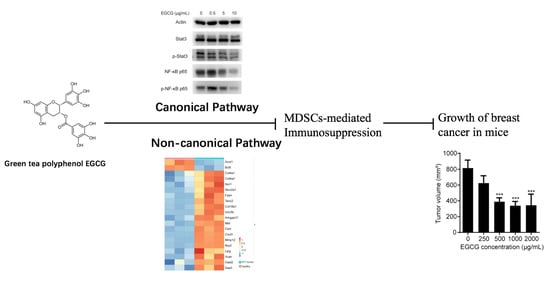
Green Tea Polyphenol EGCG Attenuates MDSCs-mediated Immunosuppression through Canonical and Non-Canonical Pathways in a 4T1 Murine Breast Cancer Model
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Reagents
2.2. 4T1 Cell Culture and In Vitro Assays
2.3. Animal Study
2.4. Flow Cytometry Analysis
2.5. Cell Sorting and MDSCs In Vitro Experiments
2.6. RNA Isolation and Quantitative Reverse Transcription PCR (qRT-PCR)
2.7. Western Blot
2.8. Detection of Arginase Activity, NO and ROS Production
2.9. RNA Sequencing and Microarray Data Analysis
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. EGCG Inhibits 4T1 Tumor Growth Both In Vitro and In Vivo
3.2. EGCG Ameliorates MDSCs-Mediated Immunosuppression in 4T1 Tumor-Bearing Mice
3.3. EGCG Suppresses Growth and Increases Apoptosis of MDSCs In Vitro
3.4. EGCG Targets MDSCs through the Canonical Pathways
3.5. EGCG Restores MDSCs through Non-Canonical Signaling Pathways
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dou, Q.P. Tea in health and disease. Nutrients 2019, 11, 929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yang, C.S.; Wang, X.; Lu, G.; Picinich, S.C. Cancer prevention by tea: Animal studies, molecular mechanisms and human relevance. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2009, 9, 429–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fujiki, H.; Sueoka, E.; Watanabe, T.; Suganuma, M. Primary cancer prevention by green tea, and tertiary cancer prevention by the combination of green tea catechins and anticancer compounds. J. Cancer Prev. 2015, 20, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.-Y.; Zhao, C.-N.; Cao, S.-Y.; Tang, G.-Y.; Gan, R.-Y.; Li, H.-B. Effects and mechanisms of tea for the prevention and management of cancers: An updated review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2019, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.S.; Zhang, J. Studies on the prevention of cancer and cardiometabolic diseases by tea: Issues on mechanisms, effective doses, and toxicities. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 5446–5456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sang, S.; Lambert, J.D.; Yang, C.S. Bioavailability and stability issues in understanding the cancer preventive effects of tea polyphenols. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2006, 86, 2256–2265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambert, J.D.; Yang, C.S. Cancer chemopreventive activity and bioavailability of tea and tea polyphenols. Mutat. Res. Fundam. Mol. Mech. Mutagen. 2003, 523, 201–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, V.; Patel, S.; Tcyganov, E.; Gabrilovich, D.I. The nature of myeloid-derived suppressor cells in the tumor microenvironment. Trends Immunol. 2016, 37, 208–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parker, K.H.; Beury, D.W.; Ostrand-Rosenberg, S. Myeloid-derived suppressor cells: Critical cells driving immune suppression in the tumor microenvironment. Adv. Cancer Res. 2015, 128, 95–139. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.; Ye, Y.; Liu, P.; Yu, W.; Wei, F.; Li, H.; Yu, J. Suppression of T cells by myeloid-derived suppressor cells in cancer. Hum. Immunol. 2017, 78, 113–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corzo, C.A.; Cotter, M.J.; Cheng, P.; Cheng, F.; Kusmartsev, S.; Sotomayor, E.; Padhya, T.; McCaffrey, T.V.; McCaffrey, J.C.; Gabrilovich, D.I. Mechanism regulating reactive oxygen species in tumor-induced myeloid-derived suppressor cells. J. Immunol. 2009, 182, 5693–5701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santilli, G.; Piotrowska, I.; Cantilena, S.; Chayka, O.; D’Alicarnasso, M.; Morgenstern, D.A.; Himoudi, N.; Pearson, K.; Anderson, J.; Thrasher, A.J.; et al. Polyphenol E enhances the antitumor immune response in neuroblastoma by inactivating myeloid suppressor cells. Clin. Cancer Res. 2013, 19, 1116–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cardoso, F.; Spence, D.; Mertz, S.; Corneliussen-James, D.; Sabelko, K.; Gralow, J.; Cardoso, M.J.; Peccatori, F.; Paonessa, D.; Benares, A.; et al. Global analysis of advanced/metastatic breast cancer: Decade report (2005–2015). Breast 2018, 39, 131–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sledge, G.W. Curing metastatic breast cancer. J. Oncol. Pract. 2016, 12, 6–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alizadeh, D.; Trad, M.; Hanke, N.T.; Larmonier, C.B.; Janikashvili, N.; Bonnotte, B.; Katsanis, E.; Larmonier, N. Doxorubicin eliminates myeloid-derived suppressor cells and enhances the efficacy of adoptive T-cell transfer in breast cancer. Cancer Res. 2014, 74, 104–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Markowitz, J.; Wesolowski, R.; Papenfuss, T.; Brooks, T.R.; Carson, W.E. Myeloid-derived suppressor cells in breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2013, 140, 13–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, P.; Wan, X.; Cui, B.; Liu, Y.; Qiu, C.; Rong, J.; Zheng, M.; Song, Y.; Chen, L.; He, J.; et al. Interleukin 33 in tumor microenvironment is crucial for the accumulation and function of myeloid-derived suppressor cells. Oncoimmunology 2016, 5, e1063772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ying, L.; Yan, F.; Williams, B.R.; Xu, P.; Li, X.; Zhao, Y.; Hu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Xu, D.; Dai, J. (−)-Epigallocatechin-3-gallate and EZH2 inhibitor GSK343 have similar inhibitory effects and mechanisms of action on colorectal cancer cells. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol. 2018, 45, 58–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, F.; Ying, L.; Li, X.; Qiao, B.; Meng, Q.; Yu, L.; Yuan, X.; Ren, S.-T.; Chan, D.W.; Shi, L.; et al. Overexpression of the transcription factor ATF3 with a regulatory molecular signature associates with the pathogenic development of colorectal cancer. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 47020–47036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liao, Y.; Smyth, G.K.; Shi, W. FeatureCounts: An efficient general purpose program for assigning sequence reads to genomic features. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 923–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Robinson, M.D.; McCarthy, D.J.; Smyth, G.K. edgeR: A Bioconductor package for differential expression analysis of digital gene expression data. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 139–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sonda, N.; Simonato, F.; Peranzoni, E.; Calì, B.; Bortoluzzi, S.; Bisognin, A.; Wang, E.; Marincola, F.M.; Naldini, L.; Gentner, B.; et al. MiR-142-3p prevents macrophage differentiation during cancer-induced myelopoiesis. Immunity 2013, 38, 1236–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ritchie, M.E.; Phipson, B.; Wu, D.; Hu, Y.; Law, C.W.; Shi, W.; Smyth, G.K. Limma powers differential expression analyses for RNA-sequencing and microarray studies. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, e47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, G.; Wang, L.-G.; Han, Y.; He, Q.-Y. clusterProfiler: An R Package for Comparing Biological Themes Among Gene Clusters. Omics A J. Integr. Biol. 2012, 16, 284–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Subramanian, A.; Tamayo, P.; Mootha, V.K.; Mukherjee, S.; Ebert, B.L.; Gillette, M.A.; Paulovich, A.; Pomeroy, S.L.; Golub, T.R.; Lander, E.S.; et al. Gene set enrichment analysis: A knowledge-based approach for interpreting genome-wide expression profiles. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 15545–15550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- De Veirman, K.; Van Ginderachter, J.A.; Lub, S.; De Beule, N.; Thielemans, K.; Bautmans, I.; Oyajobi, B.O.; De Bruyne, E.; Menu, E.; Lemaire, M.; et al. Multiple myeloma induces Mcl-1 expression and survival of myeloid-derived suppressor cells. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 10532–10547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hu, X.; Bardhan, K.; Paschall, A.V.; Yang, D.; Waller, J.L.; Park, M.A.; Nayak-Kapoor, A.; Samuel, T.A.; Abrams, S.I.; Liu, K. Deregulation of apoptotic factors Bcl-xL and Bax confers apoptotic resistance to myeloid-derived suppressor cells and contributes to their persistence in cancer. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 19103–19115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ostrand-Rosenberg, S.; Sinha, P.; Chornoguz, O.; Ecker, C. Regulating the suppressors: Apoptosis and inflammation govern the survival of tumor-induced myeloid-derived suppressor cells (MDSC). Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2012, 61, 1319–1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trikha, P.; Carson, W.E. Signaling pathways involved in MDSC regulation. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2014, 1846, 55–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lambert, J.D.; Lee, M.-J.; Diamond, L.; Ju, J.; Hong, J.; Bose, M.; Newmark, H.L.; Yang, C.S. Dose-dependent levels of epigallocatechin-3-gallate in human colon cancer cells and mouse plasma and tissues. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2006, 34, 8–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ando, Y.; Oku, T.; Tsuji, T. Platelet supernatant suppresses LPS-induced nitric oxide production from macrophages accompanied by inhibition of NF-κB signaling and increased arginase-1 expression. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0162208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, D.J.; Ratnam, N.M.; Byrd, J.C.; Guttridge, D.C. NF-κB functions in tumor initiation by suppressing the surveillance of both innate and adaptive immune cells. Cell Rep. 2014, 9, 90–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gu, J.; Sun, X.; Wang, G.; Li, M.; Chi, M. Icariside II enhances Nrf2 nuclear translocation to upregulate phase II detoxifying enzyme expression coupled with the ERK, Akt and JNK signaling pathways. Molecules 2011, 16, 9234–9244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arslan, M.; Melek, M.; Demir, H.; Eseoglu, M.; Gudu, B.O.; Demir, I.; Cetin, C. Relationship of antioxidant enzyme activities with myelomeningocele. Turk. Neurosurg. 2012, 22, 300–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, W.; Overman, M.J.; Boutin, A.T.; Shang, X.; Zhao, D.; Dey, P.; Li, J.; Wang, G.; Lan, Z.; Li, J.; et al. KRAS-IRF2 axis drives immune suppression and immune therapy resistance in colorectal cancer. Cancer Cell 2019, 35, 559–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, J.-M.; Kim, E.-K.; Seo, H.; Jeon, I.; Chae, M.-J.; Park, Y.-J.; Song, B.; Kim, Y.-S.; Kim, Y.-J.; Ko, H.-J.; et al. Serum amyloid A3 exacerbates cancer by enhancing the suppressive capacity of myeloid-derived suppressor cells via TLR2-dependent STAT3 activation. Eur. J. Immunol. 2014, 44, 1672–1684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhang, X.; Liu, Q.; Yang, M.; Zhou, Z.; Ye, Y.; Zhou, Z.; He, X.; Wang, L. Myeloid-derived suppressor cells accumulate among myeloid cells contributing to tumor growth in matrix metalloproteinase 12 knockout mice. Cell. Immunol. 2018, 327, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipinski, C.A.; Lombardo, F.; Dominy, B.W.; Feeney, P.J. Experimental and computational approaches to estimate solubility and permeability in drug discovery and development settings. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2001, 46, 3–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chow, H.H.S.; Hakim, I.A.; Vining, D.R.; Crowell, J.A.; Ranger-Moore, J.; Chew, W.M.; Celaya, C.A.; Rodney, S.R.; Hara, Y.; Alberts, D.S. Effects of dosing condition on the oral bioavailability of green tea catechins after single-dose administration of polyphenon E in healthy individuals. Clin. Cancer Res. 2005, 11, 4627–4633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, G.-X.; Chen, Y.-K.; Hou, Z.; Xiao, H.; Jin, H.; Lu, G.; Lee, M.-J.; Liu, B.; Guan, F.; Yang, Z.; et al. Pro-oxidative activities and dose-response relationship of (-)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate in the inhibition of lung cancer cell growth: A comparative study in vivo and in vitro. Carcinogenesis 2010, 31, 902–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, C.S.; Sang, S.; Lambert, J.D.; Lee, M.J. Bioavailability issues in studying the health effects of plant polyphenolic compounds. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2008, 52, S139–S151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ugel, S.; Delpozzo, F.; Desantis, G.; Papalini, F.; Simonato, F.; Sonda, N.; Zilio, S.; Bronte, V. Therapeutic targeting of myeloid-derived suppressor cells. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2009, 9, 470–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wesolowski, R.; Markowitz, J.; Carson, W.E. Myeloid derived suppressor cells—A new therapeutic target in the treatment of cancer. J. Immunother. Cancer 2013, 1, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ostrand-Rosenberg, S.; Sinha, P.; Beury, D.W.; Clements, V.K. Cross-talk between myeloid-derived suppressor cells (MDSC), macrophages, and dendritic cells enhances tumor-induced immune suppression. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2012, 22, 275–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Z.; Li, Z.; Wang, Y.; Cao, D.; Wang, X.; Jiang, M.; Li, M.; Yan, X.; Li, Y.; Liu, Y.; et al. Versican silencing improves the antitumor efficacy of endostatin by alleviating its induced inflammatory and immunosuppressive changes in the tumor microenvironment. Oncol. Rep. 2015, 33, 2981–2991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, Y.; Taylor, N.E.; Lu, L.; Usa, K.; Cowley, A.W.; Ferreri, N.R.; Yeo, N.C.; Liang, M. Renal medullary MicroRNAs in dahl salt-sensitive rats: MiR-29b regulates several collagens and related genes. Hypertension 2010, 55, 974–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ying, L.; Yan, F.; Zhao, Y.; Gao, H.; Williams, B.R.; Hu, Y.; Li, X.; Tian, R.; Xu, P.; Wang, Y. (-)-Epigallocatechin-3-gallate and atorvastatin treatment down-regulates liver fibrosis-related genes in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol. 2017, 44, 1180–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jassal, B.; Matthews, L.; Viteri, G.; Gong, C.; Lorente, P.; Fabregat, A.; Sidiropoulos, K.; Cook, J.; Gillespie, M.; Haw, R.; et al. The reactome pathway knowledgebase. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020, 48, D498–D503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, A.; Shao, L.; Sampath, P.; Zhao, B.; Patel, N.V.; Zhu, J.; Behl, B.; Parise, R.A.; Beumer, J.H.; O’Sullivan, R.J.; et al. Oligoadenylate-synthetase-family protein OASL inhibits activity of the DNA sensor cGAS during DNA virus infection to limit interferon production. Immunity 2019, 50, 51–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Comoglio, P.M.; Trusolino, L.; Boccaccio, C. Known and novel roles of the MET oncogene in cancer: A coherent approach to targeted therapy. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2018, 18, 341–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, A.; O’Bryan, J.P. Intersectin 1 is required for neuroblastoma tumorigenesis. Oncogene 2012, 31, 4828–4834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, F.; Wu, J.; Qiu, Z.; Ge, X.; Liu, X.; Zhang, C.; Xu, W.; Wang, F.; Hua, D.; Qi, X.; et al. ACOT1 expression is associated with poor prognosis in gastric adenocarcinoma. Hum. Pathol. 2018, 77, 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Del Paggio, J.C. Immunotherapy: Cancer immunotherapy and the value of cure. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 15, 268–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukumura, D.; Kloepper, J.; Amoozgar, Z.; Duda, D.G.; Jain, R.K. Enhancing cancer immunotherapy using antiangiogenics: Opportunities and challenges. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 15, 325–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ribas, A.; Wolchok, J.D. Cancer immunotherapy using checkpoint blockade. Science 2018, 359, 1350–1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Riley, R.S.; June, C.H.; Langer, R.; Mitchell, M.J. Delivery technologies for cancer immunotherapy. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2019, 18, 175–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baniyash, M. Myeloid-derived suppressor cells as intruders and targets: Clinical implications in cancer therapy. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2016, 65, 857–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, P.; Yan, F.; Zhao, Y.; Chen, X.; Sun, S.; Wang, Y.; Ying, L. Green Tea Polyphenol EGCG Attenuates MDSCs-mediated Immunosuppression through Canonical and Non-Canonical Pathways in a 4T1 Murine Breast Cancer Model. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1042. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12041042
Xu P, Yan F, Zhao Y, Chen X, Sun S, Wang Y, Ying L. Green Tea Polyphenol EGCG Attenuates MDSCs-mediated Immunosuppression through Canonical and Non-Canonical Pathways in a 4T1 Murine Breast Cancer Model. Nutrients. 2020; 12(4):1042. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12041042
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Ping, Feng Yan, Yueling Zhao, Xiangbo Chen, Shili Sun, Yuefei Wang, and Le Ying. 2020. "Green Tea Polyphenol EGCG Attenuates MDSCs-mediated Immunosuppression through Canonical and Non-Canonical Pathways in a 4T1 Murine Breast Cancer Model" Nutrients 12, no. 4: 1042. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12041042
APA StyleXu, P., Yan, F., Zhao, Y., Chen, X., Sun, S., Wang, Y., & Ying, L. (2020). Green Tea Polyphenol EGCG Attenuates MDSCs-mediated Immunosuppression through Canonical and Non-Canonical Pathways in a 4T1 Murine Breast Cancer Model. Nutrients, 12(4), 1042. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12041042