An Antiviral Peptide from Alopecosa nagpag Spider Targets NS2B–NS3 Protease of Flaviviruses
Abstract
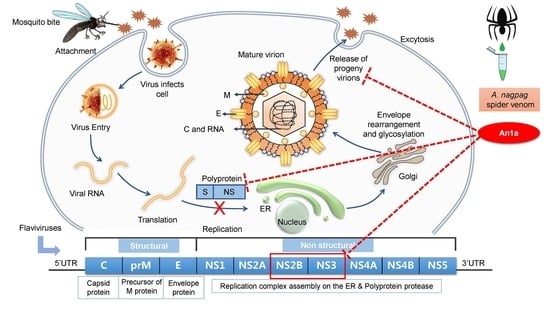
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Identification of An1a from the Venom of A. nagpag
2.2. An1a Inhibits DENV2 Replication
2.3. The Inhibitory Activity of An1a on the DENV2 NS2B–NS3 Protease
2.4. An1a Also Restricts ZIKV Replication by Inhibiting the NS2B–NS3 Protease
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Venom Collection
4.2. Toxin Purification and the Sequence Determination of An1a
4.3. Recombinant Expression of An1a
4.4. Cells and Viruses
4.5. In Vitro Virus Infection Assays and Antiviral Activity Measurement
4.6. Immunofluorescence Staining and Microscopy
4.7. Recombinant Protease Expression, Protease Inhibition and the Mechanism of Inhibition
4.8. Assays of Hemolysis and Cytotoxicity
4.9. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Barrows, N.J.; Campos, R.K.; Liao, K.C.; Prasanth, K.R.; Soto-Acosta, R.; Yeh, S.C.; Schott-Lerner, G.; Pompon, J.; Sessions, O.M.; Bradrick, S.S.; et al. Biochemistry and molecular biology of flaviviruses. Chem. Rev. 2018, 118, 4448–4482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slon Campos, J.L.; Mongkolsapaya, J.; Screaton, G.R. The immune response against flaviviruses. Nat. Immunol. 2018, 19, 1189–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baud, D.; Gubler, D.J.; Schaub, B.; Lanteri, M.C.; Musso, D. An update on zika virus infection. Lancet 2017, 390, 2099–2109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, P.D.; Malhotra, B.; Sapkal, G.; Nyayanit, D.A.; Deshpande, G.; Gupta, N.; Padinjaremattathil, U.T.; Sharma, H.; Sahay, R.R.; Sharma, P.; et al. Zika virus outbreak in rajasthan, india in 2018 was caused by a virus endemic to asia. Infect. Genet. Evol. J. Mol. Epidemiol. Evol. Genet. Infect. Dis. 2019, 69, 199–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Valderramos, S.G.; Wu, A.; Ouyang, S.; Li, C.; Brasil, P.; Bonaldo, M.; Coates, T.; Nielsen-Saines, K.; Jiang, T.; et al. From mosquitos to humans: Genetic evolution of zika virus. Cell Host Microbe 2016, 19, 561–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Liu, J.; Du, S.; Shan, C.; Nie, K.; Zhang, R.; Li, X.F.; Zhang, R.; Wang, T.; Qin, C.F.; et al. Evolutionary enhancement of zika virus infectivity in aedes aegypti mosquitoes. Nature 2017, 545, 482–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beaver, J.T.; Lelutiu, N.; Habib, R.; Skountzou, I. Evolution of two major zika virus lineages: Implications for pathology, immune response, and vaccine development. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 1640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, P.; Xue, Y.; Gao, W.; Li, J.; Zu, X.; Fu, D.; Feng, S.; Bai, X.; Zuo, Y.; Li, P. Actinobacteria-derived peptide antibiotics since 2000. Peptides 2018, 103, 48–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruzzoni-Giovanelli, H.; Alezra, V.; Wolff, N.; Dong, C.Z.; Tuffery, P.; Rebollo, A. Interfering peptides targeting protein-protein interactions: The next generation of drugs? Drug Discov. Today 2018, 23, 272–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boto, A.; Perez de la Lastra, J.M.; Gonzalez, C.C. The road from host-defense peptides to a new generation of antimicrobial drugs. Molecules 2018, 23, 311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, W.; Li, T.; Song, Y.; Zhang, R.; Zeng, Z.; Han, S.; Zhang, X.; Wu, Y.; Li, W.; Cao, Z. Inhibitory activity and mechanism of two scorpion venom peptides against herpes simplex virus type 1. Antivir. Res. 2014, 102, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rothan, H.A.; Bahrani, H.; Rahman, N.A.; Yusof, R. Identification of natural antimicrobial agents to treat dengue infection: In vitro analysis of latarcin peptide activity against dengue virus. BMC Microbiol. 2014, 14, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rothan, H.A.; Bahrani, H.; Shankar, E.M.; Rahman, N.A.; Yusof, R. Inhibitory effects of a peptide-fusion protein (latarcin-pap1-thanatin) against chikungunya virus. Antivir. Res. 2014, 108, 173–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Hong, W.; Xie, Y.; Liu, Y.; Li, W.; Wu, Y.; Cao, Z. A scorpion defensin bmkdfsin4 inhibits hepatitis b virus replication in vitro. Toxins 2016, 8, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shartouny, J.R.; Jacob, J. Mining the tree of life: Host defense peptides as antiviral therapeutics. In Seminars in Cell & Developmental Biology; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- da Silva-Júnior, E.F.; de Araújo-Júnior, J.X. Peptide derivatives as inhibitors of ns2b-ns3 protease from dengue, west nile, and zika flaviviruses. Bioorganic Med. Chem. 2019, 27, 3963–3978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phoo, W.W.; Zhang, Z.; Wirawan, M.; Chew, E.J.C.; Chew, A.B.L.; Kouretova, J.; Steinmetzer, T.; Luo, D. Structures of zika virus ns2b-ns3 protease in complex with peptidomimetic inhibitors. Antivir. Res. 2018, 160, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Sakamuru, S.; Huang, R.; Brecher, M.; Koetzner, C.A.; Zhang, J.; Chen, H.; Qin, C.F.; Zhang, Q.Y.; Zhou, J.; et al. Erythrosin b is a potent and broad-spectrum orthosteric inhibitor of the flavivirus ns2b-ns3 protease. Antivir. Res. 2018, 150, 217–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coronado, M.A.; Eberle, R.J.; Bleffert, N.; Feuerstein, S.; Olivier, D.S.; de Moraes, F.R.; Willbold, D.; Arni, R.K. Zika virus ns2b/ns3 proteinase: A new target for an old drug—Suramin a lead compound for ns2b/ns3 proteinase inhibition. Antivir. Res. 2018, 160, 118–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, S.; Chan, J.F.; den-Haan, H.; Chik, K.K.; Zhang, A.J.; Chan, C.C.; Poon, V.K.; Yip, C.C.; Mak, W.W.; Zhu, Z.; et al. Structure-based discovery of clinically approved drugs as zika virus ns2b-ns3 protease inhibitors that potently inhibit zika virus infection in vitro and in vivo. Antivir. Res. 2017, 145, 33–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, J.F.; Chik, K.K.; Yuan, S.; Yip, C.C.; Zhu, Z.; Tee, K.M.; Tsang, J.O.; Chan, C.C.; Poon, V.K.; Lu, G.; et al. Novel antiviral activity and mechanism of bromocriptine as a zika virus ns2b-ns3 protease inhibitor. Antivir. Res. 2017, 141, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saez, N.J.; Senff, S.; Jensen, J.E.; Er, S.Y.; Herzig, V.; Rash, L.D.; King, G.F. Spider-venom peptides as therapeutics. Toxins 2010, 2, 2851–2871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Primon-Barros, M.; Jose Macedo, A. Animal venom peptides: Potential for new antimicrobial agents. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2017, 17, 1119–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Song, D.X.; Kim, J.P. Three new species of the genus alopecosa simon from china (araneae: Lycosidae). Acta Zootaxonomica Sin. 2001, 26, 18–23. [Google Scholar]
- King, G.F.; Gentz, M.C.; Escoubas, P.; Nicholson, G.M. A rational nomenclature for naming peptide toxins from spiders and other venomous animals. Toxicon 2008, 52, 264–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rothan, H.A.; Mohamed, Z.; Suhaeb, A.M.; Rahman, N.A.; Yusof, R. Antiviral cationic peptides as a strategy for innovation in global health therapeutics for dengue virus: High yield production of the biologically active recombinant plectasin peptide. Omics J. Integr. Biol. 2013, 17, 560–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rothan, H.A.; Bahrani, H.; Mohamed, Z.; Abd Rahman, N.; Yusof, R. Fusion of protegrin-1 and plectasin to map30 shows significant inhibition activity against dengue virus replication. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e94561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brecher, M.; Li, Z.; Liu, B.; Zhang, J.; Koetzner, C.A.; Alifarag, A.; Jones, S.A.; Lin, Q.; Kramer, L.D.; Li, H. A conformational switch high-throughput screening assay and allosteric inhibition of the flavivirus ns2b-ns3 protease. PLoS Pathog. 2017, 13, e1006411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fjell, C.D.; Hiss, J.A.; Hancock, R.E.; Schneider, G. Designing antimicrobial peptides: Form follows function. Nature reviews. Drug Discov. 2011, 11, 37–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lei, J.; Hansen, G.; Nitsche, C.; Klein, C.D.; Zhang, L.; Hilgenfeld, R. Crystal structure of zika virus ns2b-ns3 protease in complex with a boronate inhibitor. Science 2016, 353, 503–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, L.; Bai, X.; Luan, N.; Yao, H.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, W.; Chen, Y.; Yan, X.; Rong, M.; Lai, R.; et al. A designed tryptophan- and lysine/arginine-rich antimicrobial peptide with therapeutic potential for clinical antibiotic-resistant candida albicans vaginitis. J. Med. Chem. 2016, 59, 1791–1799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mygind, P.H.; Fischer, R.L.; Schnorr, K.M.; Hansen, M.T.; Sonksen, C.P.; Ludvigsen, S.; Raventos, D.; Buskov, S.; Christensen, B.; De Maria, L.; et al. Plectasin is a peptide antibiotic with therapeutic potential from a saprophytic fungus. Nature 2005, 437, 975–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, P.S.; Link, N.; Jang, G.M.; Sharp, P.P.; Zhu, T.; Swaney, D.L.; Johnson, J.R.; Von Dollen, J.; Ramage, H.R.; Satkamp, L.; et al. Comparative flavivirus-host protein interaction mapping reveals mechanisms of dengue and zika virus pathogenesis. Cell 2018, 175, 1931–1945.e1918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez-Garcia, M.D.; Mazzon, M.; Jacobs, M.; Amara, A. Pathogenesis of flavivirus infections: Using and abusing the host cell. Cell Host Microbe 2009, 5, 318–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Li, Y.; Loh, Y.R.; Phoo, W.W.; Hung, A.W.; Kang, C.; Luo, D. Crystal structure of unlinked ns2b-ns3 protease from zika virus. Science 2016, 354, 1597–1600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, C.J.; Taggart, C.C. Biologic protease inhibitors as novel therapeutic agents. Biochimie 2010, 92, 1681–1688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabotic, J.; Kos, J. Microbial and fungal protease inhibitors—Current and potential applications. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2012, 93, 1351–1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, L.; Fang, M.; Chen, M.; Zhou, C.; Ombati, R.; Hakim, M.A.; Mo, G.; Lai, R.; Yan, X.; Wang, Y.; et al. An insecticidal toxin from nephila clavata spider venom. Amino Acids 2017, 49, 1237–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ji, M.; Zhu, T.; Xing, M.; Luan, N.; Mwangi, J.; Yan, X.; Mo, G.; Rong, M.; Li, B.; Lai, R.; et al. An Antiviral Peptide from Alopecosa nagpag Spider Targets NS2B–NS3 Protease of Flaviviruses. Toxins 2019, 11, 584. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins11100584
Ji M, Zhu T, Xing M, Luan N, Mwangi J, Yan X, Mo G, Rong M, Li B, Lai R, et al. An Antiviral Peptide from Alopecosa nagpag Spider Targets NS2B–NS3 Protease of Flaviviruses. Toxins. 2019; 11(10):584. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins11100584
Chicago/Turabian StyleJi, Mengyao, Tengyu Zhu, Meichen Xing, Ning Luan, James Mwangi, Xiuwen Yan, Guoxiang Mo, Mingqiang Rong, Bowen Li, Ren Lai, and et al. 2019. "An Antiviral Peptide from Alopecosa nagpag Spider Targets NS2B–NS3 Protease of Flaviviruses" Toxins 11, no. 10: 584. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins11100584
APA StyleJi, M., Zhu, T., Xing, M., Luan, N., Mwangi, J., Yan, X., Mo, G., Rong, M., Li, B., Lai, R., & Jin, L. (2019). An Antiviral Peptide from Alopecosa nagpag Spider Targets NS2B–NS3 Protease of Flaviviruses. Toxins, 11(10), 584. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins11100584