Gut Feelings: How Microbiota Might Impact the Development and Course of Anorexia Nervosa
Abstract
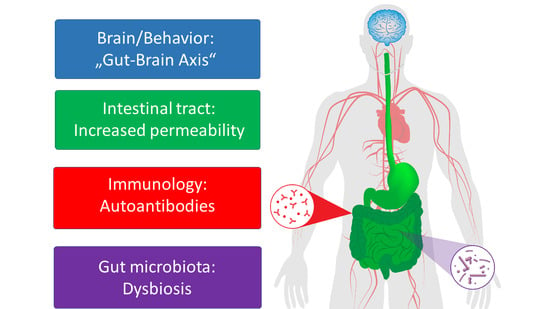
:1. Introduction
2. Body Weight
3. Altered Intestinal Permeability and Inflammation
4. First Findings in Patients with AN and Animal Models
5. Outlook
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Javaras, K.N.; Runfola, C.D.; Thornton, L.M.; Agerbo, E.; Birgegård, A.; Norring, C.; Yao, S.; Råstam, M.; Larsson, H.; Lichtenstein, P.; et al. Sex- and age-specific incidence of healthcare-register-recorded eating disorders in the complete swedish 1979–2001 birth cohort. Int. J. Eat. Disord. 2018, 48, 1070–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smink, F.R.E.; van Hoeken, D.; Donker, G.A.; Susser, E.S.; Oldehinkel, A.J.; Hoek, H.W. Three decades of eating disorders in Dutch primary care: Decreasing incidence of bulimia nervosa but not of anorexia nervosa. Psychol. Med. 2016, 46, 1189–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Herpertz-Dahlmann, B. Adolescent Eating Disorders: Update on Definitions, Symptomatology, Epidemiology, and Comorbidity. Child Adolesc. Psychiatr. Clin. N. Am. 2015, 24, 177–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watson, H.J.; Yilmaz, Z.; Thornton, L.M.; Hübel, C.; Coleman, J.R.I.; Gaspar, H.A.; Bryois, J.; Hinney, A.; Leppä, V.M.; Mattheisen, M.; et al. Genome-wide association study identifies eight risk loci and implicates metabo-psychiatric origins for anorexia nervosa. Nat. Genet. 2019, 51, 1207–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Holland, J.; Hall, N.; Yeates, D.G.R.; Goldacre, M. Trends in hospital admission rates for anorexia nervosa in Oxford (1968–2011) and England (1990–2011): Database studies. J. R. Soc. Med. 2016, 109, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- German Institute for Federal Statistics. The Information System of the Federal Health Monitoring 2018. Available online: www.gbe-bund.de (accessed on 20 August 2020).
- Hoang, U.; Goldacre, M.; James, A. Mortality following hospital discharge with a diagnosis of eating disorder: National record linkage study, England, 2001–2009. Int. J. Eat. Disord. 2014, 47, 507–515. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Schmidt, U.; Adan, R.; Böhm, I.; Campbell, I.C.; Dingemans, A.; Ehrlich, S.; Elzakkers, I.; Favaro, A.; Giel, K.; Harrison, A.; et al. Eating disorders: The big issue. Lancet Psychiatry 2016, 3, 313–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Treasure, J.; Stein, D.; Maguire, S. Has the time come for a staging model to map the course of eating disorders from high risk to severe enduring illness? An examination of the evidence. Early Interv. Psychiatry 2015, 9, 173–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armougom, F.; Henry, M.; Vialettes, B.; Raccah, D.; Raoult, D. Monitoring Bacterial Community of Human Gut Microbiota Reveals an Increase in Lactobacillus in Obese Patients and Methanogens in Anorexic Patients. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e7125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borgo, F.; Riva, A.; Benetti, A.; Casiraghi, M.C.; Bertelli, S.; Garbossa, S.; Anselmetti, S.; Scarone, S.; Pontiroli, A.E.; Morace, G.; et al. Microbiota in anorexia nervosa: The triangle between bacterial species, metabolites and psychological tests. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0179739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanachi, M.; Manichanh, C.; Schoenenberger, A.; Pascal, V.; Levenez, F.; Cournède, N.; Doré, J.; Melchior, J.-C. Altered host-gut microbes symbiosis in severely malnourished anorexia nervosa (AN) patients undergoing enteral nutrition: An explicative factor of functional intestinal disorders? Clin. Nutr. 2019, 38, 2304–2310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kleiman, S.C.; Watson, H.J.; Bulik-Sullivan, E.C.; Huh, E.Y.; Tarantino, L.M.; Bulik, C.M.; Carroll, I.M. The Intestinal Microbiota in Acute Anorexia Nervosa and During Renourishment: Relationship to Depression, Anxiety, and Eating Disorder Psychopathology. Psychosom. Med. 2015, 77, 969–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mack, I.; Cuntz, U.; Grämer, C.; Niedermaier, S.; Pohl, C.; Schwiertz, A.; Zimmermann, K.; Zipfel, S.; Enck, P.; Penders, J. Weight gain in anorexia nervosa does not ameliorate the faecal microbiota, branched chain fatty acid profiles and gastrointestinal complaints. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 26752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Million, M.; Angelakis, E.; Maraninchi, M.; Henry, M.; Giorgi, R.; Valero, R.; Vialettes, B.; Raoult, D. Correlation between body mass index and gut concentrations of Lactobacillus reuteri, Bifidobacterium animalis, Methanobrevibacter smithii and Escherichia coli. Int. J. Obes. 2013, 37, 1460–1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Morita, C.; Tsuji, H.; Hata, T.; Gondo, M.; Takakura, S.; Kawai, K.; Yoshihara, K.; Ogata, K.; Nomoto, K.; Miyazaki, K.; et al. Gut Dysbiosis in Patients with Anorexia Nervosa. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0145274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mörkl, S.; Lackner, S.; Müller, W.; Gorkiewicz, G.; Kashofer, K.; Oberascher, A.; Painold, A.; Holl, A.; Holzer, P.; Meinitzer, A. Gut microbiota and body composition in anorexia nervosa inpatients in comparison to athletes, overweight, obese, and normal weight controls. Int. J. Eat. Disord. 2017, 50, 1421–1431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prochazkova, P.; Roubalova, R.; Dvorak, J.; Tlaskalova-Hogenova, H.; Cermakova, M.; Tomasova, P.; Sediva, B.; Kuzma, M.; Bulant, J.; Bilej, M.; et al. Microbiota, Microbial Metabolites, and Barrier Function in A Patient with Anorexia Nervosa after Fecal Microbiota Transplantation. Microorganisms 2019, 7, 338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De Clercq, N.C.; Frissen, M.N.; Davids, M.; Groen, A.K.; Nieuwdorp, M. Weight Gain after Fecal Microbiota Transplantation in a Patient with Recurrent Underweight following Clinical Recovery from Anorexia Nervosa. Psychother. Psychosom. 2019, 88, 58–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hata, T.; Miyata, N.; Takakura, S.; Yoshihara, K.; Asano, Y.; Kimura-Todani, T.; Yamashita, M.; Zhang, X.-T.; Watanabe, N.; Mikami, K.; et al. The Gut Microbiome Derived From Anorexia Nervosa Patients Impairs Weight Gain and Behavioral Performance in Female Mice. Endocrinology 2019, 160, 2441–2452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinan, T.G.; Cryan, J.F. Gut instincts: Microbiota as a key regulator of brain development, ageing and neurodegeneration. J. Physiol. 2017, 595, 489–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinan, T.G.; Cryan, J.F. The Microbiome-Gut-Brain Axis in Health and Disease. Gastroenterol. Clin. N. Am. 2017, 46, 77–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Almeida, A.; Mitchell, A.L.; Boland, M.; Forster, S.C.; Gloor, G.B.; Tarkowska, A.; Lawley, T.D.; Finn, R.D. A new genomic blueprint of the human gut microbiota. Nature 2019, 568, 499–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Clavel, T.; Lagkouvardos, I.; Hiergeist, A. Microbiome sequencing: Challenges and opportunities for molecular medicine. Expert Rev. Mol. Diagn. 2016, 16, 795–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langgartner, D.; Lowry, C.A.; Reber, S.O. Old Friends, immunoregulation, and stress resilience. Pflug. Arch. 2019, 471, 237–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Neuman, H.; Debelius, J.W.; Knight, R.; Koren, O. Microbial endocrinology: The interplay between the microbiota and the endocrine system. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2015, 39, 509–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cryan, J.F.; O’Riordan, K.J.; Cowan, C.S.M.; Sandhu, K.V.; Bastiaanssen, T.F.S.; Boehme, M.; Codagnone, M.G.; Cussotto, S.; Fulling, C.; Golubeva, A.V.; et al. The Microbiota-Gut-Brain Axis. Physiol. Rev. 2019, 99, 1877–2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleiman, S.C.; Carroll, I.M.; Tarantino, L.M.; Bulik, C.M. Gut feelings: A role for the intestinal microbiota in anorexia nervosa? Int. J. Eat. Disord. 2015, 48, 449–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Herpertz-Dahlmann, B.; Seitz, J.; Baines, J. Food matters: How the microbiome and gut–brain interaction might impact the development and course of anorexia nervosa. Eur. Child Adolesc. Psychiatry 2017, 26, 1031–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Seitz, J.; Trinh, S.; Herpertz-Dahlmann, B. The Microbiome and Eating Disorders. Psychiatr. Clin. N. Am. 2019, 42, 93–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ley, R.E.; Bäckhed, F.; Turnbaugh, P.; Lozupone, C.A.; Knight, R.D.; Gordon, J.I. Obesity alters gut microbial ecology. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2005, 102, 11070–11075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Turnbaugh, P.J.; Ley, R.E.; Mahowald, M.A.; Magrini, V.; Mardis, E.R.; Gordon, J.I. An obesity-associated gut microbiome with increased capacity for energy harvest. Nature 2006, 444, 1027–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ridaura, V.K.; Faith, J.J.; Rey, F.E.; Cheng, J.; Duncan, A.E.; Kau, A.L.; Griffin, N.W.; Lombard, V.; Henrissat, B.; Bain, J.R. Gut microbiota from twins discordant for obesity modulate metabolism in mice. Science 2013, 341, 1241214. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tremaroli, V.; Karlsson, F.; Werling, M.; Ståhlman, M.; Kovatcheva-Datchary, P.; Olbers, T.; Fändriks, L.; Le Roux, C.W.; Nielsen, J.; Bäckhed, F. Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass and Vertical Banded Gastroplasty Induce Long-Term Changes on the Human Gut Microbiome Contributing to Fat Mass Regulation. Cell Metab. 2015, 22, 228–238. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Depommier, C.; Everard, A.; Druart, C.; Plovier, H.; Van Hul, M.; Vieira-Silva, S.; Falony, G.; Raes, J.; Maiter, D.; Delzenne, N.M.; et al. Supplementation with Akkermansia muciniphila in overweight and obese human volunteers: A proof-of-concept exploratory study. Nat. Med. 2019, 25, 1096–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, M.I.; Yatsunenko, T.; Manary, M.J.; Trehan, I.; Mkakosya, R.; Cheng, J.; Kau, A.L.; Rich, S.S.; Concannon, P.; Mychaleckyj, J.C.; et al. Gut microbiomes of Malawian twin pairs discordant for kwashiorkor. Science 2013, 339, 548–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Marzola, E.; Nasser, J.A.; Hashim, S.A.; Shih, P.-A.B.; Kaye, W.H. Nutritional rehabilitation in anorexia nervosa: Review of the literature and implications for treatment. BMC Psychiatry 2013, 13, 290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khan, A.A.; Yurkovetskiy, L.; O’Grady, K.; Pickard, J.M.; de Pooter, R.; Antonopoulos, D.A.; Golovkina, T.; Chervonsky, A. Polymorphic Immune Mechanisms Regulate Commensal Repertoire. Cell Rep. 2019, 29, 541–550.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tabrett, A.; Horton, M.W. The influence of host genetics on the microbiome. F1000 Res. 2020, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, J.R.; Kennedy, P.J.; Cryan, J.F.; Dinan, T.G.; Clarke, G.; Hyland, N.P. Breaking down the barriers: The gut microbiome, intestinal permeability and stress-related psychiatric disorders. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2015, 9, 392. [Google Scholar]
- Jakobsson, H.E.; Rodríguez-Piñeiro, A.M.; Schütte, A.; Ermund, A.; Boysen, P.; Bemark, M.; Sommer, F.; Bäckhed, F.; Hansson, G.C.; Johansson, M.E. The composition of the gut microbiota shapes the colon mucus barrier. EMBO Rep. 2015, 16, 164–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elamin, E.E.; Masclee, A.A.; Dekker, J.; Pieters, H.-J.; Jonkers, D.M. Short-Chain Fatty Acids Activate AMP-Activated Protein Kinase and Ameliorate Ethanol-Induced Intestinal Barrier Dysfunction in Caco-2 Cell Monolayers. J. Nutr. 2013, 143, 1872–1881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cichon, C.; Sabharwal, H.; Rüter, C.; Schmidt, M.A. MicroRNAs regulate tight junction proteins and modulate epithelial/endothelial barrier functions. Tissue Barriers 2014, 2, e944446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Petra, A.I.; Panagiotidou, S.; Stewart, J.M.; Conti, P.; Theoharides, T.C. Spectrum of mast cell activation disorders. Expert Rev. Clin. Immunol. 2014, 10, 729–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monteleone, P.; Carratù, R.; Cartenì, M.; Generoso, M.; Lamberti, M.; Magistris, L.D.; Brambilla, F.; Colurcio, B.; Secondulfo, M.; Maj, M. Intestinal permeability is decreased in anorexia nervosa. Mol. Psychiatry 2004, 9, 76–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mörkl, S.; Lackner, S.; Meinitzer, A.; Mangge, H.; Lehofer, M.; Halwachs, B.; Gorkiewicz, G.; Kashofer, K.; Painold, A.; Holl, A.K.; et al. Gut microbiota, dietary intakes and intestinal permeability reflected by serum zonulin in women. Eur. J. Nutr. 2018, 57, 2985–2997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jesus, P.; Ouelaa, W.; Francois, M.; Riachy, L.; Guerin, C.; Aziz, M.; do Rego, J.-C.; Dechelotte, P.; Fetissov, S.O.; Coeffier, M. Alteration of intestinal barrier function during activity-based anorexia in mice. Clin. Nutr. 2014, 33, 1046–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Routtenberg; Kuznesof Self-Starvation of Rats Living in Activity Wheels on a Restricted Feeding Schedule. J. Comp. Physiol. Psychol. 1967, 64, 414–421.
- Achamrah, N.; Nobis, S.; Breton, J.; Jésus, P.; Belmonte, L.; Maurer, B.; Legrand, R.; Bôle-Feysot, C.; do Rego, J.L.; Goichon, A.; et al. Maintaining physical activity during refeeding improves body composition, intestinal hyperpermeability and behavior in anorectic mice. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 21887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bambury, A.; Sandhu, K.; Cryan, J.F.; Dinan, T.G. Finding the needle in the haystack: Systematic identification of psychobiotics. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2017, 175, 4430–4438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kelly, J.R.; Borre, Y.; O’Brien, C.; Patterson, E.; El Aidy, S.; Deane, J.; Kennedy, P.J.; Beers, S.; Scott, K.; Moloney, G. Transferring the blues: Depression-associated gut microbiota induces neurobehavioural changes in the rat. J. Psychiatr. Res. 2016, 82, 109–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalton, B.; Bartholdy, S.; Robinson, L.; Solmi, M.; Ibrahim, M.A.A.; Breen, G.; Schmidt, U.; Himmerich, H. A meta-analysis of cytokine concentrations in eating disorders. J. Psychiatr. Res. 2018, 103, 252–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Solmi, M.; Veronese, N.; Favaro, A.; Santonastaso, P.; Manzato, E.; Sergi, G.; Correll, C.U. Inflammatory cytokines and anorexia nervosa: A meta-analysis of cross-sectional and longitudinal studies. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2015, 51, 237–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibson, D.; Mehler, P.S. Anorexia Nervosa and the Immune System-A Narrative Review. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 1915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fetissov, S.O. Role of the gut microbiota in host appetite control: Bacterial growth to animal feeding behaviour. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2017, 13, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fetissov, S.O.; Lucas, N.; Legrand, R. Ghrelin-Reactive Immunoglobulins in Conditions of Altered Appetite and Energy Balance. Front. Endocrinol. (Lausanne) 2017, 8, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- François, M.; Takagi, K.; Legrand, R.; Lucas, N.; Beutheu, S.; Bôle-Feysot, C.; Cravezic, A.; Tennoune, N.; do Rego, J.-C.; Coëffier, M. Increased ghrelin but low ghrelin-reactive immunoglobulins in a rat model of methotrexate chemotherapy-induced anorexia. Front. Nutr. 2016, 3, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tennoune, N.; Chan, P.; Breton, J.; Legrand, R.; Chabane, Y.N.; Akkermann, K.; Jarv, A.; Ouelaa, W.; Takagi, K.; Ghouzali, I.; et al. Bacterial ClpB heat-shock protein, an antigen-mimetic of the anorexigenic peptide alpha-MSH, at the origin of eating disorders. Transl. Psychiatry 2014, 4, e458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Breton, J.; Legrand, R.; Akkermann, K.; Järv, A.; Harro, J.; Déchelotte, P.; Fetissov, S.O. Elevated plasma concentrations of bacterial ClpB protein in patients with eating disorders: Plasma CLPB in Eating Disorders. Int. J. Eat. Disord. 2016, 49, 805–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takagi, K.; Legrand, R.; Asakawa, A.; Amitani, H.; François, M.; Tennoune, N.; Coëffier, M.; Claeyssens, S.; do Rego, J.-C.; Déchelotte, P.; et al. Anti-ghrelin immunoglobulins modulate ghrelin stability and its orexigenic effect in obese mice and humans. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 2685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hedman, A.; Breithaupt, L.; Hübel, C.; Thornton, L.M.; Tillander, A.; Norring, C.; Birgegård, A.; Larsson, H.; Ludvigsson, J.F.; Sävendahl, L.; et al. Bidirectional relationship between eating disorders and autoimmune diseases. J. Child. Psychol. Psychiatry 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raevuori, A.; Haukka, J.; Vaarala, O.; Suvisaari, J.M.; Gissler, M.; Grainger, M.; Linna, M.S.; Suokas, J.T. The increased risk for autoimmune diseases in patients with eating disorders. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e104845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zerwas, S.; Larsen, J.T.; Petersen, L.; Thornton, L.M.; Quaranta, M.; Koch, S.V.; Pisetsky, D.; Mortensen, P.B.; Bulik, C.M. Eating Disorders, Autoimmune, and Autoinflammatory Disease. Pediatrics 2017, 140, e20162089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Duncan, L.; Yilmaz, Z.; Gaspar, H.; Walters, R.; Goldstein, J.; Anttila, V.; Bulik-Sullivan, B.; Ripke, S.; Eating Disorders Working Group of the Psychiatric Genomics Consortium; Thornton, L.; et al. Significant Locus and Metabolic Genetic Correlations Revealed in Genome-Wide Association Study of Anorexia Nervosa. Am. J. Psychiatry 2017, 174, 850–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zallot, C.; Quilliot, D.; Chevaux, J.-B.; Peyrin-Biroulet, C.; Guéant-Rodriguez, R.M.; Freling, E.; Collet-Fenetrier, B.; Williet, N.; Ziegler, O.; Bigard, M.-A.; et al. Dietary Beliefs and Behavior Among Inflammatory Bowel Disease Patients. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2013, 19, 66–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kleiman, S.C.; Glenny, E.M.; Bulik-Sullivan, E.C.; Huh, E.Y.; Tsilimigras, M.C.B.; Fodor, A.A.; Bulik, C.M.; Carroll, I.M. Daily Changes in Composition and Diversity of the Intestinal Microbiota in Patients with Anorexia Nervosa: A Series of Three Cases: Gut Microbes in AN. Eur. Eat. Disord. Rev. 2017, 25, 423–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mack, I.; Penders, J.; Cook, J.; Dugmore, J.; Mazurak, N.; Enck, P. Is the Impact of Starvation on the Gut Microbiota Specific or Unspecific to Anorexia Nervosa? A Narrative Review Based on a Systematic Literature Search. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2018, 16, 1131–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mörkl, S.; Lackner, S.; Meinitzer, A.; Gorkiewicz, G.; Kashofer, K.; Painold, A.; Holl, A.; Holasek, S. Pilot study: Gut microbiome and intestinal barrier in anorexia nervosa. Fortschr. Neurol. Psychiatr. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulz, N.; Belheouane, M.; Dahmen, B.; Ruan, V.; Specht, H.; Dempfle, A.; Herpertz-Dahlmann, B.; Baines, J.F.; Seitz, J. Gut microbiota alteration in adolescent anorexia nervosa does not normalize with short-term weight restoration. Int. J. Eat Dis. in revison.
- Dysbiosis. Available online: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Dysbiosis (accessed on 2 October 2020).
- Tamboli, C.P. Dysbiosis in inflammatory bowel disease. Gut 2004, 53, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kostic, A.D.; Xavier, R.J.; Gevers, D. The microbiome in inflammatory bowel disease: Current status and the future ahead. Gastroenterology 2014, 146, 1489–1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Geirnaert, A.; Calatayud, M.; Grootaert, C.; Laukens, D.; Devriese, S.; Smagghe, G.; De Vos, M.; Boon, N.; Van de Wiele, T. Butyrate-producing bacteria supplemented in vitro to Crohn’s disease patient microbiota increased butyrate production and enhanced intestinal epithelial barrier integrity. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 11450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vieira, A.T.; Fukumori, C.; Ferreira, C.M. New insights into therapeutic strategies for gut microbiota modulation in inflammatory diseases. Clin. Transl. Immunol. 2016, 5, e87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holzer, P.; Farzi, A. Neuropeptides and the microbiota-gut-brain axis. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2014, 817, 195–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, D.; Wen, B.; Zhu, K.; Luo, Y.; Li, J.; Li, Y.; Lin, H.; Huang, J.; Liu, Z. Antibiotics-induced perturbations in gut microbial diversity influence metabolic phenotypes in a murine model of high-fat diet-induced obesity. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2019, 103, 5269–5283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kameyama, K.; Itoh, K. Intestinal colonization by a Lachnospiraceae bacterium contributes to the development of diabetes in obese mice. Microbes Environ. 2014, 29, 427–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vital, M.; Karch, A.; Pieper, D.H. Colonic Butyrate-Producing Communities in Humans: An Overview Using Omics Data. mSystems 2017, 2, e00130-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Maukonen, J.; Kolho, K.-L.; Paasela, M.; Honkanen, J.; Klemetti, P.; Vaarala, O.; Saarela, M. Altered Fecal Microbiota in Paediatric Inflammatory Bowel Disease. J. Crohns. Colitis 2015, 9, 1088–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lobionda, S.; Sittipo, P.; Kwon, H.Y.; Lee, Y.K. The Role of Gut Microbiota in Intestinal Inflammation with Respect to Diet and Extrinsic Stressors. Microorganisms 2019, 7, 271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kao, D.; Roach, B.; Silva, M.; Beck, P.; Rioux, K.; Kaplan, G.G.; Chang, H.-J.; Coward, S.; Goodman, K.J.; Xu, H.; et al. Effect of Oral Capsule- vs Colonoscopy-Delivered Fecal Microbiota Transplantation on Recurrent Clostridium difficile Infection: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA 2017, 318, 1985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Queipo-Ortuño, M.I.; Seoane, L.M.; Murri, M.; Pardo, M.; Gomez-Zumaquero, J.M.; Cardona, F.; Casanueva, F.; Tinahones, F.J. Gut microbiota composition in male rat models under different nutritional status and physical activity and its association with serum leptin and ghrelin levels. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e65465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hebebrand, J.; Muller, T.D.; Holtkamp, K.; Herpertz-Dahlmann, B. The role of leptin in anorexia nervosa: Clinical implications. Mol. Psychiatry 2007, 12, 23–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Breton, J.; Tirelle, P.; Hasanat, S.; Pernot, A.; L’Huillier, C.; do Rego, J.-C.; Déchelotte, P.; Coëffier, M.; Bindels, L.B.; Ribet, D. Gut microbiota alteration in a mouse model of Anorexia Nervosa. Clin. Nutr. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Möhle, L.; Mattei, D.; Heimesaat, M.M.; Bereswill, S.; Fischer, A.; Alutis, M.; French, T.; Hambardzumyan, D.; Matzinger, P.; Dunay, I.R. Ly6Chi monocytes provide a link between antibiotic-induced changes in gut microbiota and adult hippocampal neurogenesis. Cell Rep. 2016, 15, 1945–1956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Paulukat, L.; Frintrop, L.; Liesbrock, J.; Heussen, N.; Johann, S.; Exner, C.; Martien, K.J.; Tolba, R.; Neulen, J.; Konrad, K. Memory impairment is associated with the loss of regular oestrous cycle and plasma oestradiol levels in an activity-based anorexia animal model. World J. Biol. Psychiatry 2016, 17, 274–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frintrop, L.; Liesbrock, J.; Paulukat, L.; Johann, S.; Kas, M.J.; Tolba, R.; Heussen, N.; Neulen, J.; Konrad, K.; Herpertz-Dahlmann, B.; et al. Reduced astrocyte density underlying brain volume reduction in activity-based anorexia rats. World J. Biol. Psychiatry 2018, 19, 225–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frintrop, L.; Trinh, S.; Liesbrock, J.; Leunissen, C.; Kempermann, J.; Etdöger, S.; Kas, M.J.; Tolba, R.; Heussen, N.; Neulen, J.; et al. The reduction of astrocytes and brain volume loss in anorexia nervosa-the impact of starvation and refeeding in a rodent model. Transl. Psychiatry 2019, 9, 159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seitz, J.; Konrad, K.; Herpertz-Dahlmann, B. Extend, Pathomechanism and Clinical Consequences of Brain Volume Changes in Anorexia Nervosa. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2018, 16, 1164–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seitz, J.; Walter, M.; Mainz, V.; Herpertz-Dahlmann, B.; Konrad, K.; Polier, G. von Brain volume reduction predicts weight development in adolescent patients with anorexia nervosa. J. Psychiatr. Res. 2015, 68, 228–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trinh, S.; Kogel, V.; Voelz, C.; Schlösser, A.; Schwenzer, C.; Kabbert, J.; Heussen, N.; Clavel, T.; Herpertz-Dahlmann, B.; Beyer, C.; et al. Gut microbiota and brain alterations in a translational anorexia nervosa rat model. J. Psychiatry Res. 2020. resubmitted. [Google Scholar]
- Monteleone, P.; Monteleone, A.M.; Troisi, J.; Dalle Grave, R.; Corrivetti, G.; Calugi, S.; Scala, G.; Patriciello, G.; Zanetti, A.; Maj, M. Metabolomics signatures of acutely ill and short-term weight recovered women with anorexia nervosa. Mol. Psychiatry 2019, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monteleone, A.M.; Troisi, J.; Fasano, A.; Dalle Grave, R.; Marciello, F.; Serena, G.; Calugi, S.; Scala, G.; Corrivetti, G.; Cascino, G.; et al. Multi-omics data integration in anorexia nervosa patients before and after weight regain: A microbiome-metabolomics investigation. Clin. Nutr. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pirbaglou, M.; Katz, J.; de Souza, R.J.; Stearns, J.C.; Motamed, M.; Ritvo, P. Probiotic supplementation can positively affect anxiety and depressive symptoms: A systematic review of randomized controlled trials. Nutr. Res. 2016, 36, 889–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costantini, L.; Molinari, R.; Farinon, B.; Merendino, N. Impact of Omega-3 Fatty Acids on the Gut Microbiota. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 2645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mauler, B.; Dubben, S.; Pawelzik, M.; Pawelzik, D.; Weigle, D.S.; Kratz, M. Hypercaloric diets differing in fat composition have similar effects on serum leptin and weight gain in female subjects with anorexia nervosa. Nutr. Res. 2009, 29, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herpertz-Dahlmann, B. Microbiome Gut-Brain Interaction in Anorexia Nervosa (MiGBAN); Bundesministerium für Bildung und Forschung: Berlin, Germany, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Shih, P.B.; Morisseau, C.; Le, T.; Woodside, B.; German, J.B. Personalized polyunsaturated fatty acids as a potential adjunctive treatment for anorexia nervosa. Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat. 2017, 133, 11–19. [Google Scholar]
- David, L.A.; Maurice, C.F.; Carmody, R.N.; Gootenberg, D.B.; Button, J.E.; Wolfe, B.E.; Ling, A.V.; Devlin, A.S.; Varma, Y.; Fischbach, M.A.; et al. Diet rapidly and reproducibly alters the human gut microbiome. Nature 2014, 505, 559–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Maier, L.; Pruteanu, M.; Kuhn, M.; Zeller, G.; Telzerow, A.; Anderson, E.E.; Brochado, A.R.; Fernandez, K.C.; Dose, H.; Mori, H. Extensive impact of non-antibiotic drugs on human gut bacteria. Nature 2018, 555, 623. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kaplan, A.S.; Strober, M. Severe and enduring anorexia nervosa: Can risk of persisting illness be identified, and prevented, in young patients? Int. J. Eat. Disord. 2019, 52, 478–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demmler, J.C.; Brophy, S.T.; Marchant, A.; John, A.; Tan, J.O.A. Shining the light on eating disorders, incidence, prognosis and profiling of patients in primary and secondary care: National data linkage study. Br. J. Psychiatry 2020, 216, 105–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Seitz, J.; Dahmen, B.; Keller, L.; Herpertz-Dahlmann, B. Gut Feelings: How Microbiota Might Impact the Development and Course of Anorexia Nervosa. Nutrients 2020, 12, 3295. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12113295
Seitz J, Dahmen B, Keller L, Herpertz-Dahlmann B. Gut Feelings: How Microbiota Might Impact the Development and Course of Anorexia Nervosa. Nutrients. 2020; 12(11):3295. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12113295
Chicago/Turabian StyleSeitz, Jochen, Brigitte Dahmen, Lara Keller, and Beate Herpertz-Dahlmann. 2020. "Gut Feelings: How Microbiota Might Impact the Development and Course of Anorexia Nervosa" Nutrients 12, no. 11: 3295. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12113295
APA StyleSeitz, J., Dahmen, B., Keller, L., & Herpertz-Dahlmann, B. (2020). Gut Feelings: How Microbiota Might Impact the Development and Course of Anorexia Nervosa. Nutrients, 12(11), 3295. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12113295