Diversity and Toxicity of the Genus Coolia Meunier in Brazil, and Detection of 44-methyl Gambierone in Coolia tropicalis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Phylogenetics
2.2. Morphology and Geographical Distribution
2.3. Toxicity
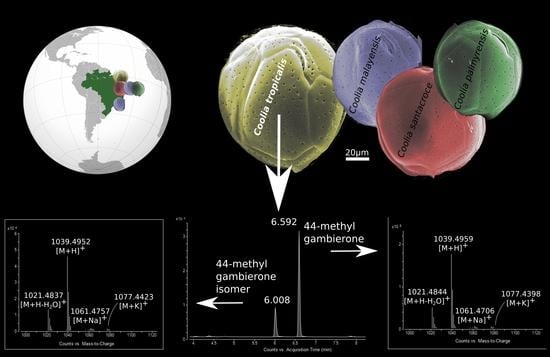
2.4. Toxin Analysis in Coolia spp. Using Low and High Resolution Mass Spectrometry, and Discovery of Gambierone Toxins in C. tropicalis
2.4.1. Screening of Coolia spp. Extracts Using High Resolution Mass Spectrometry (System A)
2.4.2. Comparative Fragmentation Between 44-Methyl Gambierone and the New 44-Methyl Gambierone Isomer
2.4.3. Quantification of Gambierone Toxins with LC-LRMS/MS (System B) in C. tropicalis
3. Discussion
3.1. Taxonomy and Phylogeny of Coolia Species
3.2. Species Distribution and Diversity in Brazil
3.3. Toxicity and Toxin Production
4. Conclusions
5. Materials and Methods
5.1. Sampling and Cultures
5.2. DNA Amplification, Sequencing and Molecular Phylogeny
5.3. Morphological Observations
5.4. Toxicity Experiments
5.5. Toxin Analysis
5.5.1. System A: HR-MS/MS
5.5.2. System B: LR-MS/MS
5.5.3. Quantification of Gambierone Toxins in C. tropicalis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hoppenrath, M.; Murray, S.A.; Chomérat, N.; Horiguchi, T. Marine Benthic Dinoflagellates—Unveiling Their Worldwide Biodiversity; Senckenberg-Reihe: Frankfurt, Germany, 2014; ISBN 978-3-510-61402-8. [Google Scholar]
- Parsons, M.L.; Aligizaki, K.; Bottein, M.Y.D.; Fraga, S.; Morton, S.L.; Penna, A.; Rhodes, L. Gambierdiscus and Ostreopsis: Reassessment of the state of knowledge of their taxonomy, geography, ecophysiology, and toxicology. Harmful Algae 2012, 14, 107–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yogi, K.; Oshiro, N.; Inafuku, Y.; Hirama, M.; Yasumoto, T. Detailed LC-MS/MS Analysis of Ciguatoxins Revealing Distinct Regional and Species Characteristics in Fish and Causative Alga from the Pacific. Anal. Chem. 2011, 83, 8886–8891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friedman, M.A.; Fernandez, M.; Backer, L.C.; Dickey, R.W.; Bernstein, J.; Schrank, K.; Kibler, S.; Stephan, W.; Gribble, M.O.; Bienfang, P.; et al. An updated review of ciguatera fish poisoning: Clinical, epidemiological, environmental, and public health management. Mar. Drugs 2017, 15, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boente-Juncal, A.; Álvarez, M.; Antelo, Á.; Rodríguez, I.; Calabro, K.; Vale, C.; Thomas, O.P.; Botana, L.M. Structure elucidation and biological evaluation of maitotoxin-3, a homologue of gambierone, from Gambierdiscus belizeanus. Toxins 2019, 11, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nagai, H.; Torigoe, K.; Satake, M.; Murata, M.; Yasumoto, T.; Hirota, H. Gambieric Acids: Unprecedented Potent Antifungal Substances Isolated from Cultures of a Marine Dinoflagellate Gambierdiscus toxicus. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1992, 114, 1102–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cagide, E.; Louzao, M.C.; Espiña, B.; Ares, I.R.; Vieytes, M.R.; Sasaki, M.; Fuwa, H.; Tsukano, C.; Konno, Y.; Yotsu-Yamashita, M.; et al. Comparative cytotoxicity of gambierol versus other marine neurotoxins. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2011, 24, 835–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, R.; Uchida, H.; Suzuki, T.; Matsushima, R.; Nagae, M.; Toyohara, Y.; Satake, M.; Oshima, Y.; Inoue, A.; Yasumoto, T. Gambieroxide, a novel epoxy polyether compound from the dinoflagellate Gambierdiscus toxicus GTP2 strain. Tetrahedron 2013, 69, 10299–10303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Longo, S.; Sibat, M.; Viallon, J.; Darius, H.T.; Hess, P.; Chinain, M. Intraspecific variability in the toxin production and toxin profiles of in vitro cultures of Gambierdiscus polynesiensis (Dinophyceae) from French polynesia. Toxins 2019, 11, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hoppenrath, M.; Chomérat, N.; Horiguchi, T.; Schweikert, M.; Nagahama, Y.; Murray, S. Taxonomy and phylogeny of the benthic Prorocentrum species (Dinophyceae)—A proposal and review. Harmful Algae 2013, 27, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karafas, S.; Teng, S.T.; Leaw, C.P.; Alves-de-Souza, C. An evaluation of the genus Amphidinium (Dinophyceae) combining evidence from morphology, phylogenetics, and toxin production, with the introduction of six novel species. Harmful Algae 2017, 68, 128–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreira-González, A.R.; Fernandes, L.F.; Uchida, H.; Uesugi, A.; Suzuki, T.; Chomérat, N.; Bilien, G.; Pereira, T.A.; Mafra, L.L. Morphology, growth, toxin production, and toxicity of cultured marine benthic dinoflagellates from Brazil and Cuba. J. Appl. Phycol. 2019, 31, 3699–3719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lassus, P.; Chomérat, N.; Hess, P.; Nézan, E. Toxic and Harmful Microalgae of the World Ocean; Intergovernmental Oceanographic Commission of UNESCO: Copenhagen, Denmark, 2016; ISBN 978-87-990827-6-6. [Google Scholar]
- Leaw, C.P.; Tan, T.H.; Lim, H.C.; Teng, S.T.; Yong, H.L.; Smith, K.F.; Rhodes, L.; Wolf, M.; Holland, W.C.; Vandersea, M.W.; et al. New scenario for speciation in the benthic dinoflagellate genus Coolia (Dinophyceae). Harmful Algae 2016, 55, 137–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- David, H.; Laza-Martínez, A.; Rodríguez, F.; Fraga, S.; Orive, E. Coolia guanchica sp. nov. (Dinophyceae) a new epibenthic dinoflagellate from the Canary Islands (NE Atlantic Ocean). Eur. J. Phycol. 2020, 55, 76–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faust, M.A. Observation of sand-dwelling toxic dinoflagellates (Dinophyceae) from widely differing sites, including two new species. J. Phycol. 1995, 31, 996–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammad-Noor, N.; Moestrup, Ø.; Lundholm, N.; Fraga, S.; Adam, A.; Holmes, M.J.; Saleh, E. Autecology and phylogeny of Coolia tropicalis and Coolia malayensis (Dinophyceae), with emphasis on taxonomy of C. tropicalis based on light microscopy, scanning electron microscopy and LSU rDNA1. J. Phycol. 2013, 49, 536–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leaw, C.P.; Lim, P.T.; Cheng, K.W.; Ng, B.K.; Usup, G. Morphology and molecular characterization of a new species of thecate benthic dinoflagellate, Coolia malayensis sp. nov. (Dinophyceae). J. Phycol. 2010, 46, 162–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karafas, S.; York, R.; Tomas, C. Morphological and genetic analysis of the Coolia monotis species complex with the introduction of two new species, Coolia santacroce sp. nov. and Coolia palmyrensis sp. nov. (Dinophyceae). Harmful Algae 2015, 46, 18–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karafas, S.J.; Tomas, C.R. Further observations on the genetics and morphometrics of Coolia santacroce (Dinophyceae). Algae 2015, 30, 275–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Durán-Riveroll, L.M.; Cembella, A.D.; Okolodkov, Y.B. A review on the biodiversity and biogeography of toxigenic benthic marine dinoflagellates of the coasts of Latin America. Front. Mar. Sci. 2019, 6, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsson, M.E.; Smith, K.F.; Doblin, M.A. First description of the environmental niche of the epibenthic dinoflagellate species Coolia palmyrensis, C. malayensis, and C. tropicalis (Dinophyceae) from Eastern Australia. J. Phycol. 2019, 55, 565–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fraga, S.; Penna, A.; Bianconi, I.; Paz, B.; Zapata, M. Coolia canariensis sp. nov. (Dinophyceae), a new nontoxic epiphytic benthic dinoflagellate from the Canary Islands. J. Phycol. 2008, 44, 1060–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- David, H.; Laza-Martínez, A.; Miguel, I.; Orive, E. Broad distribution of Coolia monotis and restricted distribution of Coolia cf. canariensis (Dinophyceae) on the Atlantic coast of the Iberian Peninsula. Phycologia 2014, 53, 342–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ten-Hage, L.; Turquet, J.; Quod, J.P.; Coute, A. Coolia areolata sp. nov. (Dinophyceae), a new sand-dwelling dinoflagellate from the southwestern Indian Ocean. Phycologia 2009, 39, 377–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez, F.; Qiu, D.; Otero-Morales, E.; Lopes, R.M.; Lin, S. Circumtropical distribution of the epiphytic dinoflagellate Coolia malayensis (Dinophyceae): Morphology and molecular phylogeny from Puerto Rico and Brazil. Phycol. Res. 2016, 64, 194–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Queiro sMendes, M.C.; De Castro Nunes, J.M.; Fraga, S.; Rodríguez, F.; Franco, J.M.; Riobó, P.; Branco, S.; Menezes, M. Morphology, molecular phylogeny and toxinology of Coolia and Prorocentrum strains isolated from the tropical South Western Atlantic Ocean. Bot. Mar. 2019, 62, 125–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nascimento, S.M.; da Silva, R.A.F.; Oliveira, F.; Fraga, S.; Salgueiro, F. Morphology and molecular phylogeny of Coolia tropicalis, Coolia malayensis and a new lineage of the Coolia canariensis species complex (Dinophyceae) isolated from Brazil. Eur. J. Phycol. 2019, 54, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakajima, I.; Oshima, Y.; Yasumoto, T. Toxicity of Benthic Dinoflagellates in Okinawa. Nippon Suisan Gakkaishi 1981, 47, 1029–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Holmes, M.J.; Lewis, R.J.; Jones, A.; Hoy, A.W.W. Cooliatoxin, the first toxin from Coolia monotis (dinophyceae). Nat. Toxins 1995, 3, 355–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhodes, L.; Adamson, J.; Suzuki, T.; Briggs, L.; Garthwaite, I. Toxic marine epiphytic dinoflagellates, Ostreopsis siamensis and Coolia monotis (Dinophyceae), in New Zealand. N. Z. J. Mar. Freshw. Res. 2000, 34, 371–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wakeman, K.C.; Yamaguchi, A.; Roy, M.C.; Jenke-Kodama, H. Morphology, phylogeny and novel chemical compounds from Coolia malayensis (Dinophyceae) from Okinawa, Japan. Harmful Algae 2015, 44, 8–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penna, A.; Vila, M.; Fraga, S.; Giacobbe, M.G.; Francesco, A.; Riobó, P.; Vernesi, C. Characterization of Ostreopsis and Coolia (Dinophyceae) isolates in the western Mediterranean Sea based on morphology, toxicity and internal transcribed spacer 5.8s rDNA sequences. J. Phycol. 2005, 41, 212–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laza-Martinez, A.; Orive, E.; Miguel, I. Morphological and genetic characterization of benthic dinoflagellates of the genera Coolia, Ostreopsis and Prorocentrum from the south-eastern Bay of Biscay. Eur. J. Phycol. 2011, 46, 45–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, J.S.; Selwood, A.I.; Harwood, D.T.; van Ginkel, R.; Puddick, J.; Rhodes, L.L.; Rise, F.; Wilkins, A.L. 44-Methylgambierone, a new gambierone analogue isolated from Gambierdiscus australes. Tetrahedron Lett. 2019, 60, 621–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estevez, P.; Sibat, M.; Leao, J.M.; Tudó, A.; Rambla-Alegre, M.; Aligizak, K.; Gago-Martinez, A.; Diogène, J.; Hess, P. Use of Mass Spectrometry to determine the Diversity of Toxins Produced by Gambierdiscus and Fukuyoa Species from Balearic Islands and Crete (Mediterranean Sea) and the Canary Islands (Northeast Atlantic). Toxins 2020, 12, 305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ho, T.V.; Nguyen, L.N. Morphology and Distribution of the Three Epiphytic Dinoflagellate species Coolia monotis, C. tropicalis, and C. canariensis (Ostreopsidaceae, Gonyaulacales, Dinophyceae) from Vietnamese Coastal Waters. Ocean Sci. J. 2014, 49, 211–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, H.J.; Yih, W.; Kang, N.S.; Lee, S.Y.; Yoon, E.Y.; Yoo, Y. Du; Kim, H.S.; Kim, J.H. First report of the epiphytic benthic dinoflagellates Coolia canariensis and Coolia malayensis in the waters off Jeju Island, Korea: Morphology and rDNA sequences. J. Eukaryot. Microbiol. 2012, 59, 114–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhodes, L.L.; Smith, K.F.; Munday, R.; Selwood, A.I.; McNabb, P.S.; Holland, P.T.; Bottein, M.Y. Toxic dinoflagellates (Dinophyceae) from Rarotonga, Cook Islands. Toxicon 2010, 56, 751–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Litaker, R.W.; Vandersea, M.W.; Faust, M. a.; Kibler, S.R.; Chinain, M.; Holmes, M.J.; Holland, W.C.; Tester, P. a. Taxonomy of Gambierdiscus including four new species, Gambierdiscus caribaeus, Gambierdiscus carolinianus, Gambierdiscus carpenteri and Gambierdiscus ruetzleri (Gonyaulacales, Dinophyceae). Phycologia 2009, 48, 344–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tester, P.A.; Kibler, S.R.; Holland, W.C.; Usup, G.; Vandersea, M.W.; Leaw, C.P.; Teen, L.P.; Larsen, J.; Mohammad-Noor, N.; Faust, M.A.; et al. Sampling harmful benthic dinoflagellates: Comparison of artificial and natural substrate methods. Harmful Algae 2014, 39, 8–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chomérat, N.; Bilien, G.; Derrien, A.; Henry, K.; Ung, A.; Viallon, J.; Darius, H.T.; Mahana iti Gatti, C.; Roué, M.; Hervé, F.; et al. Ostreopsis lenticularis Y. Fukuyo (Dinophyceae, Gonyaulacales) from French Polynesia (South Pacific Ocean): A revisit of its morphology, molecular phylogeny and toxicity. Harmful Algae 2019, 84, 95–111. [Google Scholar]
- Katoh, K.; Standley, D.M. MAFFT multiple sequence alignment software version 7: Improvements in performance and usability. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2013, 30, 772–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Castresana, J. Selection of conserved blocks from multiple alignments for their use in phylogenetic analysis. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2000, 17, 540–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Darriba, D.; Taboada, G.L.; Doallo, R.; Posada, D. JModelTest 2: More models, new heuristics and parallel computing. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Adam, R.D.; Ortega, Y.R.; Gilman, R.H.; Sterling, C.R. Intervening transcribed spacer region 1 variability in Cyclospora cayetanensis. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2000, 38, 2339–2343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scholin, C.A.; Herzog, M.; Sogin, M.; Anderson, D.M. Identification of group- and strain-specific genetic markers for globally distributed Alexandrium (Dinophyceae). II. Sequence analysis of a fragment of the LSU rRNA gene1. J. Phycol. 1994, 30, 999–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunn, G.B.; Theisen, B.F.; Christensen, B.; Arctander, P. Simplicity-correlated size growth of the nuclear 28S ribosomal RNA D3 expansion segment in the crustacean order Isopoda. J. Mol. Evol. 1996, 42, 211–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hillebrand, H.; Dürselen, C.D.; Kirschtel, D.; Pollingher, U.; Zohary, T. Biovolume calculation for pelagic and benthic microalgae. J. Phycol. 1999, 35, 403–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menden-Deuer, S.; Lessard, E.J. Carbon to volume relationships for dinoflagellates, diatoms, and other protist plankton. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2000, 45, 569–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]











| Measurement | C. malayensis | C. santacroce | C. palmyrensis | C. tropicalis | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cell size | DV | 26.7 (23.3–29.8, 26) | 27.6 (24.0–30.7, 30) | 24.1 (19.1–28.4, 27) | 34.1 (24.3–39.8, 29) |
| W | 24.3 (19.6–29.3, 13) | 26.5 (23.2–29.7, 26) | 22.2 (17.4–27.3, 29) | 32.9 (23.6–39.7, 29) | |
| AP | 22.0 (16.6–25.3, 15) | 23.8 (18.0–30.0, 16) | 21.0 (16.9–26.1, 8) | 28.0 (25.6–31.3, 9) | |
| DV/W | 1.12 (0.98–1.37, 11) | 1.05 (0.98–1.21, 20) | 1.11 (0.97–1.29, 22) | 1.08 (0.97–1.24, 20) | |
| APC length | 6.3 (5.3–7.4, 13) | 5.9 (4.9–7.4, 8) | 6.3 (5.5–7.5, 8) | 7.2 (6.3–8.6, 9) | |
| Pore size | 0.33 (0.26–0.42, 36) | 0.31 (0.25–0.44, 40) | 0.27 (0.23–0.42, 31) | 0.35 (0.27–0.42, 31) | |
| Pore density | Plate 1’ | 0.30 (0.20–0.44, 16) | 0.29 (0.20–0.36, 12) | 0.24 (0.20–0.28, 8) | 0.23 (0.16–0.28, 11) |
| Plate 6’’ | 0.24 (0.16–0.32, 14) | 0.25 (0.20–0.32, 10) | 0.18 (0.16–0.20, 7) | 0.22 (0.16–0.28, 8) | |
| Plate 3’’’ | 0.18 (0.12–0.24, 14) | 0.22 (0.16–0.28, 8) | 0.16 (0.11–0.20, 11) | 0.22 (0.16–0.28, 5) | |
| Pore number | Plate 7’’ | 6.8 (4–9, 19) | 6.9 (4–10, 13) | 4.0 (3–5, 6) | 13.3 (7–15, 10) |
| Plate 2’’’’ | 5.1 (3–8, 13) | 6.1 (4–9, 7) | 3.5 (2–7, 8) | 9.7 (8–12, 7) | |
| Origin of strains (Brazilian states) | São Paulo, Rio de Janeiro, Bahia, Alagoas and Rio Grande do Norte | Abrolhos Archipelago (Bahia) | Abrolhos Archipelago (Bahia) and Pernambuco | Rio Grande do Norte | |
| Ion Species (Mono-Isotopic m/z) | 44-Methyl Gambierone | 44-Methyl Gambierone Isomer |
|---|---|---|
| RT = 6.6 min | RT = 6.0 min | |
| [M+H]+ | 1039.4959 (−2.1) | 1039.4952 (+2.0) |
| [M+H-H2O]+ | 1021.4844 (+0.9) | 1021.4837 (+3.3) |
| [M+Na]+ | 1061.4706 (−2.1) | 1061.4757 (+0.4) |
| [M+K]+ | 1077.4398 (−8.5) | 1077.4423 (−6.2) |
| [M-H]− | 1037.4797 (+1.1) | 1037.4766 (−1.9) |
| [M-H-H2O]− | 1019.4651 (−2.8) | 1019.4587 (−9.1) |
| Parent or Fragment Ion | Formula | 44-methyl Gambierone | 44-methyl Gambierone Isomer | Ref. | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (m/z) | Δppm | (m/z) | Δppm | |||
| Parent ion [M+H]+ | C52H79O19S+ | 1039.4909 | −2.1 | 1039.4952 | +2.0 | |
| ESI+ Fragment ions | C52H77O18S+ | 1021.4834 | +0.9 | 1021.4859 | +3.3 | [5] |
| C52H75O17S+ | 1003.4773 | +5.3 | 1003.4750 | +3.0 | ||
| C52H79O16+ | 959.5364 | +0.1 | 959.5330 | −3.4 | ||
| C52H77O15+ | 941.5254 | −0.3 | 941.5216 | −4.4 | ||
| C52H75O14+ | 923.5175 | +2.5 | 923.5133 | −2.0 | ||
| C52H73O13+ | 905.5004 | −4.6 | 905.5012 | −3.7 | ||
| C52H71O12+ | 887.4902 | −4.3 | 887.4945 | +0.6 | ||
| C43H65O18S+ | 901.3847 | −4.3 | 901.3880 | −0.7 | [36] | |
| C43H63O14+ | 803.4191 | −2.7 | 803.4237 | +3.1 | ||
| C15H21O2+ | 233.1551 | +6.4 | 233.1544 | +3.4 | ||
| C15H19O+ | 215.1438 | +3.5 | 215.1443 | +5.9 | ||
| C8H11O+ | 123.0802 | −2.0 | 123.0810 | −5.2 | ||
| C7H9O+ | 109.0652 | +3.8 | 109.0645 | −2.7 | ||
| C7H11+ | 95.0855 | −0.3 | 95.0854 | −1.3 | ||
| Parent ion [M-H]− | C52H77O19S− | 1037.4797 | +1.1 | 1037.4766 | −1.9 | |
| ESI− Fragment ions | C43H63O18S− | 899.3743 | +0.3 | 899.3732 | −1.0 | [35] |
| [HOSO3]− | 96.9601 | 0 | 96.9599 | −2.1 | ||
| Specie | Strain | Brazilian state | Latitude (S) | Longitude (W) | Date |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Coolia malayensis | LM-034 | São Paulo | 23°50′36.90″ | 45°24′15.66″ | 12/11/2016 |
| C. malayensis | LM-036 | Rio de Janeiro | 23°03′19.20″ | 44°19′45.42″ | 10/11/2016 |
| C. malayensis | LM-058 | Rio de Janeiro | 23°01′16.20″ | 44°19′47.52″ | 23/01/2017 |
| C. malayensis | LM-066 | Bahia | 12°34′54.30″ | 38°00′03.90″ | 11/03/2017 |
| C. malayensis | LM-085 | Bahia | 12°57′20.46″ | 38°21′36.06″ | 10/03/2017 |
| C. malayensis | LM-132 | Alagoas | 09°40′07.52″ | 35°42′45.37″ | 22/02/2018 |
| C. malayensis | LM-140 | Rio Grande do Norte | 05°33′53.30″ | 35°04′20.90″ | 10/03/2018 |
| Coolia palmyrensis | LM-075 | Pernambuco | 08°35′31.02″ | 34°54′43.02″ | 28/03/2017 |
| C. palmyrensis | LM-076 | Pernambuco | 08°35′31.02″ | 34°54′43.02″ | 28/03/2017 |
| C. palmyrensis | LM-112 | Bahia (Abrolhos) | 18°02′00.00″ | 38°41′53.88″ | 15/10/2017 |
| Coolia santacroce | LM-113 | Bahia (Abrolhos) | 18°02′00.00″ | 38°41′53.88″ | 15/10/2017 |
| C. santacroce | LM-122 | Bahia (Abrolhos) | 18°02′00.00″ | 38°41′53.88″ | 15/10/2017 |
| C. santacroce | LM-123 | Bahia (Abrolhos) | 18°02′53.88″ | 38°41′53.88″ | 15/10/2017 |
| Coolia tropicalis | LM-141 | Rio Grande do Norte | 05°33′53.30″ | 35°04′20.90″ | 11/03/2018 |
| Primer | Sequence | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| ITSfw | 5′-GTAGGTGAACCTGCGGAAGG-3ʹ | [46] |
| Coo5.8f | 5′-ATGCAGAATCCCGTGAATCA-3ʹ | Present study |
| D1R | 5′-ACCCGCTGAATTTAAGCATA-3ʹ | [47] |
| 364R | 5’-CTCTCTTTTCAAAGTCCTTTTC-3’ | Present study |
| D3B | 5′-TCGGAGGGAACCAGCTACTA-3ʹ | [48] |
| Compound | MRM transitions (m/z) | CE (eV) | CXP (eV) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MTX1 | 1689.8 >1689.6 | [M-2H]2−/[M-2H]2− | −40 | −15 |
| 1689.8 > 96.9 | [M-2H]2−/[HOSO3]2− | −125 | −21 | |
| 1126.2 > 1126.2 | [M-3H]3−/[M-3H]3− | −40 | −15 | |
| 1126.2 > 96.9 | [M-3H]3−/[HOSO3]3− | −125 | −21 | |
| MTX2 | 1637.5 > 1637.5 | [M-2H]2−/[M-2H]2− | −40 | −15 |
| 1637.5 > 96.9 | [M-2H]2−/[HOSO3]2− | −125 | −21 | |
| 1091.5 > 1091.5 | [M-3H]3−/[M-3H]3− | −40 | −15 | |
| 1091.5 > 96.9 | [M-3H]3−/[HOSO3]3− | −125 | −21 | |
| MTX4 | 1646.2 > 1646.2 | [M-2H]2−/[M-2H]2− | −40 | −15 |
| 1646.2 > 96.9 | [M-2H]2−/[HOSO3]2− | −125 | −21 | |
| desulfo-MTX1 | 1649.8 > 1649.8 | [M-2H]2−/[M-2H]2− | −40 | −15 |
| 1649.8 > 96.9 | [M-2H]2−/[HOSO3]2− | −125 | −21 | |
| didehydro-demethyl- desulfo-MTX1 | 1641.8 > 1641.8 | [M-2H]2−/[M-2H]2− | −40 | −15 |
| 1641.8 > 96.9 | [M-2H]2−/[HOSO3]2− | −125 | −21 | |
| Gambierone | 1023.5 > 1023.5 | [M-H]−/[M-H]− | −40 | −15 |
| 1023.5 > 96.9 | [M-H]−/[HOSO3]− | −125 | −21 | |
| 44-methylgambierone | 1037.6 > 1037.6 | [M-H]−/[M-H]− | −40 | −15 |
| 1037.6 > 96.9 | [M-H]−/[HOSO3]− | −125 | −21 | |
| Gambieroxide | 1193.6 > 1193.6 | [M-H]−/[M-H]− | −20 | −15 |
| 1193.6 > 96.9 | [M-H]−/[HOSO3] − | −125 | −21 | |
| Gambieric acid A | 1055.1 > 1055.1 | [M-H]−/[M-H]− | −20 | −15 |
| 1055.1 > 1037.1 | [M-H]−/[M-H-H2O] − | −40 | −15 | |
| Gambieric acid B | 1069.1 > 1069.1 | [M-H]−/[M-H]− | −20 | −15 |
| 1069.1 > 1051.1 | [M-H]−/[M-H-H2O] − | −40 | −15 | |
| Gambieric acid C | 1183.7 > 1183.7 | [M-H]−/[M-H]− | −20 | −15 |
| 1183.7 > 1165.7 | [M-H]−/[M-H-H2O] − | −40 | −15 | |
| Gambieric acid D | 1197.7 > 1197.7 | [M-H]−/[M-H]− | −20 | −15 |
| 1197.7 > 1179.7 | [M-H]−/[M-H-H2O] − | −40 | −15 | |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tibiriçá, C.E.J.d.A.; Sibat, M.; Fernandes, L.F.; Bilien, G.; Chomérat, N.; Hess, P.; Mafra Jr, L.L. Diversity and Toxicity of the Genus Coolia Meunier in Brazil, and Detection of 44-methyl Gambierone in Coolia tropicalis. Toxins 2020, 12, 327. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins12050327
Tibiriçá CEJdA, Sibat M, Fernandes LF, Bilien G, Chomérat N, Hess P, Mafra Jr LL. Diversity and Toxicity of the Genus Coolia Meunier in Brazil, and Detection of 44-methyl Gambierone in Coolia tropicalis. Toxins. 2020; 12(5):327. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins12050327
Chicago/Turabian StyleTibiriçá, Carlos Eduardo Junqueira de Azevedo, Manoella Sibat, Luciano Felício Fernandes, Gwenaël Bilien, Nicolas Chomérat, Philipp Hess, and Luiz L. Mafra Jr. 2020. "Diversity and Toxicity of the Genus Coolia Meunier in Brazil, and Detection of 44-methyl Gambierone in Coolia tropicalis" Toxins 12, no. 5: 327. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins12050327
APA StyleTibiriçá, C. E. J. d. A., Sibat, M., Fernandes, L. F., Bilien, G., Chomérat, N., Hess, P., & Mafra Jr, L. L. (2020). Diversity and Toxicity of the Genus Coolia Meunier in Brazil, and Detection of 44-methyl Gambierone in Coolia tropicalis. Toxins, 12(5), 327. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins12050327