Targeting Tissue Factor to Tumor Vasculature to Induce Tumor Infarction
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Brief Introduction on Tissue Factor (TF) in Cancer
1.1. TF and Tumor Biology beyond Coagulation
1.2. TF as a Target for Tumor Therapy
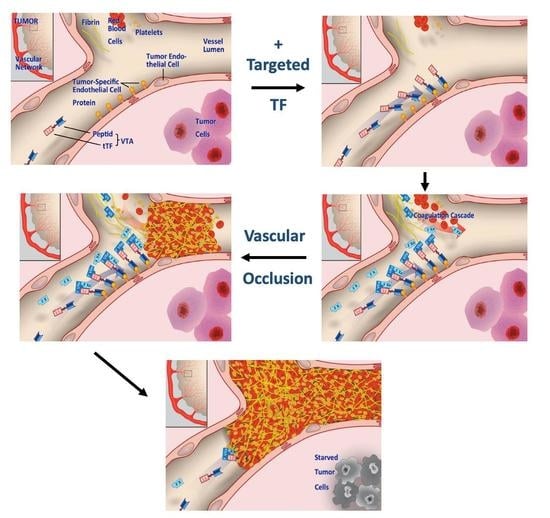
2. Re-Targeting TF to Tumors as Experimental Cancer Therapy
2.1. Major Histocompatibility Complex Class II (MHC II) Antigens
2.2. Vascular Adhesion Molecule-1 (VCAM-1, CD106)
2.3. ED-B Domain of Fibronectin
2.4. Prostate-Specific Membrane Antigen (PSMA)
2.5. Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Receptors (VEGFR) and Co-Receptors
2.6. Integrins
2.7. Fibroblast Activation Protein (FAP)
2.8. NG2 Proteoglycan on Angiogenic Pericytes
2.9. Microthrombus-Associated Fibrin-Fibronectin Complexes
2.10. Acidic Tumor Endothelium
3. Re-Targeting TF to Tumors—Non-Clinical Results and Translation into the Clinic
3.1. CD13, Aminopeptidase N
3.1.1. Non-Clinical Pharmacodynamic Data with tTF-NGR
3.1.2. Translational Considerations and Non-Clinical Safety and Pharmacokinetic Data for tTF-NGR
3.1.3. Clinical Data—Phase I Trial with tTF-NGR in Cancer Patients
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
6. Patents
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cimmino, G.; Ciccarelli, G.; Golino, P. Role of tissue factor in the coagulation network. Semin. Thromb. Hemost. 2015, 41, 708–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Sim, M.M.S.; Wood, J.P.A. Recent insights Into the regulation of coagulation and thrombosis. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2020, 40, e119–e125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campello, E.; Henderson, M.W.; Noubouossie, D.F.; Simioni, P.; Key, N.S. Contact system activation and cancer: New insights in the pathophysiology of cancer associated thrombosis. Thromb. Haemost. 2018, 118, 251–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ruf, W.; Rothmeier, A.S.; Graf, C. Targeting clotting proteins in cancer therapy—Progress and challenges. Thromb. Res. 2016, 140, S1–S7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khorana, A.A.; Connolly, G.C. Assessing risk of venous thromboembolism in the patient with cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2009, 27, 4839–4847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khorana, A.A.; Culakova, F.E.; Kuderer, N.M.; Lyman, G.L. Thromboembolism is a leading cause of death in cancer patients receiving outpatient chemotherapy. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2007, 5, 632–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khorana, A.A.; Kamphuisen, P.W.; Meyer, G.; Bauersachs, R.; Janas, M.S.; Jarner, M.F.; Lee, A.Y.Y. Tissue factor as a predictor of recurrent venous thromboembolism in malignancy: Biomarker analyses of the CATCH trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 35, 1078–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rondon, A.M.R.; Kroone, C.; Kapteijn, M.Y.; Versteeg, H.H.; Buijs, J.T. Role of tissue factor in tumor progression and cancer-associated thrombosis. Semin. Thromb. Hemost. 2019, 45, 396–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Versteeg, H.H. Tissue factor: Old and new links with cancer biology. Semin. Thromb. Hemost. 2015, 41, 747–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mueller, B.M.; Reisfeld, R.; Edgington, T.S.; Ruf, W. Expression of tissue factor by melanoma cells promotes efficient hematogenous metastasis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1992, 89, 11832–11836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Van den Berg, Y.W.; Osanto, S.; Reitsma, P.H.; Versteeg, H.H. The relationship between tissue factor and cancer progression: Insights from bench and bedside. Blood 2012, 119, 924–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bourcy, M.; Suarez-Carmona, M.; Lambert, J.; Francart, M.-E.; Schroeder, H.; Delierneux, C.; Skrypek, N.; Thompson, E.W.; Jérusalem, G.; Berx, G.; et al. Tissue factor induced by epithelial–mesenchymal transition triggers a procoagulant state that drives metastasis of circulating tumor cells. Cancer Res. 2016, 76, 4270–4282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bromberg, M.E.; Konigsberg, W.H.; Madison, J.F.; Pawashe, A.; Garen, A. Tissue factor promotes melanoma metastasis by a pathway independent of blood coagulation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1995, 92, 8205–8209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Versteeg, H.H.; Schaffner, F.; Kerver, M.; Petersen, H.H.; Ahamed, J.; Felding-Habermann, B.; Takada, Y.; Mueller, B.M.; Ruf, W. Inhibition of tissue factor signaling suppresses tumor growth. Blood 2008, 111, 190–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liang, H.P.H.; Kerschen, E.J.; Hernandez, I.; Basu, S.; Zogg, M.; Botros, F.; Jia, S.; Hessner, M.J.; Griffin, J.H.; Ruf, W.; et al. EPCR-dependent PAR2 activation by the blood coagulation initiation complex regulates LPS-triggered interferon responses in mice. Blood 2015, 125, 2845–2854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Graf, C.; Wilgenbus, P.; Pagel, S.; Pott, J.; Marini, F.; Reyda, S.; Kitano, M.; Macher-Göppinger, S.; Weller, H.; Ruf, W. Myeloid cell–synthesized coagulation factor X dampens antitumor immunity. Sci. Immunol. 2019, 4, eaaw8405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patry, G.; Hovington, H.; Larue, H.; Harel, F.; Fradet, Y.; Lacombe, L. Tissue factor expression correlates with disease-specific survival in patients with node-negative muscle-invasive bladder cancer. Int. J. Cancer 2008, 122, 1592–1597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nitori, N.; Ino, Y.; Nakanishi, Y.; Yamada, T.; Honda, K.; Yanagihara, K.; Kosuge, T.; Kanai, Y.; Kitajima, M.; Hirohashi, S. Prognostic significance of tissue factor in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2005, 11, 2531–2539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Breij, E.C.W.; de Goeij, B.E.C.G.; Verploegen, S.; Schuurhuis, D.H.; Amirkhosravi, A.; Francis, J.; Breinholt-Miller, V.; Houtkamp, M.; Bleeker, W.K.; Satijn, D.; et al. An antibody–drug conjugate that targets tissue factor exhibits potent therapeutic activity against a broad range of solid tumors. Cancer Res. 2013, 74, 1214–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hu, Z.; Shen, R.; Campbell, A.; McMichael, E.; Yu, L.; Ramaswamy, B.; London, C.A.; Xu, T.; Carson, W.E., III. Targeting tissue factor for immunotherapy of triple-negative breast cancer using a second-generation ICON. Cancer Immunol. Res. 2018, 6, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, B.; Berger, M.; Masters, G.; Albone, E.; Yang, Q.; Sheedy, J.; Kirksey, Y.; Grimm, L.; Wang, B.; Singleton, J.; et al. Radiotherapy of human xenograft NSCLC tumors in nude mice with a 90 Y-labeled anti-tissue factor antibody. Cancer Biother. Radiopharm. 2005, 20, 300–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Z.; Rao, B.; Chen, S.; Duanmu, J. Targeting tissue factor on tumor cells and angiogenic vascular endothelial cells by factor VII-targeted verteporfin photodynamic therapy for breast cancer in vitro and in vivo in mice. BMC Cancer 2010, 10, 235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hu, Z.; Rao, B.; Chen, S.; Duanmu, J. Selective and effective killing of angiogenic vascular endothelial cells and cancer cells by targeting tissue factor using a factor VII-targeted photodynamic therapy for breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2011, 126, 589–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De Bono, J.S.; Concin, N.; Hong, D.S.; Thistlethwaite, F.C.; Machiels, J.-P.; Arkenau, H.-T.; Plummer, R.; Jones, R.H.; Nielsen, D.; Windfeld, K.; et al. Tisotumab vedotin in patients with advanced or metastatic solid tumours (InnovaTV 201): A first-in-human, multicentre, phase 1–2 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2019, 20, 383–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Folkman, J. Tumor angiogenesis: Therapeutic implications. N. Engl. J. Med. 1971, 285, 1182–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denekamp, J. Endothelial cell proliferation as a novel approach to targeting tumour therapy. Br. J. Cancer 1982, 45, 136–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Denekamp, J. Vascular attack as a therapeutic strategy for cancer. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 1990, 9, 267–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Molema, G.; King, S.; Watkins, L.; Edgington, T.S.; Thorpe, P.E. Tumor infarction in mice by antibody-directed targeting of tissue factor to tumor vasculature. Science 1997, 275, 547–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ran, S.; Gao, B.; Duffy, S.; Watkins, L.; Rote, N.; Thorpe, P.E. Infarction of solid Hodgkin´s tumors in mice by antibody-directed targeting of tissue factor to tumor vasculature. Cancer Res. 1998, 58, 4646–4653. [Google Scholar]
- Gottstein, C.; Wels, W.; Ober, B.; Thorpe, P.E. Generation and characterization of recombinant vascular targeting agents from hybridoma cell lines. BioTechniques 2001, 30, 190–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dienst, A.; Grunow, A.; Unruh, M.; Rabausch, B.; Nör, J.E.; Fries, J.W.U.; Gottstein, C. Specific occlusion of murine and human tumor vasculature by VCAM-1–targeted recombinant fusion proteins. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2005, 97, 733–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Neri, D.; Bicknell, R. Tumour vascular targeting. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2005, 5, 436–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nilsson, F.; Kosmehl, H.; Zardi, L.; Neri, D. Targeted delivery of tissue factor to the ED-B domain of fibronectin, a marker of angiogenesis, mediates the infarction of solid tumors in mice. Cancer Res. 2001, 61, 711–716. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Huang, H.; Donate, F.; Dickinson, C.; Santucci, R.; El-Sheikh, A.; Vessela, R.; Edgington, T.S. Prostate-specific membrane antigen directed selective thrombotic infarction of tumors. Cancer Res. 2002, 62, 5470–5475. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- El-Sheikh, A.; Borgstrom, P.; Bhattacharjee, G.; Belting, M.; Edgington, T.S. A selective tumor microvasculature thrombogen that targets a novel receptor complex in the tumor angiogenic microenvironment. Cancer Res. 2005, 65, 11109–11117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lv, S.; Ye, M.; Wang, X.; Li, Z.; Chen, X.; Dou, X.; Dai, Y.; Zeng, F.; Luo, L.; Wang, C.; et al. A recombinant fusion protein SP5.2/tTF induces thrombosis in tumor blood vessels. Neoplasma 2015, 62, 531–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xu, P.; Zou, M.; Wang, S.; Li, T.; Liu, C.; Wang, L.; Wang, L.; Luo, F.; Wu, T.; Yan, J. Construction and characterization of a truncated tissue factor-coagulation-based composite system for selective thrombosis in tumor blood vessels. Int. J. Oncol. 2019, 55, 823–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zou, M.; Samiullah, M.; Xu, P.; Wang, S.; He, J.; Wu, T.; Luo, F.; Yan, J. Construction of a novel procoagulant protein targeting neuropilin-1 on tumour vasculature for tumour embolization therapy. J. Drug Target. 2019, 27, 885–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pasqualini, R.; Ruoshlathi, E. Organ targeting in vivo using phage display peptide libraries. Nature 1996, 380, 364–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koivunen, E.; Gay, D.A.; Ruoslahti, E. Selection of peptides binding to the α5β1 integrin from phage display library. J. Biol. Chem. 1993, 268, 20205–20210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koivunen, E.; Wang, B.; Ruoslahti, E. Phage libraries displaying cyclic peptides with different ring sizes: Ligand specificities of the RGD-directed integrins. Biotechnology 1995, 13, 265–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasqualini, R.; Koivunen, E.; Ruoslahti, E. Alpha v integrins as receptors for tumor targeting by circulating ligands. Nat. Biotechnol. 1997, 15, 542–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arap, W.; Pasqualini, R.; Ruoslahti, E. Cancer treatment by targeted drug delivery to tumor vasculature in a mouse model. Science 1998, 279, 377–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hu, P.; Yan, J.; Sharifi, J.; Bai, T.; Khawli, L.A.; Epstein, A.L. Comparison of three different targeted tissue factor fusion proteins for inducing tumor vessel thrombosis. Cancer Res. 2003, 63, 5046–5053. [Google Scholar]
- Epstein, A.L.; Chen, F.-M.; Taylor, C.R. A novel method for the detection of necrotic lesions in human cancers. Cancer Res. 1988, 48, 5842–5848. [Google Scholar]
- Hornick, J.L.; Sharifi, J.; Khawli, L.A.; Hu, P.; Biela, B.H.; Mizokami, M.M.; Yun, A.; Taylor, C.R.; Epstein, A.L. A new chemically modified chimeric TNT-3 monoclonal antibody directed against DNA for the radioimmunotherapy of solid tumors. Cancer Biother. Radiopharm. 1998, 13, 255–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Epstein, A.L.; Khawli, L.A.; Hornick, J.L.; Taylor, C.R. Identification of a monoclonal antibody, TV-1, directed against the basement membrane of tumor vessels, and its use to enhance the delivery of macromolecules to tumors after conjugation with interleukin 2. Cancer Res. 1995, 55, 2673–2680. [Google Scholar]
- Kessler, T.; Bieker, R.; Padró, T.; Schwöppe, C.; Persigehl, T.; Bremer, C.; Kreuter, M.; Berdel, W.E.; Mesters, R.M. Inhibition of tumor growth by RGD peptide-directed delivery of truncated tissue factor to the tumor vasculature. Clin. Cancer Res. 2005, 11, 6317–6324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Banner, D.W.; D’Arcy, A.; Chène, C.; Winkler, F.K.; Guha, A.; Konigsberg, W.H.; Nemerson, Y.; Kirchhofer, D. The crystal structure of the complex of blood coagulation factor VIIa with soluble tissue factor. Nature 1996, 380, 41–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rippmann, J.F.; Pfizenmaier, K.; Mattes, R.; Rettig, W.J.; Moosmayer, D. Fusion of the tissue factor extracellular domain to a tumor stroma specific single-chain fragment variable antibody results in an antigen-specific coagulation-promoting molecule. Biochem. J. 2000, 349, 805–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Brand, C.; Schliemann, C.; Ring, J.; Kessler, T.; Bäumer, S.; Angenendt, L.; Mantke, V.; Ross, R.; Hintelmann, H.; Spieker, T.; et al. NG2 proteoglycan as a pericyte target for anticancer therapy by tumor vessel infarction with retargeted tissue factor. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 6774–6789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Simberg, D.; Duza, T.; Park, J.H.; Essler, M.; Pilch, J.; Zhang, L.; Derfus, A.M.; Yang, M.; Hoffman, R.M.; Bhatia, S.; et al. Biomimetic amplification of nanoparticle homing to tumors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 932–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, Z.; Qutaish, M.; Han, Z.; Schur, R.M.; Liu, Y.; Wilson, D.L.; Lu, Z.R. MRI detection of breast cancer micrometastases with a fibronectin-targeting contrast agent. Nat. Commun. 2005, 6, 7984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shi, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, S.; Liu, G.; Xu, J.; Zhao, X.; Anderson, G.J.; Nie, G.; Li, S. Specific tissue factor delivery using a tumor-homing peptide for inducing tumor infarction. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2018, 156, 501–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Tian, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Su, S.; Wang, J.; Wu, M.; Shi, Q.; Anderson, G.J.; Thomsen, J.; et al. pHLIP-mediated targeting of truncated tissue factor to tumor vessels causes vascular occlusion and impairs tumor growth. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 23523–23532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pasqualini, R.; Koivunen, E.; Kain, R.; Lahdenranta, J.; Sakamoto, M.; Stryhn, A.; Ashmun, R.A.; Shapiro, L.H.; Arap, W.; Ruoshlahti, E. Aminopeptidase N is a receptor for tumor-homing peptides and a target for inhibiting angiogenesis. Cancer Res. 2000, 60, 722–727. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Curnis, F.; Arrigoni, G.; Sacchi, A.; Fischetti, L.; Arap, W.; Pasqualini, R.; Corti, A. Differential binding of drugs containing the NGR motif to CD13 isoforms in tumor vessels, epithelia, and myeloid cells. Cancer Res. 2002, 62, 867–874. [Google Scholar]
- Wickström, M.; Larsson, R.; Nygren, P.; Gullbo, J. Aminopeptidase N (CD13) as a target for cancer chemotherapy. Cancer Sci. 2011, 102, 501–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guzman-Rojas, L.; Rangel, R.; Salameh, A.; Edwards, J.K.; Dondossola, E.; Kim, Y.G.; Saghatelian, A.; Giordano, R.J.; Kolonin, M.G.; Staquicini, F.I.; et al. Cooperative effects of aminopeptidase N (CD13) expressed by nonmalignant and cancer cells within the tumor microenvironment. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 1637–1642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tokuhara, T.; Hattori, N.; Ishida, H.; Hirai, T.; Higashiyama, M.; Kodama, K.; Miyake, M. Clinical significance of aminopeptidase N in non-small cell lung cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2006, 12, 3971–3978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ikeda, N.; Nakajima, Y.; Tokuhara, T.; Hattori, N.; Sho, M.; Kanehiro, H.; Miyake, M. Clinical significance of aminopeptidase N/CD13 expression in human pancreatic carcinoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2003, 9, 1503–1508. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hashida, H.; Takabayashi, A.; Kanai, M.; Adachi, M.; Kondo, K.; Kohno, N.; Yamaoka, Y.; Miyake, M. Aminopeptidase N is involved in cell motility and angiogenesis: Its clinical significance in human colon cancer. Gastroenterology 2002, 122, 376–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, L.H.; Brand, C.; Stucke-Ring, J.; Schliemann, C.; Kessler, T.; Harrach, S.; Mohr, M.; Görlich, D.; Marra, A.; Hillejan, L.; et al. Potential therapeutic impact of CD13 expression in non-small cell lung cancer. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0177146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Surowiak, P.; Drag, M.; Materna, V.; Suchocki, S.; Grzywa, R.; Spaczynski, M.; Dietel, M.; Oleksyszyn, J.; Zabel, M.; Lage, H. Expression of aminopeptidase N/CD13 in human ovarian cancers. Int. J. Gynecol. Cancer 2006, 16, 1783–1788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, L.H.; Stucke-Ring, J.; Brand, C.; Schliemann, C.; Harrach, S.; Muley, T.; Herpel, E.; Kessler, T.; Mohr, M.; Görlich, D.; et al. CD13 as target for tissue factor induced tumor vascular infarction in small cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer 2017, 113, 121–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kessler, T.; Baumeier, A.; Brand, C.; Grau, M.; Angenendt, L.; Harrach, S.; Stalmann, U.; Schmidt, L.H.; Gosheger, G.; Hardes, J.; et al. Aminopeptidase N (CD13): Expression, prognostic impact, and use as therapeutic target for tissue factor induced tumor vascular infarction in soft tissue sarcoma. Transl. Oncol. 2018, 11, 1271–1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Persigehl, T.; Bieker, R.; Matuszewski, L.; Wall, A.; Kessler, T.; Kooijman, H.; Meier, N.; Ebert, W.; Berdel, W.E.; Heindel, W.; et al. Antiangiogenic tumor treatment: Early noninvasive monitoring with USPIO-enhanced MR imaging in mice. Radiology 2007, 244, 449–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Persigehl, T.; Matuszewski, L.; Kessler, T.; Wall, A.; Meier, N.; Ebert, W.; Berdel, W.E.; Heindel, W.; Mesters, R.; Bremer, C. Prediction of antiangiogenic treatment efficacy by iron oxide enhanced parametric magnetic resonance imaging. Investig. Radiol. 2007, 42, 791–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kessler, T.; Schwöppe, C.; Liersch, R.; Schliemann, C.; Hintelmann, H.; Bieker, R.; Berdel, W.E.; Mesters, R.M. Generation of fusion proteins for selective occlusion of tumor vessels. Curr. Drug Discov. Technol. 2008, 5, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bieker, R.; Kessler, T.; Schwöppe, C.; Padro, T.; Persigehl, T.; Bremer, C.; Dreischalück, J.; Kolkmeyer, A.; Heindel, W.; Mesters, R.M.; et al. Infarction of tumor vessels by NGR-peptide directed targeting of tissue factor. Experimental results and first-in-man experience. Blood 2009, 113, 5019–5027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schwöppe, C.; Kessler, T.; Persigehl, T.; Liersch, R.; Hintelmann, H.; Dreischalück, J.; Ring, J.; Bremer, C.; Heindel, W.; Mesters, R.M.; et al. Tissue-factor fusion proteins induce occlusion of tumor vessels. Thromb. Res. 2010, 125, S143–S150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dreischalück, J.; Schwöppe, C.; Spieker, T.; Kessler, T.; Tiemann, K.; Liersch, R.; Schliemann, C.; Kreuter, M.; Kolkmeyer, A.; Hintelmann, H.; et al. Vascular infarction by subcutaneous application of tissue factor targeted to tumor vessels with NGR-peptides: Activity and toxicity profile. Int. J. Oncol. 2010, 37, 1389–1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Von Maltzahn, G.; Park, J.-H.; Lin, K.Y.-M.; Singh, N.; Schwöppe, C.; Mesters, R.M.; Berdel, W.E.; Ruoslahti, E.; Sailor, M.J.; Bhatia, S.N. Nanoparticles that communicate in vivo to amplify tumour targeting. Nat. Mater. 2011, 10, 545–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brand, C.; Dencks, S.; Schmitz, G.; Mühlmeister, M.; Stypmann, J.; Ross, R.; Hintelmann, H.; Schliemann, C.; Müller-Tidow, C.; Mesters, R.M.; et al. Low-energy ultrasound treatment improves regional tumor vessel infarction by retargeted tissue factor. J. Ultrasound Med. 2015, 34, 1227–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Persigehl, T.; Ring, J.; Bremer, C.; Heindel, W.; Holtmeier, R.; Stypmann, J.; Claesener, M.; Hermann, S.; Schäfers, M.; Zerbst, C.; et al. Non-invasive monitoring of tumor-vessel infarction by retargeted truncated tissue factor tTF-NGR using multi-modal imaging. Angiogenesis 2014, 17, 235–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwöppe, C.; Zerbst, C.; Fröhlich, M.; Schliemann, C.; Kessler, T.; Liersch, R.; Overkamp, L.; Holtmeier, R.; Stypmann, J.; Dreiling, A.; et al. Anticancer therapy by tumor vessel infarction with polyethylene glycol conjugated retargeted tissue factor. J. Med. Chem. 2013, 56, 2337–2347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brand, C.; Fröhlich, M.; Ring, J.; Schliemann, C.; Kessler, T.; Mantke, V.; König, S.; Lücke, M.; Mesters, R.M.; Berdel, W.E.; et al. Tumor growth inhibition via occlusion of tumor vasculature induced by N-terminally PEGylated retargeted tissue factor tTF-NGR. Mol. Pharm. 2015, 12, 3749–3758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwöppe, C.; Hintelmann, H.; Mesters, R.M.; Berdel, W.E.; König, S. Using native gel electrophoresis or isoelectric focusing as experimental “clock” for the (iso)aspartate formation of tTF-NGR fusion proteins. Biomacromol. Mass Spectrom. 2012, 2, 285–293. [Google Scholar]
- Stucke-Ring, J.; Ronnacker, J.; Brand, C.; Höltke, C.; Schliemann, C.; Kessler, T.; Schmidt, L.H.; Harrach, S.; Mantke, V.; Hintelmann, H.; et al. Combinatorial effects of doxorubicin and retargeted tissue factor by intratumoral entrapment of doxorubicin and proapoptotic increase of tumor vascular infarction. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 82458–82472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Höink, A.; Persigehl, T.; Kwiecien, R.; Balthasar, M.; Mesters, R.; Berdel, W.E.; Heindel, W.; Bremer, C.; Schwöppe, C. Gadofosveset-enhanced MRI as simple surrogate parameter for real-time evaluation of the initial tumour vessel infarction by retargeted tissue factor tTF-NGR. Oncol. Lett. 2019, 17, 270–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Brand, C.; Greve, B.; Bölling, T.; Eich, H.T.; Willich, N.; Harrach, S.; Hintelmann, H.; Lenz, G.; Mesters, R.M.; Kessler, T.; et al. Radiation synergizes with antitumor activity of CD13-targeted tissue factor in a HT1080 xenograft model of human soft tissue sarcoma. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0229271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neuenschwander, P.F.; Morrissey, J.H. Deletion of the membrane anchoring region of tissue factor abolishes autoactivation of factor VII but not cofactor function. J. Biol. Chem. 1992, 267, 14477–14482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morrissey, J.H.; Macik, B.G.; Neuenschwander, P.F.; Comb, P.C. Quantitation of activated factor VII levels in plasma using a tissue factor mutant selectively deficient in promoting factor VII activation. Blood 1993, 81, 734–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bogdanov, V.Y.; Balasubramanian, V.; Hathcock, J.; Vele, O.; Lieb, M.; Nemerson, Y. Alternatively spliced human tissue factor: A circulating, soluble, thrombogenic protein. Nat. Med. 2003, 9, 458–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The Human Protein Atlas. Available online: http://www.proteinatlas.org/ENSG00000166825-ANPEP/tissue (accessed on 26 November 2020).
- Berdel, W.E.; Harrach, S.; Brand, C.; Brömmel, K.; Berdel, A.F.; Hintelmann, H.; Schliemann, C.; Schwöppe, C. Animal safety, toxicology, and pharmacokinetic studies according to the ICH S9 guideline for a novel fusion protein tTF-NGR targeting procoagulatory activity into tumor vasculature: Are results predictive for humans? Cancers 2020, 12, 3536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerwing, M.; Herrmann, K.; Helfen, A.; Schliemann, C.; Berdel, W.E.; Eisenblätter, M.; Wildgruber, M. The beginning of the end for conventional RECIST—Novel therapies require novel imaging approaches. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 16, 442–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schliemann, C.; Gerwing, M.; Heinzow, H.S.; Harrach, S.; Schwöppe, C.; Wildgruber, M.; Hansmeier, A.A.; Angenendt, L.; Berdel, A.F.; Stalmann, U.; et al. First-in-class CD13-targeted tissue factor tTF-NGR in patients with recurrent or refractory malignant tumors: Results of a phase I dose-escalation study. Cancers 2020, 12, 1488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhagwat, S.V.; Lahdenranta, J.; Giordano, R.; Arap, W.; Pasqualini, R.; Shapiro, L.H. CD13/APN is activated by angiogenic signals and is essential for capillary tube formation. Blood 2001, 97, 652–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liang, W.; Gao, B.; Xu, G.; Weng, D.; Xie, M.; Quian, Y. Possible contribution of aminopeptidase N (APN/CD13) to migration and invasion of human osteosarcoma cell lines. Int. J. Oncol. 2014, 45, 2475–2485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Corti, A.; Curnis, F.; Rossoni, G.; Marcucci, F.; Gregorc, V. Peptide-mediated targeting of cytokines to tumor vasculature: The NGR-hTNF example. BioDrugs 2013, 27, 591–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gregorc, V.; Zucali, P.A.; Santoro, A.; Ceresoli, G.L.; Citterio, G.; de Pas, T.M.; Zilembo, N.; de Vincenzo, F.; Simonelli, M.; Rossoni, G.; et al. Phase II study of asparagine-glycine-arginine-human tumor necrosis factor alpha, a selective vascular targeting agent, in previously treated patients with malignant pleural mesothelioma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2010, 28, 2604–2611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferreri, A.J.M.; Calimeri, T.; Conte, G.M.; Cattaneo, D.; Fallanca, F.; Ponzoni, M.; Scarano, E.; Curnis, F.; Nonis, A.; Lopedote, P.; et al. R-CHOP preceded by blood-brain barrier permeabilization with engineered tumor necrosis factor-alpha in primary CNS lymphoma. Blood 2019, 134, 252–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bauvois, B.; Dauzonne, D. Aminopeptidase-N/CD13 (EC 3.4.11.2) inhibitors: Chemistry, biological evaluations, and therapeutic prospects. Med. Res. Rev. 2006, 26, 88–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ichinose, Y.; Genka, K.; Koike, T.; Kato, H.; Watanabe, Y.; Mori, T.; Iioka, S.; Sakuma, A.; Ohta, M. Randomized double-blind placebo controlled trial of bestatin in patients with resected stage I squamous-cell cancer. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2003, 95, 605–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Faintuch, B.L.; Oliveira, E.A.; Targino, R.C.; Moro, A.M. Radiolabeled NGR phage display peptide sequence for tumor targeting. Appl. Radiat. Lsot. 2014, 86, 41–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.-W.; Kim, W.H.; Kim, M.H.; Kim, C.G. Synthesis and evaluation of novel Tc-99m labeled NGR-containig hexapeptides as tumor imaging agents. J. Label. Compd. Radiopharm. 2015, 58, 30–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Wang, X.; Zong, S.; Wang, J.; Conti, P.S.; Chen, K. MicroPET imaging of CD13 expression using a 64 Cu-labeled dimeric NGR peptide based on sacophagine cage. Mol. Pharm. 2014, 11, 3938–3946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mate, G.; Kertesz, I.; Enyedi, K.N.; Mezö, G.; Angyal, J.; Vasas, N.; Kis, A.; Szabo, E.; Emri, M.; Biro, T.; et al. In vivo imaging of aminopeptidase N (CD13) receptors in experimental renal tumors using the novel radiotracer 68 Ga-NOTA-c(NGR). Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2015, 69, 61–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Oostendorp, M.; Douma, K.; Hackeng, T.M.; Dirksen, A.; Post, M.J.; van Zandvoort, M.A.M.J.; Backes, W.H. Quantitative molecular magnetic resonance imaging of tumor angiogenesis using cNGR-labeled paramagnetic quantum dots. Cancer Res. 2008, 68, 7676–7683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Corti, A.; Curnis, F.; Arap, W.; Pasqualini, R. The neovasculature homing motif NGR: More than meets the eye. Blood 2008, 112, 2628–2635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Curnis, F.; Longhi, R.; Crippa, L.; Cattaneo, A.; Dondossola, E.; Bachi, A.; Corti, A. Spontaneous formation of L-isoaspartate and gain of function in fibronectin. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 36466–36476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Brooks, P.C.; Clark, R.A.; Cheresh, D.A. Requirement of vascular Integrin alpha V beta 3 for angiogenesis. Science 1994, 264, 569–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corti, A.; Gasparri, A.M.; Sacchi, A.; Colombo, B.; Monieri, M.; Rrapaj, E.; Ferreri, A.J.M.; Curnis, F. NGR-TNF engineering with an N-terminal serine reduces degradation and post-translational modifications and improves its tumor-targeting activity. Mol. Pharm. 2020, 17, 3813–3824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Philipp, J.; Dienst, A.; Unruh, M.; Wagener, A.; Grunow, A.; Engert, A.; Fries, J.W.U.; Gottstein, C. Soluble tissue factor induces coagulation on tumor endothelial cells in vivo if coadministered with low-dose lipopolysaccharides. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2003, 23, 905–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tu, J.; Hu, Z.; Chen, Z. A combination of radiosurgery and soluble tissue factor enhances vascular targeting for experimental glioblastoma. BioMed Res. Internat. 2013, 2013, 390714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guba, M.; Yezhelyev, M.; Eichhorn, M.E.; Schmid, G.; Ischenko, I.; Papyan, A.; Graeb, C.; Seliger, H.; Geissler, E.K.; Jauch, K.-W.; et al. Rapamycin induces tumor-specific thrombosis via tissue factor in the presence of VEGF. Blood 2005, 105, 4463–4469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Jiang, Q.; Liu, S.; Zhang, Y.; Tiang, Y.; Song, C.; Wang, J.; Zou, Y.; Anderson, G.J.; Han, J.-Y.; et al. A DNA nanorobot functions as a cancer therapeutic in response to a molecular trigger in vivo. Nat. Biotech. 2018, 36, 258–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Zhang, Y.; Ho, S.-H.; Li, B.; Wang, M.; Deng, X.; Yang, N.; Liu, G.; Lu, Z.; Xu, J.; et al. Combination of tumour-infarction therapy and chemotherapy via the co-delivery of doxorubicin and thrombin encapsulated in tumour-targeted nanoparticles. Nat. Biomed. Eng. 2020, 4, 732–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seidi, K.; Jahanban-Esfahlan, R.; Monhemi, H.; Zare, P.; Minofar, B.; Adli, A.D.F.; Farajzadeh, D.; Behzadi, R.; Abbasi, M.M.; Neubauer, H.A.; et al. NGR (Asn-Gly-Arg)-targeted delivery of coagulase to tumor vasculature arrests cancer cell growth. Oncogene 2018, 37, 3967–3980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teicher, B.A. Flipping the wound that doesn´t heal: The upside of coagulation in cancer. Blood 2009, 113, 4827–4828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]




| Xenograft Model (Cell Line/ Mouse Strain nu/nu) | Histology (Human) | No. of Experim. with ≥ 5 Mice/Group | Therapeutic Effect a (+/−) | Imaging Effect b (+/−) |
| A549/BALB-c | lung adenocarcinoma | 1 | + | n.e. |
| A549/CD-1 | lung adenocarcinoma | 3 | + (3x) | n.e. |
| HTB119/CD-1 | small-cell lung carcinoma | 2 | + (2x) | n.e. |
| HT1080/BALB-c | fibrosarcoma | 2 | + (2x) | + |
| HT1080/CD-1 | fibrosarcoma | 37 c | + (29x) | + |
| M21/BALB-c | melanoma | 6 | + (6x) | n.e. |
| M21/CD-1 | melanoma | 5 | + (4x) | n.e. |
| MCF-1/CD-1 | breast carcinoma | 1 | + | n.e. |
| MDA-MB-435/BALB-c | melanoma | 2 | + (2x) | + |
| SKBR3/CD-1 | breast carcinoma | 5 | + (4x) | + |
| U87/CD-1 | glioblastoma | 4 | + (4x) | + |
| Syngeneic Mouse Tumor Model (Cell Line/Mouse Strain) | Histology (Murine) | No. of Experim. with ≥ 5 Mice/Group | Therapeutic Effect a (+/−) | Imaging Effect b (+/−) |
| B-16/C57BL6 | melanoma | 2 | + (2x) d | + d |
| LLC/C57BL6 | lung carcinoma | 1 | (-) | n.e. |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Berdel, A.F.; Schwöppe, C.; Brand, C.; Harrach, S.; Brömmel, K.; Hintelmann, H.; Lenz, G.; Liersch, R.; Heinzow, H.; Schliemann, C.; et al. Targeting Tissue Factor to Tumor Vasculature to Induce Tumor Infarction. Cancers 2021, 13, 2841. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13112841
Berdel AF, Schwöppe C, Brand C, Harrach S, Brömmel K, Hintelmann H, Lenz G, Liersch R, Heinzow H, Schliemann C, et al. Targeting Tissue Factor to Tumor Vasculature to Induce Tumor Infarction. Cancers. 2021; 13(11):2841. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13112841
Chicago/Turabian StyleBerdel, Andrew F., Christian Schwöppe, Caroline Brand, Saliha Harrach, Kathrin Brömmel, Heike Hintelmann, Georg Lenz, Ruediger Liersch, Hauke Heinzow, Christoph Schliemann, and et al. 2021. "Targeting Tissue Factor to Tumor Vasculature to Induce Tumor Infarction" Cancers 13, no. 11: 2841. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13112841
APA StyleBerdel, A. F., Schwöppe, C., Brand, C., Harrach, S., Brömmel, K., Hintelmann, H., Lenz, G., Liersch, R., Heinzow, H., Schliemann, C., Mesters, R. M., Berdel, W. E., & Kessler, T. (2021). Targeting Tissue Factor to Tumor Vasculature to Induce Tumor Infarction. Cancers, 13(11), 2841. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13112841