Surgical Resection vs. Percutaneous Ablation for Single Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Exploring the Impact of Li-RADS Classification on Oncological Outcomes
Abstract
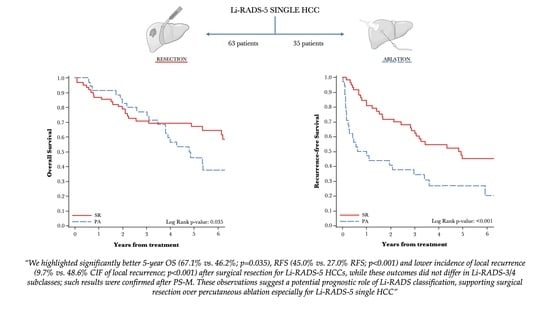
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Perioperative Management
2.3. Study Endopints
2.4. Statistical Analysis
2.5. Surgical Technique
2.6. Ablative Technique
3. Results
3.1. Patients and HCC Characteristics
3.2. Short-term Outcomes of PA and SR
3.3. Survival Analysis
3.4. Survival Analysis of Li-RADS Subclasses
3.5. Oncological Outcomes of PS-M Population
3.6. Pathological Analysis of Resected Specimens
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bray, F.; Ferlay, J.; Soerjomataram, I.; Siegel, R.L.; Torre, L.A.; Jemal, A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2018, 68, 394–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lafaro, K.J.; Demirjian, A.N.; Pawlik, T.M. Epidemiology of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Surg. Oncol. Clin. N. Am. 2015, 24, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gheorghe, G.; Stoian, A.P.; Gaman, M.-A.; Socea, B.; Neagu, T.P.; Stanescu, A.M.A.; Bratu, O.G.; Mischianu, D.L.D.; Suceveanu, A.I.; Diaconu, C.C. The Benefits and Risks of Antioxidant Treatment in Liver Diseases. Rev. Chim. 2019, 70, 651–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Association for the Study of the Liver. Electronic address eee, European Association for the Study of the L. EASL Clinical Practice Guidelines: Management of hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Hepatol. 2018, 69, 182–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Marrero, J.A.; Kulik, L.M.; Sirlin, C.B.; Zhu, A.X.; Finn, R.S.; Abecassis, M.M.; Roberts, L.R.; Heimbach, J.K. Diagnosis, Staging, and Management of Hepatocellular Carcinoma: 2018 Practice Guidance by the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases. Clin. Liver Dis. 2019, 13, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chernyak, V.; Fowler, K.J.; Kamaya, A.; Kielar, A.Z.; Elsayes, K.M.; Bashir, M.R.; Kono, Y.; Do, R.K.; Mitchell, D.G.; Singal, A.G.; et al. Liver Imaging Reporting and Data System (LI-RADS) Version 2018: Imaging of Hepatocellular Carcinoma in At-Risk Patients. Radiology 2018, 289, 816–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, E.S.-T.; Hall, G.; Yu, D.; Menard, A.; Hopman, W.; Nanji, S. Predictors and Cumulative Frequency of Hepatocellular Carcinoma in High and Intermediate LI-RADS Lesions: A Cohort Study from a Canadian Academic Institution. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2019, 26, 2560–2567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forner, A.; Reig, M.; Bruix, J. Hepatocellular carcinoma. Lancet 2018, 391, 1301–1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pompili, M.; Saviano, A.; de Matthaeis, N.; Cucchetti, A.; Ardito, F.; Federico, B.; Brunello, F.; Pinna, A.D.; Giorgio, A.; Giulini, S.M.; et al. Long-term effectiveness of resection and radiofrequency ablation for single hepatocellular carcinoma ≤3cm. Results of a multicenter Italian survey. J. Hepatol. 2013, 59, 89–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.-H.; Wang, C.-C.; Hung, C.-H.; Chen, C.-L.; Lu, S.-N. Survival comparison between surgical resection and radiofrequency ablation for patients in BCLC very early/early stage hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Hepatol. 2012, 56, 412–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.; Kang, T.W.; Cha, D.I.; Song, K.D.; Lee, M.W.; Rhim, H.; Lim, H.K.; Sinn, D.H.; Kim, J.M.; Kim, K. Radiofrequency ablation vs. surgery for perivascular hepatocellular carcinoma: Propensity score analyses of long-term outcomes. J. Hepatol. 2018, 69, 70–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, P.-H.; Hsu, C.-Y.; Hsia, C.-Y.; Lee, Y.-H.; Huang, Y.-H.; Chiou, Y.-Y.; Lin, H.-C.; Huo, T.-I. Surgical Resection Versus Radiofrequency Ablation for Single Hepatocellular Carcinoma ≤ 2 cm in a Propensity Score Model. Ann. Surg. 2016, 263, 538–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, K.; Yan, J.; Li, X.; Xia, F.; Ma, K.; Wang, S.; Bie, P.; Dong, J. A randomized controlled trial of radiofrequency ablation and surgical resection in the treatment of small hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Hepatol. 2012, 57, 794–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Sandro, S.; Sposito, C.; Lauterio, A.; Najjar, M.; Busset, M.D.D.; Buscemi, V.; Reyes, M.F.; De Carlis, R.; Mazzaferro, V.; De Carlis, L. Proposal of Prognostic Survival Models before and after Liver Resection for Hepatocellular Carcinoma in Potentially Transplantable Patients. J. Am. Coll. Surg. 2018, 226, 1147–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, Q.; Vitale, A.; Iesari, S.; Finkenstedt, A.; Mennini, G.; Spoletini, G.; Hoppe-Lotichius, M.; Vennarecci, G.; Manzia, T.M.; Nicolini, D.; et al. Intention-to-treat survival benefit of liver transplantation in patients with hepatocellular cancer. Hepatology 2017, 66, 1910–1919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Di Sandro, S.; Bagnardi, V.; Cucchetti, A.; Lauterio, A.; De Carlis, R.; Benuzzi, L.; Danieli, M.; Botta, F.; Centonze, L.; Najjar, M.; et al. From a Philosophical Framework to a Valid Prognostic Staging System of the New "Comprehensive Assessment" for Transplantable Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Cancers 2019, 11, 741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Von Elm, E.; Altman, D.G.; Egger, M.; Pocock, S.J.; Gøtzsche, P.C.; Vandenbroucke, J.P.; Initiative, F.T.S. The Strengthening the Reporting of Observational Studies in Epidemiology (STROBE) Statement: Guidelines for Reporting Observational Studies. PLoS Med. 2007, 4, 296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dindo, D.; Demartines, N.; Clavien, P.-A. Classification of Surgical Complications: A new proposal with evaluation in a cohort of 6336 patients and results of a survey. Ann. Surg. 2004, 240, 205–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slankamenac, K.; Graf, R.; Barkun, J.; Puhan, M.A.; Clavien, P.-A. The Comprehensive Complication Index. Ann. Surg. 2013, 258, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Koch, M.; Garden, O.J.; Padbury, R.; Rahbari, N.N.; Adam, R.; Capussotti, L.; Fan, S.T.; Yokoyama, Y.; Crawford, M.; Makuuchi, M.; et al. Bile leakage after hepatobiliary and pancreatic surgery: A definition and grading of severity by the International Study Group of Liver Surgery. Surgery 2011, 149, 680–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahbari, N.N.; Garden, O.J.; Padbury, R.; Brooke-Smith, M.; Crawford, M.; Adam, R.; Koch, M.; Makuuchi, M.; Dematteo, R.P.; Christophi, C.; et al. Posthepatectomy liver failure: A definition and grading by the International Study Group of Liver Surgery (ISGLS). Surgery 2011, 149, 713–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, A.C.Y.; Chan, S.C.; Chok, K.S.H.; Cheung, T.T.; Chiu, D.W.; Poon, R.T.P.; Fan, S.T.; Lo, C.M. Treatment strategy for recurrent hepatocellular carcinoma: Salvage transplantation, repeated resection, or radiofrequency ablation? Liver Transplant. 2013, 19, 411–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Sandro, S.; Bagnardi, V.; Najjar, M.; Buscemi, V.; Lauterio, A.; De Carlis, R.; Danieli, M.; Pinotti, E.; Benuzzi, L.; De Carlis, L. Minor laparoscopic liver resection for Hepatocellular Carcinoma is safer than minor open resection, especially for less compensated cirrhotic patients: Propensity score analysis. Surg. Oncol. 2018, 27, 722–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.-S.; Lim, H.K.; Rhim, H.; Lee, M.W.; Choi, D.; Lee, W.J.; Paik, S.W.; Koh, K.C.; Lee, J.H.; Choi, M.S.; et al. Ten-year outcomes of percutaneous radiofrequency ablation as first-line therapy of early hepatocellular carcinoma: Analysis of prognostic factors. J. Hepatol. 2013, 58, 89–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, T.W.; Kim, J.M.; Rhim, H.; Lee, M.W.; Kim, Y.-S.; Lim, H.K.; Choi, D.; Song, K.D.; Kwon, C.H.D.; Joh, J.-W.; et al. Small Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Radiofrequency Ablation versus Nonanatomic Resection—Propensity Score Analyses of Long-term Outcomes. Radiology 2015, 275, 908–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, G.C.; Ferrone, C.R.; Vagefi, P.A.; Uppot, R.N.; Tanabe, K.K.; Lillemoe, K.D.; Blaszkowsky, L.S.; Qadan, M. Surgical resection versus ablation for early-stage hepatocellular carcinoma: A retrospective cohort analysis. Am. J. Surg. 2019, 218, 157–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uhlig, J.; Sellers, C.M.; Stein, S.M.; Kim, H.S. Radiofrequency ablation versus surgical resection of hepatocellular carcinoma: Contemporary treatment trends and outcomes from the United States National Cancer Database. Eur. Radiol. 2018, 29, 2679–2689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vitale, A.; Peck-Radosavljevic, M.; Giannini, E.G.; Vibert, E.; Sieghart, W.; Van Poucke, S.; Pawlik, T.M. Personalized treatment of patients with very early hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Hepatol. 2017, 66, 412–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mulier, S.; Ni, Y.; Jamart, J.; Ruers, T.; Marchal, G.; Michel, L. Local Recurrence After Hepatic Radiofrequency Coagulation. Ann. Surg. 2005, 242, 158–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ito, T.; Tanaka, S.; Iwai, S.; Takemura, S.; Hagihara, A.; Uchida-Kobayashi, S.; Shinkawa, H.; Nishioka, T.; Kawada, N.; Kubo, S. Outcomes of laparoscopic hepatic resection versus percutaneous radiofrequency ablation for hepatocellular carcinoma located at the liver surface: A case-control study with propensity score matching. Hepatol. Res. 2015, 46, 565–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsuchiya, K.; Asahina, Y.; Tamaki, N.; Yasui, Y.; Hosokawa, T.; Ueda, K.; Nakanishi, H.; Itakura, J.; Kurosaki, M.; Enomoto, N.; et al. Risk factors for exceeding the Milan criteria after successful radiofrequency ablation in patients with early-stage hepatocellular carcinoma. Liver Transplant. 2013, 20, 291–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kutlu, O.C.; Chan, J.A.; Aloia, T.A.; Chun, Y.S.; Kaseb, A.O.; Passot, G.; Yamashita, S.; Vauthey, J.-N.; Conrad, C. Comparative effectiveness of first-line radiofrequency ablation versus surgical resection and transplantation for patients with early hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer 2017, 123, 1817–1827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, J.; Yan, L.; Cheng, Z.; Wu, H.; Du, L.; Wang, J.; Xu, Y.; Zeng, Y. A Randomized Trial Comparing Radiofrequency Ablation and Surgical Resection for HCC Conforming to the Milan Criteria. Ann. Surg. 2010, 252, 903–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Wang, Z.; Fu, S.; Li, A.; Pan, Z.; Zhou, W.; Lau, W.; Wu, M. Randomized clinical trial of chemoembolization plus radiofrequency ablation versus partial hepatectomy for hepatocellular carcinoma within the Milan criteria. Br. J. Surg. 2016, 103, 348–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kim, G.; Shim, J.H.; Kim, M.; Kim, S.Y.; Won, H.J.; Shin, Y.M.; Kim, P.N.; Kim, K.; Lee, S.; Lee, H.C. Radiofrequency ablation as an alternative to hepatic resection for single small hepatocellular carcinomas. Br. J. Surg. 2015, 103, 126–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, Y.; Chen, W.; Liang, X.; Li, D.; Lou, H.; Chen, R.; Wang, K.; Pan, H. Comparison of long-term effectiveness and complications of radiofrequency ablation with hepatectomy for small hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2014, 29, 193–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rössler, F.; Sapisochin, G.; Song, G.; Lin, Y.-H.; Simpson, M.A.; Hasegawa, K.; Laurenzi, A.; Cabús, S.S.; Nunez, M.I.; Gatti, A.; et al. Defining Benchmarks for Major Liver Surgery. Ann. Surg. 2016, 264, 492–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pompili, M.; Mirante, V.G.; Rondinara, G.; Fassati, L.R.; Piscaglia, F.; Agnes, S.; Covino, M.; Ravaioli, M.; Fagiuoli, S.; Gasbarrini, G.; et al. Percutaneous ablation procedures in cirrhotic patients with hepatocellular carcinoma submitted to liver transplantation: Assessment of efficacy at explant analysis and of safety for tumor recurrence. Liver Transplant. 2005, 11, 1117–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hori, T.; Nagata, K.; Hasuike, S.; Onaga, M.; Motoda, M.; Moriuchi, A.; Iwakiri, H.; Uto, H.; Kato, J.; Ido, A.; et al. Risk factors for the local recurrence of hepatocellular carcinoma after a single session of percutaneous radiofrequency ablation. J. Gastroenterol. 2003, 38, 977–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, T.W.; Lim, H.K.; Lee, M.W.; Kim, Y.-S.; Rhim, H.; Lee, W.J.; Paik, Y.H.; Kim, M.J.; Ahn, J.H. Long-term Therapeutic Outcomes of Radiofrequency Ablation for Subcapsular versus Nonsubcapsular Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Propensity Score Matched Study. Radiology 2016, 280, 300–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Teratani, T.; Yoshida, H.; Shiina, S.; Obi, S.; Sato, S.; Tateishi, R.; Mine, N.; Kondo, Y.; Kawabe, T.; Omata, M. Radiofrequency ablation for hepatocellular carcinoma in so-called high-risk locations. Hepatology 2006, 43, 1101–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komorizono, Y.; Oketani, M.; Sako, K.; Yamasaki, N.; Shibatou, T.; Maeda, M.; Kohara, K.; Shigenobu, S.; Ishibashi, K.; Arima, T. Risk factors for local recurrence of small hepatocellular carcinoma tumors after a single session, single application of percutaneous radiofrequency ablation. Cancer 2003, 97, 1253–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Li, Q.; Sun, Y.; Zheng, H.; Cui, Y.; Li, H.; Zhou, H.; Hao, X. Clinicopathologic features between multicentric occurence and intrahepatic metastasis of multiple hepatocellular carcinomas related to HBV. Surg. Oncol. 2009, 18, 25–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poon, R.T.-P.; Fan, S.-T.; Wong, J. Risk Factors, Prevention, and Management of Postoperative Recurrence After Resection of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Ann. Surg. 2000, 232, 10–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Bisceglie, A.M.; Sterling, R.K.; Chung, R.T.; Everhart, J.E.; Dienstag, J.L.; Bonkovsky, H.L.; Wright, E.C.; Everson, G.T.; Lindsay, K.L.; Lok, A.S.; et al. Serum alpha-fetoprotein levels in patients with advanced hepatitis C: Results from the HALT-C Trial. J. Hepatol. 2005, 43, 434–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cucchetti, A.; Piscaglia, F.; Caturelli, E.; Benvegnù, L.; Vivarelli, M.; Ercolani, G.; Cescon, M.; Ravaioli, M.; Grazi, G.L.; Bolondi, L.; et al. Comparison of Recurrence of Hepatocellular Carcinoma After Resection in Patients with Cirrhosis to Its Occurrence in a Surveilled Cirrhotic Population. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2008, 16, 413–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LaRoia, S.T.; Yadav, K.; Rastogi, A.; Kumar, G.; Kumar, S.; Sarin, S.K. Diagnostic efficacy of dynamic liver imaging using qualitative diagnostic algorithm versus LI-RADS v2018 lexicon for atypical versus classical HCC lesions: A decade of experience from a tertiary liver institute. Eur. J. Radiol. Open 2020, 7, 100219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Granata, V.; Fusco, R.; Setola, S.V.; Picone, C.; Vallone, P.; Belli, A.; Incollingo, P.; Albino, V.; Tatangelo, F.; Izzo, F.; et al. Microvascular invasion and grading in hepatocellular carcinoma: Correlation with major and ancillary features according to LIRADS. Abdom. Radiol. 2019, 44, 2788–2800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Variable | Level | Before Propensity Score | After Propensity Score | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SR (N = 86) | PA (N = 54) | p1 | SR (N = 25) | PA (N = 25) | p2 | ||
| Age (year), median (IQR) | 67 (62, 74) | 71 (59, 76) | 0.37 | 66 (62, 73) | 71 (59, 76) | 0.64 | |
| MELD score, median (IQR) | 8 (7, 9) | 9 (8, 10) | 0.071 | 8 (7, 9) | 10 (7, 11) | 0.062 | |
| PLT, median (IQR) | 159 (109, 229) | 98 (78, 139) | <0.001 | 126 (100, 159) | 106 (79, 171) | * | |
| ALT, median (IQR) | 36 (26, 73) | 43 (26, 86) | 0.51 | 30 (23, 56) | 49 (24, 91) | 0.31 | |
| INR, median (IQR) | 1.10 (1.04, 1.20) | 1.17 (1.10, 1.33) | 0.002 | 1.10 (1.06, 1.16) | 1.19 (1.06, 1.38) | 0.074 | |
| Bilirubin, median (IQR) | 0.71 (0.50, 1.03) | 0.92 (0.70, 1.28) | 0.013 | 1.03 (0.64, 1.19) | 0.82 (0.70, 1.13) | 0.98 | |
| Albumin, median (IQR) | 3.85 (3.42, 4.08) | 3.80 (3.43, 4.07) | 0.82 | 4.00 (3.49, 4.32) | 3.80 (3.52, 4.10) | 0.91 | |
| Nodule Size (mm), median (IQR) | 30 (24, 45) | 18 (15, 22) | <0.001 | 23 (20, 27) | 20 (17, 24) | * | |
| Sex, N (%) | Men | 71 (82.6) | 37 (68.5) | 0.086 | 17 (68.0) | 21 (84.0) | 0.32 |
| Women | 15 (17.4) | 17 (31.5) | 8 (32.0) | 4 (16.0) | |||
| Child score, N (%) | A | 66 (86.8) | 38 (79.2) | 0.38 | 21 (87.5) | 18 (75.0) | 0.46 |
| B | 10 (13.2) | 10 (20.8) | 3 (12.5) | 6 (25.0) | |||
| ALBI score, N (%) | Grade I | 35 (40.7) | 16 (32.7) | 0.40 | 11 (44.0) | 10 (40.0) | 1.00 |
| Grade II | 49 (57.0) | 30 (61.2) | 14 (56.0) | 14 (56.0) | |||
| Grade III | 2 (2.3) | 3 (6.1) | 0 (0.0) | 1 (4.0) | |||
| a-FP, N (%) | ≤5 | 24 (34.3) | 19 (39.6) | 0.81 | 9 (36.0) | 10 (40.0) | * |
| >5–22 | 27 (38.6) | 16 (33.3) | 9 (36.0) | 8 (32.0) | |||
| >22 | 19 (27.1) | 13 (27.1) | 7 (28.0) | 7 (28.0) | |||
| Presence of satellitosis, N (%) | No | 71 (82.6) | 51 (94.4) | 0.074 | 23 (92.0) | 23 (92.0) | * |
| Yes | 15 (17.4) | 3 (5.6) | 2 (8.0) | 2 (8.0) | |||
| Type of nodule, N (%) | Superficial | 45 (52.3) | 30 (55.6) | 0.71 | 18 (72.0) | 17 (68.0) | 0.76 |
| Deep | 41 (47.7) | 24 (44.4) | 7 (28.0) | 8 (32.0) | |||
| Li-RADS, N (%) | Li-RADS-3 | 8 (9.3) | 7 (13.0) | 0.56 | 5 (20.0) | 3 (12.0) | 0.68 |
| Li-RADS-4 | 15 (17.4) | 12 (22.2) | 4 (16.0) | 3 (12.0) | |||
| Li-RADS-5 | 63 (73.3) | 35 (64.8) | 16 (64.0) | 19 (76.0) | |||
| Outcomes | |||||||
| Hospital-stay (days), median (IQR) | 8 (6, 12) | 4 (3, 5) | <0.001 | 7 (6, 10) | 3 (3, 5) | <0.001 | |
| Complications, N (%) | None | 51 (59.3) | 47 (87.0) | 0.002 | 19 (76.0) | 20 (80.0) | 1.00 |
| Clavien 1–2 | 24 (27.9) | 6 (11.1) | 5 (20.0) | 5 (20.0) | |||
| Clavien 3–5 | 11 (12.8) | 1 (1.9) | 1 (4.0) | 0 (0.0) | |||
| Comprehensive Complication Index | Mean (SD) | 12.1 (22.5) | 2.2 (6.4) | <0.001 | 3.8 (7.7) | 3.4 (7.6) | 0.81 |
| Median (IQR) | 0 (0, 20.9) | 0 (0, 0) | 0 (0, 0) | 0 (0, 0) | |||
| R0 | No | 4 (4.7) | - | - | 0 (0.0) | - | - |
| Yes | 82 (95.3) | - | 25 (100.0) | - | |||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Centonze, L.; Di Sandro, S.; Lauterio, A.; De Carlis, R.; Frassoni, S.; Rampoldi, A.; Tuscano, B.; Bagnardi, V.; Vanzulli, A.; De Carlis, L. Surgical Resection vs. Percutaneous Ablation for Single Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Exploring the Impact of Li-RADS Classification on Oncological Outcomes. Cancers 2021, 13, 1671. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13071671
Centonze L, Di Sandro S, Lauterio A, De Carlis R, Frassoni S, Rampoldi A, Tuscano B, Bagnardi V, Vanzulli A, De Carlis L. Surgical Resection vs. Percutaneous Ablation for Single Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Exploring the Impact of Li-RADS Classification on Oncological Outcomes. Cancers. 2021; 13(7):1671. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13071671
Chicago/Turabian StyleCentonze, Leonardo, Stefano Di Sandro, Andrea Lauterio, Riccardo De Carlis, Samuele Frassoni, Antonio Rampoldi, Bruno Tuscano, Vincenzo Bagnardi, Angelo Vanzulli, and Luciano De Carlis. 2021. "Surgical Resection vs. Percutaneous Ablation for Single Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Exploring the Impact of Li-RADS Classification on Oncological Outcomes" Cancers 13, no. 7: 1671. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13071671
APA StyleCentonze, L., Di Sandro, S., Lauterio, A., De Carlis, R., Frassoni, S., Rampoldi, A., Tuscano, B., Bagnardi, V., Vanzulli, A., & De Carlis, L. (2021). Surgical Resection vs. Percutaneous Ablation for Single Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Exploring the Impact of Li-RADS Classification on Oncological Outcomes. Cancers, 13(7), 1671. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13071671