A High-Fat, High-Cholesterol Diet Promotes Intestinal Inflammation by Exacerbating Gut Microbiome Dysbiosis and Bile Acid Disorders in Cholecystectomy
Abstract
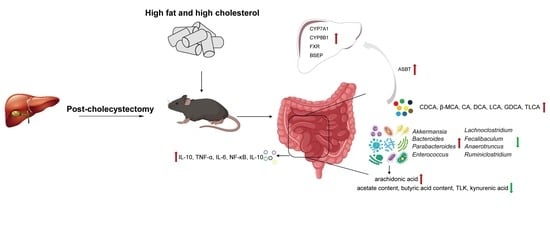
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals and Feeding
2.2. Histological Analysis
2.3. Microbiome Analysis
2.4. BA Measurements
2.5. RNA Extraction and Quantitative Real-Time PCR (RT-qPCR)
2.6. Analysis of Cytokines in the Colonic Tissues by Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA)
2.7. Untargeted Metabolomics
2.8. Determination of Plasma Biochemical Indices
2.9. Determination of Fecal SCFA Contents
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Pro-Inflammatory Effects of Cholecystectomy on the Intestine Exacerbated by an HFHC Diet
3.2. HFHC Diet Exacerbates the Dysbiosis of Gut Microbial Homeostasis in Cholecystectomy
3.3. Disturbed BA Metabolism Attributed to Cholecystectomy Exacerbated by HFHC Diet
3.4. Alterations in Gut Microbiota Associated with BA Metabolism
3.5. HFHC Diet Exacerbates the Effects of Cholecystectomy on the Metabolic Function of the Gut Microbiota
3.6. HFHC Diet Exacerbates Dysbiosis of Metabolite Metabolism by Cholecystectomy
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shaffer, E.A. Review article: Control of gall-bladder motor function. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2000, 14, 2–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maldonado-Valderrama, J.; Wilde, P.; Macierzanka, A.; Mackie, A. The role of bile salts in digestion. Adv. Colloid. Interface Sci. 2011, 165, 36–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertolini, A.; Fiorotto, R.; Strazzabosco, M. Bile acids and their receptors: Modulators and therapeutic targets in liver inflammation. Semin. Immunopathol. 2022, 44, 547–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kullak-Ublick, G.A.; Paumgartner, G.; Berr, F. Long-term effects of cholecystectomy on bile acid metabolism. Hepatology 1995, 21, 41–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagergren, J.; Ye, W.; Ekbom, A. Intestinal cancer after cholecystectomy: Is bile involved in carcinogenesis? Gastroenterology 2001, 121, 542–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruhl, C.E.; Everhart, J.E. Relationship of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease with cholecystectomy in the US population. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2013, 108, 952–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.; Wang, J.; Wu, X.; Jing, H.; Zhang, S.; Hu, Z.; Rao, L.; Chang, Q.; Wang, L.; Zhang, Z. Gut microbiota alteration after cholecystectomy contributes to post-cholecystectomy diarrhea via bile acids stimulating colonic serotonin. Gut Microbes 2023, 15, 2168101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barre, A.; Gusto, G.; Cadeau, C.; Carbonnel, F.; Boutron-Ruault, M.C. Diet and Risk of Cholecystectomy: A Prospective Study Based on the French E3N Cohort. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2017, 112, 1448–1456.e1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yueh, T.P.; Chen, F.Y.; Lin, T.E.; Chuang, M.T. Diarrhea after laparoscopic cholecystectomy: Associated factors and predictors. Asian J. Surg. 2014, 37, 171–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Xu, J.; Ren, X.; Zhang, Y.; Ke, Z.; Zhou, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Y. Cholecystectomy-induced secondary bile acids accumulation ameliorates colitis through inhibiting monocyte/macrophage recruitment. Gut Microbes 2022, 14, 2107387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.; Zhang, T.; Yue, Y.; Wu, X. Effects of Bile Acid Modulation by Dietary Fat, Cholecystectomy, and Bile Acid Sequestrant on Energy, Glucose, and Lipid Metabolism and Gut Microbiota in Mice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 5935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collins, S.L.; Stine, J.G.; Bisanz, J.E.; Okafor, C.D.; Patterson, A.D. Bile acids and the gut microbiota: Metabolic interactions and impacts on disease. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2023, 21, 236–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahlstrom, A.; Sayin, S.I.; Marschall, H.U.; Backhed, F. Intestinal Crosstalk between Bile Acids and Microbiota and Its Impact on Host Metabolism. Cell Metab. 2016, 24, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Begley, M.; Gahan, C.G.; Hill, C. The interaction between bacteria and bile. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2005, 29, 625–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Gui, W.; Koo, I.; Smith, P.B.; Allman, E.L.; Nichols, R.G.; Rimal, B.; Cai, J.; Liu, Q.; Patterson, A.D. The microbiome modulating activity of bile acids. Gut Microbes 2020, 11, 979–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, J.; Sun, L.; Gonzalez, F.J. Gut microbiota-derived bile acids in intestinal immunity, inflammation, and tumorigenesis. Cell Host Microbe 2022, 30, 289–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, T.; Coulter, S.; Yoshihara, E.; Oh, T.G.; Fang, S.; Cayabyab, F.; Zhu, Q.; Zhang, T.; Leblanc, M.; Liu, S.; et al. FXR Regulates Intestinal Cancer Stem Cell Proliferation. Cell 2019, 176, 1098–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayr, L.; Grabherr, F.; Schwärzler, J.; Reitmeier, I.; Sommer, F.; Gehmacher, T.; Niederreiter, L.; He, G.-W.; Ruder, B.; Kunz, K.T.R.; et al. Dietary lipids fuel GPX4-restricted enteritis resembling Crohn’s disease. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 1775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massironi, S.; Viganò, C.; Palermo, A.; Pirola, L.; Mulinacci, G.; Allocca, M.; Peyrin-Biroulet, L.; Danese, S. Inflammation and malnutrition in inflammatory bowel disease. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2023, 8, 579–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, Y.; Yuan, J.; Li, J.; Li, H.; Zhang, J.; Tang, J.; Ni, Y.; Huang, T.; Wang, F.; Zhao, F.; et al. Unconjugated and secondary bile acid profiles in response to higher-fat, lower-carbohydrate diet and associated with related gut microbiota: A 6-month randomized controlled-feeding trial. Clin. Nutr. 2020, 39, 395–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrell, J.M.; Boehme, S.; Li, F.; Chiang, J.Y. Cholesterol 7alpha-hydroxylase-deficient mice are protected from high-fat/high-cholesterol diet-induced metabolic disorders. J. Lipid Res. 2016, 57, 1144–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makki, K.; Deehan, E.C.; Walter, J.; Backhed, F. The Impact of Dietary Fiber on Gut Microbiota in Host Health and Disease. Cell Host Microbe 2018, 23, 705–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalile, B.; Van Oudenhove, L.; Vervliet, B.; Verbeke, K. The role of short-chain fatty acids in microbiota-gut-brain communication. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 16, 461–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.Y.; Chen, J.; Yi, K.; Peng, L.; Xie, J.; Gou, X.; Peng, T.; Tang, L. Phlorizin ameliorates obesity-associated endotoxemia and insulin resistance in high-fat diet-fed mice by targeting the gut microbiota and intestinal barrier integrity. Gut Microbes 2020, 12, 1842990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Li, Y.; Qiang, G.; Wang, K.; Dai, J.; McCann, M.; Munoz, M.D.; Gil, V.; Yu, Y.; Li, S.; et al. Secreted EMC10 is upregulated in human obesity and its neutralizing antibody prevents diet-induced obesity in mice. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 7323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadjihambi, A.; Konstantinou, C.; Klohs, J.; Monsorno, K.; Le Guennec, A.; Donnelly, C.; Cox, I.J.; Kusumbe, A.; Hosford, P.S.; Soffientini, U.; et al. Partial MCT1 invalidation protects against diet-induced non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and the associated brain dysfunction. J. Hepatol. 2023, 78, 180–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Sheraji, S.H.; Ismail, A.; Manap, M.Y.; Mustafa, S.; Yusof, R.M.; Hassan, F.A. Hypocholesterolaemic effect of yoghurt containing Bifidobacterium pseudocatenulatum G4 or Bifidobacterium longum BB536. Food Chem. 2012, 135, 356–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Sheng, Y.; Pan, Q.; Xue, Y.; Yu, L.; Tian, F.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, H.; Zhai, Q.; Chen, W. Identification of the key physiological characteristics of Lactobacillus plantarum strains for ulcerative colitis alleviation. Food Funct. 2020, 11, 1279–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, W.; Li, M.; Yu, L.; Tian, F.; Zhao, J.; Zhai, Q. Effects of Taurine on Gut Microbiota Homeostasis: An Evaluation Based on Two Models of Gut Dysbiosis. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- John, C.; Werner, P.; Worthmann, A.; Wegner, K.; Todter, K.; Scheja, L.; Rohn, S.; Heeren, J.; Fischer, M. A liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry-based method for the simultaneous determination of hydroxy sterols and bile acids. J. Chromatogr. A 2014, 1371, 184–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, W.; Deng, Y.; Fang, Z.; Zhai, Q.; Cui, S.; Zhao, J.; Chen, W.; Zhang, H. Potential Role of Probiotics in Ameliorating Psoriasis by Modulating Gut Microbiota in Imiquimod-Induced Psoriasis-Like Mice. Nutrients 2021, 13, 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, B.; Yu, L.; Zhai, Q.; Li, M.; Li, L.; Tian, F.; Chen, W. Effect of water-soluble polysaccharides from Morchella esculenta on high-fat diet-induced obese mice: Changes in gut microbiota and metabolic functions. Food Funct. 2023, 14, 5217–5231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, P.; O’Riordan, K.J.; Lee, Y.K.; Wang, G.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, H.; Cryan, J.F.; Chen, W. Towards a psychobiotic therapy for depression: Bifidobacterium breve CCFM1025 reverses chronic stress-induced depressive symptoms and gut microbial abnormalities in mice. Neurobiol. Stress. 2020, 12, 100216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Hu, L.; Xu, Q.; Jiang, T.; Fang, S.; Wang, G.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, H.; Chen, W. Bifidobacteria exert species-specific effects on constipation in BALB/c mice. Food Funct. 2017, 8, 3587–3600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Clavijo Garcia, D.; Vila Costas, J.; Prieto Martinez, C.; Elizalde Apesteguia, I.; Tarifa Castilla, A.; Mercado Gutierrez, M.; Casi Villarroya, M.; Urman Fernandez, J.M.; Herrera Cabezon, F.J. Cystic duct remnant syndrome as a cause of post-cholecystectomy syndrome. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2016, 39, 722–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yokota, A.; Fukiya, S.; Islam, K.B.; Ooka, T.; Ogura, Y.; Hayashi, T.; Hagio, M.; Ishizuka, S. Is bile acid a determinant of the gut microbiota on a high-fat diet? Gut Microbes 2012, 3, 455–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, Y.; Choi, D.; Lee, K.G.; Choi, H.S.; Park, Y. Association between dietary intake and postlaparoscopic cholecystectomic symptoms in patients with gallbladder disease. Korean J. Intern. Med. 2018, 33, 829–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shim, P.; Choi, D.; Park, Y. Association of Blood Fatty Acid Composition and Dietary Pattern with the Risk of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Patients Who Underwent Cholecystectomy. Ann. Nutr. Metab. 2017, 70, 303–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peredo-Lovillo, A.; Romero-Luna, H.E.; Jimenez-Fernandez, M. Health promoting microbial metabolites produced by gut microbiota after prebiotics metabolism. Food Res. Int. 2020, 136, 109473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pickard, J.M.; Zeng, M.Y.; Caruso, R.; Núñez, G. Gut microbiota: Role in pathogen colonization, immune responses, and inflammatory disease. Immunol. Rev. 2017, 279, 70–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohr, M.W.; Narasimhulu, C.A.; Rudeski-Rohr, T.A.; Parthasarathy, S. Negative Effects of a High-Fat Diet on Intestinal Permeability: A Review. Adv. Nutr. 2020, 11, 77–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Wei, J.; Liu, T.; Tang, J.; Zhang, X.; Feng, F.; Cai, H.; Zhao, M. Food additive glycerol monocaprylate modulated systemic inflammation and gut microbiota without stimulating metabolic dysfunction in high-fat diet fed mice. Food Res. Int. 2023, 167, 112734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Z.; Cai, Y.; Lao, X.; Wang, X.; Lin, X.; Cui, Y.; Kalavagunta, P.K.; Liao, J.; Jin, L.; Shang, J.; et al. Taxonomic profiling and populational patterns of bacterial bile salt hydrolase (BSH) genes based on worldwide human gut microbiome. Microbiome 2019, 7, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, X.; Feng, Z.; Chen, Y.; Zhu, L.; Li, X.; Wang, X.; Sun, H.; Li, J. Effects of High-Fructose Corn Syrup on Bone Health and Gastrointestinal Microbiota in Growing Male Mice. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 829396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lozano, C.P.; Wilkens, L.R.; Shvetsov, Y.B.; Maskarinec, G.; Park, S.Y.; Shepherd, J.A.; Boushey, C.J.; Hebert, J.R.; Wirth, M.D.; Ernst, T.; et al. Associations of the Dietary Inflammatory Index with total adiposity and ectopic fat through the gut microbiota, LPS, and C-reactive protein in the Multiethnic Cohort-Adiposity Phenotype Study. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2022, 115, 1344–1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ridlon, J.M.; Harris, S.C.; Bhowmik, S.; Kang, D.J.; Hylemon, P.B. Consequences of bile salt biotransformations by intestinal bacteria. Gut Microbes 2016, 7, 22–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foley, M.H.; O’Flaherty, S.; Allen, G.; Rivera, A.J.; Stewart, A.K.; Barrangou, R.; Theriot, C.M. Lactobacillus bile salt hydrolase substrate specificity governs bacterial fitness and host colonization. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2017709118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, F.; Ma, R.; Yang, X.; Yang, K.; Mi, A.; Ran, L.; Wu, Y. Deletion of hepatic growth hormone receptor (GHR) alters the mouse gut microbiota by affecting bile acid metabolism. Gut Microbes 2023, 15, 2221098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, Y.; Atarashi, K.; Plichta, D.R.; Arai, Y.; Sasajima, S.; Kearney, S.M.; Suda, W.; Takeshita, K.; Sasaki, T.; Okamoto, S.; et al. Novel bile acid biosynthetic pathways are enriched in the microbiome of centenarians. Nature 2021, 599, 458–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuge, A.; Li, S.; Lou, P.; Wu, W.; Wang, K.; Yuan, Y.; Xia, J.; Li, B.; Li, L. Longitudinal 16S rRNA Sequencing Reveals Relationships among Alterations of Gut Microbiota and Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Progression in Mice. Microbiol. Spectr. 2022, 10, e0004722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Fan, J.; Li, T.; Yan, X.; Jiang, Y. Nuciferine Protects Against High-Fat Diet-Induced Hepatic Steatosis via Modulation of Gut Microbiota and Bile Acid Metabolism in Rats. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2022, 70, 12014–12028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, Z.; Zhang, D.; Wu, X.; Yin, Y.; Wan, D. Ferrous Bisglycinate Supplementation Modulates Intestinal Antioxidant Capacity via the AMPK/FOXO Pathway and Reconstitutes Gut Microbiota and Bile Acid Profiles in Pigs. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2022, 70, 4942–4951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, S.; He, S.; Li, X.; Zheng, B.; Zhang, Y.; Zeng, H. Effect of lotus seed resistant starch on small intestinal flora and bile acids in hyperlipidemic rats. Food Chem. 2023, 404, 134599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, K.; Liu, C.; Peng, M.; Su, Q.; Liu, R.; Guo, Z.; Chen, S.; Li, Z.; Chang, G. Glycoursodeoxycholic Acid Ameliorates Atherosclerosis and Alters Gut Microbiota in Apolipoprotein E-Deficient Mice. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2021, 10, e019820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, K.; Song, Y.; Zhang, D.; Wei, Y.; Jiang, S.; Xu, F.; Wang, H.; Zhang, X.; Shao, X. Thinned peach polyphenols alleviate obesity in high fat mice by affecting gut microbiota. Food Res. Int. 2022, 157, 111255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, S.; Zhu, M.; Wang, K.; Zhao, X.; Hu, L.; Jing, W.; Lu, H.; Wang, S. Dihydromyricetin improves DSS-induced colitis in mice via modulation of fecal-bacteria-related bile acid metabolism. Pharmacol. Res. 2021, 171, 105767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, J.; Li, H.; Zhang, X.; Yang, T.; Yue, M.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, S.; Cui, N.; Yuan, C.; Li, J.; et al. Akkermansia muciniphila protects mice against an emerging tick-borne viral pathogen. Nat. Microbiol. 2023, 8, 91–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, S.; Zheng, Y.; Huang, Y.; Feng, Y.; Xu, K.; Zhang, W.; Wang, Y.; Nie, K.; Qin, M. Excessive consumption of mucin by over-colonized Akkermansia muciniphila promotes intestinal barrier damage during malignant intestinal environment. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1111911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, W.; Khan, I.; Li, X.A.; Huang, G.; Yu, Z.; Leong, W.K.; Han, R.; Ho, L.T.; Wendy Hsiao, W.L. Adaptogenic flower buds exert cancer preventive effects by enhancing the SCFA-producers, strengthening the epithelial tight junction complex and immune responses. Pharmacol. Res. 2020, 159, 104809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, T.; Xie, X.; Wu, L.; Li, L.; Yang, L.; Jiang, T.; Du, M.; Chen, M.; Xue, L.; Zhang, J.; et al. Metabolism of resistant starch RS3 administered in combination with Lactiplantibacillus plantarum strain 84-3 by human gut microbiota in simulated fermentation experiments in vitro and in a rat model. Food Chem. 2023, 411, 135412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, F.; Li, N.; Shi, J.; Li, H.; Yue, Y.; Jiao, W.; Wang, N.; Song, Y.; Huo, G.; Li, B. Lactobacillus acidophilus alleviates type 2 diabetes by regulating hepatic glucose, lipid metabolism and gut microbiota in mice. Food Funct. 2019, 10, 5804–5815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Tao, X.; Zhang, G.; Zhang, P.; Wang, H.; Ye, J.; Li, F.; Zhang, Q.; Nabi, M. Benefit of solid-liquid separation on volatile fatty acid production from grass clipping with ultrasound-calcium hydroxide pretreatment. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 274, 97–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, L.; Liu, Y.; Wang, S.; Zhang, Q.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, H.; Narbad, A.; Tian, F.; Zhai, Q.; Chen, W. Cholestasis: Exploring the triangular relationship of gut microbiota-bile acid-cholestasis and the potential probiotic strategies. Gut Microbes 2023, 15, 2181930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kullak-Ublick, G.A.; Stieger, B.; Meier, P.J. Enterohepatic bile salt transporters in normal physiology and liver disease. Gastroenterology 2004, 126, 322–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiang, J.Y. Bile acid metabolism and signaling. Compr. Physiol. 2013, 3, 1191–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, W.; Xie, G.; Jia, W. Bile acid-microbiota crosstalk in gastrointestinal inflammation and carcinogenesis. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2018, 15, 111–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woolbright, B.L.; Jaeschke, H. Novel insight into mechanisms of cholestatic liver injury. World J. Gastroenterol. 2012, 18, 4985–4993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Shen, Y.; Cen, M.; Zhu, Y.; Cheng, F.; Tang, L.; Zheng, X.; Kim, J.J.; Dai, N.; Hu, W. Modulation of the Gut Microbiota-farnesoid X Receptor Axis Improves Deoxycholic Acid-induced Intestinal Inflammation in Mice. J. Crohns Colitis 2021, 15, 1197–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hetemaki, I.; Jian, C.; Laakso, S.; Makitie, O.; Pajari, A.M.; de Vos, W.M.; Arstila, T.P.; Salonen, A. Fecal Bacteria Implicated in Biofilm Production Are Enriched and Associate to Gastrointestinal Symptoms in Patients With APECED—A Pilot Study. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 668219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoppe, M.M.; Sundar, R.; Tan, D.S.P.; Jeyasekharan, A.D. Biomarkers for Homologous Recombination Deficiency in Cancer. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2018, 110, 704–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baretti, M.; Le, D.T. DNA mismatch repair in cancer. Pharmacol. Ther. 2018, 189, 45–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Segura-Bayona, S.; Villamor-Paya, M.; Attolini, C.S.; Koenig, L.M.; Sanchiz-Calvo, M.; Boulton, S.J.; Stracker, T.H. Tousled-Like Kinases Suppress Innate Immune Signaling Triggered by Alternative Lengthening of Telomeres. Cell Rep. 2020, 32, 107983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Liu, N.; Ge, Y.; Yang, Y.; Ren, F.; Wu, Z. Tryptophan and the innate intestinal immunity: Crosstalk between metabolites, host innate immune cells, and microbiota. Eur. J. Immunol. 2022, 52, 856–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Luo, L.; Zhu, J.; Yan, H.; Yang, X.; Tang, W.; Li, D.; He, D.; Wang, J.; Dai, W.; et al. Water extract of Cayratia albifolia C.L.Li root relieves zymosan A-induced inflammation by restraining M1 macrophage polarization. Phytomedicine 2022, 96, 153901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, F.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, M.; Guo, C.; Cao, Z.; Zhang, R.; Peng, C. A review of pharmacological and pharmacokinetic properties of stachydrine. Pharmacol. Res. 2020, 155, 104755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]







Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, F.; Yu, Z.; Liu, Y.; Du, T.; Yu, L.; Tian, F.; Chen, W.; Zhai, Q. A High-Fat, High-Cholesterol Diet Promotes Intestinal Inflammation by Exacerbating Gut Microbiome Dysbiosis and Bile Acid Disorders in Cholecystectomy. Nutrients 2023, 15, 3829. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15173829
Xu F, Yu Z, Liu Y, Du T, Yu L, Tian F, Chen W, Zhai Q. A High-Fat, High-Cholesterol Diet Promotes Intestinal Inflammation by Exacerbating Gut Microbiome Dysbiosis and Bile Acid Disorders in Cholecystectomy. Nutrients. 2023; 15(17):3829. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15173829
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Fusheng, Zhiming Yu, Yaru Liu, Ting Du, Leilei Yu, Fengwei Tian, Wei Chen, and Qixiao Zhai. 2023. "A High-Fat, High-Cholesterol Diet Promotes Intestinal Inflammation by Exacerbating Gut Microbiome Dysbiosis and Bile Acid Disorders in Cholecystectomy" Nutrients 15, no. 17: 3829. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15173829
APA StyleXu, F., Yu, Z., Liu, Y., Du, T., Yu, L., Tian, F., Chen, W., & Zhai, Q. (2023). A High-Fat, High-Cholesterol Diet Promotes Intestinal Inflammation by Exacerbating Gut Microbiome Dysbiosis and Bile Acid Disorders in Cholecystectomy. Nutrients, 15(17), 3829. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15173829