The Dinoflagellate Toxin 20-Methyl Spirolide-G Potently Blocks Skeletal Muscle and Neuronal Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptors
Abstract
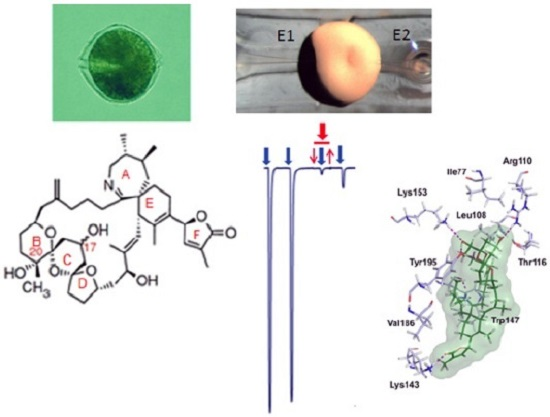
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Block of Nerve-Evoked Muscle Contraction
2.2. Local Neuromuscular Block in Vivo
2.3. Block of Torpedo Muscle-Type nAChR Incorporated to Xenopus Oocytes
2.4. Block of Neuronal nAChRs Expressed in Oocytes
2.5. Binding-Competition Assays between 20-meSPX-G and Radioligands
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
5. Materials and Methods
5.1. Reagents and Materials
5.2. Animals and Biological Materials
5.3. Muscle Tension Measurements
5.4. Action on the Mouse Neuromuscular System in Vivo
5.5. Expression of Human α7 and α4β2 nAChRs in Xenopus Oocytes
5.6. Microtransplantation of Torpedo nAChR to Xenopus Oocytes
5.7. Voltage-Clamp Recording on Oocytes
5.8. Expression of nAChRs in Human Embryonic Kidney Cells and Competition Binding Assays
Competition Binding Assays
5.9. Molecular Modeling
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hu, T.M.; Curtis, J.M.; Oshima, Y.; Quilliam, M.A.; Walter, J.A.; Watsonwright, W.M.; Wright, J.L.C. Spirolide-B and spirolide-D, 2 novel macrocycles isolated from the digestive glands of shellfish. J. Chem. Soc. Chem. Commun. 1995, 20, 2159–2161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, T.M.; Curtis, J.M.; Walter, J.A.; Wright, J.L.C. Characterization of biologically inactive spirolides E and F: Identification of the spirolide pharmacophore. Tetrahedron Lett. 1996, 37, 7671–7674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stivala, C.E.; Benoit, E.; Aráoz, R.; Servent, D.; Novikov, A.; Molgó, J.; Zakarian, A. Synthesis and biology of cyclic imine toxins, an emerging class of potent, globally distributed marine toxins. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2015, 32, 411–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molgó, J.; Girard, E.; Benoit, E. Cyclic imines: An insight into this emerging group of bioactive marine toxins. In Phycotoxins: Chemistry and biochemistry; Botana, L., Ed.; Blackwell Publishing: Iowa, IA, USA, 2007; pp. 319–335. [Google Scholar]
- Otero, A.; Chapela, M.J.; Atanassova, M.; Vieites, J.M.; Cabado, A.G. Cyclic imines: Chemistry and mechanism of action: A review. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2011, 24, 1817–1829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cembella, A.D.; Lewis, N.I.; Quilliam, M.A. Spirolide composition of micro-extracted pooled cells isolated from natural plankton assemblages and from cultures of the dinoflagellate Alexandrium ostenfeldii. Nat. Toxins 1999, 7, 197–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cembella, A.D.; Lewis, N.I.; Quilliam, M.A. The marine dinoflagellate Alexandrium ostenfeldii (dinophyceae) as the causative organism of spirolide shellfish toxins. Phycologia 2000, 39, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Touzet, N.; Franco, J.M.; Raine, R. Morphogenetic diversity and biotoxin composition of Alexandrium (dinophyceae) in Irish coastal waters. Harmful Algae 2008, 7, 782–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, D.M.; Cembella, A.D.; Hallegraeff, G.M. Progress in understanding harmful algal blooms: Paradigm shifts and new technologies for research, monitoring, and management. Annu. Rev. Mar. Sci. 2012, 4, 143–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Salgado, P.; Riobo, P.; Rodriguez, F.; Franco, J.M.; Bravo, I. Differences in the toxin profiles of Alexandrium ostenfeldii (dinophyceae) strains isolated from different geographic origins: Evidence of paralytic toxin, spirolide, and gymnodimine. Toxicon 2015, 103, 85–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aasen, J.; MacKinnon, S.L.; LeBlanc, P.; Walter, J.A.; Hovgaard, P.; Aune, T.; Quilliam, M.A. Detection and identification of spirolides in norwegian shellfish and plankton. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2005, 18, 509–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aasen, J.A.B.; Hardstaff, W.; Aune, T.; Quilliam, M.A. Discovery of fatty acid ester metabolites of spirolide toxins in mussels from Norway using liquid chromatography/tandem mass spectrometry. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2006, 20, 1531–1537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rundberget, T.; Aasen, J.A.; Selwood, A.I.; Miles, C.O. Pinnatoxins and spirolides in norwegian blue mussels and seawater. Toxicon 2011, 58, 700–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MacKinnon, S.L.; Cembella, A.D.; Burton, I.W.; Lewis, N.; LeBlanc, P.; Walter, J.A. Biosynthesis of 13-desmethyl spirolide C by the dinoflagellate Alexandrium ostenfeldii. J. Org. Chem. 2006, 71, 8724–8731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, L.; Bresnan, E.; Graham, J.; Lacaze, J.P.; Turrell, E.; Collins, C. Distribution, diversity and toxin composition of the genus Alexandrium (dinophyceae) in scottish waters. Eur. J. Phycol. 2010, 45, 375–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kremp, A.; Lindholm, T.; Dressler, N.; Erler, K.; Gerdts, G.; Eirtovaara, S.; Leskinen, E. Bloom forming Alexandrium ostenfeldii (dinophyceae) in shallow waters of the aland archipelago, northern baltic sea. Harmful Algae 2009, 8, 318–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richard, D.; Arsenault, E.; Cembella, A.D.; Quilliam, M.A. Investigations into the toxicology and pharmacology of spirolides, a novel group of shellfish toxins. In Harmful Algal Blooms 2000; Hallegraeff, G.M., Blackburn, S.I., Bolch, C.J., Lewis, R.J., Eds.; Intergovernmental Oceanographic Commission of UNESCO: Paris, France, 2001; pp. 383–386. [Google Scholar]
- Munday, R.; Quilliam, M.A.; LeBlanc, P.; Lewis, N.; Gallant, P.; Sperker, S.A.; Ewart, H.S.; MacKinnon, S.L. Investigations into the toxicology of spirolides, a group of marine phycotoxins. Toxins 2012, 4, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Otero, P.; Alfonso, A.; Rodriguez, P.; Rubiolo, J.A.; Cifuentes, J.M.; Bermudez, R.; Vieytes, M.R.; Botana, L.M. Pharmacokinetic and toxicological data of spirolides after oral and intraperitoneal administration. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2012, 50, 232–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kharrat, R.; Servent, D.; Girard, E.; Ouanounou, G.; Amar, M.; Marrouchi, R.; Benoit, E.; Molgó, J. The marine phycotoxin gymnodimine targets muscular and neuronal nicotinic acetylcholine receptor subtypes with high affinity. J. Neurochem. 2008, 107, 952–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bourne, Y.; Radic, Z.; Aráoz, R.; Talley, T.T.; Benoit, E.; Servent, D.; Taylor, P.; Molgó, J.; Marchot, P. Structural determinants in phycotoxins and AChBP conferring high affinity binding and nicotinic AChR antagonism. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 6076–6081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hauser, T.A.; Hepler, C.D.; Kombo, D.C.; Grinevich, V.P.; Kiser, M.N.; Hooker, D.N.; Zhang, J.H.; Mountfort, D.; Selwood, A.; Akireddy, S.R.; et al. Comparison of acetylcholine receptor interactions of the marine toxins, 13-desmethylspirolide C and gymnodimine. Neuropharmacolology 2012, 62, 2239–2250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aráoz, R.; Ouanounou, G.; Iorga, B.I.; Goudet, A.; Alili, D.; Amar, M.; Benoit, E.; Molgó, J.; Servent, D. The neurotoxic effect of 13,19-didesmethyl and 13-desmethyl spirolide C phycotoxins is mainly mediated by nicotinic rather than muscarinic acetylcholine receptors. Toxicol. Sci. 2015, 147, 156–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aráoz, R.; Servent, D.; Molgó, J.; Iorga, B.I.; Fruchart-Gaillard, C.; Benoit, E.; Gu, Z.H.; Stivala, C.; Zakarian, A. Total synthesis of pinnatoxins A and G and revision of the mode of action of pinnatoxin A. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 10499–10511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bourne, Y.; Sulzenbacher, G.; Radic, Z.; Aráoz, R.; Reynaud, M.; Benoit, E.; Zakarian, A.; Servent, D.; Molgó, J.; Taylor, P.; et al. Marine macrocyclic imines, pinnatoxins A and G: Structural determinants and functional properties to distinguish neuronal α7 from muscle (α1)2βγδ nAChRs. Structure 2015, 23, 1106–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hellyer, S.D.; Indurthi, D.; Balle, T.; Runder-Varga, V.; Selwood, A.I.; Tyndall, J.D.; Chebib, M.; Rhodes, L.; Kerr, D.S. Pinnatoxins E, F and G target multiple nicotinic receptor subtypes. J. Neurochem. 2015, 135, 479–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marrouchi, R.; Rome, G.; Kharrat, R.; Molgó, J.; Benoit, E. Analysis of the action of gymnodimine-A and 13-desmethyl spirolide C on the mouse neuromuscular system in vivo. Toxicon 2013, 75, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen-Huu, T.; Dobbertin, A.; Barbier, J.; Minic, J.; Krejci, E.; Duvaldestin, P.; Molgó, J. Cholinesterases and the resistance of the mouse diaphragm to the effect of tubocurarine. Anesthesiology 2005, 103, 788–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hellyer, S.D.; Selwood, A.I.; Rhodes, L.; Kerr, D.S. Neuromuscular blocking activity of pinnatoxins E, F and G. Toxicon 2013, 76, 214–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mourier, G.; Servent, D.; Zinn-Justin, S.; Menez, A. Chemical engineering of a three-fingered toxin with anti-α7 neuronal acetylcholine receptor activity. Protein Eng. 2000, 13, 217–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albuquerque, E.X.; Pereira, E.F.; Alkondon, M.; Rogers, S.W. Mammalian nicotinic acetylcholine receptors: From structure to function. Physiol. Rev. 2009, 89, 73–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zoli, M.; Pistillo, F.; Gotti, C. Diversity of native nicotinic receptor subtypes in mammalian brain. Neuropharmacolology 2015, 96, 302–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daly, J.W. Nicotinic agonists, antagonists, and modulators from natural sources. Cell. Mol. Neurobiol. 2005, 25, 513–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerzanich, V.; Peng, X.; Wang, F.; Wells, G.; Anand, R.; Fletcher, S.; Lindstrom, J. Comparative pharmacology of epibatidine: A potent agonist for neuronal nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. Mol. Pharmacol. 1995, 48, 774–782. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Alkondon, M.; Albuquerque, E.X. Diversity of nicotinic acetylcholine receptors in rat hippocampal neurons. III. Agonist actions of the novel alkaloid epibatidine and analysis of type II current. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1995, 274, 771–782. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wonnacott, S.; Albuquerque, E.X.; Bertrand, D. Methyllycaconitine: A new probe that discriminates between nicotinic acetylcholine receptor subclasses. Methods Neurosci. 1993, 12, 263–275. [Google Scholar]
- Schlumberger, S.; Ouanounou, G.; Girard, E.; Sasaki, M.; Fuwa, H.; Louzao, M.C.; Botana, L.M.; Benoit, E.; Molgó, J. The marine polyether gambierol enhances muscle contraction and blocks a transient K+ current in skeletal muscle cells. Toxicon 2010, 56, 785–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hill, J.A., Jr.; Nghiem, H.O.; Changeux, J.P. Serine-specific phosphorylation of nicotinic receptor associated 43 K protein. Biochemistry 1991, 30, 5579–5585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miledi, R.; Palma, E.; Eusebi, F. Microtransplantation of neurotransmitter receptors from cells to Xenopus oocyte membranes: New procedure for ion channel studies. Methods. Mol. Biol. 2006, 322, 347–355. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sands, S.B.; Costa, A.C.; Patrick, J.W. Barium permeability of neuronal nicotinic receptor α7 expressed in Xenopus oocytes. Biophys. J. 1993, 65, 2614–2621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eisele, J.L.; Bertrand, S.; Galzi, J.L.; Devillers-Thiery, A.; Changeux, J.P.; Bertrand, D. Chimaeric nicotinic-serotonergic receptor combines distinct ligand binding and channel specificities. Nature 1993, 366, 479–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Servent, D.; Winckler-Dietrich, V.; Hu, H.Y.; Kessler, P.; Drevet, P.; Bertrand, D.; Menez, A. Only snake curaremimetic toxins with a fifth disulfide bond have high affinity for the neuronal α7 nicotinic receptor. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 24279–24286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, Y.; Prusoff, W.H. Relationship between the inhibition constant (K1) and the concentration of inhibitor which causes 50 per cent inhibition (I50) of an enzymatic reaction. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1973, 22, 3099–3108. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]







| Antagonist | α12β1γδ (Torpedo) | α7-5HT3 (Chick) | α3β2 (Human) | α4β2 (Human) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 20-meSPX-G | 0.028 ± 0.005 a | 0.11 ± 0.08 | 0.040 ± 0.001 | 3.60 ± 0.07 |
| α-Toxin (snake) b | 0.011 ± 0.002 | - | - | - |
| MLA | - | 0.83 ± 0.12 | - | - |
| Epibatidine | - | - | 0.034 ± 0.002 | 0.054 ± 0.011 |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Couesnon, A.; Aráoz, R.; Iorga, B.I.; Benoit, E.; Reynaud, M.; Servent, D.; Molgó, J. The Dinoflagellate Toxin 20-Methyl Spirolide-G Potently Blocks Skeletal Muscle and Neuronal Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptors. Toxins 2016, 8, 249. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins8090249
Couesnon A, Aráoz R, Iorga BI, Benoit E, Reynaud M, Servent D, Molgó J. The Dinoflagellate Toxin 20-Methyl Spirolide-G Potently Blocks Skeletal Muscle and Neuronal Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptors. Toxins. 2016; 8(9):249. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins8090249
Chicago/Turabian StyleCouesnon, Aurélie, Rómulo Aráoz, Bogdan I. Iorga, Evelyne Benoit, Morgane Reynaud, Denis Servent, and Jordi Molgó. 2016. "The Dinoflagellate Toxin 20-Methyl Spirolide-G Potently Blocks Skeletal Muscle and Neuronal Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptors" Toxins 8, no. 9: 249. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins8090249
APA StyleCouesnon, A., Aráoz, R., Iorga, B. I., Benoit, E., Reynaud, M., Servent, D., & Molgó, J. (2016). The Dinoflagellate Toxin 20-Methyl Spirolide-G Potently Blocks Skeletal Muscle and Neuronal Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptors. Toxins, 8(9), 249. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins8090249