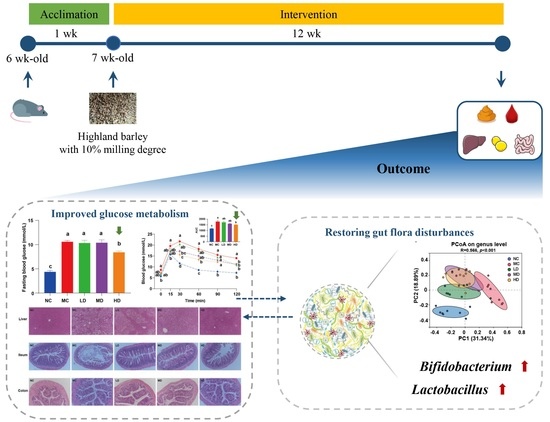
Beneficial Effects of Partly Milled Highland Barley on the Prevention of High-Fat Diet-Induced Glycometabolic Disorder and the Modulation of Gut Microbiota in Mice
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Reagents
2.2. Animals and Diets
2.3. Sample Collection
2.4. Biochemical Parameters
2.5. Histological Analysis
2.6. Gut Microbiota Analysis
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Effects of PHB on the Bodyweight, Food Intake, and Tissues Weight
3.2. Effects of PHB on Glucose Tolerance
3.3. Effects of PHB Supplementation on Triglyceride and Total Cholesterol Levels in the Serum
3.4. Effects of PHB on Histopathological Alterations of Liver Tissues
3.5. Effects of PHB on Histopathological Alterations of Ileum Tissues and Colon Tissues
3.6. Effects of PHB on the Diversity of Mice Fecal Microbiome
3.7. Effects of PHB on the Composition of Mice Fecal Microbiota
3.8. Correlation between Gut Microbiota and Related Indicators of Glucose and Lipid Metabolism
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, W.; Hu, M.; Liu, H.; Zhang, X.; Li, H.; Zhou, F.; Liu, Y.; Lei, F.; Qin, J.; Zhao, Y.; et al. Global Burden of Disease Study 2019 suggests that metabolic risk factors are the leading drivers of the burden of ischemic heart disease. Cell Metab. 2021, 33, 1943–1956.e1942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feigin, V.; Stark, B.; Johnson, C.; Roth, G.; Bisignano, C.; Abady, G.; Abbasifard, M.; Abbasi-Kangevari, M.; Abd-Allah, F.; Abedi, V.; et al. Global, regional, and national burden of stroke and its risk factors, 1990–2019: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. Lancet Neurol. 2021, 20, 795–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwingshackl, L.; Schwedhelm, C.; Hoffmann, G.; Knüppel, S.; Iqbal, K.; Andriolo, V.; Bechthold, A.; Schlesinger, S.; Boeing, H. Food Groups and Risk of Hypertension: A Systematic Review and Dose-Response Meta-Analysis of Prospective Studies. Adv. Nutr. 2017, 8, 793–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Li, J.; Chen, X.; Yu, M.; Pan, Q.; Guo, L. Whole grain food diet slightly reduces cardiovascular risks in obese/overweight adults: A systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Cardiovasc. Disord. 2020, 20, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.; Duan, Y.; Zhu, L.; Fang, Z.; He, L.; Ai, D.; Jin, Y. Whole grain and cereal fiber intake and the risk of type 2 diabetes: A meta-analysis. Int. J. Mol. Epidemiol. Genet. 2019, 10, 38–46. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hu, Y.; Ding, M.; Sampson, L.; Willett, W.C.; Manson, J.E.; Wang, M.; Rosner, B.; Hu, F.B.; Sun, Q. Intake of whole grain foods and risk of type 2 diabetes: Results from three prospective cohort studies. BMJ 2020, 370, m2206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwingshackl, L.; Schwedhelm, C.; Hoffmann, G.; Knüppel, S.; Laure Preterre, A.; Iqbal, K.; Bechthold, A.; De Henauw, S.; Michels, N.; Devleesschauwer, B.; et al. Food groups and risk of colorectal cancer. Int. J. Cancer 2018, 142, 1748–1758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, X.F.; Wang, X.K.; Tang, Y.J.; Guan, X.X.; Guo, Y.; Fan, J.M.; Cui, L.L. Association of whole grains intake and the risk of digestive tract cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Nutr. J. 2020, 19, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ievina, S.; Arta, K.; Vija, S.; Aina, K.; Mauritz, A.; Kari, B.O.A.; Vita, S.; Evita, S. Adaptability of hull-less barley varieties to different cropping systems and climatic conditions. Acta Agric. Scand. Sect. B-Soil Plant Sci. 2018, 69, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sterna, V.; Zute, S.; Jansone, I.; Kantane, I. Chemical Composition of Covered and Naked Spring Barley Varieties and Their Potential for Food Production. Pol. J. Food Nutr. Sci. 2017, 67, 151–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Junmei, W.; Jinxin, C. Analysis of β-glucan content in barley cultivars from different locations of China. Food Chem. 2002, 79, 251–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obadi, M.; Sun, J.; Xu, B. Highland barley: Chemical composition, bioactive compounds, health effects, and applications. Food Res. Int. 2021, 140, 110065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, J.; Wu, Y.; Xie, H.; Shi, W.; Chen, Z.; Jiang, D.; Hu, H.; Zheng, X.; Xu, J.; Yang, Y.; et al. Purification, Preliminary Structural Characterization, and In Vitro Inhibitory Effect on Digestive Enzymes by beta-Glucan from Qingke (Tibetan Hulless Barley). Adv. Polym. Tech. 2020, 2020, 2709536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Li, B. Chlorogenic acid and beta-glucan from highland barley grain ameliorate beta-cell dysfunction via inhibiting apoptosis and improving cell proliferation. Food Funct. 2021, 12, 10040–10052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Li, B. (-)-Epicatechin and beta-glucan from highland barley grain modulated glucose metabolism and showed synergistic effect via Akt pathway. J. Funct. Foods 2021, 87, 104793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, D.; Zhang, X.; Meng, M.; Han, L.; Li, C.; Hou, L.; Qi, W.; Wang, C. Inhibitory effect on HT-29 colon cancer cells of a water-soluble polysaccharide obtained from highland barley. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2016, 92, 88–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Z.; Cai, H.; Xu, e.; Wang, J.; Qiu, C.; Xie, J.; Huang, W.; Sui, Z. Protective Role of Antioxidant Huskless Barley Extracts on TNF-α-Induced Endothelial Dysfunction in Human Vascular Endothelial Cells. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2018, 2018, 3846029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, L.; Wang, X.; Li, Y.; Sun, C. Postprandial Differences in the Amino Acid and Biogenic Amines Profiles of Impaired Fasting Glucose Individuals after Intake of Highland Barley. Nutrients 2015, 7, 5556–5571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gong, L.; Gong, L.; Zhang, Y. Intake of Tibetan hull-less barley is associated with a reduced risk of metabolic related syndrome in rats fed high-fat-sucrose diets. Nutrients 2014, 6, 1635–1648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, N.; Guo, R.; Zheng, B.; Li, T.; Liu, R.H. IRS-1/PI3K/Akt pathway and miRNAs are involved in whole grain highland barley (Hordeum vulgare L.) ameliorating hyperglycemia of db/db mice. Food Funct. 2020, 11, 9535–9546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, N.; He, Z.; Guo, R.; Zheng, B.; Li, T.; Liu, R.H. Highland Barley Whole Grain (Hordeum vulgare L.) Ameliorates Hyperlipidemia by Modulating Cecal Microbiota, miRNAs, and AMPK Pathways in Leptin Receptor-Deficient db/db Mice. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2020, 68, 11735–11746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, T.; Horvath, C.; Chen, L.; Chen, J.; Zheng, B. Understanding the nutrient composition and nutritional functions of highland barley (Qingke): A review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 103, 109–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lian, Q.; Cui, M.; Li, J.; Jia, P.; Xiao, M. Analysis on factors affecting mycotoxin production in highland barley raw grains. Food Safe Qual. Detec. Technol. 2021, 12, 5967–5973. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, N.; Yue, X.; Yu, Q.; Zhang, F. Study on mycotoxin contamination and toxigenic fungi pollution of main crops in Tibet plateau. J. Triticeae Crops 2020, 40, 510–516. [Google Scholar]
- Barrett, E.M.; Batterham, M.J.; Ray, S.; Beck, E.J. Whole grain, bran and cereal fibre consumption and CVD: A systematic review. Br. J. Nutr. 2019, 121, 914–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aune, D.; Norat, T.; Romundstad, P.; Vatten, L.J. Whole grain and refined grain consumption and the risk of type 2 diabetes: A systematic review and dose-response meta-analysis of cohort studies. Eur. J. Epidemiol. 2013, 28, 845–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Lai, H.; Mi, B.; Qi, X.; Gan, W.; Du, H. Associations of Coarse Grain Intake with Undiagnosed Hypertension among Chinese Adults: Results from the China Kadoorie Biobank. Nutrients 2020, 12, 3814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, K.B. Review of whole grain and dietary fiber recommendations and intake levels in different countries. Nutr. Rev. 2020, 78, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, B.; Wu, N.; Zhai, X. Solutions for whole grain food development. Nutr. Rev. 2020, 78, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMackin, E.; Dean, M.; Woodside, J.V.; McKinley, M.C. Whole grains and health: Attitudes to whole grains against a prevailing background of increased marketing and promotion. Public Health Nutr. 2013, 16, 743–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jones, J.M.; Adams, J.; Harriman, C.; Miller, C.; Van Der Kamp, J.W. Nutritional Impacts of Different Whole Grain Milling Techniques: A Review of Milling Practices and Existing Data. Cereal Foods World 2015, 60, 130–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obadi, M.; Qi, Y.; Xu, B. Highland barley starch (Qingke): Structures, properties, modifications, and applications. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 185, 725–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thielecke, F.; Jonnalagadda, S.S. Can Whole Grain Help in Weight Management? J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2014, 48, S70–S77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.M.; Willett, W.C.; Manson, J.E.; Hu, F.B.; Rosner, B.; Colditz, G. Relation between changes in intakes of dietary fiber and grain products and changes in weight and development of obesity among middle-aged women. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2003, 78, 920–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sadeghi, O.; Sadeghian, M.; Rahmani, S.; Maleki, V.; Larijani, B.; Esmaillzadeh, A. Whole-Grain Consumption Does Not Affect Obesity Measures: An Updated Systematic Review and Meta-analysis of Randomized Clinical Trials. Adv. Nutr. 2020, 11, 280–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, B.; Zhong, S.; Tang, Y.; Chen, L. Understanding the nutritional functions of thermally-processed whole grain highland barley in vitro and in vivo. Food Chem. 2020, 310, 125979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, X.; Li, G.; Song, J.; Zheng, J.; Kan, J. Hypocholesterolaemic effect of whole-grain highland hull-less barley in rats fed a high-fat diet. Br. J. Nutr. 2018, 119, 1102–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xia, X.; Li, G.; Ding, Y.; Ren, T.; Zheng, J.; Kan, J. Effect of Whole Grain Qingke (Tibetan Hordeum vulgare L. Zangqing 320) on the Serum Lipid Levels and Intestinal Microbiota of Rats under High-Fat Diet. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2017, 65, 2686–2693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Lin, S.; Lu, M.; Gong, J.D.B.; Wang, L.; Zhang, Q.; Lin, D.R.; Qin, W.; Wu, D.T. Characterization, in vitro binding properties, and inhibitory activity on pancreatic lipase of beta-glucans from different Qingke (Tibetan hulless barley) cultivars. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 120, 2517–2522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.J.; Dang, B.; Fan, M.T. Free and Bound Phenolic Compound Content and Antioxidant Activity of Different Cultivated Blue Highland Barley Varieties from the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Molecules 2018, 23, 879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Deng, N.; Zheng, B.; Li, T.; Liu, R.H. Assessment of the Phenolic Profiles, Hypoglycemic Activity, and Molecular Mechanism of Different Highland Barley (Hordeum vulgare L.) Varieties. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, Z.H.; Li, B. Procyanidin B1 and p-Coumaric Acid from Highland Barley Grain Showed Synergistic Effect on Modulating Glucose Metabolism via IRS-1/PI3K/Akt Pathway. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2021, 65, e2100454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.J.; Li, S.; Gan, R.Y.; Zhou, T.; Xu, D.P.; Li, H.B. Impacts of Gut Bacteria on Human Health and Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 7493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seal, C.J.; Courtin, C.M.; Venema, K.; de Vries, J. Health benefits of whole grain: Effects on dietary carbohydrate quality, the gut microbiome, and consequences of processing. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2021, 20, 2742–2768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, L.; Cao, W.; Gao, J.; Wang, J.; Zhang, H.; Sun, B.; Yin, M. Whole Tibetan Hull-Less Barley Exhibit Stronger Effect on Promoting Growth of Genus Bifidobacterium than Refined Barley In Vitro. J. Food Sci. 2018, 83, 1116–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, C.; Yan, X.; Xie, X.; Zhang, Z.; Zhu, J.; Wang, Y.; Wang, X.; Xu, N.; Luo, Y.; Sa, Z.; et al. Structure of beta-glucan from Tibetan hull-less barley and its in vitro fermentation by human gut microbiota. Chem. Biol. Technol. Agric. 2021, 8, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soleimani, A.; Zarrati Mojarrad, M.; Bahmani, F.; Taghizadeh, M.; Ramezani, M.; Tajabadi-Ebrahimi, M.; Jafari, P.; Esmaillzadeh, A.; Asemi, Z. Probiotic supplementation in diabetic hemodialysis patients has beneficial metabolic effects. Kidney Int. 2017, 91, 435–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toshimitsu, T.; Gotou, A.; Sashihara, T.; Hachimura, S.; Shioya, N.; Suzuki, S.; Asami, Y. Effects of 12-Week Ingestion of Yogurt Containing Lactobacillus plantarum OLL2712 on Glucose Metabolism and Chronic Inflammation in Prediabetic Adults: A Randomized Placebo-Controlled Trial. Nutrients 2020, 12, 374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tiderencel, K.A.; Hutcheon, D.A.; Ziegler, J. Probiotics for the treatment of type 2 diabetes: A review of randomized controlled trials. Diabetes Metab. Res. Rev. 2020, 36, e3213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakai, Y.; Arie, H.; Ni, Y.; Zhuge, F.; Xu, L.; Chen, G.; Nagata, N.; Suzuki, T.; Kaneko, S.; Ota, T.; et al. Lactobacillus pentosus strain S-PT84 improves steatohepatitis by maintaining gut permeability. J. Endocrinol. 2020, 247, 169–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, P.; Li, B.; He, C.; Song, W.; Hou, A.; Tian, S.; Meng, X.; Li, K.; Shan, Y. Antidiabetic (type 2) effects of Lactobacillus G15 and Q14 in rats through regulation of intestinal permeability and microbiota. Food Funct. 2016, 7, 3789–3797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandez-Julia, P.J.; Munoz-Munoz, J.; van Sinderen, D. A comprehensive review on the impact of β-glucan metabolism by Bacteroides and Bifidobacterium species as members of the gut microbiota. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 181, 877–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cummings, J.H.; Pomare, E.W.; Branch, W.J.; Naylor, C.; Macfarlane, G.T. Short chain fatty acids in human large intestine, portal, hepatic and venous blood. Gut 1987, 28, 1221–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, H.; Ren, P.; Mang, L.; Shen, N.; Chen, J.; Zhang, Y. In vitro fermentation of novel microwave-synthesized non-digestible oligosaccharides and their impact on the composition and metabolites of human gut microbiota. J. Funct. Foods 2019, 55, 156–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunkwall, L.; Orho-Melander, M. The gut microbiome as a target for prevention and treatment of hyperglycaemia in type 2 diabetes: From current human evidence to future possibilities. Diabetologia 2017, 60, 943–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, Q.; Hou, D.; Laraib, Y.; Xue, Y.; Shen, Q. Comparison of the effects of raw and cooked adzuki bean on glucose/lipid metabolism and liver function in diabetic mice. Cereal Chem. 2021, 98, 1081–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, S.; Wang, M.; Li, C.; Meng, Q.; Meng, Y.; Ying, J.; Bai, S.; Shen, Q.; Xue, Y. Beneficial Effects of Partly Milled Highland Barley on the Prevention of High-Fat Diet-Induced Glycometabolic Disorder and the Modulation of Gut Microbiota in Mice. Nutrients 2022, 14, 762. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14040762
Li S, Wang M, Li C, Meng Q, Meng Y, Ying J, Bai S, Shen Q, Xue Y. Beneficial Effects of Partly Milled Highland Barley on the Prevention of High-Fat Diet-Induced Glycometabolic Disorder and the Modulation of Gut Microbiota in Mice. Nutrients. 2022; 14(4):762. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14040762
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Siqi, Mengqian Wang, Chang Li, Qingjia Meng, Yantong Meng, Jian Ying, Shuqun Bai, Qun Shen, and Yong Xue. 2022. "Beneficial Effects of Partly Milled Highland Barley on the Prevention of High-Fat Diet-Induced Glycometabolic Disorder and the Modulation of Gut Microbiota in Mice" Nutrients 14, no. 4: 762. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14040762
APA StyleLi, S., Wang, M., Li, C., Meng, Q., Meng, Y., Ying, J., Bai, S., Shen, Q., & Xue, Y. (2022). Beneficial Effects of Partly Milled Highland Barley on the Prevention of High-Fat Diet-Induced Glycometabolic Disorder and the Modulation of Gut Microbiota in Mice. Nutrients, 14(4), 762. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14040762