(S)-10-Hydroxycamptothecin Inhibits Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma Growth In Vitro and In Vivo Via Decreasing Topoisomerase I Enzyme Activity
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
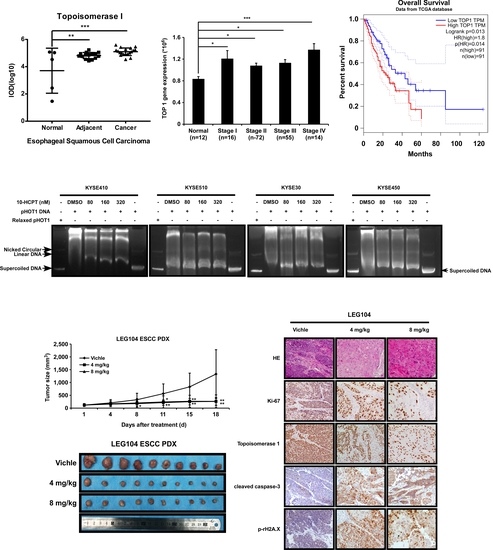
2.1. TOP I Enzyme Acts as an Indicator of ESCC
2.2. HCPT Inhibits the Proliferation of Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma Cells
2.3. HCPT Interrupts G2/M Cell Cycle Transition and Induces Apoptosis in ESCC Cells
2.4. HCPT Decreases TOP I Enzyme Activity and Inhibits its Expression in ESCC
2.5. HCPT Attenuated ESCC PDX Tumor Growth in Mice
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Reagents
4.2. Cell Culture
4.3. MTT Assay
4.4. Foci Formation Assay
4.5. Anchorage-Independent Cell Growth
4.6. Cell Cycle Analysis
4.7. Annexin V Apoptosis Assay
4.8. Western Blotting
4.9. Immunohistochemical (IHC) Analysis
4.10. TOP I Assay
4.11. PDX Tumor Model in Mice
4.12. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, Y. Epidemiology of esophageal cancer. World J. Gastroenterol. 2013, 19, 5598–5606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bollschweiler, E.; Plum, P.; Monig, S.P.; Holscher, A.H. Current and future treatment options for esophageal cancer in the elderly. Expert Opin. Pharmacother. 2017, 18, 1001–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cesas, A.; Bagajevas, A. [Combined treatment of esophageal cancer: A review]. Medicina 2004, 40 (Suppl. 1), 161–165. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Liu, Y. Topoisomerase I in Human Disease Pathogenesis and Treatments. Genom. Proteom. Bioinform. 2016, 14, 166–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gilmour, D.S.; Pflugfelder, G.; Wang, J.C.; Lis, J.T. Topoisomerase I interacts with transcribed regions in Drosophila cells. Cell 1986, 44, 401–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.C. Cellular roles of DNA topoisomerases: A molecular perspective. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2002, 3, 430–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aguilera, A.; Garcia-Muse, T. R loops: from transcription byproducts to threats to genome stability. Mol. Cell 2012, 46, 115–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Proszek, J.; Roy, A.; Jakobsen, A.K.; Frohlich, R.; Knudsen, B.R.; Stougaard, M. Topoisomerase I as a biomarker: Detection of activity at the single molecule level. Sensors 2014, 14, 1195–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Holden, J.A.; Rahn, M.P.; Jolles, C.J.; Vorobyev, S.V.; Bronstein, I.B. Immunohistochemical detection of DNA topoisomerase I in formalin fixed, paraffin wax embedded normal tissues and in ovarian carcinomas. Mol. Pathol. 1997, 50, 247–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hafian, H.; Venteo, L.; Sukhanova, A.; Nabiev, I.; Lefevre, B.; Pluot, M. Immunohistochemical study of DNA topoisomerase I, DNA topoisomerase II alpha, p53, and Ki-67 in oral preneoplastic lesions and oral squamous cell carcinomas. Hum. Pathol. 2004, 35, 745–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coleman, L.W.; Perkins, S.L.; Bronstein, I.B.; Holden, J.A. Expression of DNA toposiomerase I and DNA topoisomerase II-alpha in testicular seminomas. Hum. Pathol. 2000, 31, 728–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, D.; Bronstein, I.B.; Holden, J.A. Expression of DNA topoisomerase I in neoplasms of the kidney: correlation with histological grade, proliferation, and patient survival. Hum. Pathol. 2000, 31, 214–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coleman, L.W.; Bronstein, I.B.; Holden, J.A. Immunohistochemical staining for DNA topoisomerase I, DNA topoisomerase II-alpha and p53 in gastric carcinomas. Anticancer Res. 2001, 21, 1167–1172. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ikeguchi, M.; Arai, Y.; Maeta, Y.; Ashida, K.; Katano, K.; Wakatsuki, T. Topoisomerase I expression in tumors as a biological marker for CPT-11 chemosensitivity in patients with colorectal cancer. Surg. Today 2011, 41, 1196–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gallo, R.C.; Whang-Peng, J.; Adamson, R.H. Studies on the antitumor activity, mechanism of action, and cell cycle effects of camptothecin. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 1971, 46, 789–795. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kessel, D.; Bosmann, H.B.; Lohr, K. Camptothecin effects on DNA synthesis in murine leukemia cells. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1972, 269, 210–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Z.F.; Tang, Y.M.; Xu, X.J.; Li, S.S.; Zhang, J.Y. 10-Hydroxycamptothecin induces apoptosis in human neuroblastoma SMS-KCNR cells through p53, cytochrome c and caspase 3 pathways. Neoplasma 2016, 63, 72–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fei, B.; Chi, A.L.; Weng, Y. Hydroxycamptothecin induces apoptosis and inhibits tumor growth in colon cancer by the downregulation of survivin and XIAP expression. World J. Surg. Oncol. 2013, 11, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, L.; Hong, J.; Di, J.; Guo, Y.; Han, M.; Liu, M.; Wang, X. 10-Hydroxycamptothecin (HCPT) nanosuspensions stabilized by mPEG1000-HCPT conjugate: high stabilizing efficiency and improved antitumor efficacy. Int. J. Nanomed. 2017, 12, 3681–3695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, H.; Feng, J.; Liu, G.; Chen, B.; Jiang, Y.; Xie, Q. In vitro and in vivo anti-tumor efficacy of 10-hydroxycamptothecin polymorphic nanoparticle dispersions: Shape- and polymorph-dependent cytotoxicity and delivery of 10-hydroxycamptothecin to cancer cells. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2016, 12, 881–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hidalgo, M.; Amant, F.; Biankin, A.V.; Budinska, E.; Byrne, A.T.; Caldas, C.; Clarke, R.B.; de Jong, S.; Jonkers, J.; Maelandsmo, G.M.; et al. Patient-derived xenograft models: an emerging platform for translational cancer research. Cancer Discov. 2014, 4, 998–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nakajima, Y.; Miyake, S.; Nagai, K.; Kawano, T.; Iwai, T. CPT-11 may provide therapeutic efficacy for esophageal squamous cell cancer and the effects correlate with the level of DNA topoisomerase I protein. Jpn. J. Cancer Res. 2001, 92, 1335–1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia-Carbonero, R.; Supko, J.G. Current perspectives on the clinical experience, pharmacology, and continued development of the camptothecins. Clin. Cancer Res. 2002, 8, 641–661. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ling, Y.H.; Tseng, M.T.; Nelson, J.A. Differentiation induction of human promyelocytic leukemia cells by 10-hydroxycamptothecin, a DNA topoisomerase I inhibitor. Differentiation 1991, 46, 135–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ling, Y.H.; Andersson, B.S.; Nelson, J.A. DNA topoisomerase I as a site of action for 10-hydroxycamptothecin in human promyelocytic leukemia cells. Cancer Biochem. Biophys. 1990, 11, 23–30. [Google Scholar]
- Zou, J.; Li, S.; Chen, Z.; Lu, Z.; Gao, J.; Zou, J.; Lin, X.; Li, Y.; Zhang, C.; Shen, L. A novel oral camptothecin analog, gimatecan, exhibits superior antitumor efficacy than irinotecan toward esophageal squamous cell carcinoma in vitro and in vivo. Cell Death Dis. 2018, 9, 661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Xu, B.; Liu, Y.; Huang, J.; Lu, P.; Ba, Y.; Wu, L.; Bai, Y.; Zhang, S.; Feng, J.; et al. Irinotecan plus S-1 versus S-1 in patients with previously treated recurrent or metastatic esophageal cancer (ESWN 01): A prospective randomized, multicenter, open-labeled phase 3 trial. Cancer Commun. 2019, 39, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wei, Y.; Li, C.; Zhang, Y.; He, H.; Zhang, G.; Hao, X.; Liu, H.; Wang, H.; Tian, W. Hydroxycamptothecin mediates antiproliferative effects through apoptosis and autophagy in A549 cells. Oncol. Lett. 2018, 15, 6322–6328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ping, Y.H.; Lee, H.C.; Lee, J.Y.; Wu, P.H.; Ho, L.K.; Chi, C.W.; Lu, M.F.; Wang, J.J. Anticancer effects of low-dose 10-hydroxycamptothecin in human colon cancer. Oncol. Rep. 2006, 15, 1273–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Min, X.; Heng, H.; Yu, H.L.; Dan, M.; Jie, C.; Zeng, Y.; Ning, H.; Liu, Z.G.; Wang, Z.Y.; Lin, W. Anticancer effects of 10-hydroxycamptothecin induce apoptosis of human osteosarcoma through activating caspase-3, p53 and cytochrome c pathways. Onco. Lett. 2018, 15, 2459–2464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, X.W.; Qing, C.; Xu, B. Apoptosis induction and cell cycle perturbation in human hepatoma hep G2 cells by 10-hydroxycamptothecin. Anticancer. Drugs 1999, 10, 569–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alagoz, M.; Gilbert, D.C.; El-Khamisy, S.; Chalmers, A.J. DNA repair and resistance to topoisomerase I inhibitors: Mechanisms, biomarkers and therapeutic targets. Curr. Med. Chem. 2012, 19, 3874–3885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weyemi, U.; Redon, C.E.; Choudhuri, R.; Aziz, T.; Maeda, D.; Boufraqech, M.; Parekh, P.R.; Sethi, T.K.; Kasoji, M.; Abrams, N.; et al. The histone variant H2A.X is a regulator of the epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 10711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Baltanas, F.C.; Weruaga, E.; Valero, J.; Recio, J.S.; Alonso, J.R. Albumin attenuates DNA damage in primary-cultured neurons. Neurosci. Lett. 2009, 450, 23–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Long, Y.H.; Wang, S.Q.; Li, Y.F.; Zhang, J.H. Phosphorylation of H2A.X(T)(yr39) positively regulates DNA damage response and is linked to cancer progression. FEBS J. 2016, 283, 4462–4473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Capranico, G.; Marinello, J.; Chillemi, G. Type I DNA Topoisomerases. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 60, 2169–2192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, E.; Federico, S.M.; Chen, X.; Shelat, A.A.; Bradley, C.; Gordon, B.; Karlstrom, A.; Twarog, N.R.; Clay, M.R.; Bahrami, A.; et al. Orthotopic patient-derived xenografts of paediatric solid tumours. Nature 2017, 549, 96–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Z.Y.; Xu, L.Y.; Li, E.M.; Shen, J.; Zheng, R.M.; Cai, W.J.; Zeng, Y. Immortal phenotype of the esophageal epithelial cells in the process of immortalization. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2002, 10, 641–646. [Google Scholar]






© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Song, M.; Yin, S.; Zhao, R.; Liu, K.; Kundu, J.K.; Shim, J.-H.; Lee, M.-H.; Dong, Z. (S)-10-Hydroxycamptothecin Inhibits Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma Growth In Vitro and In Vivo Via Decreasing Topoisomerase I Enzyme Activity. Cancers 2019, 11, 1964. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers11121964
Song M, Yin S, Zhao R, Liu K, Kundu JK, Shim J-H, Lee M-H, Dong Z. (S)-10-Hydroxycamptothecin Inhibits Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma Growth In Vitro and In Vivo Via Decreasing Topoisomerase I Enzyme Activity. Cancers. 2019; 11(12):1964. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers11121964
Chicago/Turabian StyleSong, Mengqiu, Shuying Yin, Ran Zhao, Kangdong Liu, Joydeb Kumar Kundu, Jung-Hyun Shim, Mee-Hyun Lee, and Zigang Dong. 2019. "(S)-10-Hydroxycamptothecin Inhibits Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma Growth In Vitro and In Vivo Via Decreasing Topoisomerase I Enzyme Activity" Cancers 11, no. 12: 1964. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers11121964
APA StyleSong, M., Yin, S., Zhao, R., Liu, K., Kundu, J. K., Shim, J. -H., Lee, M. -H., & Dong, Z. (2019). (S)-10-Hydroxycamptothecin Inhibits Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma Growth In Vitro and In Vivo Via Decreasing Topoisomerase I Enzyme Activity. Cancers, 11(12), 1964. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers11121964