A Candidate Gliotransmitter, L-β-Aminoisobutyrate, Contributes to Weight Gain and Metabolic Complication Induced by Atypical Antipsychotics
Abstract
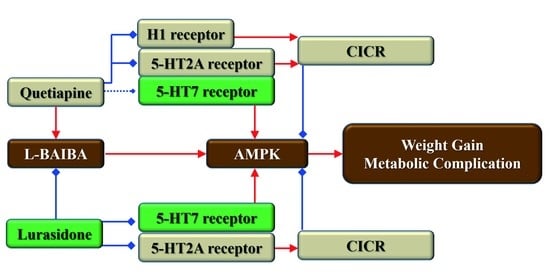
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Animals
2.2. Chemical Agents
2.3. Primary Cultured Astrocytes
2.4. Microdialysis
2.5. Capillary Immunoblotting Analysis
2.6. Extractions
2.7. UHPLC and UHPLC-MS
2.8. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Body Weight
3.2. In Vivo Experiments
3.2.1. Plasma BAIBA Enantiomer Levels
3.2.2. BAIBA Enantiomer Levels in the Hypothalamus
3.2.3. Effects of Chronic Administration of Lurasidone and Quetiapine on Intracellular Levels of Second Messengers in the Hypothalamus
3.2.4. L-BAIBA Release in the Hypothalamus
3.2.5. Intracellular and Extracellular Levels of D-serine in the Hypothalamus
3.3. In Vitro Experiments
3.3.1. BAIBA Enantiomer Levels in the Astrocyte
3.3.2. Effects of Chronic Exposures of Lurasidone and Quetiapine on Second Messengers in the Astrocytes
3.3.3. Astroglial L-BAIBA Release
3.3.4. Interaction between Chronic Administrations of Quetiapine and SB269970 on AMPK Signaling
4. Discussion
4.1. Candidate Mechanisms of Weight Gain Associated with AMPK Signalings Induced by Antipsychotics
4.2. Releasing Mechanisms as Candidate Gliotransmitter of L-BAIBA
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- De Hert, M.; Correll, C.U.; Bobes, J.; Cetkovich-Bakmas, M.; Cohen, D.A.N.; Asai, I.; Detraux, J.; Gautam, S.; MÖLler, H.-J.; Ndetei, D.M.; et al. Physical illness in patients with severe mental disorders. I. Prevalence, impact of medications and disparities in health care. World Psychiatry 2011, 10, 52–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- De Hert, M.A.; van Winkel, R.; Van Eyck, D.; Hanssens, L.; Wampers, M.; Scheen, A.; Peuskens, J. Prevalence of the metabolic syndrome in patients with schizophrenia treated with antipsychotic medication. Schizophr. Res. 2006, 83, 87–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carli, M.; Kolachalam, S.; Longoni, B.; Pintaudi, A.; Baldini, M.; Aringhieri, S.; Fasciani, I.; Annibale, P.; Maggio, R.; Scarselli, M. Atypical Antipsychotics and Metabolic Syndrome: From Molecular Mechanisms to Clinical Differences. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, H.; Siafis, S.; Hamza, T.; Schneider-Thoma, J.; Davis, J.M.; Salanti, G.; Leucht, S. Antipsychotic-Induced Weight Gain: Dose-Response Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Schizophr. Bull. 2022, 48, 643–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawrence, D.; Hancock, K.J.; Kisely, S. The gap in life expectancy from preventable physical illness in psychiatric patients in Western Australia: Retrospective analysis of population based registers. BMJ 2013, 346, f2539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fukuyama, K.; Motomura, E.; Okada, M. Therapeutic Potential and Limitation of Serotonin Type 7 Receptor Modulation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 2070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okada, M.; Yoshida, S.; Zhu, G.; Hirose, S.; Kaneko, S. Biphasic actions of topiramate on monoamine exocytosis associated with both soluble N-ethylmaleimide-sensitive factor attachment protein receptors and Ca(2+)-induced Ca(2+)-releasing systems. Neuroscience 2005, 134, 233–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Brito, O.M.; Scorrano, L. An intimate liaison: Spatial organization of the endoplasmic reticulum-mitochondria relationship. EMBO J. 2010, 29, 2715–2723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fukuyama, K.; Tanahashi, S.; Nakagawa, M.; Yamamura, S.; Motomura, E.; Shiroyama, T.; Tanii, H.; Okada, M. Levetiracetam inhibits neurotransmitter release associated with CICR. Neurosci. Lett. 2012, 518, 69–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Decrock, E.; De Bock, M.; Wang, N.; Gadicherla, A.K.; Bol, M.; Delvaeye, T.; Vandenabeele, P.; Vinken, M.; Bultynck, G.; Krysko, D.V.; et al. IP3, a small molecule with a powerful message. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2013, 1833, 1772–1786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fukuyama, K.; Motomura, E.; Okada, M. Opposing effects of clozapine and brexpiprazole on beta-aminoisobutyric acid: Pathophysiology of antipsychotics-induced weight gain. Schizophrenia 2023, 9, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez, M. Hypothalamic AMPK as a possible target for energy balance-related diseases. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2022, 43, 546–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foretz, M.; Guigas, B.; Bertrand, L.; Pollak, M.; Viollet, B. Metformin: From mechanisms of action to therapies. Cell Metab. 2014, 20, 953–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Siskind, D.J.; Leung, J.; Russell, A.W.; Wysoczanski, D.; Kisely, S. Metformin for Clozapine Associated Obesity: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0156208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Leucht, S.; Crippa, A.; Siafis, S.; Patel, M.X.; Orsini, N.; Davis, J.M. Dose-Response Meta-Analysis of Antipsychotic Drugs for Acute Schizophrenia. Am. J. Psychiatry 2020, 177, 342–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, L.D.; Bostrom, P.; O’Sullivan, J.F.; Schinzel, R.T.; Lewis, G.D.; Dejam, A.; Lee, Y.K.; Palma, M.J.; Calhoun, S.; Georgiadi, A.; et al. beta-Aminoisobutyric acid induces browning of white fat and hepatic beta-oxidation and is inversely correlated with cardiometabolic risk factors. Cell Metab. 2014, 19, 96–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jung, T.W.; Hwang, H.J.; Hong, H.C.; Yoo, H.J.; Baik, S.H.; Choi, K.M. BAIBA attenuates insulin resistance and inflammation induced by palmitate or a high fat diet via an AMPK-PPARdelta-dependent pathway in mice. Diabetologia 2015, 58, 2096–2105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, C.X.; Zhao, M.X.; Shu, X.D.; Xiong, X.Q.; Wang, J.J.; Gao, X.Y.; Chen, Q.; Li, Y.H.; Kang, Y.M.; Zhu, G.Q. beta-aminoisobutyric acid attenuates hepatic endoplasmic reticulum stress and glucose/lipid metabolic disturbance in mice with type 2 diabetes. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 21924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Okada, M.; Fukuyama, K.; Motomura, E. Dose-Dependent Biphasic Action of Quetiapine on AMPK Signalling via 5-HT7 Receptor: Exploring Pathophysiology of Clinical and Adverse Effects of Quetiapine. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 9103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukuyama, K.; Motomura, E.; Shiroyama, T.; Okada, M. Impact of 5-HT7 receptor inverse agonism of lurasidone on monoaminergic tripartite synaptic transmission and pathophysiology of lower risk of weight gain. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2022, 148, 112750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukuyama, K.; Motomura, E.; Okada, M. Brexpiprazole reduces 5-HT7 receptor function on astroglial transmission systems. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 6571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horikoshi, T.; Asanuma, A.; Yanagisawa, K.; Anzai, K.; Goto, S. Taurine and beta-alanine act on both GABA and glycine receptors in Xenopus oocyte injected with mouse brain messenger RNA. Brain Res. 1988, 464, 97–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmieden, V.; Betz, H. Pharmacology of the inhibitory glycine receptor: Agonist and antagonist actions of amino acids and piperidine carboxylic acid compounds. Mol. Pharm. 1995, 48, 919–927. [Google Scholar]
- Lilley, E.; Stanford, S.C.; Kendall, D.E.; Alexander, S.P.H.; Cirino, G.; Docherty, J.R.; George, C.H.; Insel, P.A.; Izzo, A.A.; Ji, Y.; et al. ARRIVE 2.0 and the British Journal of Pharmacology: Updated guidance for 2020. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2020, 177, 3611–3616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiemke, C.; Bergemann, N.; Clement, H.W.; Conca, A.; Deckert, J.; Domschke, K.; Eckermann, G.; Egberts, K.; Gerlach, M.; Greiner, C.; et al. Consensus Guidelines for Therapeutic Drug Monitoring in Neuropsychopharmacology: Update 2017. Pharmacopsychiatry 2018, 51, 9–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schoretsanitis, G.; Paulzen, M.; Unterecker, S.; Schwarz, M.; Conca, A.; Zernig, G.; Grunder, G.; Haen, E.; Baumann, P.; Bergemann, N.; et al. TDM in psychiatry and neurology: A comprehensive summary of the consensus guidelines for therapeutic drug monitoring in neuropsychopharmacology, update 2017; a tool for clinicians. World J. Biol. Psychiatry 2018, 19, 162–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukuyama, K.; Okada, M. Effects of Atypical Antipsychotics, Clozapine, Quetiapine and Brexpiprazole on Astroglial Transmission Associated with Connexin43. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 5623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okada, M.; Matsumoto, R.; Yamamoto, Y.; Fukuyama, K. Effects of Subchronic Administrations of Vortioxetine, Lurasidone, and Escitalopram on Thalamocortical Glutamatergic Transmission Associated with Serotonin 5-HT7 Receptor. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okada, M.; Fukuyama, K.; Okubo, R.; Shiroyama, T.; Ueda, Y. Lurasidone Sub-Chronically Activates Serotonergic Transmission via Desensitization of 5-HT1A and 5-HT7 Receptors in Dorsal Raphe Nucleus. Pharmaceuticals 2019, 12, 149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Okada, M.; Fukuyama, K.; Ueda, Y. Lurasidone inhibits NMDA receptor antagonist-induced functional abnormality of thalamocortical glutamatergic transmission via 5-HT7 receptor blockade. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2019, 176, 4002–4018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamura, S.; Ohoyama, K.; Hamaguchi, T.; Kashimoto, K.; Nakagawa, M.; Kanehara, S.; Suzuki, D.; Matsumoto, T.; Motomura, E.; Shiroyama, T.; et al. Effects of quetiapine on monoamine, GABA, and glutamate release in rat prefrontal cortex. Pharmaceuticals 2009, 206, 243–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucke, A.; Musshoff, U.; Kohling, R.; Osterfeld, M.; Mayer, T.; Wolf, P.; Schutte, W.; Speckmann, E.J. Gabapentin potentiation of the antiepileptic efficacy of vigabatrin in an in vitro model of epilepsy. Br. J. Pharmacol. 1998, 124, 370–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dewey, S.L.; Brodie, J.D.; Gerasimov, M.; Horan, B.; Gardner, E.L.; Ashby, C.R., Jr. A pharmacologic strategy for the treatment of nicotine addiction. Synapse 1999, 31, 76–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukuyama, K.; Ueda, Y.; Okada, M. Effects of Carbamazepine, Lacosamide and Zonisamide on Gliotransmitter Release Associated with Activated Astroglial Hemichannels. Pharmaceuticals 2020, 13, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanahashi, S.; Yamamura, S.; Nakagawa, M.; Motomura, E.; Okada, M. Clozapine, but not haloperidol, enhances glial D-serine and L-glutamate release in rat frontal cortex and primary cultured astrocytes. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2012, 165, 1543–1555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yamamura, S.; Hoshikawa, M.; Dai, K.; Saito, H.; Suzuki, N.; Niwa, O.; Okada, M. ONO-2506 inhibits spike-wave discharges in a genetic animal model without affecting traditional convulsive tests via gliotransmission regulation. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2013, 168, 1088–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukuyama, K.; Okubo, R.; Murata, M.; Shiroyama, T.; Okada, M. Activation of Astroglial Connexin is Involved in Concentration-Dependent Double-Edged Sword Clinical Action of Clozapine. Cells 2020, 9, 414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fukuyama, K.; Okada, M. High frequency oscillations play important roles in development of epileptogenesis/ictogenesis via activation of astroglial signallings. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2022, 149, 112846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latchoumane, C.V.; Ngo, H.V.; Born, J.; Shin, H.S. Thalamic Spindles Promote Memory Formation during Sleep through Triple Phase-Locking of Cortical, Thalamic, and Hippocampal Rhythms. Neuron 2017, 95, 424–435.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fukuyama, K.; Nakano, T.; Shiroyama, T.; Okada, M. Chronic Administrations of Guanfacine on Mesocortical Catecholaminergic and Thalamocortical Glutamatergic Transmissions. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 4122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukuyama, K.; Okada, M. Age-Dependent and Sleep/Seizure-Induced Pathomechanisms of Autosomal Dominant Sleep-Related Hypermotor Epilepsy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 8142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukuyama, K.; Fukuzawa, M.; Shiroyama, T.; Okada, M. Pathogenesis and pathophysiology of autosomal dominant sleep-related hypermotor epilepsy with S284L-mutant alpha4 subunit of nicotinic ACh receptor. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2020, 177, 2143–2162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iversen, L.L.; Glowinski, J. Regional studies of catecholamines in the rat brain. II. Rate of turnover of catecholamines in various brain regions. J. Neurochem. 1966, 13, 671–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azevedo, C.; Saiardi, A. Extraction and analysis of soluble inositol polyphosphates from yeast. Nat. Protoc. 2006, 1, 2416–2422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shiroyama, T.; Fukuyama, K.; Okada, M. Distinct Effects of Escitalopram and Vortioxetine on Astroglial L-Glutamate Release Associated with Connexin43. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 10013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Connor, W.T.; O’Shea, S.D. Clozapine and GABA transmission in schizophrenia disease models: Establishing principles to guide treatments. Pharmacol. Ther. 2015, 150, 47–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanianskii, D.A.; Jarzebska, N.; Birkenfeld, A.L.; O’Sullivan, J.F.; Rodionov, R.N. Beta-Aminoisobutyric Acid as a Novel Regulator of Carbohydrate and Lipid Metabolism. Nutrients 2019, 11, 524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Silverman, R.B. Design and Mechanism of GABA Aminotransferase Inactivators. Treatments for Epilepsies and Addictions. Chem. Rev. 2018, 118, 4037–4070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanahashi, S.; Ueda, Y.; Nakajima, A.; Yamamura, S.; Nagase, H.; Okada, M. Novel delta1-receptor agonist KNT-127 increases the release of dopamine and L-glutamate in the striatum, nucleus accumbens and median pre-frontal cortex. Neuropharmacology 2012, 62, 2057–2067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okada, M.; Zhu, G.; Yoshida, S.; Kanai, K.; Hirose, S.; Kaneko, S. Exocytosis mechanism as a new targeting site for mechanisms of action of antiepileptic drugs. Life Sci. 2002, 72, 465–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okada, M.; Wada, K.; Kiryu, K.; Kawata, Y.; Mizuno, K.; Kondo, T.; Tasaki, H.; Kaneko, S. Effects of Ca2+ channel antagonists on striatal dopamine and DOPA release, studied by in vivo microdialysis. Br. J. Pharmacol. 1998, 123, 805–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yoshida, S.; Okada, M.; Zhu, G.; Kaneko, S. Carbamazepine prevents breakdown of neurotransmitter release induced by hyperactivation of ryanodine receptor. Neuropharmacology 2007, 52, 1538–1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, S.; Yamamura, S.; Ohoyama, K.; Nakagawa, M.; Motomura, E.; Kaneko, S.; Okada, M. Effects of valproate on neurotransmission associated with ryanodine receptors. Neurosci. Res. 2010, 68, 322–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crumpler, H.R.; Dent, C.E.; Harris, H.; Westall, R.G. beta-Aminoisobutyric acid (alpha-methyl-beta-alanine); a new amino-acid obtained from human urine. Nature 1951, 167, 307–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, K.J.; Park, J.; Lee, S.Y.; Hwang, I.; Kim, J.B.; Park, T.S.; Lee, H.J.; Koo, S.H. Atypical antipsychotic drugs perturb AMPK-dependent regulation of hepatic lipid metabolism. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2011, 300, E624–E632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, S.F.; Huang, A.S.; Snowman, A.M.; Teuscher, C.; Snyder, S.H. From the Cover: Antipsychotic drug-induced weight gain mediated by histamine H1 receptor-linked activation of hypothalamic AMP-kinase. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 3456–3459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, I.S.; Nishikimi, M.; Inoue, M.; Muragaki, Y.; Ooshima, A. Specific expression of alanine-glyoxylate aminotransferase 2 in the epithelial cells of Henle’s loop. Nephron 1999, 83, 184–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pollitt, R.J.; Green, A.; Smith, R. Excessive excretion of beta-alanine and of 3-hydroxypropionic, R- and S-3-aminoisobutyric, R- and S-3-hydroxyisobutyric and S-2-(hydroxymethyl)butyric acids probably due to a defect in the metabolism of the corresponding malonic semialdehydes. J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 1985, 8, 75–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roe, C.R.; Struys, E.; Kok, R.M.; Roe, D.S.; Harris, R.A.; Jakobs, C. Methylmalonic semialdehyde dehydrogenase deficiency: Psychomotor delay and methylmalonic aciduria without metabolic decompensation. Mol. Genet. Metab. 1998, 65, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kakimoto, Y.; Kanazawa, A.; Taniguchi, K.; Sano, I. Beta-aminoisobutyrate-alpha-ketoglutarate transaminase in relation to beta-aminoisobutyric aciduria. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1968, 156, 374–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armstrong, M.D.; Yates, K.; Kakimoto, Y.; Taniguchi, K.; Kappe, T. Excretion of β-aminoisobutyric acid by man. J. Biol. Chem. 1963, 238, 1447–1455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gejyo, F.; Kinoshita, Y.; Ikenaka, T. Identification of beta-aminoisobutyric acid in uremic serum. Clin. Chim. Acta 1976, 70, 407–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stautemas, J.; Van Kuilenburg, A.B.P.; Stroomer, L.; Vaz, F.; Blancquaert, L.; Lefevere, F.B.D.; Everaert, I.; Derave, W. Acute Aerobic Exercise Leads to Increased Plasma Levels of R- and S-beta-Aminoisobutyric Acid in Humans. Front. Physiol. 2019, 10, 1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Okubo, R.; Hasegawa, T.; Fukuyama, K.; Shiroyama, T.; Okada, M. Current Limitations and Candidate Potential of 5-HT7 Receptor Antagonism in Psychiatric Pharmacotherapy. Front. Psychiatry 2021, 12, 623684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukuyama, K.; Okada, M. Effects of an Atypical Antipsychotic, Zotepine, on Astroglial L-Glutamate Release through Hemichannels: Exploring the Mechanism of Mood-Stabilising Antipsychotic Actions and Antipsychotic-Induced Convulsion. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salminen, A.; Kaarniranta, K.; Kauppinen, A. Age-related changes in AMPK activation: Role for AMPK phosphatases and inhibitory phosphorylation by upstream signaling pathways. Ageing Res. Rev. 2016, 28, 15–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okada, M.; Zhu, G.; Yoshida, S.; Hirose, S.; Kaneko, S. Protein kinase associated with gating and closing transmission mechanisms in temporoammonic pathway. Neuropharmacology 2004, 47, 485–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okada, M.; Fukuyama, K.; Shiroyama, T.; Ueda, Y. Brivaracetam prevents astroglial l-glutamate release associated with hemichannel through modulation of synaptic vesicle protein. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2021, 138, 111462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okada, M.; Oka, T.; Nakamoto, M.; Fukuyama, K.; Shiroyama, T. Astroglial Connexin43 as a Potential Target for a Mood Stabiliser. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 22, 339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okada, M. Can rodent models elucidate the pathomechanisms of genetic epilepsy? Br. J. Pharmacol. 2022, 179, 1620–1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viejo, G.; Peyrache, A. Precise coupling of the thalamic head-direction system to hippocampal ripples. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 2524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferraris, M.; Cassel, J.C.; Pereira de Vasconcelos, A.; Stephan, A.; Quilichini, P.P. The nucleus reuniens, a thalamic relay for cortico-hippocampal interaction in recent and remote memory consolidation. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2021, 125, 339–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banquet, J.P.; Gaussier, P.; Cuperlier, N.; Hok, V.; Save, E.; Poucet, B.; Quoy, M.; Wiener, S.I. Time as the fourth dimension in the hippocampus. Prog. Neurobiol. 2021, 199, 101920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikeda, A.; Takeyama, H.; Bernard, C.; Nakatani, M.; Shimotake, A.; Daifu, M.; Matsuhashi, M.; Kikuchi, T.; Kunieda, T.; Matsumoto, R. Active direct current (DC) shifts and “Red slow”: Two new concepts for seizure mechanisms and identification of the epileptogenic zone. Neurosci. Res. 2020, 156, 95–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukuyama, K.; Okada, M. Brivaracetam and Levetiracetam Suppress Astroglial L-Glutamate Release through Hemichannel via Inhibition of Synaptic Vesicle Protein. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 4473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]











Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fukuyama, K.; Motomura, E.; Okada, M. A Candidate Gliotransmitter, L-β-Aminoisobutyrate, Contributes to Weight Gain and Metabolic Complication Induced by Atypical Antipsychotics. Nutrients 2023, 15, 1621. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15071621
Fukuyama K, Motomura E, Okada M. A Candidate Gliotransmitter, L-β-Aminoisobutyrate, Contributes to Weight Gain and Metabolic Complication Induced by Atypical Antipsychotics. Nutrients. 2023; 15(7):1621. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15071621
Chicago/Turabian StyleFukuyama, Kouji, Eishi Motomura, and Motohiro Okada. 2023. "A Candidate Gliotransmitter, L-β-Aminoisobutyrate, Contributes to Weight Gain and Metabolic Complication Induced by Atypical Antipsychotics" Nutrients 15, no. 7: 1621. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15071621
APA StyleFukuyama, K., Motomura, E., & Okada, M. (2023). A Candidate Gliotransmitter, L-β-Aminoisobutyrate, Contributes to Weight Gain and Metabolic Complication Induced by Atypical Antipsychotics. Nutrients, 15(7), 1621. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15071621