Apigenin Ameliorates Dyslipidemia, Hepatic Steatosis and Insulin Resistance by Modulating Metabolic and Transcriptional Profiles in the Liver of High-Fat Diet-Induced Obese Mice
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
2.2. Levels of Fasting Blood Glucose, Plasma Insulin and Homeostatic Index of Insulin Resistance
2.3. Plasma Adipocytokines, Lipids, Apolipoproteins and Aminotransferases Levels
2.4. Morphology of Liver
2.5. Hepatic Enzymes Activity
2.6. RNA Preparation
2.7. Microarray Analysis and RT-qPCR
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Apigenin Did Not Alter Food Intake, Body Weight Gain and Fat Accumulation
3.2. Apigenin Decreased Fasting Blood Glucose and Plasma Insulin Levels and Ameliorated Insulin Resistance and Inflammation
3.3. Apigenin Improved Dyslipidemia, Hepatic Steatosis and Hepatomegaly
3.4. Liver Gene Expression Profiles in Response to Apigenin
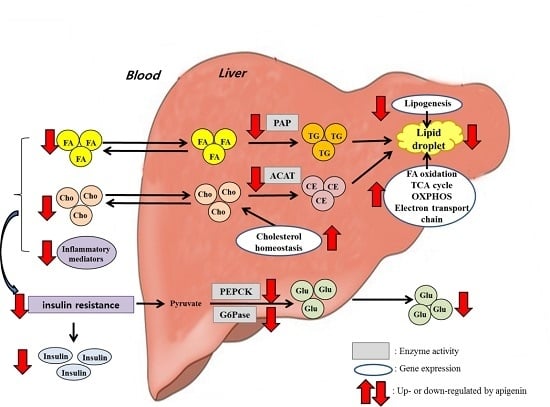
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Padwal, R.S.; Sharma, A.M. Prevention of cardiovascular disease: Obesity, diabetes and the metabolic syndrome. Can. J. Cardiol. 2010, 26 (Suppl. C), 18C–20C. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, U.J.; Choi, M.S. Obesity and its metabolic complications: The role of adipokines and the relationship between obesity, inflammation, insulin resistance, dyslipidemia and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 6184–6223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidt, M.I.; Duncan, B.B.; Sharrett, A.R.; Lindberg, G.; Savage, P.J.; Offenbacher, S.; Azambuja, M.I.; Tracy, R.P.; Heiss, G. Markers of inflammation and prediction of diabetes mellitus in adults (Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities study): A cohort study. Lancet 1999, 353, 1649–1652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, R.; Kim, C.S.; Kang, J.H. Inflammatory components of adipose tissue as target for treatment of metabolic syndrome. Forum Nutr. 2009, 61, 95–103. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Abenavoli, L.; di Renzo, L.; Guzzi, P.H.; Pellicano, R.; Milic, N.; de Lorenzo, A. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease severity, central fat mass and adinopectin: A close relationship. Clujul Med. 2015, 88, 489–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Miller, B.; Matthan, N.R.; Goktas, Z.; Wu, D.; Reed, D.B.; Yin, X.; Grammas, P.; Moustaid-Moussa, N.; Shen, C.L.; et al. Aortic cholesterol accumulation correlates with systemic inflammation but not hepatic and gonadal adipose tissue inflammation in low-density lipoprotein receptor null mice. Nutr. Res. 2013, 33, 1072–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milosević, N.; Milanović, M.; Abenavoli, L.; Milić, N. Phytotherapy and NAFLD—From goals and challenges to clinical practice. Rev. Recent Clin. Trials 2014, 9, 195–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shukla, S.; Gupta, S. Apigenin: A promising molecule for cancer prevention. Pharm. Res. 2010, 27, 962–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ono, M.; Fujimori, K. Antiadipogenic effect of dietary apigenin through activation of AMPK in 3T3-L1 cells. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2011, 59, 13346–13352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, M.A.; Kang, K.; Lee, H.J.; Kim, M.; Kim, C.Y.; Nho, C.W. Apigenin isolated from Daphne genkwa Siebold et Zucc. inhibits 3T3-L1 preadipocyte differentiation through a modulation of mitotic clonal expansion. Life Sci. 2014, 101, 64–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Escande, C.; Nin, V.; Price, N.L.; Capellini, V.; Gomes, A.P.; Barbosa, M.T.; O’Neil, L.; White, T.A.; Sinclair, D.A.; Chini, E.N. Flavonoid apigenin is an inhibitor of the NAD+ ase CD38: Implications for cellular NAD+ metabolism, protein acetylation, and treatment of metabolic syndrome. Diabetes 2013, 62, 1084–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Myoung, H.J.; Kim, G.; Nam, K.W. Apigenin isolated from the seeds of Perilla frutescens britton var crispa (Benth.) inhibits food intake in C57BL/6J mice. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2010, 33, 1741–1746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seo, K.I.; Choi, M.S.; Jung, U.J.; Kim, H.J.; Yeo, J.; Jeon, S.M.; Lee, M.K. Effect of curcumin supplementation on blood glucose, plasma insulin, and glucose homeostasis related enzyme activities in diabetic db/db mice. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2008, 52, 995–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, S.J.; Jung, U.J.; Choi, M.S. Differential effects of low-dose resveratrol on adiposity and hepatic steatosis in diet-induced obese mice. Br. J. Nutr. 2012, 108, 2166–2175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Do, G.M.; Oh, H.Y.; Kwon, E.Y.; Cho, Y.Y.; Shin, S.K.; Park, H.J.; Jeon, S.M.; Kim, E.; Hur, C.G.; Park, T.S.; et al. Long-term adaptation of global transcription and metabolism in the liver of high-fat diet-fed C57BL/6J mice. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2011, 55 (Suppl. 2), S173–S185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wallace, T.M.; Levy, J.C.; Matthews, D.R. Use and abuse of HOMA modeling. Diabetes Care 2004, 27, 1487–1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, B.; Saxena, A. Surrogate markers of insulin resistance: A review. World J. Diabetes 2010, 1, 36–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barthel, A.; Schmoll, D. Novel concepts in insulin regulation of hepatic gluconeogenesis. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2003, 285, E685–E692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gastaldelli, A.; Baldi, S.; Pettiti, M.; Toschi, E.; Camastra, S.; Natali, A.; Landau, B.R.; Ferrannini, E. Influence of obesity and type 2 diabetes on gluconeogenesis and glucose output in humans: A quantitative study. Diabetes 2000, 49, 1367–1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bumke-Vogt, C.; Osterhoff, M.A.; Borchert, A.; Guzman-Perez, V.; Sarem, Z.; Birkenfeld, A.L.; Bähr, V.; Pfeiffer, A.F. The flavones apigenin and luteolin induce FOXO1 translocation but inhibit gluconeogenic and lipogenic gene expression in human cells. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e104321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, C.M.; Ghosh, M.K.; Satapathy, B.S.; Dey, N.S.; Mukherjee, B. Apigenin causes biochemical modulation, GLUT4 and CD38 alterations to improve diabetes and to protect damages of some vital organs in experimental diabetes. Am. J. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2014, 9, 39–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polyzos, S.A.; Kountouras, J.; Mantzoros, C.S. Adipokines in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Metabolism 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abenavoli, L.; Peta, V. Role of adipokines and cytokines in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Rev. Recent Clin. Trials 2014, 9, 134–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Senn, J.J.; Klover, P.J.; Nowak, I.A.; Mooney, R.A. Interleukin-6 induces cellular insulin resistance in hepatocytes. Diabetes 2002, 51, 3391–3399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryan, A.S.; Nicklas, B.J. Reductions in plasma cytokine levels with weight loss improve insulin sensitivity in overweight and obese postmenopausal women. Diabetes Care 2004, 27, 1699–1705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grosso, A.F.; de Oliveira, S.F.; Higuchi, M.L.; Favarato, D.; Dallan, L.A.; da Luz, P.L. Synergistic anti-inflammatory effect: Simvastatin and pioglitazone reduce inflammatory markers of plasma and epicardial adipose tissue of coronary patients with metabolic syndrome. Diabetol. Metab. Syndr. 2014, 6, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rocha, V.Z.; Folco, E.J.; Sukhova, G.; Shimizu, K.; Gotsman, I.; Vernon, A.H.; Libby, P. Interferon-gamma, a Th1 cytokine, regulates fat inflammation: A role for adaptive immunity in obesity. Circ. Res. 2008, 103, 467–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Rourke, R.W.; White, A.E.; Metcalf, M.D.; Winters, B.R. Systemic inflammation and insulin sensitivity in obese IFN-γ knockout mice. Metabolism 2012, 61, 1152–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicholas, C.; Batra, S.; Vargo, M.A.; Voss, O.H.; Gavrilin, M.A.; Wewers, M.D.; Guttridge, D.C.; Grotewold, E.; Doseff, A.I. Apigenin blocks lipopolysaccharide-induced lethality in vivo and proinflammatory cytokines expression by inactivating NF-κB through the suppression of p65 phosphorylation. J. Immunol. 2007, 179, 7121–7127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, M.T.; Satoh, H.; Favelyukis, S.; Babendure, J.L.; Imamura, T.; Sbodio, J.I.; Zalevsky, J.; Dahiyat, B.I.; Chi, N.W.; Olefsky, J.M. JNK and TNF-α mediate free fatty acid-induced insulin resistance in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 35361–35371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braunersreuther, V.; Viviani, G.L.; Mach, F.; Montecucco, F. Role of cytokines and chemokines in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. World J. Gastroenterol. 2012, 18, 727–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Q.; Bengmark, S.; Qu, S. The role of hepatic fat accumulation in pathogenesis of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). Lipids Health Dis. 2010, 9, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Yokoyama, N.; Yoshida, S.; Tsutsumi, K.; Hatakeyama, S.; Sato, T.; Ishihara, K.; Akiba, S. Alleviation of high-fat diet-induced fatty liver damage in group IVA phospholipase A2-knockout mice. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e8089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, D.; Oh, K.J.; Jo, H.Y.; Hedrick, S.; Kim, Y.N.; Hwang, Y.J.; Park, T.S.; Han, J.S.; Choi, C.S.; Montminy, M.; et al. TORC2 regulates hepatic insulin signaling via a mammalian phosphatidic acid phosphatase, LIPIN1. Cell Metab. 2009, 9, 240–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, R.A.; Joyce, C.; Davis, M.; Reagan, J.W.; Clark, M.; Shelness, G.S.; Rudel, L.L. Identification of a form of acyl-CoA:cholesterol acyltransferase specific to liver and intestine in nonhuman primates. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 26747–26754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamamoto, T.; Yamaguchi, H.; Miki, H.; Shimada, M.; Nakada, Y.; Ogino, M.; Asano, K.; Aoki, K.; Tamura, N.; Masago, M.; et al. Coenzyme A: Diacylglycerol acyltransferase 1 inhibitor ameliorates obesity, liver steatosis, and lipid metabolism abnormality in KKAy mice fed high-fat or high-carbohydrate diets. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2010, 640, 243–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alger, H.M.; Mark Brown, J.; Sawyer, J.K.; Kelley, K.L.; Shah, R.; Wilson, M.D.; Willingham, M.C.; Rudel, L.L. Inhibition of acyl-coenzyme A: Cholesterol acyltransferase 2 (ACAT2) prevents dietary cholesterol-associated steatosis by enhancing hepatic triglyceride mobilization. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 14267–14274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Post, P.M.; Zoeteweij, J.P.; Bos, M.H.; de Wit, E.C.; Havinga, R.; Kuipers, F.; Princen, H.M. Acyl-coenzyme A: Cholesterol acyltransferase inhibitor, avasimibe, stimulates bile acid synthesis and cholesterol 7alpha-hydroxylase in cultured rat hepatocytes and in vivo in the rat. Hepatolohy 1999, 30, 491–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huff, M.W.; Telford, D.E.; Barrett, P.H.; Billheimer, J.T.; Gillies, P.J. Inhibition of hepatic ACAT decreases ApoB secretion in miniature pigs fed a cholesterol-free diet. Arterioscler. Thromb. 1994, 14, 1498–1508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, Z.; Wei, W.; Yang, M.; Du, Y.; Wan, Y. Mitochondrial complex I activity suppresses inflammation and enhances bone resorption by shifting macrophage-osteoclast polarization. Cell Metab. 2014, 20, 483–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dahlman, I.; Forsgren, M.; Sjögren, A.; Nordström, E.A.; Kaaman, M.; Näslund, E.; Attersand, A.; Arner, P. Downregulation of electron transport chain genes in visceral adipose tissue in type 2 diabetes independent of obesity and possibly involving tumor necrosis factor-alpha. Diabetes 2006, 55, 1792–1799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaswal, J.S.; Keung, W.; Wang, W.; Ussher, J.R.; Lopaschuk, G.D. Targeting fatty acid and carbohydrate oxidation—A novel therapeutic intervention in the ischemic and failing heart. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2011, 1813, 1333–1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elam, M.B.; Cowan, G.S.; Rooney, R.J., Jr.; Hiler, M.L.; Yellaturu, C.R.; Deng, X.; Howell, G.E.; Park, E.A.; Gerling, I.C.; Patel, D.; et al. Hepatic gene expression in morbidly obese women: Implications for disease susceptibility. Obesity 2009, 17, 1563–1573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, W.D.; Li, B.Y.; Yu, F.; Cai, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Yin, M.; Gao, H.Q. Quantitative proteomics study on the protective mechanism of phlorizin on hepatic damage in diabetic db/db mice. Mol. Med. Rep. 2012, 5, 1285–1294. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sprecher, H. Metabolism of highly unsaturated n-3 and n-6 fatty acids. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2000, 1486, 219–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martín-Pozuelo, G.; Navarro-González, I.; González-Barrio, R.; Santaella, M.; García-Alonso, J.; Hidalgo, N.; Gómez-Gallego, C.; Ros, G.; Periago, M.J. The effect of tomato juice supplementation on biomarkers and gene expression related to lipid metabolism in rats with induced hepatic steatosis. Eur. J. Nutr. 2015, 54, 933–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van der Leij, F.R.; Bloks, V.W.; Grefhorst, A.; Hoekstra, J.; Gerding, A.; Kooi, K.; Gerbens, F.; te Meerman, G.; Kuipers, F. Gene expression profiling in livers of mice after acute inhibition of beta-oxidation. Genomics 2007, 90, 680–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perez, M.J.; Briz, O. Bile-acid-induced cell injury and protection. World J. Gastroenterol. 2009, 15, 1677–1689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hadžić, N.; Bull, L.N.; Clayton, P.T.; Knisely, A.S. Diagnosis in bile acid-CoA: Amino acid N-acyltransferase deficiency. World J. Gastroenterol. 2012, 18, 3322–3326. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pircher, P.C.; Kitto, J.L.; Petrowski, M.L.; Tangirala, R.K.; Bischoff, E.D.; Schulman, I.G.; Westin, S.K. Farnesoid X receptor regulates bile acid-amino acid conjugation. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 27703–27711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamanashi, Y.; Takada, T.; Yoshikado, T.; Shoda, J.; Suzuki, H. NPC2 regulates biliary cholesterol secretion via stimulation of ABCG5/G8-mediated cholesterol transport. Gastroenterology 2011, 140, 1664–1674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abi-Mosleh, L.; Infante, R.E.; Radhakrishnan, A.; Goldstein, J.L.; Brown, M.S. Cyclodextrin overcomes deficient lysosome-to-endoplasmic reticulum transport of cholesterol in Niemann-Pick type C cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 19316–19321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, M.R.; Mathur, R.; Cui, J.; Guo, X.; Azziz, R.; Goodarzi, M.O. Independent confirmation of association between metabolic phenotypes of polycystic ovary syndrome and variation in the type 6 17beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase gene. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2009, 94, 5034–5038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morita, M.; Oike, Y.; Nagashima, T.; Kadomatsu, T.; Tabata, M.; Suzuki, T.; Nakamura, T.; Yoshida, N.; Okada, M.; Yamamoto, T. Obesity resistance and increased hepatic expression of catabolism-related mRNAs in Cnot3+/− mice. EMBO J. 2011, 30, 4678–4691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahara, Y.; Takahashi, M.; Wagatsuma, H.; Yokoya, F.; Zhang, Q.W.; Yamaguchi, M.; Aburatani, H.; Kawada, N. Gene expression profiles of hepatic cell-type specific marker genes in progression of liver fibrosis. World J. Gastroenterol. 2006, 12, 6473–6499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bandsma, R.H.; Wiegman, C.H.; Herling, A.W.; Burger, H.J.; ter Harmsel, A.; Meijer, A.J.; Romijn, J.A.; Reijngoud, D.J.; Kuipers, F. Acute inhibition of glucose-6-phosphate translocator activity leads to increased de novo lipogenesis and development of hepatic steatosis without affecting VLDL production in rats. Diabetes 2001, 50, 2591–2597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van de Pas, N.C.; Soffers, A.E.; Freidig, A.P.; van Ommen, B.; Woutersen, R.A.; Rietjens, I.M.; de Graaf, A.A. Systematic construction of a conceptual minimal model of plasma cholesterol levels based on knockout mouse phenotypes. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2010, 1801, 646–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimamura, M.; Matsuda, M.; Yasumo, H.; Okazaki, M.; Fujimoto, K.; Kono, K.; Shimizugawa, T.; Ando, Y.; Koishi, R.; Kohama, T.; et al. Angiopoietin-like protein3 regulates plasma HDL cholesterol through suppression of endothelial lipase. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2007, 27, 366–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quagliarini, F.; Wang, Y.; Kozlitina, J.; Grishin, N.V.; Hyde, R.; Boerwinkle, E.; Valenzuela, D.M.; Murphy, A.J.; Cohen, J.C.; Hobbs, H.H. Atypical angiopoietin-like protein that regulates ANGPTL3. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 19751–19756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pardina, E.; Baena-Fustegueras, J.A.; Catalán, R.; Galard, R.; Lecube, A.; Fort, J.M.; Allende, H.; Vargas, V.; Peinado-Onsurbe, J. Increased expression and activity of hepatic lipase in the liver of morbidly obese adult patients in relation to lipid content. Obes. Surg. 2008, 19, 894–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.K.; Fillmore, J.J.; Chen, Y.; Yu, C.; Moore, I.K.; Pypaert, M.; Lutz, E.P.; Kako, Y.; Velez-Carrasco, W.; Goldberg, I.J.; et al. Tissue-specific overexpression of lipoprotein lipase causes tissue-specific insulin resistance. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 7522–7527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fabbrini, E.; Sullivan, S.; Klein, S. Obesity and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: Biochemical, metabolic, and clinical implications. Hepatology 2010, 51, 679–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monetti, M.; Levin, M.C.; Watt, M.J.; Sajan, M.P.; Marmor, S.; Hubbard, B.K.; Stevens, R.D.; Bain, J.R.; Newgard, C.B.; Farese, R.V., Sr.; et al. Dissociation of hepatic steatosis and insulin resistance in mice overexpressing DGAT in the liver. Cell Metab. 2007, 6, 69–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morán-Salvador, E.; López-Parra, M.; García-Alonso, V.; Titos, E.; Martínez-Clemente, M.; González-Périz, A.; López-Vicario, C.; Barak, Y.; Arroyo, V.; Clària, J. Role for PPARγ in obesity-induced hepatic steatosis as determined by hepatocyte- and macrophage-specific conditional knockouts. FASEB J. 2011, 25, 2538–2550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, L.; Xu, L.; Ye, J.; Li, D.; Wang, W.; Li, X.; Wu, L.; Wang, H.; Guan, F.; Li, P. Cidea promotes hepatic steatosis by sensing dietary fatty acids. Hepatology 2012, 56, 95–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyazaki, M.; Flowers, M.T.; Sampath, H.; Chu, K.; Otzelberger, C.; Liu, X.; Ntambi, J.M. Hepatic stearoyl-CoA desaturase-1 deficiency protects mice from carbohydrate-induced adiposity and hepatic steatosis. Cell Metab. 2007, 6, 484–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]






© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jung, U.J.; Cho, Y.-Y.; Choi, M.-S. Apigenin Ameliorates Dyslipidemia, Hepatic Steatosis and Insulin Resistance by Modulating Metabolic and Transcriptional Profiles in the Liver of High-Fat Diet-Induced Obese Mice. Nutrients 2016, 8, 305. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu8050305
Jung UJ, Cho Y-Y, Choi M-S. Apigenin Ameliorates Dyslipidemia, Hepatic Steatosis and Insulin Resistance by Modulating Metabolic and Transcriptional Profiles in the Liver of High-Fat Diet-Induced Obese Mice. Nutrients. 2016; 8(5):305. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu8050305
Chicago/Turabian StyleJung, Un Ju, Yun-Young Cho, and Myung-Sook Choi. 2016. "Apigenin Ameliorates Dyslipidemia, Hepatic Steatosis and Insulin Resistance by Modulating Metabolic and Transcriptional Profiles in the Liver of High-Fat Diet-Induced Obese Mice" Nutrients 8, no. 5: 305. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu8050305
APA StyleJung, U. J., Cho, Y. -Y., & Choi, M. -S. (2016). Apigenin Ameliorates Dyslipidemia, Hepatic Steatosis and Insulin Resistance by Modulating Metabolic and Transcriptional Profiles in the Liver of High-Fat Diet-Induced Obese Mice. Nutrients, 8(5), 305. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu8050305