Neurokinin-1 Receptor (NK-1R) Antagonists as a New Strategy to Overcome Cancer Resistance
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
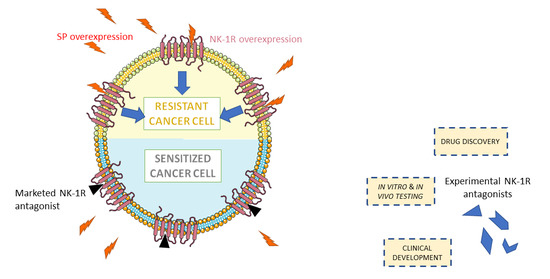
1.1. The Challenge of Drug-Resistant Tumors
1.2. Tachykinins
- The transcription of the TAC1 gene (NCBI Gene ID: 6863) produces the pre-protachykinin-A (PPTA)-mRNA, which is converted into one of four splice variants coding for a pro-tachykinin polypeptide that contains NK-1 [29], Neurokinin A (NKA, formerly known as substance K) and the NH2-terminally extended forms of NAK neuropeptide K (NPK) and neuropeptide gamma (NPγ) [22,26,30]. These peptides function as neurotransmitters by interacting with nerve receptors and smooth muscle cells [30].
- TAC3 (NCBI Gene ID: 6866) encodes a preprotein that is further cleaved to generate a mature secreted neuropeptide (neurokinin B, NKB). NKB is primarily expressed in the central and peripheral nervous systems and functions as a neurotransmitter [31]. NKB is a critical central regulator of gonadal function and its alterations are mainly associated with hypogonadotropic hypogonadism [32].
- Finally, TAC4 (NCBI Gene ID: 255061) produces endokinins (EK) A, A/B, C and D as well as hemokinins [12,28], which are associated with the hematopoietic system and lymphocyte B maturation [12]. TAC4 gene products are thought to regulate different peripheral endocrine and paracrine functions, including blood pressure, the immune system and endocrine gland secretion [33].
1.3. Tachykinins and Tachykinin Receptors in Human Disease and as Pharmacological Targets
1.3.1. Tachykinins and Tachykinin Receptors in Human Disease
- Respiratory disorders
- Smooth muscle disfunction:
- Central nervous system disorders:
- Hormonal disorders:
1.3.2. Marketed Tachykinin Receptor Antagonists
1.3.3. Aprepitant as Candidate for Drug Repurposing
2. Substance P/Neurokinin-1 System as a Target for Cancer Treatment
2.1. NK-1 Receptor
2.2. NK-1 Receptor Signaling Pathways with a Role in Cancer
2.3. Targeting NK-1R/SP Axis to Overcome Tumor Resistance
2.4. Preclinical Research
2.5. Clinical Research
3. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García-Aranda, M.; Pérez-Ruiz, E.; Redondo, M. Bcl-2 inhibition to overcome resistance to chemo-and immunotherapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bukowski, K.; Kciuk, M.; Kontek, R. Mechanisms of multidrug resistance in cancer chemotherapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 3233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cree, I.A.; Charlton, P. Molecular chess? Hallmarks of anti-cancer drug resistance. BMC Cancer 2017, 17, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hanahan, D.; Weinberg, R.A. Hallmarks of cancer: The next generation. Cell 2011, 144, 646–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ye, Q.; Liu, K.; Shen, Q.; Li, Q.; Hao, J.; Han, F.; Jiang, R.-W. Reversal of Multidrug Resistance in Cancer by Multi-Functional Flavonoids. Front. Oncol. 2019, 9, 487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Frantzi, M.; Latosinska, A.; Mokou, M.; Mischak, H.; Vlahou, A. Drug repurposing in oncology. Lancet Oncol. 2020, 21, e543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhou, L.; Xie, N.; Nice, E.C.; Zhang, T.; Cui, Y.; Huang, C. Overcoming cancer therapeutic bottleneck by drug repurposing. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2020, 5, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pillaiyar, T.; Meenakshisundaram, S.; Manickam, M.; Sankaranarayanan, M. A medicinal chemistry perspective of drug repositioning: Recent advances and challenges in drug discovery. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2020, 195, 112275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sriram, K.; Insel, P.A. G Protein-Coupled Receptors as Targets for Approved Drugs: How Many Targets and How Many Drugs? Mol. Pharmacol. 2018, 93, 251–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- European Medicines Agency. EMEND, INN-Aprepitant: Scientific Discussion. 2004. Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/documents/scientific-discussion/emend-epar-scientific-discussion_en.pdf (accessed on 28 May 2021).
- Garcia-Recio, S.; Gascón, P. Biological and Pharmacological Aspects of the NK1-Receptor. BioMed Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 495704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rosso, M.; Munoz, M.; Berger, M. The role of neurokinin-1 receptor in the microenvironment of inflammation and cancer. Sci. World J. 2012, 2012, 381434. [Google Scholar]
- Muñoz, M.; Rosso, M.; Coveñas, R. A new frontier in the treatment of cancer: NK-1 receptor antagonists. Curr. Med. Chem. 2010, 17, 504–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muñoz, M.; Coveñas, R. Neurokinin-1 receptor antagonists as antitumor drugs in gastrointestinal cancer: A new approach. Saudi J. Gastroenterol. Off. J. Saudi Gastroenterol. Assoc. 2016, 22, 260–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muñoz, M.; Coveñas, R. The Neurokinin-1 Receptor Antagonist Aprepitant: An Intelligent Bullet against Cancer? Cancers 2020, 12, 2682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muñoz, M.; Crespo, J.C.; Crespo, J.P.; Coveñas, R. Neurokinin-1 receptor antagonist aprepitant and radiotherapy, a successful combination therapy in a patient with lung cancer: A case report. Mol. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 11, 50–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz, M.; Rosso, M. The NK-1 receptor antagonist aprepitant as a broad spectrum antitumor drug. Investig. New Drugs 2010, 28, 187–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayordomo, C.; García-Recio, S.; Ametller, E.; Fernández-Nogueira, P.; Pastor-Arroyo, E.M.; Vinyals, L.; Casas, I.; Gascón, P.; Almendro, V. Targeting of substance P induces cancer cell death and decreases the steady state of EGFR and Her2. J. Cell. Physiol. 2012, 227, 1358–1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Recio, S.; Fuster, G.; Fernandez-Nogueira, P.; Pastor-Arroyo, E.M.; Park, S.Y.; Mayordomo, C.; Ametller, E.; Mancino, M.; Gonzalez-Farre, X.; Russnes, H.G.; et al. Substance P Autocrine Signaling Contributes to Persistent HER2 Activation That Drives Malignant Progression and Drug Resistance in Breast Cancer. Cancer Res. 2013, 73, 6424–6434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Robinson, P.; Kasembeli, M.; Bharadwaj, U.; Engineer, N.; Eckols, K.T.; Tweardy, D.J. Substance P Receptor Signaling Mediates Doxorubicin-Induced Cardiomyocyte Apoptosis and Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Chemoresistance. BioMed Res. Int. 2016, 2016, 1959270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Steinhoff, M.S.; von Mentzer, B.; Geppetti, P.; Pothoulakis, C.; Bunnett, N.W. Tachykinins and their receptors: Contributions to physiological control and the mechanisms of disease. Physiol. Rev. 2014, 94, 265–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Werge, T. The tachykinin tale: Molecular recognition in a historical perspective. J. Mol. Recognit. 2007, 20, 145–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bremer, A.A.; Leeman, S.E.; Boyd, N.D. The common C-terminal sequences of substance P and neurokinin A contact the same region of the NK-1 receptor. FEBS Lett. 2000, 486, 43–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Goldsmith, L.E.; Kwatra, M.M. Tachykinin/Substance P/Neurokinin-1 Receptors. In Encyclopedia of Biological Chemistry, 2nd ed.; Lennarz, W.J., Lane, M.D., Eds.; Academic Press: Waltham, MA, USA, 2013; pp. 360–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UniProt. UniProtKB–P20366 (TKN1_HUMAN). Available online: https://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/P20366 (accessed on 12 May 2021).
- UniProt. UniProtKB–Q9UHF0 (TKNK_HUMAN). Available online: https://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/Q9UHF0 (accessed on 21 May 2021).
- UNIProt. UniProtKB–Q86UU9 (TKN4_HUMAN). Available online: https://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/Q86UU9 (accessed on 20 May 2021).
- Douglas, S.D.; Leeman, S.E. Neurokinin-1 receptor: Functional significance in the immune system in reference to selected infections and inflammation. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2011, 1217, 83–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- NCBI. TAC1 Tachykinin Precursor 1 [Homo Sapiens (human)]. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/gene/6863 (accessed on 20 May 2021).
- The Human Gene Database. TAC3 Gene. Available online: https://www.genecards.org/cgi-bin/carddisp.pl?gene=TAC3 (accessed on 20 May 2021).
- NCBI. TAC3 Tachykinin Precursor 3 [Homo Sapiens (human)]. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/gene/6866 (accessed on 20 May 2021).
- NCBI. TAC4 Tachykinin Precursor 4 [Homo Sapiens (human)]. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/gene/255061 (accessed on 20 May 2021).
- Onaga, T. Tachykinin: Recent developments and novel roles in health and disease. Biomol. Concepts 2014, 5, 225–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Groneberg, D.A.; Harrison, S.; Dinh, Q.T.; Geppetti, P.; Fischer, A. Tachykinins in the respiratory tract. Curr. Drug Targets 2006, 7, 1005–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joos, G.F.; Pauwels, R.A. Tachykinin receptor antagonists: Potential in airways diseases. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2001, 1, 235–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joos, G.F.; Van Schoor, J.; Kips, J.C.; Pauwels, R.A. The effect of inhaled FK224, a tachykinin NK-1 and NK-2 receptor antagonist, on neurokinin A-induced bronchoconstriction in asthmatics. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 1996, 153, 1781–1784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lördal, M.; Navalesi, G.; Theodorsson, E.; Maggi, C.A.; Hellström, P.M. A novel tachykinin NK2 receptor antagonist prevents motility-stimulating effects of neurokinin A in small intestine. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2001, 134, 215–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Simonsen, K.B.; Juhl, K.; Steiniger-Brach, B.; Nielsen, S.M. Novel NK (3) receptor antagonists for the treatment of schizophrenia and other CNS indications. Curr. Opin. Drug Discov. Dev. 2010, 13, 379–388. [Google Scholar]
- Martinez, A.N.; Philipp, M.T. Substance P and antagonists of the neurokinin-1 receptor in neuroinflammation associated with infectious and neurodegenerative diseases of the central nervous system. J. Neurol. Neuromed. 2016, 1, 29–36. [Google Scholar]
- Fraser, G.L.; Ramael, S.; Hoveyda, H.R.; Gheyle, L.; Combalbert, J. The NK3 receptor antagonist ESN364 suppresses sex hormones in men and women. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2016, 101, 417–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- FDA. Emend (Aprepitant) Capsule and Oral Suspension Pediatric Postmarketing Pharmacovigilance Review; FDA: Silver Spring, MD, USA, 2017.
- Hargreaves, R.; Ferreira, J.C.; Hughes, D.; Brands, J.; Hale, J.; Mattson, B.; Mills, S. Development of aprepitant, the first neurokinin-1 receptor antagonist for the prevention of chemotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2011, 1222, 40–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- FDA. Akynzeo FDA Approval History. Available online: https://www.drugs.com/history/akynzeo.html (accessed on 9 April 2022).
- Center for Drug Evaluation and Research. Varubi Tablets 90mg; Food and Drug Administration: Silver Spring, MD, USA, 2015.
- Center for Drug Evaluation and Research. Approval Package for Varubi Injectable Emulsion for Intravenous Use; Administration, F.A.D., Ed.; Food and Drug Administration: Silver Spring, MD, USA, 2017.
- Goldberg, T.; Fidler, B.; Cardinale, S. Rolapitant (Varubi): A Substance P/Neurokinin-1 Receptor Antagonist for the Prevention of Chemotherapy-Induced Nausea and Vomiting. P T Peer Rev. J. Formul. Manag. 2017, 42, 168–172. [Google Scholar]
- Kakuta, N.; Tsutsumi, Y.M.; Horikawa, Y.T.; Kawano, H.; Kinoshita, M.; Tanaka, K.; Oshita, S. Neurokinin-1 receptor antagonism, aprepitant, effectively diminishes post-operative nausea and vomiting while increasing analgesic tolerance in laparoscopic gynecological procedures. J. Med. Investig. 2011, 58, 246–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Majkowska-Pilip, A.; Halik, P.K.; Gniazdowska, E. The significance of NK1 receptor ligands and their application in targeted radionuclide tumour therapy. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, 443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aapro, M.; Carides, A.; Rapoport, B.L.; Schmoll, H.-J.; Zhang, L.; Warr, D. Aprepitant and fosaprepitant: A 10-year review of efficacy and safety. Oncologist 2015, 20, 450–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Muñoz, M.; Rosso, M.; Coveñas, R. Triple Negative Breast Cancer: How Neurokinin-1 Receptor Antagonists Could Be Used as a New Therapeutic Approach. Mini Rev. Med. Chem. 2020, 20, 408–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nygren, P.; Hande, K.; Petty, K.J.; Fedgchin, M.; van Dyck, K.; Majumdar, A.; Panebianco, D.; de Smet, M.; Ahmed, T.; Murphy, M.G.; et al. Lack of effect of aprepitant on the pharmacokinetics of docetaxel in cancer patients. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2005, 55, 609–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, C.; Huang, H.; Huang, F.; Yang, T.; Zhang, T.; Wu, H.; Zhou, H.; Chen, Q.; Shi, Y.; Sun, Y.; et al. Neurokinin-1 receptor is an effective target for treating leukemia by inducing oxidative stress through mitochondrial calcium overload. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 19635–19645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- UniProt. UniProtKB–P25103 (NK1R_HUMAN). Available online: https://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/P25103 (accessed on 21 May 2021).
- Gerard, N.P.; Garraway, L.A.; Eddy, R.L., Jr.; Shows, T.B.; Iijima, H.; Paquet, J.L.; Gerard, C. Human substance P receptor (NK-1): Organization of the gene, chromosome localization and functional expression of cDNA clones. Biochemistry 1991, 30, 10640–10646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Connor, T.M.; O’Connell, J.; O’Brien, D.I.; Goode, T.; Bredin, C.P.; Shanahan, F. The role of substance P in inflammatory disease. J. Cell. Physiol. 2004, 201, 167–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spitsin, S.; Pappa, V.; Douglas, S.D. Truncation of neurokinin-1 receptor-Negative regulation of substance P signaling. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2018, 103, 1043–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thom, C.; Ehrenmann, J.; Vacca, S.; Waltenspühl, Y.; Schöppe, J.; Medalia, O.; Plückthun, A. Structures of neurokinin 1 receptor in complex with Gq and Gs proteins reveal substance P binding mode and unique activation features. Sci. Adv. 2021, 7, eabk2872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Connor, C.; Adams, J. 4.2 G-Protein-Coupled Receptors Play Many Different Roles in Eukaryotic Cell Signaling. In Essentials of Cell Biology; NPG Education: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, J.; Feng, F.; Xu, G.; Zhang, H.; Hong, L.; Yang, J. Elevated SP/NK-1R in esophageal carcinoma promotes esophageal carcinoma cell proliferation and migration. Gene 2015, 560, 205–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Seas, A.; Kiyani, M.; Ji, K.S.; Bell, H.N. A temporal examination of calcium signaling in cancer-from tumorigenesis, to immune evasion, and metastasis. Cell Biosci. 2018, 8, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bootman, M.D.; Chehab, T.; Bultynck, G.; Parys, J.B.; Rietdorf, K. The regulation of autophagy by calcium signals: Do we have a consensus? Cell Calcium 2018, 70, 32–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.W.; Li, L.; Hu, W.Q.; Hu, M.N.; Tao, Y.; Hu, H.; Miao, X.K.; Yang, W.L.; Zhu, Q.; Mou, L.Y. Neurokinin-1 receptor promotes non-small cell lung cancer progression through transactivation of EGFR. Cell Death Dis. 2022, 13, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.; Gururaj, A.E.; Barnes, C.J. p21-activated kinases in cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2006, 6, 459–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Chen, Y.; Liu, G.; Li, C.; Song, Y.; Cao, Z.; Li, W.; Hu, J.; Lu, C.; Liu, Y. PI3K/AKT pathway as a key link modulates the multidrug resistance of cancers. Cell Death Dis. 2020, 11, 797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eblen, S.T.; Slack, J.K.; Weber, M.J.; Catling, A.D. Rac-PAK signaling stimulates extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) activation by regulating formation of MEK1-ERK complexes. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2002, 22, 6023–6033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Salaroglio, I.C.; Mungo, E.; Gazzano, E.; Kopecka, J.; Riganti, C. ERK is a Pivotal Player of Chemo-Immune-Resistance in Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- DeFea, K.A.; Vaughn, Z.D.; O’Bryan, E.M.; Nishijima, D.; Déry, O.; Bunnett, N.W. The proliferative and antiapoptotic effects of substance P are facilitated by formation of a beta-arrestin-dependent scaffolding complex. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 11086–11091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Deng, X.-T.; Tang, S.-M.; Wu, P.-Y.; Li, Q.-P.; Ge, X.-X.; Xu, B.-M.; Wang, H.-S.; Miao, L. SP/NK-1R promotes gallbladder cancer cell proliferation and migration. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2019, 23, 7961–7973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bentires-Alj, M.; Barbu, V.; Fillet, M.; Chariot, A.; Relic, B.; Jacobs, N.; Gielen, J.; Merville, M.-P.; Bours, V. NF-κB transcription factor induces drug resistance through MDR1 expression in cancer cells. Oncogene 2003, 22, 90–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, H.; Liu, K.; Dong, Z. The Role of p21-Activated Kinases in Cancer and Beyond: Where Are We Heading? Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz, M.; Coveñas, R. Involvement of substance P and the NK-1 receptor in cancer progression. Peptides 2013, 48, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tajada, S.; Villalobos, C. Calcium Permeable Channels in Cancer Hallmarks. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patergnani, S.; Danese, A.; Bouhamida, E.; Aguiari, G.; Previati, M.; Pinton, P.; Giorgi, C. Various Aspects of Calcium Signaling in the Regulation of Apoptosis, Autophagy, Cell Proliferation, and Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 8323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azimi, I.; Roberts-Thomson, S.J.; Monteith, G.R. Calcium influx pathways in breast cancer: Opportunities for pharmacological intervention. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2014, 171, 945–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shi, Y.; Wang, X.; Meng, Y.; Ma, J.; Zhang, Q.; Shao, G.; Wang, L.; Cheng, X.; Hong, X.; Wang, Y. A Novel Mechanism of Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress-and c-Myc-Degradation-Mediated Therapeutic Benefits of Antineurokinin-1 Receptor Drugs in Colorectal Cancer. Adv. Sci. 2021, 8, 2101936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munoz, M.; Gonzalez-Ortega, A.; Salinas-Martín, M.V.; Carranza, A.; Garcia-Recio, S.; Almendro, V.; Covenas, R. The neurokinin-1 receptor antagonist aprepitant is a promising candidate for the treatment of breast cancer. Int. J. Oncol. 2014, 45, 1658–1672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Javid, H.; Afshari, A.R.; Zahedi Avval, F.; Asadi, J.; Hashemy, S.I. Aprepitant Promotes Caspase-Dependent Apoptotic Cell Death and G2/M Arrest through PI3K/Akt/NF-κB Axis in Cancer Stem-Like Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma Spheres. BioMed Res. Int. 2021, 2021, 8808214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghahremanloo, A.; Javid, H.; Afshari, A.R.; Hashemy, S.I. Investigation of the Role of Neurokinin-1 Receptor Inhibition Using Aprepitant in the Apoptotic Cell Death through PI3K/Akt/NF-κB Signal Transduction Pathways in Colon Cancer Cells. BioMed Res. Int. 2021, 2021, 1383878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Godwin, P.; Baird, A.-M.; Heavey, S.; Barr, M.; O’Byrne, K.; Gately, K. Targeting Nuclear Factor-Kappa B to Overcome Resistance to Chemotherapy. Front. Oncol. 2013, 3, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Muñoz, M.; Coveñas, R. The Neurokinin-1 Receptor Antagonist Aprepitant, a New Drug for the Treatment of Hematological Malignancies: Focus on Acute Myeloid Leukemia. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 1659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halik, P.K.; Lipiński, P.F.J.; Matalińska, J.; Koźmiński, P.; Misicka, A.; Gniazdowska, E. Radiochemical Synthesis and Evaluation of Novel Radioconjugates of Neurokinin 1 Receptor Antagonist Aprepitant Dedicated for NK1R-Positive Tumors. Molecules 2020, 25, 3756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halik, P.K.; Koźmiński, P.; Matalińska, J.; Lipiński, P.F.J.; Misicka, A.; Gniazdowska, E. In Vitro Biological Evaluation of Aprepitant Based 177Lu-Radioconjugates. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nizam, E.; Erin, N. Differential consequences of neurokinin receptor 1 and 2 antagonists in metastatic breast carcinoma cells; effects independent of Substance P. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 108, 263–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mozafari, M.; Ebrahimi, S.; Darban, R.A.; Hashemy, S.I. Potential in vitro therapeutic effects of targeting SP/NK1R system in cervical cancer. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2022, 49, 1067–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz, M.; Rosso, M.; Robles-Frias, M.J.; Salinas-Martín, M.V.; Rosso, R.; González-Ortega, A.; Coveñas, R. The NK-1 receptor is expressed in human melanoma and is involved in the antitumor action of the NK-1 receptor antagonist aprepitant on melanoma cell lines. Lab. Investig. 2010, 90, 1259–1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Matalińska, J.; Świć, A.; Lipiński, P.; Misicka, A. Antiproliferative effects of [D-Pro2, D-Trp7,9]-Substance P and aprepitant on several cancer cell lines and their selectivity in comparison to normal cells. Folia Neuropathol. 2020, 58, 237–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ebrahimi, S.; Mirzavi, F.; Aghaee-Bakhtiari, S.H.; Hashemy, S.I. SP/NK1R system regulates carcinogenesis in prostate cancer: Shedding light on the antitumoral function of aprepitant. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Cell Res. 2022, 1869, 119221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korfi, F.; Javid, H.; Assaran Darban, R.; Hashemy, S.I. The Effect of SP/NK1R on the Expression and Activity of Catalase and Superoxide Dismutase in Glioblastoma Cancer Cells. Biochem. Res. Int. 2021, 2021, 6620708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dikmen, M.; Gökhaner, G.; Cantürk, Z. Evaluation of the antileukemic effects of neurokinin-1 receptor antagonists, aprepitant, and L-733,060, in chronic and acute myeloid leukemic cells. Anticancer Drugs 2019, 30, 693–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolorz, J.; Demir, S.; Gottschlich, A.; Beirith, I.; Ilmer, M.; Lüthy, D.; Walz, C.; Dorostkar, M.M.; Magg, T.; Hauck, F.; et al. The Neurokinin-1 Receptor Is a Target in Pediatric Rhabdoid Tumors. Curr. Oncol. 2021, 29, 94–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beirith, I.; Renz, B.W.; Mudusetti, S.; Ring, N.S.; Kolorz, J.; Koch, D.; Bazhin, A.V.; Berger, M.; Wang, J.; Angele, M.K.; et al. Identification of the Neurokinin-1 Receptor as Targetable Stratification Factor for Drug Repurposing in Pancreatic Cancer. Cancers 2021, 13, 2703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bashash, D.; Safaroghli-Azar, A.; Bayati, S.; Razani, E.; Pourbagheri-Sigaroodi, A.; Gharehbaghian, A.; Momeny, M.; Sanjadi, M.; Rezaie-Tavirani, M.; Ghaffari, S.H. Neurokinin-1 receptor (NK1R) inhibition sensitizes APL cells to anti-tumor effect of arsenic trioxide via restriction of NF-κB axis: Shedding new light on resistance to Aprepitant. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2018, 103, 105–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henssen, A.G.; Odersky, A.; Szymansky, A.; Seiler, M.; Althoff, K.; Beckers, A.; Speleman, F.; Schäfers, S.; De Preter, K.; Astrahanseff, K.; et al. Targeting tachykinin receptors in neuroblastoma. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 430–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinstein, I.B. Addiction to oncogenes—The Achilles heal of cancer. Science 2002, 297, 63–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legi, A.; Rodriguez, E.; Eckols, T.K.; Mistry, C.; Robinson, P. Substance P Antagonism Prevents Chemotherapy-Induced Cardiotoxicity. Cancers 2021, 13, 1732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, M.; McCloskey, M.; Staples, S. Prolonged use of aprepitant in metastatic breast cancer and a reduction in CA153 tumour marker levels. Int. J. Cancer Clin. Res. 2016, 3, 071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- U.S. National Libray of Medicine. Efficacy and Safety of High Dose Aprepitant Treatment in Patients with Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/study/NCT04840004 (accessed on 17 February 2022).


| Gene | Tachykinin | Sequence | Preferred Tachykinin Receptor |
|---|---|---|---|
| TAC1 | Neurokinin 1 (NK1),Substance P (SP) | RPKPQQFFGLM [26] | Neurokinin 1 receptor (NK-1R) |
| Neurokinin A (NKA) Substance K (SK) | HKTDSFVGLM [26] | Neurokinin 2 receptor (NK-2R) | |
| Neuropeptide K (NPK) | DADSSIEKQVALLKALYGHGQISHKRHKTDSFVGLM [26] | Neurokinin 2 receptor (NK-2R) | |
| Neuropeptide γ (NP γ) | MKILVALAVFFLVSTQLFAEEIGANDDLNYWSDWYDSDQIKEELPEPFEHLLQRARRPKPQQFFGLMGKRDADSSIEKQVALLKALYGHGQISHKRHKTDSFVGLMGKRALNSVAYERSAMQNYERRR (1st part)GHGQISHKRHKTDSFVGLM (2nd part) [26] | Neurokinin 2 receptor (NK-2R) | |
| TAC3 | Neurokinin B (NKB)Neuromedin-K | DMHDFFVGLM [27] | Neurokinin 3 receptor (NK-3R) |
| TAC4 | Endokinin A (EKA) | DGGEEQTLSTEAETWVIVALEEGAGPSIQLQLQEVKTGKASQFFGLM [28] | Neurokinin 1 receptor (NK-1R) |
| Endokinin A/B (EKA/B) | GKASQFFGLM [28] | Neurokinin 1 receptor (NK-1R) | |
| Endokinin C (EKC) | KKAYQLEHTFQGLL [28] | Neurokinin 1 receptor (NK-1R) | |
| Endokinin D (EKD) | VGAYQLEHTFQGLL | Neurokinin 1 receptor (NK-1R) |
| Cancer Type | Relevant Results |
|---|---|
| Breast |
|
| Colon cancer |
|
| Cervical cancer |
|
| Melanoma |
|
| Lung cancer, Urinary bladder carcinoma |
|
| Lung cancer |
|
| Prostate cancer |
|
| Glioblastoma |
|
| Chronic and acute myeloid leukemia |
|
| Rhabdoid tumors |
|
| Human pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma |
|
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
García-Aranda, M.; Téllez, T.; McKenna, L.; Redondo, M. Neurokinin-1 Receptor (NK-1R) Antagonists as a New Strategy to Overcome Cancer Resistance. Cancers 2022, 14, 2255. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14092255
García-Aranda M, Téllez T, McKenna L, Redondo M. Neurokinin-1 Receptor (NK-1R) Antagonists as a New Strategy to Overcome Cancer Resistance. Cancers. 2022; 14(9):2255. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14092255
Chicago/Turabian StyleGarcía-Aranda, Marilina, Teresa Téllez, Lauraine McKenna, and Maximino Redondo. 2022. "Neurokinin-1 Receptor (NK-1R) Antagonists as a New Strategy to Overcome Cancer Resistance" Cancers 14, no. 9: 2255. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14092255
APA StyleGarcía-Aranda, M., Téllez, T., McKenna, L., & Redondo, M. (2022). Neurokinin-1 Receptor (NK-1R) Antagonists as a New Strategy to Overcome Cancer Resistance. Cancers, 14(9), 2255. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14092255