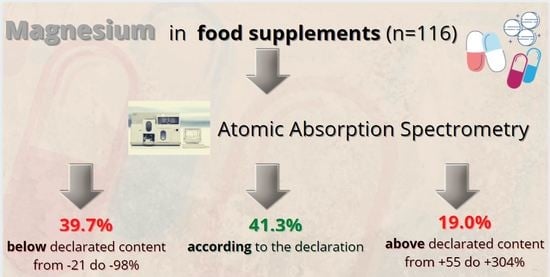
Is the Magnesium Content in Food Supplements Consistent with the Manufacturers’ Declarations?
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Sample Preparation
- Step 1: 170 °C, 10 min, 20 atm., 80% of microwave power;
- Step 2: 190 °C, 10 min, 30 atm., 90% of microwave power;
- Step 3: 210 °C, 10 min, 40 atm., 90% of microwave power;
- Step 4: 50 °C, 18 min, 40 atm., 0% of microwave power.
2.3. Determination of Mg Content
2.4. Validation of Method
2.5. Comparison of Results with the Standards Adopted by the Chief Sanitary Inspectorate in Poland
2.6. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References and Note
- The Act of 25 August 2006 on Food and Nutrition Safety. Journal of Laws 2006 No. 171 Item 1225, 25 August 2006. (In Polish)
- Announcement of the Minister of Health of 17 September 2018 on the Publication of the Uniform Text of the Regulation of the Minister of Health on the Composition and Labeling of Dietary Supplements. Journal of Laws 2018 Item 1951, 17 September 2018. (In Polish)
- Costa, J.G.; Vidovic, B.; Saraiva, N.; do Céu Costa, M.; Del Favero, G.; Marko, D.; Oliveira, N.G.; Fernandes, A.S. Contaminants: A dark side of food supplements? Free Radic. Res. 2019, 53 (Suppl. S1), 1113–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, K.; Kaaks, R.; Linseisen, J.; Rohrmann, S. Consistency of vitamin and/or mineral supplement use and demographic, lifestyle and health-status predictors: Findings from the European Prospective Investigation into Cancer and Nutrition (EPIC)-Heidelberg cohort. Br. J. Nutr. 2010, 10, 1058–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Puścion-Jakubik, A.; Kus, K.; Socha, K. Medical university students’ perspective on marketing of dietary supplements. Acta Pol. Pharm. 2021, 78, 205–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suplindex. Available online: https://suplindex.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/10/RAPORT-Suplementy-diety-30.08.2017.pdf (accessed on 10 September 2021).
- Regulation of the Minister of Health of 18 May 2010 Amending the Regulation on the Composition and Labeling of Dietary Supplements. Journal of Laws of 2010 No. 91, Item 596, 18 May 2010. (In Polish)
- Commission Regulation (EU) No 231/2012 of 9 March 2012 Laying down Specifications for Food Additives Listed in Annexes II and III to Regulation (EC) No 1333/2008 of the European Parliament and of the Council Text with EEA Relevance.
- Nielsen, F.H. Dietary magnesium and chronić disease. Adv. Chronic. Kidney Dis. 2018, 25, 230–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Laecke, S.; Caluwe, R.; Huybrechts, I.; Nagler, E.V.; Vanholder, R.; Peeters, P.; Van Vlem, B.; Van Biesen, W. Effect of magnesium supplements on insulin secretion after kidney transplantation: A randomized controlled trial. Ann. Transplant. 2017, 22, 524–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morais, J.B.; Severo, J.S.; Santos, L.R.; de Sousa Melo, S.R.; de Oliveira Santos, R.; de Oliveira, A.R.; Cruz, K.J.; do Nascimento Marreiro, D. Role of magnesium in oxidative stress in individuals with obesity. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2017, 176, 20–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mendes, P.M.V.; Bezerra, D.L.C.; Dos Santos, L.R.; de Oliveira Santos, R.; de Sousa Melo, S.R.; Morais, J.B.S.; Severo, J.S.; Vieira, S.C.; do Nascimento Marreiro, D. Magnesium in breast cancer: What is its influence on the progression of this disease? Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2018, 184, 334–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abuabat, F.; AlAlwan, A.; Masuadi, E.; Murad, M.H.; Jahdali, H.A.; Ferwana, M.S. The role of oral magnesium supplements for the management of stable bronchial asthma: A systematic review and meta-analysis. NPJ Prim. Care Respir. Med. 2019, 29, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwalfenberg, G.K.; Genius, S.J. The importance of magnesium in clinical healthcare. Hidawi Sci. 2017, 2017, 4179326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Commission; Directorate-General for Health and Consumers. December 2012 Guidance on Setting Tolerance Limits for Labeled Nutrients. Komisja Europejska, Dyrekcja generalna ds. Zdrowia i Konsumentów. Wytyczne z Grudnia 2012 r. w Zakresie Określenia Limitów Tolerancji Dla Składników Odżywczych Wymienionych na Etykiecie. Available online: https://foodsupplementseurope.org/wp-content/themes/fse-theme/documents/publications-and-guidelines/fse-setting-of-tolerances-for-nutrient-values-declared-on-a-label.pdf (accessed on 1 September 2021).
- Wawrzyniak, A.; Przybyłowicz, K.; Wądołowska, L.; Charzewska, J.; Górecka, D.; Lange, E.; Other Members of the Human Nutrition Science Committee of the Polish Academy of Sciences. Statement of the Committee of Human Nutrition Science of the Polish Academy of Sciences on the use of dietary supplements containing vitamins and minerals by adults. Rocz Panstw Zakł Hig 2021, 77, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SW Research. Available online: https://files.swresearch.pl/raportyPdf/Raport%2364-65-proc-polakow-suplementy-diety-kupuje-w-aptekach.pdf (accessed on 2 May 2021).
- Jarosz, M.; Rychlik, E.; Stoś, K.; Charzewska, J. Normy Żywienia Dla Populacji Polski i Ich Zastosowanie; Narodowy Instytut Zdrowia Publicznego-Państwowy Zakład Higieny: Warsaw, Poland, 2020; pp. 68–437. [Google Scholar]
- Institute of Medicine. Dietary Reference Intakes for Calcium, Phosphorus, Magnesium, Vitamin D, and Fluoride; The National Academies: Washington, DC, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Kutsal, E.; Aydemir, C.; Eldes, N.; Demirel, F.; Polat, R.; Taspnar, O.; Kulah, E. Severe hypermagnesemia as a result of excessive cathartic ingestion in a child without renal failure. Pediatr. Emerg. Care 2007, 23, 570–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Resolution No. 19/2019 of the Team for Diet Supplements of 13 December 2019 on Expressing an Opinion on the Maximum Dose of Magnesium in the Recommended Daily Dose in Dietary Supplements. In Polish, Uchwała nr 19/2019 Zespołu do Spraw Suplementów Diety z Dnia 13 Grudnia 2019 r. w Sprawie Wyrażenia Opinii Dotyczącej Maksymalnej Dawki Magnezu w Zalecanej Dziennej Porcji w Suplementach Diety. Available online: https://gis.gov.pl/wp-content/uploads/2019/05/uchwa%C5%82a-19-2019-Magnez.pdf (accessed on 9 September 2021).
- Moniakowska, A.; Dzierwanowska, A.; Strumińska-Parulska, D. On uranium 234U and 238U radionuclides in calcium and magnesium supplements and the potential effective radiation dose assessment to the consumers. Food Addit. Contam. Part B Surveill 2019, 12, 175–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strumińska-Parulska, D.I. 210Pb in magnesium dietary supplements. Isot. Environ. Health Stud. 2017, 53, 111–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- TNS Polska. Available online: https://www.rynekzdrowia.pl/Farmacja/Badanie-TNS-jedna-czwarta-ankietowanych-sadzi-ze-suplementu-nie-mozna-przedawkowac,139554,6.html (accessed on 23 April 2021).
- Afzali, H.; Jafari Kashi, A.H.; Momen-Heravi, M.; Razzaghi, R.; Amirani, E.; Bahmani, F.; Gilasi, H.R.; Asemi, Z. The effects of magnesium and vitamin E co-supplementation on wound healing and metabolic status in patients with diabetic foot ulcer: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Wound Repair. Regen. 2019, 27, 277–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blancquaert, L.; Vervaet, C.; Derave, W. Predicting and testing bioavailability of magnesium supplements. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schuchardt, J.P.; Hahn, A. Intestinal absorption and factors influencing bioavailability of magnesium—An update. Curr. Nutr. Food Sci. 2017, 13, 260–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jahnen-Dechent, W.; Ketteler, M. Magnesium basics. Clin. Kidney J. 2012, 5 (Suppl. S1), i3–i14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Graham, L.; Caesar, J.; Burgen, A. Gastrointestinal absorption and excretion of Mg28 in man. Metabolism 1960, 9, 646–659. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gröber, U.; Schmidt, J.; Kisters, K. Magnesium in prevention and therapy. Nutrients 2015, 7, 8199–8226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kunachowicz, H. Tabele Składu i Wartości Odżywczej Żywności; PZWL Wydawnictwo Lekarskie: Warsaw, Poland, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Boylan, S.; Welch, A.; Pikhart, H.; Malyutina, S.; Pajak, A.; Kubinova, R.; Bragina, O.; Simonova, G.; Stepaniak, U.; Gilis-Januszewska, A.; et al. Dietary habits in three Central and Eastern European countries: The HAPIEE study. BMC Public Health 2009, 9, 439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Declared Content | n | Mg Content (mg/Portion) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Av. ± SD | Min–Max | Med. | Q1 | Q3 | IQR | ||
| Less than 100 mg | 49 | 49.7 ± 38.0 | 1.5–202.0 | 40.7 | 23.7 | 73.4 | 49.7 |
| 100–200 mg | 45 | 144.9 ± 109.5 | 7.4–469.6 | 115.7 | 66.3 | 207.2 | 141.0 |
| Above 200 mg | 22 | 387.0 ± 200.2 | 39.1–795.7 | 348.7 | 249.2 | 479.2 | 230.0 |
| Form | n | Mg Content (mg/Portion) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Av. ± SD | Min–Max | Med. | Q1 | Q3 | IQR | ||
| Capsules | 13 | 103.8 ± 110.0 | 1.5–298.5 | 69.2 | 22.8 | 193.0 | 170.2 |
| Coated tablets | 11 | 68.5 ± 60.4 | 19.0–202.0 | 48.0 | 23.7 | 77.5 | 53.8 |
| Dragees | 2 | 78.3 ± 22.7 | 62.2–94.3 | 78.3 | 62.2 | 94.3 | 32.1 |
| Effervescent tablets | 24 | 231.2 ± 196.0 | 4.9–696.9 | 168.2 | 78.6 | 364.2 | 285.6 |
| Granulates | 1 | 233.1 ± 0.0 | - | - | - | - | - |
| Jelly beans | 1 | 27.5 ± 0.0 | - | - | - | - | - |
| Liquids | 7 | 198.4 ± 120.6 | 34.0–360.1 | 219.7 | 75.4 | 317.6 | 242.2 |
| Powders | 12 | 264.2 ± 247.2 | 22.1–795.7 | 189.1 | 81.2 | 367.4 | 286.2 |
| Tablets | 45 | 106.8± 133.6 | 5.8–696.5 | 60.2 | 31.4 | 120.8 | 89.4 |
| Chemical Form | n | Mg Content (mg/Portion) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Av. ± SD | Min–Max | Med. | Q1 | Q3 | IQR | ||
| Magnesium bisglycinate | 6 | 161.4 ± 103.1 | 28.5–317.6 | 154.3 | 93.8 | 219.7 | 126.0 |
| Magnesium carbonate | 34 | 132.2 ± 164.2 | 5.8–696.9 | 73.9 | 40.7 | 137.8 | 97.1 |
| Magnesium citrate | 35 | 168.4 ± 201.1 | 1.5–795.7 | 79.1 | 31.5 | 232.0 | 200.6 |
| Magnesium glycerophosphate | 1 | 78.8 ± 0.0 | - | - | - | - | - |
| Magnesium hydroxide | 2 | 215.6 ± 263.8 | 29.1–402.1 | 215.6 | 29.1 | 402.1 | 373.0 |
| Magnesium lactate | 11 | 45.7 ± 39.4 | 1.8–129.3 | 35.4 | 7.4 | 77.9 | 70.5 |
| Magnesium oxide | 8 | 207.6 ± 155.5 | 18.8–449.4 | 225.6 | 52.9 | 317.9 | 265.1 |
| Several chemical forms | 19 | 181.2 ± 148.1 | 22.8–479.2 | 145.4 | 61.2 | 267.6 | 206.4 |
| Amount of Minerals | n | Mg Content (mg/Portion) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Av. ± SD | Min–Max | Med. | Q1 | Q3 | IQR | ||
| Only magnesium (or vitamin B6) | 75 | 164.8 ± 183.6 | 1.5–795.7 | 93.8 | 34.0 | 249.2 | 215.3 |
| Multicomponent preparations | 41 | 124.7 ± 125.6 | 4.8–469.6 | 76.4 | 38.5 | 188.8 | 150.2 |
| Price (PLN) | n | Mg Content (mg/Portion) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Av. ± SD | Min–Max | Med. | Q1 | Q3 | IQR | ||
| <10 | 41 | 192.1 ± 191.1 | 13.3–696.9 | 108.3 | 35.4 | 317.6 | 282.1 |
| 10–20 | 57 | 112.0 ± 138.8 | 1.5–795.7 | 74.4 | 30.5 | 129.3 | 98.7 |
| >20 | 18 | 178.4 ± 164.2 | 22.8–649.8 | 113.1 | 71.5 | 267.6 | 196.1 |
| Criterion | Subgroups | n | Below Standard n = 46 (%) | Norm n = 48 (%) | Above Normal n = 22 (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Declared content | Less than 100 mg | 49 | 19 (16.4) | 24 (20.7) | 6 (5.2) |
| 100–200 mg | 45 | 20 (17.2) | 15 (12.9) | 10 (8.6) | |
| Above 200 mg | 22 | 7 (6.0) | 9 (7.6) | 6 (5.2) | |
| Form | Capsules | 13 | 9 (7.8) | 3 (2.6) | 1 (0.9) |
| Coated tablets | 11 | 5 (4.3) | 5 (4.3) | 1 (0.9) | |
| Dragees | 2 | 0 (0.0) | 2 (1.7) | 0 (0.0) | |
| Effervescent tablets | 24 | 5 (4.3) | 12 (10.3) | 7 (6.0) | |
| Granulates | 1 | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 1 (0.9) | |
| Jelly beans | 1 | 0 (0.0) | 1 (0.9) | 0 (0.0) | |
| Liquids | 7 | 3 (2.6) | 3 (2.6) | 1 (0.9) | |
| Powders | 12 | 3 (2.6) | 4 (3.4) | 5 (4.3) | |
| Tablets | 45 | 21 (18.1) | 18 (15.5) | 6 (5.2) | |
| Chemical form | Magnesium bisglycinate | 6 | 2 (1.7) | 3 (2.6) | 1 (0.9) |
| Magnesium carbonate | 34 | 11 (9.5) | 15 (12.9) | 8 (6.9) | |
| Magnesium citrate | 35 | 16 (13.8) | 12 (10.3) | 7 (6.0) | |
| Magnesium glycerophosphate | 1 | 0 (0.0) | 1 (0.9) | 0 (0.0) | |
| Magnesium hydroxide | 2 | 1 (0.9) | 0 (0.0) | 1 (0.9) | |
| Magnesium lactate | 11 | 6 (5.2) | 5 (4.3) | 0 (0.0) | |
| Magnesium oxide | 8 | 3 (2.6) | 4 (3.4) | 1 (0.9) | |
| Several chemical forms | 19 | 7 (6.0) | 8 (6.9) | 4 (3.4) | |
| Amount of minerals | Only magnesium (or vitamin B6) | 75 | 35 (30.2) | 25 (21.6)) | 15 (12.9 |
| Multicomponent preparations | 41 | 11 (9.5) | 23 (19.8) | 7 (6.0) | |
| Price (PLN) | <10 | 41 | 16 (13.8) | 17 (14.7) | 8 (6.9) |
| 10–20 | 57 | 25 (21.6) | 22 (18.9) | 10 (8.6) | |
| >20 | 18 | 5 (4.3) | 9 (7.8) | 4 (3.4) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Puścion-Jakubik, A.; Bartosiewicz, N.; Socha, K. Is the Magnesium Content in Food Supplements Consistent with the Manufacturers’ Declarations? Nutrients 2021, 13, 3416. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13103416
Puścion-Jakubik A, Bartosiewicz N, Socha K. Is the Magnesium Content in Food Supplements Consistent with the Manufacturers’ Declarations? Nutrients. 2021; 13(10):3416. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13103416
Chicago/Turabian StylePuścion-Jakubik, Anna, Natalia Bartosiewicz, and Katarzyna Socha. 2021. "Is the Magnesium Content in Food Supplements Consistent with the Manufacturers’ Declarations?" Nutrients 13, no. 10: 3416. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13103416
APA StylePuścion-Jakubik, A., Bartosiewicz, N., & Socha, K. (2021). Is the Magnesium Content in Food Supplements Consistent with the Manufacturers’ Declarations? Nutrients, 13(10), 3416. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13103416