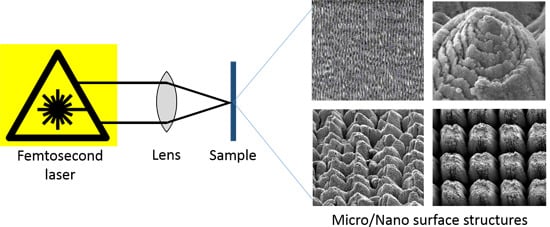
Fabrication of Micro/Nano Structures on Metals by Femtosecond Laser Micromachining
Abstract
:1. Introduction
1.1. Brief History of Surface Structuring with Femtosecond Lasers

1.2. Advantages of fs Laser Micro/Nano Texturing
1.2.1. Comparison with Other Techniques
- The equipment is simpler; there is no need for vacuum or clean room facilities.
- The laser is capable of fabricating the desired micro/nanostructure in a single step process. Hierarchical structures containing both micro- and nanostructures can be created in a single machining step; thus, the process is efficient.
- Machining is performed through a beam of light and thus contactless.
- The process is applicable to the surfaces of any 3D object.
- Many parameters can be easily adjusted resulting in a great variety of possible structures.
- It is possible to lase in many different environments, such as gases, liquids, or in a vacuum and therewith influence the surface chemistry or prevent contamination.
1.2.2. Advantages of fs Pulse over Longer Pulses
2. Surface Structuring with fs Laser
2.1. Laser-Matter Interaction and Ablation Threshold
2.1.1. Laser-Matter Interaction
2.1.2. Ablation Threshold
| Metals and Alloys | Ablation Threshold, Fth(100) (J/cm2) | Ablation Threshold, Fth(1) (J/cm2) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| In Vacuum [31] | In Air | In Air | |
| Cu | 0.170 | 0.55 * [58]; 0.084 [68] | 0.58 * [58] |
| Au | 0.210 | 0.25 [69] | 0.067 [70] |
| Ni | 0.085 | - | 0.022 [64] |
| Mo | 0.155 | - | 0.048 [64] |
| In | 0.125 | - | - |
| W | 0.4 | - | - |
| Ti | - | 0.08 * [58] | 0.28 * [58] |
| SS304 | - | - | 0.1 [71] |
| SS316L | - | 0.13 * [58] | 0.21 * [58] |
| Nb | - | 0.28 * [58] | 0.19 * [58] |
| Al | - | 0.55 * [72]; 0.4 [73] | - |
2.2. Experimental Procedure and Parameters

3. Laser Irradiated-Surface Structures

3.1. Nanostructures
3.1.1. Random Nanostructures

| Metals and Alloys | Feature Size (nm) | Fluence (J/cm2) | Environment | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ti | ≥20 | 0.067–0.16 | Air | [84] |
| 30–50 | n.s. | Vacuum | [92] | |
| Ni | ~100–1500 * | 1.39–3.08 | Air (Flat-top beam) | [87] |
| n.s. | n.s. | Ethanol | [92] | |
| Al | ~300 * | 0.05 | Water and ethanol | [88] |
| 100 | 0.25 | Air | [89] | |
| Al2024 | 10–500 * | 0.2–0.4 | Air | [90] |
| Pt | ≥20 | 0.084–1.52 | Air and vacuum | [68] |
| Cu | ≥20 | 0.084–1.52 | Air | [68] |
| ≤250 (bumps) | 0.51 | Air | [93] | |
| Ag | ≤250 (bumps) | 0.51 | Air | [93] |
| Au | ≥20 | 0.084–1.52 | Air | [68] |
| ≤250 (bumps) | 0.51 | Air | [93] | |
| ≤300 (bumps) * | 0.078–1.1 | Air | [70] |
3.1.2. Periodic Nanostructures

| Metals | λ/Λ, where λ = 800 nm (unless specified) | Orientation | Fluence, (J/cm2) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Low-Spatial-Frequency LIPSS (LSFL) | ||||
| Ti | 1.14 | ┴ | 0.25 | [29] |
| 1.51 | ┴ | 0.067–0.084 | [84] | |
| 1.6–1.14 | ┴ | 0.09–0.45 | [104] | |
| 1.55–1.18 (790) | ┴ | 0.13 * | [80] | |
| 1.47 (1030) | ┴ | 0.5 | [111] | |
| TA6V | 1.33 | ┴ | 2.04 | [78] |
| Ni | 1.33 | ┴ | 0.12 | [30] |
| Ni alloy C263 | 0.99 (775) | ┴ | 0.28 | [60] |
| Al | 1.48 | ┴ | 0.05 | [112] |
| Pt | 1.33–1.14 | ┴ | 0.18–0.44 | [104] |
| 1.45–1.29 | ┴ | 0.16 | [105] | |
| Cu | 2.00–1.18 | ┴ | 0.15–2 | [113] |
| Au | 1.38 | ┴ | 0.16 | [105] |
| SS301L | 1.23 | ┴ | 0.16 | [110] |
| SS304 | 1.33–1.19 | ┴ | 0.4–1.1 | [71] |
| AISI 316L | 1.60 | ┴ | 0.08–0.2 | [114] |
| 1.45 | ┴ | 2.04 | [78] | |
| 1.21 | ┴ | 0.2–2.0 | [30] | |
| Mo | 1.29–1.14 | ┴ | 0.2–1.1 | [104] |
| W | 1.29–1.14 | ┴ | 0.2–1.1 | [104] |
| 2.00–1.33 | ┴ | 2.5–7 | [103] | |
| High-Spatial-Frequency LIPSS (HSFL) | ||||
| Ti | 11.29–8.77 (790) | || | 0.09 * | [80] |
| Cu | 2.96 | ┴ | 0.04–0.1 | [113] |
| SS301L | 2.67 | ┴ | 0.16 | [110] |
| W | 2.29 | n.s. | n.s. (in water) | [92] |
| Ta | 2.29 | n.s. | n.s. (in water) | [18] |
3.2. Microstructures Decorated with Nanofeatures
3.2.1. Undulating Grooves/Micro-Ripples

| Metals and Alloys | Periodicity (μm) | Fluence (J/cm2) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ti | 1.5–2.4 | 0.75 | [29] |
| 1.5–4.5 * | 1 | [111] | |
| Ti-6-4 | 2.7–3.5 | 2.04 | [78] |
| AISI 304 | 1.5–3 * | 0.4–1.1 | [71] |
| AISI 304L | 2–4 * | 0.78–2.83 | [115] |
| AISI 316L | 3.5 | 0.24–0.4 (in vacuum) | [114] |
| 1.7–2.5 | 2.04 | [78] | |
| Ni | 2.5–5 | 1.392 | [87] |
| AZ31B Mg | 1–3 | 9.5 | [107] |
| FeCuNbSiB | 2.7 | 3.18 | [116] |
3.2.2. Columnar Structure

| Metals and Alloys | Size (μm) | Height (μm) | Fluence (J/cm2) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ti | 1–6 * | n.s. | 0.75 | [29] |
| 1–15 | n.s. | 0.16–0.35 | [84] | |
| >10 | 15 | 1.5–2.5 | [123] | |
| 2–3 | n.s. | 3.3–9.9 (in water) | [10] | |
| 10 | n.s. | 1 | [111] | |
| 5–10 | 15–20 | 1.2 | [117] | |
| Ti-6-4 | 12 | 12 | 5.16 | [115] |
| AISI 304L | 9 | 9 | 5.16 | [115] |
| AISI 316L | 6–8 | 5–11 | 0.8–1.6 (in vacuum) | [114] |
| <50 | n.s. | 1 | [120] | |
| Al | n.s. | n.s. | 21 | [121] |
| 30 | 40–70 | 13.5 ** | [5] | |
| 3–10 * | n.s. | 0.16 | [117] | |
| Ni | 5–15 * | n.s. | 1.392–3.08 | [87] |

3.2.3. Other Structures

4. Laser-Inscribed Surface Structures


5. Structure Optimization

6. Applications
7. Conclusions
Acknowledgements
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Vorobyev, A.Y.; Guo, C.L. Metal colorization with femtosecond laser pulses. In Proceedings of SPIE on High-Power Laser Ablation VII, Taos, NM, USA, 20–24 April 2008.
- Yao, J.W.; Zhang, C.Y.; Liu, H.Y.; Dai, Q.F.; Wu, L.J.; Lan, S.; Gopal, A.V.; Trofimov, V.A.; Lysak, T.M. Selective appearance of several laser-induced periodic surface structure patterns on a metal surface using structural colors produced by femtosecond laser pulses. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2012, 258, 7625–7632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, T.Y.; Vorobyev, A.Y.; Guo, C.L. Enhanced efficiency of solar-driven thermoelectric generator with femtosecond laser-textured metals. Opt. Expr. 2011, 19, A824–A829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayak, B.K.; Iyengar, V.V.; Gupta, M.C. Efficient light trapping in silicon solar cells by ultrafast-laser-induced self-assembled micro/nano structures. Prog. Photovolt. Res. Appl. 2011, 19, 631–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, N.; Alexander, D.R.; Schiffern, J.; Doerr, D. Femtosecond laser production of metal surfaces having unique surface structures that are broadband absorbers. J. Laser Appl. 2006, 18, 242–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kietzig, A.M.; Hatzikiriakos, S.G.; Englezos, P. Ice friction: The effects of surface roughness, structure, and hydrophobicity. J. Appl. Phys. 2009, 106, 024303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zorba, V.; Stratakis, E.; Barberoglou, M.; Spanakis, E.; Tzanetakis, P.; Anastasiadis, S.H.; Fotakis, C. Biomimetic artificial surfaces quantitatively reproduce the water repellency of a lotus leaf. Adv. Mater. 2008, 20, 4049–4054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vorobyev, A.Y.; Guo, C.L. Metal pumps liquid uphill. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2009, 94, 224102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, C.Y.; Wang, H.S.; Yang, J.J.; Li, B.; Yang, Y.; Li, H.P. Biocompatibility of the micro-patterned NiTi surface produced by femtosecond laser. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2012, 261, 337–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Yang, J.J.; Liang, C.Y.; Wang, H.S.; Zhu, X.N.; Zhang, N. Surface microstructuring of Ti plates by femtosecond lasers in liquid ambiences: A new approach to improving biocompatibility. Opt. Expr. 2009, 17, 21124–21133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fadeeva, E.; Schlie, S.; Koch, J.; Chichkov, B.N. Selective cell control by surface structuring for orthopedic applications. J. Adhes. Sci. Technol. 2010, 24, 2257–2270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fadeeva, E.; Truong, V.K.; Stiesch, M.; Chichkov, B.N.; Crawford, R.J.; Wang, J.; Ivanova, E.P. Bacterial retention on superhydrophobic titanium surfaces fabricated by femtosecond laser ablation. Langmuir 2011, 27, 3012–3019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, F.; Lehr, J.; Danielczak, L.; Leask, R.; Kietzig, A.M. Robust non-wetting PTFE surfaces by femtosecond laser machining. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 13681–13696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Truong, S.L.; Levi, G.; Bozon-Verduraz, F.; Petrovskaya, A.V.; Simakin, A.V.; Shafeev, G.A. Generation of nanospikes via laser ablation of metals in liquid environment and their activity in surface-enhanced raman scattering of organic molecules. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2007, 254, 1236–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Yang, Y.; Zhao, B.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, X. Femtosecond laser-induced surface structures to significantly improve the thermal emission of light from metals. Appl. Phys. B Lasers Opt. 2012, 106, 349–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carey, J.E.; Crouch, C.H.; Shen, M.Y.; Mazur, E. Visible and near-infrared responsivity of femtosecond-laser microstructured silicon photodiodes. Opt. Lett. 2005, 30, 1773–1775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Myers, R.A.; Farrell, R.; Karger, A.M.; Carey, J.E.; Mazur, E. Enhancing near-infrared avalanche photodiode performance by femtosecond laser microstructuring. Appl. Opt. 2006, 45, 8825–8831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barmina, E.V.; Barberoglou, M.; Zorba, V.; Simakin, A.V.; Stratakis, E.; Fotakis, C.; Shafeev, G.A. Laser control of the properties of nanostructures on Ta and Ni under their ablation in liquids. J. Optoelectron. Adv. Mater. 2010, 12, 495–499. [Google Scholar]
- Volkov, R.V.; Golishnikov, D.M.; Gordienko, V.M.; Savel’ev, A.B. Overheated plasma at the surface of a target with a periodic structure induced by femtosecond laser radiation. JETP Lett. 2003, 77, 473–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, Y.; Xiong, D.-S. The effect of laser surface texturing on frictional performance of face seal. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2008, 197, 96–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hecht, J. A short history of laser development. Appl. Opt. 2010, 49, F99–F122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fork, R.L.; Greene, B.I.; Shank, C.V. Generation of optical pulses shorter than 0.1 psec by colliding pulse mode locking. Appl. Phys. Lett. 1981, 38, 671–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maiman, T.H. Stimulated optical radiation in ruby. Nature 1960, 187, 493–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nisoli, M.; DeSilvestri, S.; Svelto, O.; Szipocs, R.; Ferencz, K.; Spielmann, C.; Sartania, S.; Krausz, F. Compression of high-energy laser pulses below 5 fs. Opt. Lett. 1997, 22, 522–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, K.; Zhang, Q.; Chini, M.; Wu, Y.; Wang, X.; Chang, Z. Tailoring a 67 attosecond pulse through advantageous phase-mismatch. Opt. Lett. 2012, 37, 3891–3893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Birnbaum, M. Semiconductor surface damage produced by ruby lasers. J. Appl. Phys. 1965, 36, 3688–3689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kautek, W.; Kruger, J. Femtosecond pulse laser-ablation of metallic, semiconducting, ceramic, and biological-materials. In Proceeding of SPIE 2207 Laser Materials Processing: Industrial and Microelectronics Applications, Vienna, Austria, 5–8 April 1994.
- Herbst, G.; Steiner, M.; Marowsky, G.; Matthias, E. Ablation of Si and Ge using UV femtosecond laser pulses. In Proceedings of Symposium on Advanced Laser Processing of Materials—Fundamentals and Applications at the 1995 MRS Fall Meeting, Boston, MA, USA, 27 November–1 December 1995; Volume 397, pp. 69–74.
- Tsukamoto, M.; Asuka, K.; Nakano, H.; Hashida, M.; Katto, M.; Abe, N.; Fujita, M. Periodic microstructures produced by femtosecond laser irradiation on titanium plate. Vacuum 2006, 80, 1346–1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuhlke, C.A.; Anderson, T.P.; Alexander, D.R. Fundamentals of layered nanoparticle covered pyramidal structures formed on nickel during femtosecond laser surface interactions. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2013, 283, 648–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preuss, S.; Demchuk, A.; Stuke, M. Subpicosecond UV laser-ablation of metals. Appl. Phys. A 1995, 61, 33–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pronko, P.P.; Dutta, S.K.; Squier, J.; Rudd, J.V.; Du, D.; Mourou, G. Machining of submicron holes using a femtosecond laser at 800-nm. Opt. Commun. 1995, 114, 106–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chichkov, B.N.; Momma, C.; Nolte, S.; vonAlvensleben, F.; Tunnermann, A. Femtosecond, picosecond and nanosecond laser ablation of solids. Appl. Phys. A 1996, 63, 109–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanavin, A.P.; Smetanin, I.V.; Isakov, V.A.; Afanasiev, Y.V.; Chichkov, B.N.; Wellegehausen, B.; Nolte, S.; Momma, C.; Tunnermann, A. Heat transport in metals irradiated by ultrashort laser pulses. Phys. Rev. B 1998, 57, 14698–14703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nolte, S.; Momma, C.; Jacobs, H.; Tunnermann, A.; Chichkov, B.N.; Wellegehausen, B.; Welling, H. Ablation of metals by ultrashort laser pulses. J. Opt. Soc. Am. B Opt. Phys. 1997, 14, 2716–2722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Du, D.; Mourou, G. Laser ablation and micromachining with ultrashort laser pulses. IEEE J. Quantum Electron. 1997, 33, 1706–1716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valette, S.; Audouard, E.; Le Harzic, R.; Huot, N.; Laporte, P.; Fortunier, R. Heat affected zone in aluminum single crystals submitted to femtosecond laser irradiations. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2005, 239, 381–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joglekar, A.P.; Liu, H.; Spooner, G.J.; Meyhofer, E.; Mourou, G.; Hunt, A.J. A study of the deterministic character of optical damage by femtosecond laser pulses and applications to nanomachining. Appl. Phys. B Lasers Opt. 2003, 77, 25–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chimmalgi, A.; Choi, T.Y.; Grigoropoulos, C.P.; Komvopoulos, K. Femtosecond laser aperturless near-field nanomachining of metals assisted by scanning probe microscopy. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2003, 82, 1146–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Momma, C.; Nolte, S.; Chichkov, B.N.; von Alvensleben, F.; Tunnermann, A. Precise laser ablation with ultrashort pulses. Appl. Surf. Sci. 1997, 109, 15–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arrigoni, M. Femtosecond lasers carve out a niche in micromachining. Photon. Spectra 2004, 38, 73. [Google Scholar]
- Schaffer, C.B.; Brodeur, A.; Mazur, E. Laser-induced breakdown and damage in bulk transparent materials induced by tightly focused femtosecond laser pulses. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2001, 12, 1784–1794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Chang, Y.C.; Yao, J.M.; Luo, C.R.; Yin, S.; Ruffin, P.; Brantley, C.; Edwards, E. Surface enhanced raman spectroscopy by interfered femtosecond laser created nanostructures. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2012, 100, 023107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kietzig, A.M.; Lehr, J.; Matus, L.; Liang, F. Laser-induced patterns on metals and polymers for biomimetic surface engineering. In Proceedings of SPIE 8967 Laser Applications in Microelectronic and Optoelectronic Manufacturing XIX, San Francisco, CA, USA, 1 February 2014.
- Murray, M.; Jose, G.; Richards, B.; Jha, A. Femtosecond pulsed laser deposition of silicon thin films. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2013, 8, 272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anisimov, S.I.; Kapeliov, B.L.; Perelman, T.L. Electron-emission from surface of metals induced by ultrashort laser pulses. Zh. Eksp. Teor. Fiz. 1974, 66, 776–781. [Google Scholar]
- Von der Linde, D.; Sokolowski-Tinten, K.; Bialkowski, J. Laser-solid interaction in the femtosecond time regime. Appl. Surf. Sci. 1997, 109, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmmed, K.M.T.; Ling, E.J.Y.; Servio, P.; Kietzig, A.-M. Introducing a new optimization tool for femtosecond laser-induced surface texturing on titanium, stainless steel, aluminum and copper. Opt. Lasers Eng. 2015, 66, 258–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miotello, A.; Kelly, R. Laser-induced phase explosion: New physical problems when a condensed phase approaches the thermodynamic critical temperature. Appl. Phys. A 1999, 69, S67–S73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, C.R.; Xu, X.F. Mechanisms of decomposition of metal during femtosecond laser ablation. Phys. Rev. B 2005, 72, 165415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouilly, D.; Perez, D.; Lewis, L.J. Damage in materials following ablation by ultrashort laser pulses: A molecular-dynamics study. Phys. Rev. B 2007, 76, 184119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez, D.; Lewis, L.J. Molecular-dynamics study of ablation of solids under femtosecond laser pulses. Phys. Rev. B 2003, 67, 184102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanov, D.S.; Zhigilei, L.V. Combined atomistic-continuum modeling of short-pulse laser melting and disintegration of metal films. Phys. Rev. B 2003, 68, 064114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoian, R.; Ashkenasi, D.; Rosenfeld, A.; Campbell, E.E.B. Coulomb explosion in ultrashort pulsed laser ablation of Al2O3. Phys. Rev. B 2000, 62, 13167–13173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirk, M.D.; Molian, P.A. A review of ultrashort pulsed laser ablation of materials. J. Laser Appl. 1998, 10, 18–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.; Liu, C.-S.; Shang, S.; Liu, D.; Perrie, W.; Dearden, G.; Watkins, K. A review of ultrafast laser materials micromachining. Opt. Laser Technol. 2013, 46, 88–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruger, J.; Kautek, W. Ultrashort pulse laser interaction with dielectrics and polymers. Adv. Polym. Sci. 2004, 168, 247–289. [Google Scholar]
- Mannion, P.T.; Magee, J.; Coyne, E.; O’Connor, G.M.; Glynn, T.J. The effect of damage accumulation behaviour on ablation thresholds and damage morphology in ultrafast laser micro-machining of common metals in air. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2004, 233, 275–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jee, Y.; Becker, M.F.; Walser, R.M. Laser-induced damage on single-crystal metal-surfaces. J. Opt. Soc. Am. B Opt. Phys. 1988, 5, 648–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semaltianos, N.G.; Perrie, W.; French, P.; Sharp, M.; Dearden, G.; Logothetidis, S.; Watkins, K.G. Femtosecond laser ablation characteristics of nickel-based superalloy C263. Appl. Phys. A 2009, 94, 999–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenfeld, A.; Lorenz, M.; Stoian, R.; Ashkenasi, D. Ultrashort-laser-pulse damage threshold of transparent materials and the role of incubation. Appl. Phys. A 1999, 69, S373–S376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gamaly, E.G.; Madsen, N.R.; Duering, M.; Rode, A.V.; Kolev, V.Z.; Luther-Davies, B. Ablation of metals with picosecond laser pulses: Evidence of long-lived nonequilibrium conditions at the surface. Phys. Rev. B 2005, 71, 174405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gamaly, E.G.; Rode, A.V.; Luther-Davies, B.; Tikhonchuk, V.T. Ablation of solids by femtosecond lasers: Ablation mechanism and ablation thresholds for metals and dielectrics. Phys. Plasmas 2002, 9, 949–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wellershoff, S.S.; Hohlfeld, J.; Gudde, J.; Matthias, E. The role of electron-phonon coupling in femtosecond laser damage of metals. Appl. Phys. A 1999, 69, S99–S107. [Google Scholar]
- Stuart, B.C.; Feit, M.D.; Herman, S.; Rubenchik, A.M.; Shore, B.W.; Perry, M.D. Optical ablation by high-power short-pulse lasers. J. Opt. Soc. Am. B Opt. Phys. 1996, 13, 459–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gudde, J.; Hohlfeld, J.; Muller, J.G.; Matthias, E. Damage threshold dependence on electron-phonon coupling in Au and Ni films. Appl. Surf. Sci. 1998, 127, 40–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yahng, J.S.; Nam, J.R.; Jeoung, S.C. The influence of substrate temperature on femtosecond laser micro-processing of silicon, stainless steel and glass. Opt. Lasers Eng. 2009, 47, 815–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vorobyev, A.Y.; Guo, C.L. Femtosecond laser nanostructuring of metals. Opt. Expr. 2006, 14, 2164–2169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruger, J.; Kautek, W. The femtosecond pulse laser: A new tool for micromachining. Laser Phys. 1999, 9, 30–40. [Google Scholar]
- Vorobyev, A.Y.; Guo, C. Enhanced absorptance of gold following multipulse femtosecond laser ablation. Phys. Rev. B 2005, 72, 195422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groenendijk, M.; Meijer, J. Microstructuring using femtosecond pulsed laser ablation. J. Laser Appl. 2006, 18, 227–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, S.; Kruger, J.; Hertwig, A.; Fiedler, A.; Kautek, W. Femtosecond laser interaction with protection materials. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2003, 208, 333–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perrie, W.; Gill, M.; Robinson, G.; Fox, P.; O’Neill, W. Femtosecond laser micro-structuring of aluminium under helium. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2004, 230, 50–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Will, M.; Nolte, S.; Chichkov, B.N.; Tunnermann, A. Optical properties of waveguides fabricated in fused silica by femtosecond laser pulses. Appl. Opt. 2002, 41, 4360–4364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noh, J.; Lee, J.H.; Na, S.; Lim, H.; Jung, D.H. Fabrication of hierarchically micro- and nano-structured mold surfaces using laser ablation for mass production of superhydrophobic surfaces. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 2010, 49, 106502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, D.G. Vector-beam solutions of Maxwell’s wave equation. Opt. Lett. 1996, 21, 9–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Semaltianos, N.G.; Perrie, W.; French, P.; Sharp, M.; Dearden, G.; Watkins, K.G. Femtosecond laser surface texturing of a nickel-based superalloy. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2008, 255, 2796–2802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bizi-Bandoki, P.; Benayoun, S.; Valette, S.; Beaugiraud, B.; Audouard, E. Modifications of roughness and wettability properties of metals induced by femtosecond laser treatment. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2011, 257, 5213–5218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurselis, K.; Kiyan, R.; Chichkov, B.N. Formation of corrugated and porous steel surfaces by femtosecond laser irradiation. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2012, 258, 8845–8852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonse, J.; Kruger, J.; Hohm, S.; Rosenfeld, A. Femtosecond laser-induced periodic surface structures. J. Laser Appl. 2012, 24, 042006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moradi, S.; Kamal, S.; Englezos, P.; Hatzikiriakos, S.G. Femtosecond laser irradiation of metallic surfaces: Effects of laser parameters on superhydrophobicity. Nanotechnology 2013, 24, 415302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bizi-bandoki, P.; Valette, S.; Audouard, E.; Benayoun, S. Effect of stationary femtosecond laser irradiation on substructures’ formation on a mold stainless steel surface. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2013, 270, 197–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehr, J.; Kietzig, A.-M. Production of homogenous micro-structures by femtosecond laser micro-machining. Opt. Lasers Eng. 2014, 57, 121–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vorobyev, A.Y.; Guo, C. Femtosecond laser structuring of titanium implants. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2007, 253, 7272–7280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vorobyev, A.Y.; Guo, C.L. Direct femtosecond laser surface nano/microstructuring and its applications. Laser Photonics Rev. 2013, 7, 385–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsibidis, G.D.; Barberoglou, M.; Loukakos, P.A.; Stratakis, E.; Fotakis, C. Dynamics of ripple formation on silicon surfaces by ultrashort laser pulses in subablation conditions. Phys. Rev. B 2012, 86, 115316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuhlke, C.A.; Anderson, T.P.; Alexander, D.R. Formation of multiscale surface structures on nickel via above surface growth and below surface growth mechanisms using femtosecond laser pulses. Opt. Express 2013, 21, 8460–8473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stratakis, E.; Zorba, V.; Barberoglou, M.; Fotakis, C.; Shafeev, G.A. Laser writing of nanostructures on bulk Al via its ablation in liquids. Nanotechnology 2009, 20, 105303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stratakis, E.; Zorba, V.; Barberoglou, M.; Fotakis, C.; Shafeev, G.A. Femtosecond laser writing of nanostructures on bulk Al via its ablation in air and liquids. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2009, 255, 5346–5350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dou, K.; Knobbe, E.T.; Parkhill, R.L.; Irwin, B.; Matthews, L.; Church, K.H. Femtosecond study of surface structure and composition and time-resolved spectroscopy in metals. Appl. Phys. A 2003, 76, 303–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.H.; Yuan, C.H.; Yang, H.D.; Li, J.W.; Huang, W.H.; Tang, D.C.; Xu, Q. Morphology and composition on Al surface irradiated by femtosecond laser pulses. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2010, 256, 4344–4349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barmina, E.V.; Stratakis, E.; Fotakis, K.; Shafeev, G.A. Generation of nanostructures on metals by laser ablation in liquids: New results. Quantum Electron. 2010, 40, 1012–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, T.Y.; Vorobyev, A.Y.; Guo, C.L. Ultrafast dynamics of femtosecond laser-induced nanostructure formation on metals. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2009, 95, 123111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guosheng, Z.; Fauchet, P.M.; Siegman, A.E. Growth of spontaneous periodic surface-structures on solids during laser illumination. Phys. Rev. B 1982, 26, 5366–5381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, J.F.; Preston, J.S.; Vandriel, H.M.; Sipe, J.E. Laser-induced periodic surface-structure. II. Experiments on Ge, Si, Al, and brass. Phys. Rev. B 1983, 27, 1155–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sipe, J.E.; Young, J.F.; Preston, J.S.; Vandriel, H.M. Laser-induced periodic surface-structure. 1. Theory. Phys. Rev. B 1983, 27, 1141–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reif, J.; Costache, F.; Henyk, M.; Pandelov, S.V. Ripples revisited: Non-classical morphology at the bottom of femtosecond laser ablation craters in transparent dielectrics. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2002, 197–198, 891–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henyk, M.; Vogel, N.; Wolfframm, D.; Tempel, A.; Reif, J. Femtosecond laser ablation from dielectric materials: Comparison to arc discharge erosion. Appl. Phys. A 1999, 69, S355–S358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borowiec, A.; Haugen, H.K. Subwavelength ripple formation on the surfaces of compound semiconductors irradiated with femtosecond laser pulses. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2003, 82, 4462–4464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, M.; Zhao, F.; Cheng, Y.; Xu, N.; Xu, Z. Origin of laser-induced near-subwavelength ripples: Interference between surface plasmons and incident laser. ACS Nano 2009, 3, 4062–4070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonchbruevich, A.M.; Libenson, M.N.; Makin, V.S.; Trubaev, V.V. Surface electromagnetic-waves in optics. Opt. Eng. 1992, 31, 718–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romer, G.R.B.E.; Huis in’t Veld, A.J.; Meijer, J.; Groenendijk, M.N.W. On the formation of laser induced self-organizing nanostructures. Cirp Ann. Manuf. Technol. 2009, 58, 201–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.Z.; Malzer, S.; Wang, L.J. Formation of subwavelength periodic structures on tungsten induced by ultrashort laser pulses. Opt. Lett. 2007, 32, 1932–1934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okamuro, K.; Hashida, M.; Miyasaka, Y.; Ikuta, Y.; Tokita, S.; Sakabe, S. Laser fluence dependence of periodic grating structures formed on metal surfaces under femtosecond laser pulse irradiation. Phys. Rev. B 2010, 82, 165417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vorobyev, A.Y.; Makin, V.S.; Guo, C.L. Periodic ordering of random surface nanostructures induced by femtosecond laser pulses on metals. J. Appl. Phys. 2007, 101, 034903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vorobyev, A.Y.; Guo, C.L. Femtosecond laser-induced periodic surface structure formation on tungsten. J. Appl. Phys. 2008, 104, 063523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, Y.C.; Zhou, W.; Li, Z.L.; Zheng, H.Y. Femtosecond laser-induced iridescent effect on AZ31B magnesium alloy surface. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2013, 46, 425305. [Google Scholar]
- Hwang, T.Y.; Guo, C.L. Angular effects of nanostructure-covered femtosecond laser induced periodic surface structures on metals. J. Appl. Phys. 2010, 108, 073523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayak, B.K.; Gupta, M.C. Ultrafast laser-induced self-organized conical micro/nano surface structures and their origin. Opt. Lasers Eng. 2010, 48, 966–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, J.W.; Zhang, C.Y.; Liu, H.Y.; Dai, Q.F.; Wu, L.J.; Lan, S.; Gopal, A.V.; Trofimov, V.A.; Lysak, T.M. High spatial frequency periodic structures induced on metal surface by femtosecond laser pulses. Opt. Express 2012, 20, 905–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliveira, V.; Ausset, S.; Vilar, R. Surface micro/nanostructuring of titanium under stationary and non-stationary femtosecond laser irradiation. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2009, 255, 7556–7560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vorobyev, A.Y.; Guoa, C.L. Colorizing metals with femtosecond laser pulses. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2008, 92, 041914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakabe, S.; Hashida, M.; Tokita, S.; Namba, S.; Okamuro, K. Mechanism for self-formation of periodic grating structures on a metal surface by a femtosecond laser pulse. Phys. Rev. B 2009, 79, 033409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, B.; Zhou, M.; Li, J.; Ye, X.; Li, G.; Cai, L. Superhydrophobic surfaces fabricated by microstructuring of stainless steel using a femtosecond laser. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2009, 256, 61–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kietzig, A.-M.; Hatzikiriakosa, S.G.; Englezosa, P. Patterned superhydrophobic metallic surfaces. Langmuir 2009, 25, 4821–4827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, W.; Peng, Z.N.; Wang, Z.J.; Ni, X.C.; Wang, C.Y. The effect of femtosecond laser micromachining on the surface characteristics and subsurface microstructure of amorphous FeCuNbSiB alloy. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2006, 253, 1299–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayak, B.K.; Gupta, M.C. Self-organized micro/nano structures in metal surfaces by ultrafast laser irradiation. Opt. Lasers Eng. 2010, 48, 940–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuhlke, C.A.; Anderson, T.P.; Alexander, D.R. Understanding the formation of self-organized micro/nanostructures on metal surfaces from femtosecond laser ablation using stop-motion SEM imaging. In Proceedings of SPIE 8968,Laser-based Micro- and Nanoprocessing VIII, San Francisco, CA, USA, 1 February 2014.
- Lehr, J.; de Marchi, F.; Matus, L.; MacLeod, J.; Rosei, F.; Kietzig, A.-M. The influence of the gas environment on morphology and chemical composition of surfaces micro-machined with a femtosecond laser. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2014, 320, 455–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kam, D.H.; Bhattacharya, S.; Mazumder, J. Control of the wetting properties of an AISI 316L stainless steel surface by femtosecond laser-induced surface modification. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2012, 22, 105019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, G.M.; Jackson, M.J. Femtosecond laser micromachining of aluminum surfaces under controlled gas atmospheres. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2006, 15, 155–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, T.Y.; Guo, C.L. Polarization and angular effects of femtosecond laser-induced conical microstructures on Ni. J. Appl. Phys. 2012, 111, 083518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayak, B.K.; Gupta, M.C.; Kolasinski, K.W. Formation of nano-textured conical microstructures in titanium metal surface by femtosecond laser irradiation. Appl. Phys. A 2008, 90, 399–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuhlke, C.A.; Anderson, T.P.; Alexander, D.R. Comparison of the structural and chemical composition of two unique micro/nanostructures produced by femtosecond laser interactions on nickel. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2013, 103, 121603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vorobyev, A.Y.; Guo, C. Femtosecond laser blackening of platinum. J. Appl. Phys. 2008, 104, 053516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vorobyev, A.Y.; Guo, C.L. Laser turns silicon superwicking. Opt. Express 2010, 18, 6455–6460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vorobyev, A.Y.; Guo, C.L. Optical and wetting properties of femtosecond laser nanostructured materials. J. Nano Res. 2011, 14, 57–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.J.; Zhou, M.; Yuan, R.; Cai, L. Fabrication of titanium-based microstructured surfaces and study on their superhydrophobic stability. J. Mater. Res. 2008, 23, 2491–2499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.J.; Mei, X.S.; Jiang, G.D.; Lei, S.T.; Yang, C.J. Effect of two typical focus positions on microstructure shape and morphology in femtosecond laser multi-pulse ablation of metals. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2008, 255, 2303–2311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eichstädt, J.; Römer, G.R.B.E.; Huis in’t Veld, A.J. Determination of irradiation parameters for laser-induced periodic surface structures. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2013, 264, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldacchini, T.; Carey, J.E.; Zhou, M.; Mazur, E. Superhydrophobic surfaces prepared by microstructuring of silicon using a femtosecond laser. Langmuir 2006, 22, 4917–4919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.K.; Zheng, H.Y.; Xia, H.M. Femtosecond laser-induced modification of surface wettability of PMMA for fluid separation in microchannels. Microfluid. Nanofluid. 2011, 10, 225–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, T.L.; Tsai, T.K.; Yang, H.P.; Huang, J.Z. Effect of ultra-fast laser texturing on surface wettability of microfluidic channels. Microelectron. Eng. 2012, 98, 684–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demir, A.G.; Lecis, N.; Previtali, B.; Ugues, D. Scratch resistance of fibre laser surface textured tin coatings. Surf. Eng. 2013, 29, 654–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tetsuo, S.; Nikolay, N.; Minoru, O. Friction characteristics of submicrometre-structured surfaces fabricated by particle-assisted near-field enhancement with femtosecond laser. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2007, 40, 7485–7491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bathe, R.; Sai Krishna, V.; Nikumb, S.K.; Padmanabham, G. Laser surface texturing of gray cast iron for improving tribological behavior. Appl. Phys. A 2014, 117, 117–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bereznai, M.; Pelsoczi, I.; Toth, Z.; Turzo, K.; Radnai, M.; Bor, Z.; Fazekas, A. Surface modifications induced by ns and sub-ps excimer laser pulses on titanium implant material. Biomaterials 2003, 24, 4197–4203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fadeeva, E.; Schlie, S.; Koch, J.; Chichkov, B.N.; Vorobyev, A.Y.; Guo, C.L. Femtosecond laser-induced surface structures on platinum and their effects on surface wettability and fibroblast cell proliferation. In Contact Angle, Wettability and Adhesion; Mittal, K.L., Ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2009; Volume 6, pp. 163–171. [Google Scholar]
- Kenar, H.; Akman, E.; Kacar, E.; Demir, A.; Park, H.; Abdul-Khaliq, H.; Aktas, C.; Karaoz, E. Femtosecond laser treatment of 316L improves its surface nanoroughness and carbon content and promotes osseointegration: An in vitro evaluation. Colloids Surf. B 2013, 108, 305–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, Y.H.; Choe, H.C.; Brantley, W.A. Nanostructured thin film formation on femtosecond laser-textured Ti-35Nb-xZr alloy for biomedical applications. Thin Solid Films 2011, 519, 4668–4675. [Google Scholar]
- Ranella, A.; Barberoglou, M.; Bakogianni, S.; Fotakis, C.; Stratakis, E. Tuning cell adhesion by controlling the roughness and wettability of 3D micro/nano silicon structures. Acta Biomater. 2010, 6, 2711–2720. [Google Scholar]
- Papadopoulou, E.L.; Samara, A.; Barberoglou, M.; Manousaki, A.; Pagakis, S.N.; Anastasiadou, E.; Fotakis, C.; Stratakis, E. Silicon scaffolds promoting three-dimensional neuronal web of cytoplasmic processes. Tissue Eng. Part C 2010, 16, 497–502. [Google Scholar]
- Vorobyev, A.Y.; Guo, C.L. Making human enamel and dentin surfaces superwetting for enhanced adhesion. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2011, 99, 193703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahsan, M.S.; Ahmed, F.; Kim, Y.G.; Lee, M.S.; Jun, M.B.G. Colorizing stainless steel surface by femtosecond laser induced micro/nano-structures. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2011, 257, 7771–7777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vorobyev, A.Y.; Guo, C.L. Spectral and polarization responses of femtosecond laser-induced periodic surface structures on metals. J. Appl. Phys. 2008, 103, 043513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vorobyev, A.Y.; Makin, V.S.; Guo, C.L. Optical properties of femtosecond laser-induced periodic surface structures on metals. In Proceedings of the 52nd IEEE International Midwest Symposium on Circuits and Systems, Cancun, Mexico, 2–5 August 2009; pp. 909–912.
- Dusser, B.; Sagan, Z.; Soder, H.; Faure, N.; Colombier, J.P.; Jourlin, M.; Audouard, E. Controlled nanostructrures formation by ultra fast laser pulses for color marking. Opt. Expr. 2010, 18, 2913–2924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmood, A.; Venkatakrishnan, K.; Tan, B. 3-D aluminum nanostructure with microhole array synthesized by femtosecond laser radiation for enhanced light extinction. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2013, 8, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, C.; Crouch, C.H.; Zhao, L.; Carey, J.E.; Younkin, R.; Levinson, J.A.; Mazur, E.; Farrell, R.M.; Gothoskar, P.; Karger, A. Near-unity below-band-gap absorption by microstructured silicon. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2001, 78, 1850–1852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vorobyev, A.Y.; Makin, V.S.; Guo, C.L. Brighter light sources from black metal: Significant increase in emission efficiency of incandescent light sources. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2009, 102, 234301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, B.; Wu, X.-Y.; Ling, S.-Q.; Luo, F.; Du, C.-L.; Sun, X.-Q. Fabrication of 3D metal micro-mold based on femtosecond laser cutting and micro-electric resistance slip welding. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2013, 66, 601–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2014 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ahmmed, K.M.T.; Grambow, C.; Kietzig, A.-M. Fabrication of Micro/Nano Structures on Metals by Femtosecond Laser Micromachining. Micromachines 2014, 5, 1219-1253. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi5041219
Ahmmed KMT, Grambow C, Kietzig A-M. Fabrication of Micro/Nano Structures on Metals by Femtosecond Laser Micromachining. Micromachines. 2014; 5(4):1219-1253. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi5041219
Chicago/Turabian StyleAhmmed, K. M. Tanvir, Colin Grambow, and Anne-Marie Kietzig. 2014. "Fabrication of Micro/Nano Structures on Metals by Femtosecond Laser Micromachining" Micromachines 5, no. 4: 1219-1253. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi5041219
APA StyleAhmmed, K. M. T., Grambow, C., & Kietzig, A. -M. (2014). Fabrication of Micro/Nano Structures on Metals by Femtosecond Laser Micromachining. Micromachines, 5(4), 1219-1253. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi5041219