Fenton vs. Intergrowth-21st: Postnatal Growth Assessment and Prediction of Neurodevelopment in Preterm Infants
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
Statistical Analyses
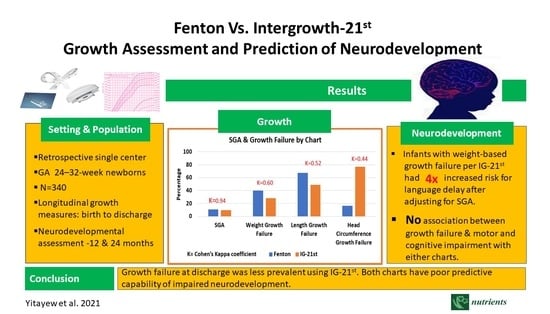
3. Results
3.1. Study Population
3.2. Characteristics of Study Population
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Colvin, M.; McGuire, W.; Fowlie, P.W. Neurodevelopmental outcomes after preterm birth. BMJ 2004, 329, 1390–1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wood, N.S.; Marlow, N.; Costeloe, K.; Gibson, A.T.; Wilkinson, A.R. Neurologic and developmental disability after extremely preterm birth. EPICure Study Group. N. Engl. J. Med. 2000, 343, 378–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehrenkranz, R.A.; Dusick, A.M.; Vohr, B.R.; Wright, L.L.; Wrage, L.A.; Poole, W.K. Growth in the neonatal intensive care unit influences neurodevelopmental and growth outcomes of extremely low birth weight infants. Pediatrics 2006, 117, 1253–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Glass, H.C.; Costarino, A.T.; Stayer, S.A.; Brett, C.M.; Cladis, F.; Davis, P.J. Outcomes for extremely premature infants. Anesth. Analg. 2015, 120, 1337–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Meyers, J.; Bann, C.; Stoll, B.; D’Angio, C.T.; Bell, E.F.; Duncan, A.F.; Guillet, R. Neurodevelopmental outcomes in postnatal growth-restricted preterm infants with postnatal head-sparing. J. Perinatol. 2016, 36, 1116–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cormack, B.E.; Harding, J.E.; Miller, S.P.; Bloomfield, F.H. The Influence of Early Nutrition on Brain Growth and Neurodevelopment in Extremely Preterm Babies: A Narrative Review. Nutrients 2019, 11, 2029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jasper, E.A.; Cho, H.; Breheny, P.J.; Bao, W.; Dagle, J.M.; Ryckman, K.K. Perinatal determinants of growth trajectories in children born preterm. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0245387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Academy of Pediatrics Committee on Nutrition. Nutritional needs of low-birth-weight infants. Pediatrics 1985, 75, 976–986. [Google Scholar]
- Giuliani, F.; Ismail, L.C.; Bertino, E.; Bhutta, Z.A.; Ohuma, E.O.; Rovelli, I.; Conde-Agudelo, A.; Villar, J.; Kennedy, S.H. Monitoring postnatal growth of preterm infants: Present and future. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2016, 103, 635s–647s. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Embleton, N.E.; Pang, N.; Cooke, R.J. Postnatal malnutrition and growth retardation: An inevitable consequence of current recommendations in preterm infants? Pediatrics 2001, 107, 270–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Euser, A.M.; Finken, M.J.J.; Keijzer-Veen, M.G.; Hille, E.T.M.; Wit, J.M.; Dekker, F.; on behalf of the Dutch POPS-19 Collaborative Study Group. Associations between prenatal and infancy weight gain and BMI, fat mass, and fat distribution in young adulthood: A prospective cohort study in males and females born very preterm. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2005, 81, 480–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Embleton, N.D.; Korada, M.; Wood, C.L.; Pearce, M.S.; Swamy, R.; Cheetham, T.D. Catch-up growth and metabolic outcomes in adolescents born preterm. Arch. Dis. Child. 2016, 101, 1026–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zozaya, C.; Díaz, C.; De Pipaón, M.S. How Should We Define Postnatal Growth Restriction in Preterm Infants? Neonatology 2018, 114, 177–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fenton, T.R.; Kim, J.H. A systematic review and meta-analysis to revise the Fenton growth chart for preterm infants. BMC Pediatr. 2013, 13, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Papageorghiou, A.T.; Kennedy, S.H.; Salomon, L.J.; Altman, D.G.; Ohuma, E.O.; Stones, W.; Gravett, M.G.; Barros, F.C.; Victora, C.; Purwar, M.; et al. The INTERGROWTH-21st fetal growth standards: Toward the global integration of pregnancy and pediatric care. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2018, 218, S630–S640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Villar, J.; Giuliani, F.; Bhutta, Z.A.; Bertino, E.; Ohuma, E.O.; Ismail, L.C.; Barros, F.C.; Altman, D.G.; Victora, C.; Noble, A.; et al. Postnatal growth standards for preterm infants: The Preterm Postnatal Follow-up Study of the INTERGROWTH-21st Project. Lancet Glob. Health 2015, 3, e681–e691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Arcangeli, T.; Thilaganathan, B.; Hooper, R.; Khan, K.S.; Bhide, A. Neurodevelopmental delay in small babies at term: A systematic review. Ultrasound Obstet. Gynecol. 2012, 40, 267–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hollanders, J.J.; on behalf of the Dutch POPS-19 Collaborative Study Group; van der Pal, S.; Van Dommelen, P.; Rotteveel, J.; Finken, M.J.J. Growth pattern and final height of very preterm vs. very low birth weight infants. Pediatr. Res. 2017, 82, 317–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tuzun, F.; Yucesoy, E.; Baysal, B.; Kumral, A.; Duman, N.; Ozkan, H. Comparison of INTERGROWTH-21 and Fenton growth standards to assess size at birth and extrauterine growth in very preterm infants. J. Matern. Neonatal Med. 2017, 31, 2252–2257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.-J.; Shin, S.H.; Cho, H.; Kim, S.H.; Song, I.G.; Kim, E.-K.; Kim, H.-S. Extrauterine growth restriction in extremely preterm infants based on the Intergrowth-21st Project Preterm Postnatal Follow-up Study growth charts and the Fenton growth charts. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2021, 180, 817–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salas, A.A.; Bhatia, A.; Carlo, W.A. Postnatal growth of preterm infants 24 to 26 weeks of gestation and cognitive outcomes at 2 years of age. Pediatr. Res. 2021, 89, 1804–1809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peila, C.; Spada, E.; Giuliani, F.; Maiocco, G.; Raia, M.; Cresi, F.; Bertino, E.; Coscia, A. Extrauterine Growth Restriction: Definitions and Predictability of Outcomes in a Cohort of Very Low Birth Weight Infants or Preterm Neonates. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reddy, K.V.; Sharma, D.; Vardhelli, V.; Bashir, T.; Deshbotla, S.K.; Murki, S. Comparison of Fenton 2013 growth curves and Intergrowth-21 growth standards to assess the incidence of intrauterine growth restriction and extrauterine growth restriction in. J. Matern. Fetal Neonatal Med. 2021, 34, 2634–2641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bendor-Samuel, O.M.; Zivanovic, S.; Odd, D.; Roehr, C.C. A Comparison of UK Preterm Anthropometric Charts and INTERGROWTH-21st: Is It Time to Change Growth Charts? Neonatology 2020, 117, 300–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Metcalfe, A.; León, J.A.; Sauve, R.; Kramer, M.S.; Joseph, K.S.; Canadian Perinatal Surveillance System (Public Health Agency of Canada). Evaluation of the INTERGROWTH-21st project newborn standard for use in Canada. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0172910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Samarani, M.; Restom, G.; Mardini, J.; Fares, G.A.; Hallit, S.; Khalife, M.-C.F. Comparative study between Fenton and intergrowth 21 charts in a sample of Lebanese premature babies. BMC Pediatr. 2020, 20, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Uberos, J.; Jimenez-Montilla, S.; Machado-Casas, I.; Laynez-Rubio, C.; Fernández-Marin, E.; Campos-Martínez, A. The association between restricted intra-uterine growth and inadequate postnatal nutrition in very-low-birth-weight infants and their neurodevelopmental outcomes: A 50-month follow-up study. Br. J. Nutr. 2021, 19, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hickey, L.; Burnett, A.; Spittle, A.J.; Roberts, G.; Anderson, P.; Lee, K.; Doyle, L.W.; Cheong, J.L.Y.; Victorian Infant Collaborative Study Group. Extreme prematurity, growth and neurodevelopment at 8 years: A cohort study. Arch. Dis. Child. 2021, 106, 160–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belfort, M.B.; Rifas-Shiman, S.L.; Sullivan, T.; Collins, C.T.; McPhee, A.J.; Ryan, P.; Kleinman, K.P.; Gillman, M.W.; Gibson, R.A.; Makrides, M. Infant Growth Before and After Term: Effects on Neurodevelopment in Preterm Infants. Pediatrics 2011, 128, e899–e906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hickey, M.; Georgieff, M.; Ramel, S. Neurodevelopmental outcomes following necrotizing enterocolitis. Semin. Fetal Neonatal Med. 2018, 23, 426–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeMauro, S.B. Neurodevelopmental outcomes of infants with bronchopulmonary dysplasia. Pediatr. Pulmonol. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gotardo, J.W.; Volkmer, N.D.F.V.; Stangler, G.P.; Dornelles, A.D.; Bohrer, B.B.D.A.; Carvalho, C.G. Impact of peri-intraventricular haemorrhage and periventricular leukomalacia in the neurodevelopment of preterms: A systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0223427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Characteristics | Median (IQR), Frequency (Percentage) [n = 340] |
|---|---|
| Gestational Age at Birth (weeks) | 30 (27, 32) |
| Birth Weight (g) | 1310 (950, 1609) |
| Birth Length (cm) | 39 (35, 41.5) |
| Head Circumference (cm) | 27 (24.2, 28.4) |
| Male | 188 (55.3) |
| Race | |
| Black | 209 (61.5) |
| White | 98 (28.8) |
| Other | 33 (9.7) |
| BPD | 58 (17.1) |
| IVH | 24 (9.2) |
| PVL | 7 (2.6) |
| ROP | 33 (14.2) |
| NEC | 5 (1.5) |
| Sepsis | 29 (8.6) |
| Postnatal Steroid | 34 (10) |
| Length of Stay | 56.00 (38.8, 90) |
| Language Neurodevelopmental Deficiency at 12 months [n = 122] | 68 (55.7) |
| Cognition Neurodevelopmental Deficiency at 12 months [n = 125] | 20 (16.0) |
| Motor Neurodevelopmental Deficiency at 12 months [n = 118] | 23 (19.5) |
| Language Neurodevelopmental Deficiency at 24 months [n = 75] | 38 (50.7) |
| Cognition Neurodevelopmental Deficiency at 24 months [n = 75] | 21 (28.0) |
| Motor Neurodevelopmental Deficiency at 24 months [n = 72] | 21 (29.2) |
| Type n = 340 | Fenton Frequency (Percentage) | IG-21st Frequency (Percentage) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| SGA a | 37 (10.9) | 33 (9.7) | 0.6137 |
| Growth Failure b | |||
| Weight | 127 (39.7) | 93 (27.9) | 0.0015 |
| Length | 215 (67.4) | 164 (49.2) | <0.0001 |
| Head Circumference | 53 (16.9) | 77 (23.5) | 0.0395 |
| Growth by Charts | Cohen’s Kappa | 95% CI |
|---|---|---|
| IG-21st vs. Fenton SGA | 0.94 | (0.87, 1.00) |
| IG-21st vs. Fenton Growth Failure (Weight) | 0.60 | (0.52, 0.69) |
| IG-21st vs. Fenton Growth Failure (Length) | 0.44 | (0.35, 0.54) |
| IG-21st vs. Fenton Growth Failure (Head Cir.) | 0.52 | (0.40, 0.64) |
| Odds Ratio | 95% CI | p-Value | AUROC | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Language | ||||
| IG-21st | 3.75 | (0.96, 24.89) | 0.094 | 0.608 |
| Fenton | 1.48 | (0.51, 4.67) | 0.486 | 0.547 |
| Cognition | ||||
| IG-21st | 1.35 | (0.49, 3.68) | 0.557 | 0.531 |
| Fenton | 0.94 | (0.34, 2.51) | 0.898 | 0.508 |
| Motor | ||||
| IG-21st | 1.60 | (0.57, 4.53) | 0.374 | 0.549 |
| Fenton | 1.05 | (0.38, 2.89) | 0.918 | 0.506 |
| Odds Ratio | 95% CI | p-Value | AUROC | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Language | ||||
| Growth Failure IG-21st | 3.949 | (1.005, 26.351) | 0.0490 | 0.6503 |
| SGA IG-21st | 3.962 | (0.702, 74.797) | 0.1330 | 0.6503 |
| Growth Failure Fenton | 1.545 | (0.526, 4.933) | 0.4338 | 0.6073 |
| SGA Fenton | 2.939 | (0.508, 55.937) | 0.2610 | 0.6073 |
| Cognition | ||||
| Growth Failure IG-21st | 1.442 | (0.516, 4.019) | 0.4812 | 0.5887 |
| SGA IG-21st | 2.407 | (0.741, 8.240) | 0.1464 | 0.5887 |
| Growth Failure Fenton | 1.008 | (0.363, 0.968) | 0.9876 | 0.5530 |
| SGA Fenton | 2.403 | (0.644, 9.356) | 0.1892 | 0.5530 |
| Motor | ||||
| Growth Failure IG-21st | 1.618 | (0.576, 4.617) | 0.3609 | 0.5480 |
| SGA IG-21st | 1.364 | (0.381, 4.907) | 0.6279 | 0.5480 |
| Growth Failure Fenton | 1.055 | (0.379, 2.906) | 0.9178 | 0.5000 |
| SGA Fenton | 1.007 | (0.233, 3.972) | 0.9918 | 0.5000 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yitayew, M.; Chahin, N.; Rustom, S.; Thacker, L.R.; Hendricks-Muñoz, K.D. Fenton vs. Intergrowth-21st: Postnatal Growth Assessment and Prediction of Neurodevelopment in Preterm Infants. Nutrients 2021, 13, 2841. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13082841
Yitayew M, Chahin N, Rustom S, Thacker LR, Hendricks-Muñoz KD. Fenton vs. Intergrowth-21st: Postnatal Growth Assessment and Prediction of Neurodevelopment in Preterm Infants. Nutrients. 2021; 13(8):2841. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13082841
Chicago/Turabian StyleYitayew, Miheret, Nayef Chahin, Salem Rustom, Leroy R. Thacker, and Karen D. Hendricks-Muñoz. 2021. "Fenton vs. Intergrowth-21st: Postnatal Growth Assessment and Prediction of Neurodevelopment in Preterm Infants" Nutrients 13, no. 8: 2841. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13082841
APA StyleYitayew, M., Chahin, N., Rustom, S., Thacker, L. R., & Hendricks-Muñoz, K. D. (2021). Fenton vs. Intergrowth-21st: Postnatal Growth Assessment and Prediction of Neurodevelopment in Preterm Infants. Nutrients, 13(8), 2841. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13082841