Bifunctional Heterometallic Metal-Organic Frameworks for Solvent-Free Heterogeneous Cascade Catalysis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Catalyst Characterization
2.2. Catalytic One-Pot Deacetalization-Knoevenagel Condensation
2.3. Selectivity of Substrates
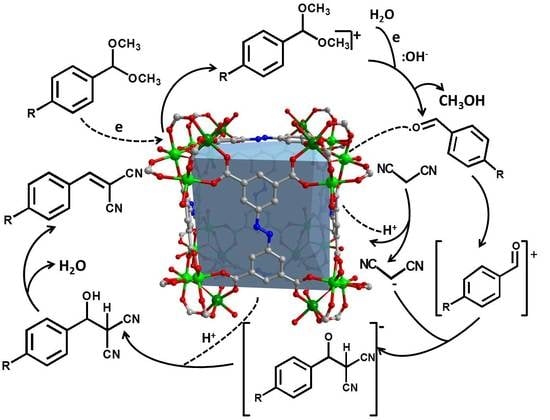
2.4. Reaction Mechanism for the One-Pot Tandem Reaction
2.5. Stability and Recyclability of the CPM200s Catalyst
3. Experimental Section
3.1. Instrumentation and Materials
3.2. General Procedure for CPM200s Preparation
3.3. General Procedure for the One-Pot Deacetalization-Knoevenagel Reaction
3.4. General Procedure for Recycling of the CPM200s
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Miyamura, H.; Kobayashi, S. Tandem oxidative processes catalyzed by polymer-incarcerated multimetallic nanoclusters with molecular oxygen. Acc. Chem. Res. 2014, 47, 1054–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raja, R.; Potter, M.E.; Newland, S.H. Predictive design of engineered multifunctional solid catalysts. Chem. Commun. 2014, 50, 5940–5957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- He, H.; Sun, F.; Aguila, B.; Perman, J.A.; Ma, S.; Zhu, G. A bifunctional metal–organic framework featuring the combination of open metal sites and Lewis basic sites for selective gas adsorption and heterogeneous cascade catalysis. J. Mater. Chem. A 2016, 4, 15240–15246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.M.; Na, Y.; Han, H.; Chang, S. Cooperative multi-catalyst systems for one-pot organic transformations. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2004, 33, 302–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wasilke, J.-C.; Obrey, S.J.; Baker, R.T.; Bazan, G.C. Concurrent tandem catalysis. Chem. Rev. 2005, 105, 1001–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choo, G.C.; Miyamura, H.; Kobayashi, S. Synergistic cascade catalysis by metal nanoparticles and Lewis acids in hydrogen autotransfer. Chem. Sci. 2015, 6, 1719–1727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Voit, B. Sequential One-Pot Reactions Using the Concept of “Site Isolation”. Angew.Chem. Int. Ed. 2006, 45, 4238–4240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gladysz, J.A. Introduction: Recoverable catalysts and reagents perspective and prospective. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2002, 102, 3215–3216. [Google Scholar]
- Margelefsky, E.L.; Zeidan, R.K.; Davis, M.E. Cooperative catalysis by silica-supported organic functional groups. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2008, 37, 1118–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Motokura, K.; Tada, M.; Iwasawa, Y. Heterogeneous organic base-catalyzed reactions enhanced by acid supports. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007, 129, 9540–9541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Jiang, H.; Wu, X.; Mao, Z.; Li, H. Organoamine-functionalized graphene oxide as a bifunctional carbocatalyst with remarkable acceleration in a one-pot multistep reaction. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 1669–1677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, F.; Jiang, H.; Li, X.; Wu, X.; Li, H. Amine-functionalized GO as an active and reusable acid–base bifunctional catalyst for one-pot cascade reactions. ACS Catal. 2014, 4, 394–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shylesh, S.; Wagner, A.; Seifert, A.; Ernst, S.; Thiel, W.R. Cooperative Acid–Base Effects with Functionalized Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles: Applications in Carbon–Carbon Bond-Formation Reactions. Chem. Eur. J. 2009, 15, 7052–7062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, J.; Zhang, X.; Lu, Y.; Liu, S.; Liu, J. Selective functionalization of hollow nanospheres with acid and base groups for cascade reactions. Chem. Eur. J. 2015, 21, 7403–7407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shylesh, S.; Wagener, A.; Seifert, A.; Ernst, S.; Thiel, W.R. Mesoporous organosilicas with acidic frameworks and basic sites in the pores: An approach to cooperative catalytic reactions. Angew.Chem. Int. Ed. 2010, 49, 184–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Wattanaprayoon, C.; Oh, S.C.; Emdadi, L.; Liu, D. Synthesis of organic pillared MFI zeolite as bifunctional acid–base catalyst. Chem. Mater. 2015, 27, 1479–1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, L.-C.; Lu, J.; Weck, M.; Jones, C.W. Acid–base bifunctional shell cross-linked micelle nanoreactor for one-pot tandem reaction. ACS Catal. 2016, 6, 784–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Fu, L.; Wei, L.; Liang, J.; Binks, B.P. Compartmentalization of incompatible reagents within pickering emulsion droplets for one-pot cascade reactions. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 1362–1371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Z.; Wang, K.; Tan, B.; Gu, Y. Hollow hyper-cross-linked nanospheres with acid and base sites as efficient and water-stable catalysts for one-pot tandem reactions. ACS Catal. 2017, 7, 3693–3702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chughtai, A.H.; Ahmad, N.; Younus, H.A.; Laypkov, A.; Verpoort, F. Metal–organic frameworks: Versatile heterogeneous catalysts for efficient catalytic organic transformations. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2015, 44, 6804–6849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Furukawa, H.; Cordova, K.E.; O’Keeffe, M.; Yaghi, O.M. The chemistry and applications of metal-organic frameworks. Science 2013, 341, 1230444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhao, M.; Ou, S.; Wu, C.-D. Porous metal–organic frameworks for heterogeneous biomimetic catalysis. Acc. Chem. Res. 2014, 47, 1199–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, S.-N.; Song, X.-Z.; Song, S.-Y.; Zhang, H.-j. Highly efficient heterogeneous catalytic materials derived from metal-organic framework supports/precursors. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2017, 337, 80–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.D.; Zhao, M. Incorporation of molecular catalysts in metal–organic frameworks for highly efficient heterogeneous catalysis. Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1605446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-García, P.; Müller, M.; Corma, A. MOF catalysis in relation to their homogeneous counterparts and conventional solid catalysts. Chem. Sci. 2014, 5, 2979–3007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Xi, F.-G.; Sun, W.; Yang, N.-N.; Gao, E.-Q. Amino-and sulfo-bifunctionalized metal–organic frameworks: One-pot tandem catalysis and the catalytic sites. Inorg. Chem. 2016, 55, 5753–5755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, S.-T.; Wu, T.; Chou, C.; Fuhr, A.; Feng, P.; Bu, X. Development of composite inorganic building blocks for MOFs. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 4517–4520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zheng, S.-T.; Zhao, X.; Lau, S.; Fuhr, A.; Feng, P.; Bu, X. Entrapment of metal clusters in metal–organic framework channels by extended hooks anchored at open metal sites. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 10270–10273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sajna, K.; Fracaroli, A.M.; Yaghi, O.M.; Tashiro, K. Modular Synthesis of Metal–Organic Complex Arrays Containing Precisely Designed Metal Sequences. Inorg. Chem. 2015, 54, 1197–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, Q.-G.; Bu, X.; Mao, C.; Zhao, X.; Feng, P. Systematic and dramatic tuning on gas sorption performance in heterometallic metal–organic frameworks. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138, 2524–2527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, G.; Zhang, L.; Zhao, Z.; Zhou, X.; Duan, A.; Xu, C.; Gao, J. Highly effective P-modified HZSM-5 catalyst for the cracking of C4 alkanes to produce light olefins. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2008, 340, 176–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, S.; Desai, A.V.; Ghosh, S.K. Potential of metal–organic frameworks for adsorptive separation of industrially and environmentally relevant liquid mixtures. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2018, 367, 82–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dau, P.V.; Cohen, S.M. A bifunctional, site-isolated metal–organic framework-based tandem catalyst. Inorg. Chem. 2015, 54, 3134–3138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prasad, R.R.; Dawson, D.M.; Cox, P.A.; Ashbrook, S.E.; Wright, P.A.; Clarke, M.L. A Bifunctional MOF Catalyst Containing Metal–Phosphine and Lewis Acidic Active Sites. Chem. Eur. J. 2018, 24, 15309–15318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yang, D.; Gates, B.C. Catalysis by metal organic frameworks: Perspective and suggestions for future research. ACS Catal. 2019, 9, 1779–1798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beheshti, S.; Morsali, A. Post-synthetic cation exchange in anionic metal–organic frameworks; a novel strategy for increasing the catalytic activity in solvent-free condensation reactions. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 41825–41830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luan, Y.; Qi, Y.; Gao, H.; Andriamitantsoa, R.S.; Zheng, N.; Wang, G. A general post-synthetic modification approach of amino-tagged metal–organic frameworks to access efficient catalysts for the Knoevenagel condensation reaction. Mater. Chem. A 2015, 3, 17320–17331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.-S.; Liang, J.; Li, L.; Lin, Z.-J.; Bag, P.P.; Gao, S.-Y.; Huang, Y.-B.; Cao, R. An anion metal–organic framework with Lewis basic sites-rich toward charge-exclusive cationic dyes separation and size-selective catalytic reaction. Inorg. Chem. 2016, 55, 2641–2649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almáši, M.; Zeleňák, V.; Opanasenko, M.; Čejka, J. A novel nickel metal–organic framework with fluorite-like structure: Gas adsorption properties and catalytic activity in Knoevenagel condensation. Dalton Trans. 2014, 43, 3730–3738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Solvent | Conversion (%) |
|---|---|
| Toluene | 6.5 |
| Dioxane | 5.5 |
| CH3CN | 15.9 |
| THF | 23.0 |
| DMF | 89.8 |
| EtOH | 90.2 |
| Solvent free | 99.4 |

| Entry | R | Catalyst | Conv. (%) e | Yield 2 (%) e | Yield 3 (%) e |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 a | H | Fe/Mg | 99.8 | 0.6 | 99.2 |
| 2 | H | V/Mg | 99.6 | 0.5 | 99.1 |
| 3b | H | MgO | 26.5 | 3.5 | 23.2 |
| 4c | H | HCl | 91.2 | 83.2 | 8.7 |
| 5c | H | TEA | 85.6 | 4.5 | 61.1 |
| 6c | H | ZIF-8 | 90 | 3.2 | 73.8 |
| 7 | Br | V/Mg | 97.3 | 1.2 | 96.5 |
| 8 | Br | Fe/Mg | 98.4 | 1.4 | 97.2 |
| 9 | OCH3 | V/Mg | 99.5 | 0.8 | 98.7 |
| 10 | OCH3 | Fe/Mg | 99.6 | 0.5 | 99.1 |
| 11 d | CH3COOCH2CN | Fe/Mg | 13.7 | 10.9 | 3.0 |
| 12 d | CH3COOCH2CN | V/Mg | 10.5 | 8.2 | 2.3 |
| MOFs | Conversion | Time (h) | Catalyst Amount (%) | TOF (h−1) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CPM200-VMg | 98.5 | 3 | 1% | 32.8 | This work |
| CPM200-FeMg | 99.6 | 33.2 | |||
| CPM200-GaMg | 81.4 | 27.1 | |||
| CPM200-ScMg | 88.0 | 29.3 | |||
| CPM200-InMg | 78.3 | 26.1 | |||
| CPM200-InCo | 70.2 | 23.4 | |||
| CPM200-InMn | 58.9 | 19.6 | |||
| J-199 | 99 | 4 | 6% | 4.1 | [3] |
| MIL-101-AB-x | 99 | 2 | 4% | 12.5 | [26] |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zheng, M.; Wang, Y.; Feng, P. Bifunctional Heterometallic Metal-Organic Frameworks for Solvent-Free Heterogeneous Cascade Catalysis. Catalysts 2020, 10, 309. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal10030309
Zheng M, Wang Y, Feng P. Bifunctional Heterometallic Metal-Organic Frameworks for Solvent-Free Heterogeneous Cascade Catalysis. Catalysts. 2020; 10(3):309. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal10030309
Chicago/Turabian StyleZheng, Mingming, Yanxiang Wang, and Pingyun Feng. 2020. "Bifunctional Heterometallic Metal-Organic Frameworks for Solvent-Free Heterogeneous Cascade Catalysis" Catalysts 10, no. 3: 309. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal10030309
APA StyleZheng, M., Wang, Y., & Feng, P. (2020). Bifunctional Heterometallic Metal-Organic Frameworks for Solvent-Free Heterogeneous Cascade Catalysis. Catalysts, 10(3), 309. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal10030309