 1984, 259, 686–691. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Newman, D.J.; Cragg, G.M. Natural Products as Sources of New Drugs from 1981 to 2014. J. Nat. Prod. 2016, 79, 629–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mishra, S.; Palanivelu, K. The Effect of Curcumin (Turmeric) on Alzheimer’s Disease: An Overview. Ann. Indian Acad. Neurol. 2008, 11, 13–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuppusamy, P.; Yusoff, M.M.; Maniam, G.P.; Ichwan, S.J.; Soundharrajan, I.; Govindan, N. Nutraceuticals as Potential Therapeutic Agents for Colon Cancer: A Review. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2014, 4, 173–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunnumakkara, A.B.; Bordoloi, D.; Harsha, C.; Banik, K.; Gupta, S.C.; Aggarwal, B.B. Curcumin Mediates Anticancer Effects by Modulating Multiple Cell Signaling Pathways. Clin. Sci. 2017, 131, 1781–1799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, S.C.; Kismali, G.; Aggarwal, B.B. Curcumin, a Component of Turmeric: From Farm to Pharmacy. Biofactors 2013, 39, 2–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Chetia, H.; Sharma, S.; Kabiraj, D.; Talukdar, N.C.; Bora, U. Curcumin Resource Database. Database 2015, 2015, bav070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.Y.; Kim, D.S. Discovery of Natural Products from Curcuma Longa that Protect Cells from Beta-Amyloid Insult: A Drug Discovery Effort against Alzheimer’s Disease. J. Nat. Prod. 2002, 65, 1227–1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.S.; Kim, J.Y. Total Synthesis of Calebin-a, Preparation of Its Analogues, and Their Neuronal Cell Protectivity against Beta-Amyloid Insult. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2001, 11, 2541–2543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aggarwal, B.B.; Yuan, W.; Li, S.; Gupta, S.C. Curcumin-Free Turmeric Exhibits Anti-Inflammatory and Anticancer Activities: Identification of Novel Components of Turmeric. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2013, 57, 1529–1542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nair, A.; Amalraj, A.; Jacob, J.; Kunnumakkara, A.B.; Gopi, S. Non-Curcuminoids from Turmeric and Their Potential in Cancer Therapy and Anticancer Drug Delivery Formulations. Biomolecules 2019, 9, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majeed, A.; Majeed, M.; Thajuddin, N.; Arumugam, S.; Ali, F.; Beede, K.; Adams, S.J.; Gnanamani, M. Bioconversion of Curcumin into Calebin-a by the Endophytic Fungus Ovatospora Brasiliensis Epe-10 Mtcc 25236 Associated with Curcuma Caesia. AMB Express 2019, 9, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyagi, A.K.; Prasad, S.; Majeed, M.; Aggarwal, B.B. Calebin a, a Novel Component of Turmeric, Suppresses Nf-Kappab Regulated Cell Survival and Inflammatory Gene Products Leading to Inhibition of Cell Growth and Chemosensitization. Phytomedicine 2017, 34, 171–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, C.S.; Liao, S.N.; Tsai, M.L.; Kalyanam, N.; Majeed, M.; Majeed, A.; Ho, C.T.; Pan, M.H. Calebin-a Inhibits Adipogenesis and Hepatic Steatosis in High-Fat Diet-Induced Obesity Via Activation of Ampk Signaling. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2015, 59, 1883–1895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyagi, A.K.; Prasad, S.; Majeed, M.; Aggarwal, B.B. Calebin a Downregulates Osteoclastogenesis through Suppression of Rankl Signalling. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2016, 593, 80–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Li, S.; Han, Y.; Liu, J.; Zhang, J.; Li, F.; Wang, Y.; Liu, X.; Yao, L. Calebin-a Induces Apoptosis and Modulates Mapk Family Activity in Drug Resistant Human Gastric Cancer Cells. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2008, 591, 252–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.J.; Tsai, Y.J.; Lin, M.Y.; You, H.L.; Kalyanam, N.; Ho, C.T.; Pan, M.H. Calebin-a Induced Death of Malignant Peripheral Nerve Sheath Tumor Cells by Activation of Histone Acetyltransferase. Phytomedicine 2019, 57, 377–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Novaes, J.T.; Lillico, R.; Sayre, C.L.; Nagabushnam, K.; Majeed, M.; Chen, Y.; Ho, E.A.; Oliveira, A.L.P.; Martinez, S.E.; Alrushaid, S.; et al. Disposition, Metabolism and Histone Deacetylase and Acetyltransferase Inhibition Activity of Tetrahydrocurcumin and Other Curcuminoids. Pharmaceutics 2017, 9, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Buhrmann, C.; Shayan, P.; Goel, A.; Shakibaei, M. Resveratrol Regulates Colorectal Cancer Cell Invasion by Modulation of Focal Adhesion Molecules. Nutrients 2017, 9, 1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buhrmann, C.; Shayan, P.; Kraehe, P.; Popper, B.; Goel, A.; Shakibaei, M. Resveratrol Induces Chemosensitization to 5-Fluorouracil through up-Regulation of Intercellular Junctions, Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition and Apoptosis in Colorectal Cancer. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2015, 98, 51–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shakibaei, M.; Kraehe, P.; Popper, B.; Shayan, P.; Goel, A.; Buhrmann, C. Curcumin Potentiates Antitumor Activity of 5-Fluorouracil in a 3d Alginate Tumor Microenvironment of Colorectal Cancer. BMC Cancer 2015, 15, 250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Buhrmann, C.; Shayan, P.; Aggarwal, B.B.; Shakibaei, M. Evidence That Tnf-Beta (Lymphotoxin Alpha) Can Activate the Inflammatory Environment in Human Chondrocytes. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2013, 15, R202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bharti, A.C.; Aggarwal, B.B. Nuclear Factor-Kappa B and Cancer: Its Role in Prevention and Therapy. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2002, 64, 883–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sethi, G.; Sung, B.; Aggarwal, B.B. Tnf: A Master Switch for Inflammation to Cancer. Front. Biosci. 2008, 13, 5094–5107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aggarwal, B.B. Nuclear Factor-Kappab: The Enemy Within. Cancer Cell 2004, 6, 203–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Garcia-Pineres, A.J.; Castro, V.; Mora, G.; Schmidt, T.J.; Strunck, E.; Pahl, H.L.; Merfort, I. Cysteine 38 in P65/Nf-Kappab Plays a Crucial Role in DNA Binding Inhibition by Sesquiterpene Lactones. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 39713–39720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ha, K.H.; Byun, M.S.; Choi, J.; Jeong, J.; Lee, K.J.; Jue, D.M. N-Tosyl-L-Phenylalanine Chloromethyl Ketone Inhibits Nf-Kappab Activation by Blocking Specific Cysteine Residues of Ikappab Kinase Beta and P65/Rela. Biochemistry 2009, 48, 7271–7278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, J.G.; Gupta, S.C.; Prasad, S.; Aggarwal, B.B. Piperlongumine Chemosensitizes Tumor Cells through Interaction with Cysteine 179 of Ikappabalpha Kinase, Leading to Suppression of Nf-Kappab-Regulated Gene Products. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2014, 13, 2422–2435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liang, M.C.; Bardhan, S.; Pace, E.A.; Rosman, D.; Beutler, J.A.; Porco, J.A., Jr.; Gilmore, T.D. Inhibition of Transcription Factor Nf-Kappab Signaling Proteins Ikkbeta and P65 through Specific Cysteine Residues by Epoxyquinone a Monomer: Correlation with Its Anti-Cancer Cell Growth Activity. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2006, 71, 634–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Natarajan, K.; Singh, S.; Burke, T.R., Jr.; Grunberger, D.; Aggarwal, B.B. Caffeic Acid Phenethyl Ester Is a Potent and Specific Inhibitor of Activation of Nuclear Transcription Factor Nf-Kappa B. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1996, 93, 9090–9095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sandur, S.K.; Ichikawa, H.; Sethi, G.; Ahn, K.S.; Aggarwal, B.B. Plumbagin (5-Hydroxy-2-Methyl-1,4-Naphthoquinone) Suppresses Nf-Kappab Activation and Nf-Kappab-Regulated Gene Products through Modulation of P65 and Ikappabalpha Kinase Activation, Leading to Potentiation of Apoptosis Induced by Cytokine and Chemotherapeutic Agents. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 17023–17033. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.Q.; Ghosh, S.; Ghosh, G. A Novel DNA Recognition Mode by the Nf-Kappa B P65 Homodimer. Nat. Struct. Biol. 1998, 5, 67–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, D.; Eide, P.W.; Eilertsen, I.A.; Danielsen, S.A.; Eknaes, M.; Hektoen, M.; Lind, G.E.; Lothe, R.A. Epigenetic and Genetic Features of 24 Colon Cancer Cell Lines. Oncogenesis 2013, 2, e71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, S.C.; Sung, B.; Kim, J.H.; Prasad, S.; Li, S.; Aggarwal, B.B. Multitargeting by Turmeric, the Golden Spice: From Kitchen to Clinic. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2013, 57, 1510–1528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Jiang, S.; Zhou, L.; Yu, F.; Ding, H.; Li, P.; Zhou, M.; Wang, K. Potential Mechanisms of Action of Curcumin for Cancer Prevention: Focus on Cellular Signaling Pathways and Mirnas. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2019, 15, 1200–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Prasad, S.; Gupta, S.C.; Tyagi, A.K.; Aggarwal, B.B. Curcumin, a Component of Golden Spice: From Bedside to Bench and Back. Biotechnol. Adv. 2014, 32, 1053–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buhrmann, C.; Kraehe, P.; Lueders, C.; Shayan, P.; Goel, A.; Shakibaei, M. Curcumin Suppresses Crosstalk between Colon Cancer Stem Cells and Stromal Fibroblasts in the Tumor Microenvironment: Potential Role of Emt. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e107514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shakibaei, M.; Buhrmann, C.; Kraehe, P.; Shayan, P.; Lueders, C.; Goel, A. Curcumin Chemosensitizes 5-Fluorouracil Resistant Mmr-Deficient Human Colon Cancer Cells in High Density Cultures. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e85397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Toden, S.; Okugawa, Y.; Buhrmann, C.; Nattamai, D.; Anguiano, E.; Baldwin, N.; Shakibaei, M.; Boland, C.R.; Goel, A. Novel Evidence for Curcumin and Boswellic Acid-Induced Chemoprevention through Regulation of Mir-34a and Mir-27a in Colorectal Cancer. Cancer Prev. Res. 2015, 8, 431–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Toden, S.; Okugawa, Y.; Jascur, T.; Wodarz, D.; Komarova, N.L.; Buhrmann, C.; Shakibaei, M.; Boland, C.R.; Goel, A. Curcumin Mediates Chemosensitization to 5-Fluorouracil through Mirna-Induced Suppression of Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition in Chemoresistant Colorectal Cancer. Carcinogenesis 2015, 36, 355–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jackson-Bernitsas, D.G.; Ichikawa, H.; Takada, Y.; Myers, J.N.; Lin, X.L.; Darnay, B.G.; Chaturvedi, M.M.; Aggarwal, B.B. Evidence that Tnf-Tnfr1-Tradd-Traf2-Rip-Tak1-Ikk Pathway Mediates Constitutive Nf-Kappab Activation and Proliferation in Human Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Oncogene 2007, 26, 1385–1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Miller, S.C.; Huang, R.; Sakamuru, S.; Shukla, S.J.; Attene-Ramos, M.S.; Shinn, P.; van Leer, D.; Leister, W.; Austin, C.P.; Xia, M. Identification of Known Drugs that Act as Inhibitors of Nf-Kappab Signaling and Their Mechanism of Action. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2010, 79, 1272–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ahn, K.S.; Sethi, G.; Chao, T.H.; Neuteboom, S.T.; Chaturvedi, M.M.; Palladino, M.A.; Younes, A.; Aggarwal, B.B. Salinosporamide a (Npi-0052) Potentiates Apoptosis, Suppresses Osteoclastogenesis, and Inhibits Invasion through Down-Modulation of Nf-Kappab Regulated Gene Products. Blood 2007, 110, 2286–2295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bharti, A.C.; Donato, N.; Singh, S.; Aggarwal, B.B. Curcumin (Diferuloylmethane) Down-Regulates the Constitutive Activation of Nuclear Factor-Kappa B and Ikappabalpha Kinase in Human Multiple Myeloma Cells, Leading to Suppression of Proliferation and Induction of Apoptosis. Blood 2003, 101, 1053–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, T., Jr.; Gotoh, Y.; Hoffmann, A.; Ono, Y. Negative Regulation of Constitutive Nf-Kappab and Jnk Signaling by Pkn1-Mediated Phosphorylation of Traf1. Genes Cells 2008, 13, 509–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaltschmidt, B.; Greiner, J.F.W.; Kadhim, H.M.; Kaltschmidt, C. Subunit-Specific Role of Nf-Kappab in Cancer. Biomedicines 2018, 6, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kumar, A.; Takada, Y.; Boriek, A.M.; Aggarwal, B.B. Nuclear Factor-Kappab: Its Role in Health and Disease. J. Mol. Med. 2004, 82, 434–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aggarwal, S.; Das, S.N. Garcinol Inhibits Tumour Cell Proliferation, Angiogenesis, Cell Cycle Progression and Induces Apoptosis Via Nf-Kappab Inhibition in Oral Cancer. Tumour Biol. 2016, 37, 7175–7184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buhrmann, C.; Yazdi, M.; Popper, B.; Kunnumakkara, A.B.; Aggarwal, B.B.; Shakibaei, M. Induction of the Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition of Human Colorectal Cancer by Human Tnf-Beta (Lymphotoxin) and Its Reversal by Resveratrol. Nutrients 2019, 11, 704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tsuboi, K.; Matsuo, Y.; Shamoto, T.; Shibata, T.; Koide, S.; Morimoto, M.; Guha, S.; Sung, B.; Aggarwal, B.B.; Takahashi, H.; et al. Zerumbone Inhibits Tumor Angiogenesis Via Nf-Kappab in Gastric Cancer. Oncol. Rep. 2014, 31, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vanden Berghe, W.; de Bosscher, K.; Boone, E.; Plaisance, S.; Haegeman, G. The Nuclear Factor-Kappab Engages Cbp/P300 and Histone Acetyltransferase Activity for Transcriptional Activation of the Interleukin-6 Gene Promoter. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 32091–32098. [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh, G.; van Duyne, G.; Ghosh, S.; Sigler, P.B. Structure of Nf-Kappa B P50 Homodimer Bound to a Kappa B Site. Nature 1995, 373, 303–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sankaranarayanan, R.; Valiveti, C.K.; Kumar, D.R.; van Slambrouck, S.; Kesharwani, S.S.; Seefeldt, T.; Scaria, J.; Tummala, H.; Bhat, G.J. The Flavonoid Metabolite 2,4,6-Trihydroxybenzoic Acid Is a Cdk Inhibitor and an Anti-Proliferative Agent: A Potential Role in Cancer Prevention. Cancers 2019, 11, 427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dachineni, R.; Kumar, D.R.; Callegari, E.; Kesharwani, S.S.; Sankaranarayanan, R.; Seefeldt, T.; Tummala, H.; Bhat, G.J. Salicylic Acid Metabolites and Derivatives Inhibit Cdk Activity: Novel Insights into Aspirin’s Chemopreventive Effects against Colorectal Cancer. Int. J. Oncol. 2017, 51, 1661–1673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joyce, D.; Albanese, C.; Steer, J.; Fu, M.; Bouzahzah, B.; Pestell, R.G. Nf-Kappab and Cell-Cycle Regulation: The Cyclin Connection. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2001, 12, 73–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Buhrmann, C.; Popper, B.; Kunnumakkara, A.B.; Aggarwal, B.B.; Shakibaei, M. Evidence That Calebin A, a Component of Curcuma Longa Suppresses NF-κB Mediated Proliferation, Invasion and Metastasis of Human Colorectal Cancer Induced by TNF-β (Lymphotoxin). Nutrients 2019, 11, 2904. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11122904
Buhrmann C, Popper B, Kunnumakkara AB, Aggarwal BB, Shakibaei M. Evidence That Calebin A, a Component of Curcuma Longa Suppresses NF-κB Mediated Proliferation, Invasion and Metastasis of Human Colorectal Cancer Induced by TNF-β (Lymphotoxin). Nutrients. 2019; 11(12):2904. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11122904
Chicago/Turabian StyleBuhrmann, Constanze, Bastian Popper, Ajaikumar B. Kunnumakkara, Bharat B. Aggarwal, and Mehdi Shakibaei. 2019. "Evidence That Calebin A, a Component of Curcuma Longa Suppresses NF-κB Mediated Proliferation, Invasion and Metastasis of Human Colorectal Cancer Induced by TNF-β (Lymphotoxin)" Nutrients 11, no. 12: 2904. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11122904
APA StyleBuhrmann, C., Popper, B., Kunnumakkara, A. B., Aggarwal, B. B., & Shakibaei, M. (2019). Evidence That Calebin A, a Component of Curcuma Longa Suppresses NF-κB Mediated Proliferation, Invasion and Metastasis of Human Colorectal Cancer Induced by TNF-β (Lymphotoxin). Nutrients, 11(12), 2904. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11122904