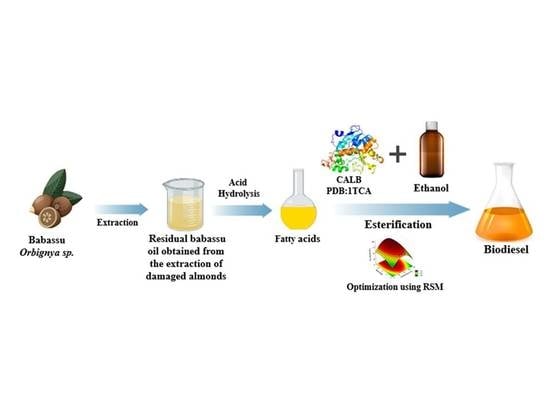
Optimization of the Production of Enzymatic Biodiesel from Residual Babassu Oil (Orbignya sp.) via RSM
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Analysis of the Chemical Composition of Residual Oil from Babassu
2.2. Physicochemical Characterization of the Residual Babassu oil and Free Fatty Acids
2.3. Statistical Analysis
2.3.1. Model Fitting and Analysis of Variance (ANOVA)
2.3.2. Effect of Reaction Parameters
2.4. Properties of Biodiesel
2.5. Operational Stability of the Biocatalyst
2.6. Modification of the External and Internal Texture of Biocatalyst
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Physicochemical Characterization of Residual Babassu Oil
3.3. Analysis of the Chemical Composition of Residual Babassu Oil
3.4. Production of Free Fatty Acids
3.5. Esterification Reactions
3.6. Analysis of the Percentage of Ethyl Esters
3.7. Design of Experiment
3.8. Statistical Analysis Using Response Surface Methodology
3.9. Gas Chromatography (GC) Analysis
3.10. Operational Stability of the Biocatalyst
3.11. Modification of the External and Internal Texture of Biocatalyst
3.11.1. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
3.11.2. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy(FTIR)
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tan, T.; Lu, J.; Nie, K.; Deng, L.; Wang, F. Biodiesel production with immobilized lipase: A review. Biotechnol. Adv. 2010, 28, 628–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barragán-Escandón, A.; Terrados-Cepeda, J.; Zalamea-León, E. The Role of Renewable Energy in the Promotion of Circular Urban Metabolism. Sustainability 2017, 9, 2341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Luque, R.; Lovett, J.C.; Datta, B.; Clancy, J.; Campelo, J.M.; Romero, A.A. Biodiesel as feasible petrol fuel replacement: A multidisciplinary overview. Energy Environ. Sci. 2010, 3, 1706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, D.; Sharma, D.; Soni, S.L.; Sharma, S.; Kumar Sharma, P.; Jhalani, A. A review on feedstocks, production processes, and yield for different generations of biodiesel. Fuel 2020, 262, 116553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acharya, N.; Nanda, P.; Panda, S.; Acharya, S. A comparative study of stability characteristics of mahua and jatropha biodiesel and their blends. J. King Saud Univ. Eng. Sci. 2019, 31, 184–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergmann, J.; Tupinambá, D.; Costa, O.Y.; Almeida, J.R.; Barreto, C.; Quirino, B. Biodiesel production in Brazil and alternative biomass feedstocks. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2013, 21, 411–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hama, S.; Kondo, A. Enzymatic biodiesel production: An overview of potential feedstocks and process development. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 135, 386–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teixeira, M.A. Heat and power demands in babassu palm oil extraction industry in Brazil. Energy Convers. Manag. 2005, 46, 2068–2074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguieiras, E.C.G.; Cavalcanti-Oliveira, E.D.; de Castro, A.M.; Langone, M.A.P.; Freire, D.M.G. Biodiesel production from Acrocomia aculeata acid oil by (enzyme/enzyme) hydroesterification process: Use of vegetable lipase and fermented solid as low-cost biocatalysts. Fuel 2014, 135, 315–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veljković, V.B.; Biberdžić, M.O.; Banković-Ilić, I.B.; Djalović, I.G.; Tasić, M.B.; Nježić, Z.B.; Stamenković, O.S. Biodiesel production from corn oil: A review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2018, 91, 531–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavalcanti-Oliveira, E.D.A.; da Silva, P.R.; Ramos, A.P.; Aranda, D.A.G.; Freire, D.M.G. Study of soybean oil hydrolysis catalyzed by thermomyces lanuginosus lipase and its application to biodiesel production via hydroesterification. Enzyme Res. 2011, 2011, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Talukder, M.M.R.; Wu, J.C.; Fen, N.M.; Melissa, Y.L.S. Two-step lipase catalysis for production of biodiesel. Biochem. Eng. J. 2010, 49, 207–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soares, D.; Pinto, A.F.; Gonçalves, A.G.; Mitchell, D.A.; Krieger, N. Biodiesel production from soybean soapstock acid oil by hydrolysis in subcritical water followed by lipase-catalyzed esterification using a fermented solid in a packed-bed reactor. Biochem. Eng. J. 2013, 81, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ching-Velasquez, J.; Fernández-Lafuente, R.; Rodrigues, R.C.; Plata, V.; Rosales-Quintero, A.; Torrestiana-Sánchez, B.; Tacias-Pascacio, V.G. Production and characterization of biodiesel from oil of fish waste by enzymatic catalysis. Renew. Energy 2020, 153, 1346–1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muanruksa, P.; Kaewkannetra, P. Combination of fatty acids extraction and enzymatic esterification for biodiesel production using sludge palm oil as a low-cost substrate. Renew. Energy 2020, 146, 901–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, L.; Feng, Y.; Wang, G.; Wang, Z.; Bilal, M.; Lv, H.; Jia, S.; Cui, J. Production and use of immobilized lipases in/on nanomaterials: A review from the waste to biodiesel production. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 152, 207–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chua, S.Y.; Periasamy, L.A.; Goh, C.M.H.; Tan, Y.H.; Mubarak, N.M.; Kansedo, J.; Khalid, M.; Walvekar, R.; Abdullah, E.C. Biodiesel synthesis using natural solid catalyst derived from biomass waste—A review. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2020, 81, 41–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merza, F.; Fawzy, A.; AlNashef, I.; Al-Zuhair, S.; Taher, H. Effectiveness of using deep eutectic solvents as an alternative to conventional solvents in enzymatic biodiesel production from waste oils. Energy Rep. 2018, 4, 77–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchetti, J.M.; Miguel, V.U.; Errazu, A.F. Possible methods for biodiesel production. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2007, 11, 1300–1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reis, C.; Sousa, E.; Serpa, J.; Oliveira, R.; Oliveira, R.; Santos, J. Design of immobilized enzyme biocatalysts: Drawbacks and opportunities. Quim. Nova 2019, 42, 768–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babaki, M.; Yousefi, M.; Habibi, Z.; Mohammadi, M. Process optimization for biodiesel production from waste cooking oil using multi-enzyme systems through response surface methodology. Renew. Energy 2017, 105, 465–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yu, D.; Tian, L.; Wu, H.; Wang, S.; Wang, Y.; Ma, D.; Fang, X. Ultrasonic irradiation with vibration for biodiesel production from soybean oil by Novozym 435. Process Biochem. 2010, 45, 519–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taher, H.; Al-Zuhair, S.; Al-Marzouqi, A.H.; Haik, Y.; Farid, M. Enzymatic biodiesel production of microalgae lipids under supercritical carbon dioxide: Process optimization and integration. Biochem. Eng. J. 2014, 90, 103–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madras, G.; Kolluru, C.; Kumar, R. Synthesis of biodiesel in supercritical fluids. Fuel 2004, 83, 2029–2033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyazawa, T.; Yamamoto, M.; Danjo, H. Chemoselective acylation of (hydroxyalkyl) phenols catalyzed by Candida antarctica lipase B. Biotechnol. Lett. 2013, 35, 625–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melo, A.; Silva, F.; dos Santos, J.; Fernández-Lafuente, R.; Lemos, T.; Dias Filho, F. Synthesis of benzyl acetate catalyzed by lipase immobilized in nontoxic chitosan-polyphosphate beads. Molecules 2017, 22, 2165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Castejón, N.; Moreno-Pérez, S.; Abreu Silveira, E.; Fernández Lorente, G.; Guisán, J.M.; Señoráns, F.J. Synthesis of omega-3 ethyl esters from chia oil catalyzed by polyethylene glycol-modified lipases with improved stability. Food Chem. 2019, 271, 433–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yousefi, M.; Marciello, M.; Guisan, J.M.; Fernandez-Lorente, G.; Mohammadi, M.; Filice, M. Fine modulation of the catalytic properties of Rhizomucor miehei lipase driven by different immobilization strategies for the selective hydrolysis of fish oil. Molecules 2020, 25, 545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Abreu Silveira, E.; Moreno-Perez, S.; Basso, A.; Serban, S.; Pestana-Mamede, R.; Tardioli, P.W.; Farinas, C.S.; Castejon, N.; Fernandez-Lorente, G.; Rocha-Martin, J.; et al. Biocatalyst engineering of Thermomyces lanuginosus lipase adsorbed on hydrophobic supports: Modulation of enzyme properties for ethanolysis of oil in solvent-free systems. J. Biotechnol. 2019, 289, 126–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Remonatto, D.; de Oliveira, J.V.; Manuel Guisan, J.; de Oliveira, D.; Ninow, J.; Fernandez-Lorente, G. Production of FAME and FAEE via Alcoholysis of Sunflower Oil by Eversa Lipases Immobilized on Hydrophobic Supports. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2018, 185, 705–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreno-Perez, S.; Luna, P.; Señorans, J.; Rocha-Martin, J.; Guisan, J.M.; Fernandez-Lorente, G. Enzymatic transesterification in a solvent-free system: Synthesis of sn-2 docosahexaenoyl monoacylglycerol. Biocatal. Biotransform. 2018, 36, 265–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinheiro, M.P.; Monteiro, R.R.C.; Silva, F.F.M.; Lemos, T.L.G.; Fernandez-Lafuente, R.; Gonçalves, L.R.B.; dos Santos, J.C.S. Modulation of Lecitase properties via immobilization on differently activated Immobead-350: Stabilization and inversion of enantiospecificity. Process Biochem. 2019, 87, 128–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Morais Júnior, W.G.; Moura Maia, A.; Alves Martins, P.; Fernández-Lorente, G.; Guisán, J.M.; Pessela, B.C. Influence of different immobilization techniques to improve the enantioselectivity of lipase from Geotrichum candidum applied on the resolution of mandelic acid. Mol. Catal. 2018, 458, 89–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gotor-Fernández, V.; Busto, E.; Gotor, V. Candida antarctica Lipase B: An Ideal Biocatalyst for the preparation of nitrogenated organic compounds. Adv. Synth. Catal. 2006, 348, 797–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Liao, M.; Chen, D. Fast and efficient recovery of lipase by polyacrylic acid-coated magnetic nano-adsorbent with high activity retention. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2006, 51, 113–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goswami, A.; Goswami, J. DMSO-triggered enhancement of enantioselectivity in Novozyme 435-catalyzed transesterification of chiral 1-phenylethanols. Tetrahedron Lett. 2005, 46, 4411–4413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Joubioux, F.; Bridiau, N.; Ben Henda, Y.; Achour, O.; Graber, M.; Maugard, T. The control of Novozym® 435 chemoselectivity and specificity by the solvents in acylation reactions of amino-alcohols. J. Mol. Catal. B Enzym. 2013, 95, 99–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Z.-Y.; Bi, Y.-H.; Li, X.-Q.; Zong, M.-H. Influence of substituent groups in regioselective acylation of nucleosides by Novozym 435 lipase. Process Biochem. 2013, 48, 1208–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bajaj, A.; Lohan, P.; Jha, P.N.; Mehrotra, R. Biodiesel production through lipase catalyzed transesterification: An overview. J. Mol. Catal. B Enzym. 2010, 62, 9–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimada, Y.; Watanabe, Y.; Sugihara, A.; Tominaga, Y. Enzymatic alcoholysis for biodiesel fuel production and application of the reaction to oil processing. J. Mol. Catal. B Enzym. 2002, 17, 133–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amini, Z.; Ong, H.C.; Harrison, M.D.; Kusumo, F.; Mazaheri, H.; Ilham, Z. Biodiesel production by lipase-catalyzed transesterification of Ocimum basilicum L. (sweet basil) seed oil. Energy Convers. Manag. 2017, 132, 82–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Marín-Suárez, M.; Méndez-Mateos, D.; Guadix, A.; Guadix, E.M. Reuse of immobilized lipases in the transesterification of waste fish oil for the production of biodiesel. Renew. Energy 2019, 140, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bueso, F.; Moreno, L.; Cedeño, M.; Manzanarez, K. Lipase-catalyzed biodiesel production and quality with Jatropha curcas oil: Exploring its potential for Central America. J. Biol. Eng. 2015, 9, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sivaramakrishnan, R.; Incharoensakdi, A. Direct transesterification of Botryococcus sp. catalysed by immobilized lipase: Ultrasound treatment can reduce reaction time with high yield of methyl ester. Fuel 2017, 191, 363–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shomal, R.; Hisham, H.; Mlhem, A.; Hassan, R.; Al-Zuhair, S. Simultaneous extraction–reaction process for biodiesel production from microalgae. Energy Rep. 2019, 5, 37–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, J.; Xin, Z.; Meng, X.; Sun, S.; Qiao, Q.; Deng, H. Studies on biodiesel production from DDGS-extracted corn oil at the catalysis of Novozym 435/super absorbent polymer. Fuel 2015, 146, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talukder, M.M.R.; Wu, J.C.; Van Nguyen, T.B.; Fen, N.M.; Melissa, Y.L.S. Novozym 435 for production of biodiesel from unrefined palm oil: Comparison of methanolysis methods. J. Mol. Catal. B Enzym. 2009, 60, 106–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maceiras, R.; Vega, M.; Costa, C.; Ramos, P.; Márquez, M.C. Effect of methanol content on enzymatic production of biodiesel from waste frying oil. Fuel 2009, 88, 2130–2134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezania, S.; Oryani, B.; Park, J.; Hashemi, B.; Yadav, K.K.; Kwon, E.E.; Hur, J.; Cho, J. Review on transesterification of non-edible sources for biodiesel production with a focus on economic aspects, fuel properties and by-product applications. Energy Convers. Manag. 2019, 201, 112155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehan, M.; Gardy, J.; Demirbas, A.; Rashid, U.; Budzianowski, W.M.; Pant, D.; Nizami, A.S. Waste to biodiesel: A preliminary assessment for Saudi Arabia. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 250, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Baskar, G.; Aiswarya, R. Trends in catalytic production of biodiesel from various feedstocks. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2016, 57, 496–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, R.; Lu, L.; Shi, Y.; Yuan, H.; Shi, J. Catalysts from renewable resources for biodiesel production. Energy Convers. Manag. 2018, 178, 277–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norjannah, B.; Ong, H.C.; Masjuki, H.H.; Juan, J.C.; Chong, W.T. Enzymatic transesterification for biodiesel production: A comprehensive review. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 60034–60055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moazeni, F.; Chen, Y.-C.; Zhang, G. Enzymatic transesterification for biodiesel production from used cooking oil, a review. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 216, 117–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melo, E.; Michels, F.; Arakaki, D.; Lima, N.; Gonçalves, D.; Cavalheiro, L.; Oliveira, L.; Caires, A.; Hiane, P.; Nascimento, V. First study on the oxidative stability and elemental analysis of Babassu (Attalea speciosa) edible oil produced in brazil using a domestic extraction machine. Molecules 2019, 24, 4235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stankovic, I. Codex Alimentarius. In Encyclopedia of Food and Health; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016; Volume 1, pp. 191–196. [Google Scholar]
- Mihaela, P.; Josef, R.; Monica, N.; Rudolf, Z. Perspectives of safflower oil as biodiesel source for South Eastern Europe (comparative study: Safflower, soybean and rapeseed). Fuel 2013, 111, 114–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, D.; Sharma, D.; Soni, S.L.; Sharma, S.; Kumari, D. Chemical compositions, properties, and standards for different generation biodiesels: A review. Fuel 2019, 253, 60–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lutz, A.; Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. Summary for Policymakers. In Climate Change 2013–The Physical Science Basis; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2008; Volume 1, pp. 1–30. [Google Scholar]
- British Standard Institution. Bs En 14214:2008 + a1:2009 Automotive fuels—Fatty acid methyl esters (FAME) for diesel engines—Requirements and test methods. Br. Stand. Inst. 2010, 1, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- ASTM International. D445-18 Standard test method for kinematic viscosity of transparent and opaque liquids (and calculation of dynamic viscosity). Annu. Book ASTM Stand. 2010, 1, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Brazilian National Standards Organization. NBR 14065: Destilados de Petróleo e Óleos Viscosos—Determinação da Densidade e da Densidade Relativa Pelo Densímetro Digital; Brazilian National Standards Organization: Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 2013; Volume 1, pp. 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- do Valle, C.P.; Rodrigues, J.S.; Fechine, L.M.U.D.; Cunha, A.P.; Queiroz Malveira, J.; Luna, F.M.T.; Ricardo, N.M.P.S. Chemical modification of Tilapia oil for biolubricant applications. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 191, 158–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibeto, C.N.; Okoye, C.O.B.; Ofoefule, A.U. Comparative Study of the physicochemical characterization of some oils as potential feedstock for biodiesel Production. ISRN Renew. Energy 2012, 2012, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ostrowska-Ligeza, E.; Bekas, W.; Kowalska, D.; Lobacz, M.; Wroniak, M.; Kowalski, B. Kinetics of commercial olive oil oxidation: Dynamic differential scanning calorimetry and Rancimat studies. Eur. J. Lipid Sci. Technol. 2010, 112, 268–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Mesa, J.A.; Luque de Castro, M.D.; Valcárcel, M. Factors affecting the gravimetric determination of the oxidative stability of oils. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 1993, 70, 245–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porto, T.S.; Porto, C.S.; Cavalcanti, M.T.H.; Filho, J.L.L.; Perego, P.; Porto, A.L.F.; Converti, A.; Pessoa, A. Kinetic and thermodynamic investigation on ascorbate oxidase activity and stability of a Cucurbita maxima extract. Biotechnol. Prog. 2006, 22, 1637–1642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hui, Y.H.; Culbertson, J.D.; Duncan, S.E.; Legarreta, I.G.; Li-Chan, E.C.Y.; Ma, C.Y.; Manley, C.; McMeekin, T.; Nip, W.K.; Nollet, L.M.L.; et al. Handbook of food science, technology, and engineering. Choice Rev. Online 2006, 43, 5852. [Google Scholar]
- Hossain, A.K.; Ouadi, M.; Siddiqui, S.U.; Yang, Y.; Brammer, J.; Hornung, A.; Kay, M.; Davies, P.A. Experimental investigation of performance, emission and combustion characteristics of an indirect injection multi-cylinder CI engine fuelled by blends of de-inking sludge pyrolysis oil with biodiesel. Fuel 2013, 105, 135–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ramírez-Verduzco, L.F.; Rodríguez-Rodríguez, J.E.; del Rayo Jaramillo-Jacob, A. Predicting cetane number, kinematic viscosity, density and higher heating value of biodiesel from its fatty acid methyl ester composition. Fuel 2012, 91, 102–111. [Google Scholar]
- Elkelawy, M.; Bastawissi, H.A.-E.; Esmaeil, K.K.; Radwan, A.M.; Panchal, H.; Sadasivuni, K.K.; Suresh, M.; Israr, M. Maximization of biodiesel production from sunflower and soybean oils and prediction of diesel engine performance and emission characteristics through response surface methodology. Fuel 2020, 266, 117072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czech Standards Institute. EN 14103. Fatty Acid Methyl Esters (FAME)—Determination of ester and linolenic acid methyl ester contents. Br. Stand. 2011, 1, 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- Ezekannagha, C.B.; Ude, C.N.; Onukwuli, O.D. Optimization of the methanolysis of lard oil in the production of biodiesel with response surface methodology. Egypt J. Pet. 2017, 26, 1001–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manan, F.M.A.; Rahman, I.N.A.; Marzuki, N.H.C.; Mahat, N.A.; Huyop, F.; Wahab, R.A. Statistical modelling of eugenol benzoate synthesis using Rhizomucor miehei lipase reinforced nanobioconjugates. Process Biochem. 2016, 51, 249–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Silveira, A.; Villarreal, R.; Garmendia, G.; Rufo, C.; Vero, S. Process conditions for a rapid in situ transesterification for biodiesel production from oleaginous yeasts. Electron. J. Biotechnol. 2019, 38, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fjerbaek, L.; Christensen, K.V.; Norddahl, B. A review of the current state of biodiesel production using enzymatic transesterification. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2009, 102, 1298–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, H.C.; Liang, S.-H.; Doan, T.T.; Su, C.-H.; Yang, P.-C. Lipase-catalyzed synthesis of biodiesel from black soldier fly (Hermetica illucens): Optimization by using response surface methodology. Energy Convers. Manag. 2017, 145, 335–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayak, M.G.; Vyas, A.P. Optimization of microwave-assisted biodiesel production from Papaya oil using response surface methodology. Renew. Energy 2019, 138, 18–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, Y.; Shimada, Y.; Baba, T.; Ohyagi, N.; Moriyama, S.; Terai, T.; Tominaga, Y.; Sugihara, A. Methyl esterification of waste fatty acids with immobilized Candida antarctica Lipase. J. Oleo Sci. 2002, 51, 655–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tupufia, S.C.; Jeon, Y.J.; Marquis, C.; Adesina, A.A.; Rogers, P.L. Enzymatic conversion of coconut oil for biodiesel production. Fuel Process. Technol. 2013, 106, 721–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Leung, D.Y.C. Optimization of biodiesel production from camelina oil using orthogonal experiment. Appl. Energy 2011, 88, 3615–3624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, X.; Liu, J.; Zeng, G.; Shi, J.; Tong, J.; Huang, G. Optimization of conversion of waste rapeseed oil with high FFA to biodiesel using response surface methodology. Renew. Energy 2008, 33, 1678–1684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM International. D6751-15c Standard Specification for Biodiesel Fuel Blend Stock (B100) for Middle Distillate Fuels. ASTM Int. 2010, 1, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- ASTM International. D1480-15. A. Standard Test Method for Density and Relative Density (Specific Gravity) of Viscous Materials by Bingham Pycnometer. Annu. Book ASTM Stand. 2010, 1, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Sakthivel, R.; Ramesh, K.; Purnachandran, R.; Mohamed Shameer, P. A review on the properties, performance and emission aspects of the third generation biodiesels. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2018, 82, 2970–2992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pratas, M.J.; Freitas, S.V.D.; Oliveira, M.B.; Monteiro, S.C.; Lima, A.S.; Coutinho, J.A.P. Biodiesel Density: Experimental Measurements and Prediction Models. Energy Fuels 2011, 25, 2333–2340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhuiya, M.M.K.; Rasul, M.G.; Khan, M.M.K.; Ashwath, N.; Azad, A.K.; Hazrat, M.A. Prospects of 2nd generation biodiesel as a sustainable fuel—Part 2: Properties, performance and emission characteristics. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2016, 55, 1129–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Li, Q.; Zeng, Q.; Zhang, J.; Yu, Z.; Liu, Z. Conversion of Solid Organic Wastes into Oil via Boettcherisca peregrine (Diptera: Sarcophagidae) Larvae and Optimization of Parameters for Biodiesel Production. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, 45940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shu, Q.; Yang, B.; Yang, J.; Qing, S. Predicting the viscosity of biodiesel fuels based on the mixture topological index method. Fuel 2007, 86, 1849–1854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dossat, V.; Combes, D.; Marty, A. Continuous enzymatic transesterification of high oleic sunflower oil in a packed bed reactor: Influence of the glycerol production. Enzyme Microb. Technol. 1999, 25, 194–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sangaletti, N.; Cea, M.; Regitano-d’Arce, M.A.B.; de Souza Vieira, T.M.F.; Navia, R. Enzymatic transesterification of soybean ethanolic miscella for biodiesel production. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2013, 88, 2098–2106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, A.-F.; Jones, K.C.; Foglia, T.A.; Marmer, W.N. Continuous production of ethyl esters of grease using an immobilized lipase. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 2004, 81, 749–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortiz, C.; Ferreira, M.L.; Barbosa, O.; dos Santos, J.C.S.; Rodrigues, R.C.; Berenguer-Murcia, Á.; Briand, L.E.; Fernandez-Lafuente, R. Novozym 435: The “perfect” lipase immobilized biocatalyst? Catal. Sci. Technol. 2019, 9, 2380–2420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bashtani, E.; Amiri, A.; Baghayeri, M. A nanocomposite consisting of poly (methyl methacrylate), graphene oxide and Fe3O4 nanoparticles as a sorbent for magnetic solid-phase extraction of aromatic amines. Microchim. Acta 2018, 185, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- José, C.; Austic, G.B.; Bonetto, R.D.; Burton, R.M.; Briand, L.E. Investigation of the stability of Novozym® 435 in the production of biodiesel. Catal. Today 2013, 213, 73–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viñambres, M.; Filice, M.; Marciello, M. Modulation of the catalytic properties of lipase B from Candida antarctica by immobilization on tailor-made magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles: The key role of nanocarrier surface engineering. Polymers 2018, 10, 615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mulinari, J.; Venturin, B.; Sbardelotto, M.; Dall Agnol, A.; Scapini, T.; Camargo, A.F.; Baldissarelli, D.P.; Modkovski, T.A.; Rossetto, V.; Dalla Rosa, C.; et al. Ultrasound-assisted hydrolysis of waste cooking oil catalyzed by homemade lipases. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2017, 35, 313–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- dos Santos, R.C.M.; Gurgel, P.C.; Pereira, N.S.; Breves, R.A.; de Matos, P.R.R.; Silva, L.P.; Sales, M.J.A.; Lopes, R.D.V.V. Ethyl esters obtained from pequi and macaúba oils by transesterification with homogeneous acid catalysis. Fuel 2020, 259, 116206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monteiro, R.R.C.; Neto, D.M.A.; Fechine, P.B.A.; Lopes, A.A.S.; Gonçalves, L.R.B.; dos Santos, J.C.S.; de Souza, M.C.M.; Fernandez-Lafuente, R. Ethyl butyrate synthesis catalyzed by Lipases A and B from Candida antarctica immobilized onto magnetic nanoparticles. Improvement of biocatalysts’ performance under ultrasonic irradiation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 5807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cavalcanti, E.D.C.; Aguieiras, É.C.G.; da Silva, P.R.; Duarte, J.G.; Cipolatti, E.P.; Fernandez-Lafuente, R.; da Silva, J.A.C.; Freire, D.M.G. Improved production of biolubricants from soybean oil and different polyols via esterification reaction catalyzed by immobilized lipase from Candida rugosa. Fuel 2018, 215, 705–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kochepka, D.M.; Dill, L.P.; Couto, G.H.; Krieger, N.; Ramos, L.P. Production of fatty acid ethyl esters from waste cooking oil using novozym 435 in a solvent-free system. Energy Fuels 2015, 29, 8074–8081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bezerra, R.M.; Neto, D.M.A.; Galvão, W.S.; Rios, N.S.; Carvalho, A.C.L.D.M.; Correa, M.A.; Bohn, F.; Fernandez-Lafuente, R.; Fechine, P.B.A.; de Mattos, M.C.; et al. Design of a lipase-nano particle biocatalysts and its use in the kinetic resolution of medicament precursors. Biochem. Eng. J. 2017, 125, 104–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Substrate | Alcohol | Conversion/Experimental Conditions | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sweet basil seed oil | Methanol | 94.58%/68 h at 47 °C | [41] |
| Fish oil | Ethanol | 52.11%/8 h at 35 °C | [42] |
| Jatropha oil | Methanol | 66.80%/24 h at 40 °C | [43] |
| Microalgal oil Botryococcus sp. | Methanol | 88.00%/4 h at 40 °C | [44] |
| Oils from microalgae | Methanol | 19.30%/6 h at 35 °C | [45] |
| Corn oil | Methanol | 91.00%/18 h at 60 °C | [46] |
| Soybean oil | Methanol | 96.00%/4 h at 40 °C | [22] |
| Palm oil | Methanol | 91.00%–92.00%/10, 20, 24 h at 40 °C | [47] |
| Frying oil | Methanol | 89.10%/4 h at 50 °C | [48] |
| Fatty Acid | Nome | Formula | Molecular Weight (g/mol) | Percentage (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C6:0 | Caproic Acid | C6H12O2 | 116.15 | 0.80 |
| C8:0 | Caprylic Acid | C8H16O2 | 144.21 | 9.64 |
| C10:0 | Capric Acid | C10H20O2 | 172.26 | 6.85 |
| C12:0 | Lauric Acid | C12H24O2 | 200.31 | 41.55 |
| C14:0 | Myristic Acid | C14H28O2 | 228.37 | 14.01 |
| C16:0 | Palmitic Acid | C16H32O2 | 256.40 | 6.96 |
| C18:0 | Stearic Acid | CH3(CH2)16COOH | 284.48 | 2.66 |
| C18:1n9c | Oleic Acid | C18H34O2 | 282.47 | 11.04 |
| C18:2n6c | Linoleic Acid | C18H32O2 | 280.44 | 1.76 |
| Others | - | - | - | 4.73 |
| Analytical Parameter | Technical Norm | Residual Babassu Oil | Babassu Oil [58] | Soy Oil [57,58] | CODEX [56] | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Acidity Level (mgKOH/g) | Adolfo Lutz Institute [59] | 4.851 174.442 | - | 0.41 | 0.28 | 0.50 |
| Saponification Index (mgKOH/g) | Adolfo Lutz Institute [59] | 271.94 | - | - | - | 245–256 |
| Oxidative Stability (hours) | EN 14.214 [60] | 1.30 | - | - | 7.16 | - |
| Kinematic Viscosity at 40 °C (mm2/s) | ASTM D445-18 [61] | 3.96 7.782 | 2.95 | 3.18 | 3.15 | 1.44–1.45 |
| Density at 20 °C (g/cm3) | NBR 14.065 [62] | 0.92 0.872 | 0.92 | 0.92 | 0.92 | 0.914–0.917 |
| Run | Temperature (°C) | Time (hours) | Molar Ratio (FFAs/alcohol) | Biocatalyst Content (grams) | Conversion (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 30 | 2 | 1:1 | 0.05 | 70.42 ± 0.04 |
| 2 | 30 | 2 | 1:1 | 0.15 | 65.19 ± 0.03 |
| 3 | 30 | 2 | 1:15 | 0.05 | 85.94 ± 0.04 |
| 4 | 30 | 2 | 1:15 | 0.15 | 91.11 ± 0.05 |
| 5 | 30 | 6 | 1:1 | 0.05 | 71.22 ± 0.04 |
| 6 | 30 | 6 | 1:1 | 0.15 | 70.69 ± 0.04 |
| 7 | 30 | 6 | 1:15 | 0.05 | 91.10 ± 0.05 |
| 8 | 30 | 6 | 1:15 | 0.15 | 91.07 ± 0.05 |
| 9 | 50 | 2 | 1:1 | 0.05 | 67.88 ± 0.03 |
| 10 | 50 | 2 | 1:1 | 0.15 | 68.61 ± 0.03 |
| 11 | 50 | 2 | 1:15 | 0.05 | 89.92 ± 0.04 |
| 12 | 50 | 2 | 1:15 | 0.15 | 91.10 ± 0.05 |
| 13 | 50 | 6 | 1:1 | 0.05 | 68.90 ± 0.03 |
| 14 | 50 | 6 | 1:1 | 0.15 | 68.07 ± 0.03 |
| 15 | 50 | 6 | 1:15 | 0.05 | 90.49 ± 0.05 |
| 16 | 50 | 6 | 1:15 | 0.15 | 91.12 ± 0.05 |
| 17 | 30 | 4 | 1:8 | 0.10 | 86.07 ± 0.04 |
| 18 | 50 | 4 | 1:8 | 0.10 | 85.97 ± 0.04 |
| 19 | 40 | 2 | 1:8 | 0.10 | 88.63 ± 0.04 |
| 20 | 40 | 6 | 1:8 | 0.10 | 84.81 ± 0.04 |
| 21 | 40 | 4 | 1:1 | 0.10 | 69.77 ± 0.03 |
| 22 | 40 | 4 | 1:15 | 0.10 | 91.08 ± 0.05 |
| 23 | 40 | 4 | 1:8 | 0.05 | 91.07 ± 0.05 |
| 24 | 40 | 4 | 1:8 | 0.15 | 89.85 ± 0.04 |
| 25 (C) | 40 | 4 | 1:8 | 0.10 | 89.79 ± 0.04 |
| 26 (C) | 40 | 4 | 1:8 | 0.10 | 89.84 ± 0.04 |
| 27 (C) | 40 | 4 | 1:8 | 0.10 | 89.92 ± 0.04 |
| Source of Variation | Sum of Squares | Degrees of Freedom | Mean Squares | Fcal | Probability (P) > F |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Regression | 2568.10 | 14 | 183.44 | 58.98 | 0.0001 |
| Residual error | 37.32 | 12 | 3.11 | - | - |
| Lack of fit | 37.31 | 10 | 3.73 | 867.68 | 0.001152 |
| Pure error | 0.009 | 2 | 0.00 | - | - |
| Total | 2605.41 | 26 | 100.21 | - | - |
| Analytical Parameter | Technical Norm Adopted | Biodiesel Babassu | Reference [58] | ASTM D6751 [83] | EN 14,214 [60] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Acidity Level (mgKOH/g) | Adolfo Lutz Institute [59] | 0.41 | 0.425 | 0.5 maximum | 0.5 maximum |
| Ester content (%) | EN 14,103 [72] | 96.8 | nra | nra | 96.5 |
| Kinematic Viscosity at 40 °C (mm2/s) | ASTM D445-18 [61] | 1.6 | 4.2 | 1.9–6.0 | 3.5–5.0 |
| Density at 20 °C (kg/m3) | ASTM D1480 [84] | 820 | 872 | <880 | 860–900 |
| Map Sum Spectrum (%) | ||
|---|---|---|
| Elements | Novozym® 435 before Reaction | Novozym® 435 after Reaction |
| C | 84.9 | 83.3 |
| O | 15.0 | 14.9 |
| S | 0.2 | 0.2 |
| Al | - | 0.2 |
| Ca | - | 1.2 |
| Si | - | 0.1 |
| Analytical Parameter | Technical Standard |
|---|---|
| Acidity level (mgKOH/g) | Instituto Adolfo Lutz [59] |
| Saponification Index (mgKOH/g) | Instituto Adolfo Lutz [59] |
| Oxidative Stability (hours) | EN14214 2003 [60] |
| Kinematic Viscosity at 40 °C (mm2/s) | ASTM D445-18 [61] |
| Density at 20 °C (g/cm3) | NBR 14,065 [62] |
| Codes | Variable | Levels | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| - | - | −1 | 0 | 1 |
| X1 | Temperature (°C) | 30 | 40 | 50 |
| X2 | Time (hour) | 2 | 4 | 6 |
| X3 | Molar Ratio Fatty Acid: Alcohol (m/v) | 1:1 | 1:8 | 1:15 |
| X4 | Biocatalyst Content (%m/m) | 5 | 10 | 15 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Moreira, K.S.; Moura Júnior, L.S.; Monteiro, R.R.C.; de Oliveira, A.L.B.; Valle, C.P.; Freire, T.M.; Fechine, P.B.A.; de Souza, M.C.M.; Fernandez-Lorente, G.; Guisan, J.M.; et al. Optimization of the Production of Enzymatic Biodiesel from Residual Babassu Oil (Orbignya sp.) via RSM. Catalysts 2020, 10, 414. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal10040414
Moreira KS, Moura Júnior LS, Monteiro RRC, de Oliveira ALB, Valle CP, Freire TM, Fechine PBA, de Souza MCM, Fernandez-Lorente G, Guisan JM, et al. Optimization of the Production of Enzymatic Biodiesel from Residual Babassu Oil (Orbignya sp.) via RSM. Catalysts. 2020; 10(4):414. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal10040414
Chicago/Turabian StyleMoreira, Katerine S., Lourembergue S. Moura Júnior, Rodolpho R. C. Monteiro, André L. B. de Oliveira, Camila P. Valle, Tiago M. Freire, Pierre B. A. Fechine, Maria C. M. de Souza, Gloria Fernandez-Lorente, José M. Guisan, and et al. 2020. "Optimization of the Production of Enzymatic Biodiesel from Residual Babassu Oil (Orbignya sp.) via RSM" Catalysts 10, no. 4: 414. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal10040414
APA StyleMoreira, K. S., Moura Júnior, L. S., Monteiro, R. R. C., de Oliveira, A. L. B., Valle, C. P., Freire, T. M., Fechine, P. B. A., de Souza, M. C. M., Fernandez-Lorente, G., Guisan, J. M., & dos Santos, J. C. S. (2020). Optimization of the Production of Enzymatic Biodiesel from Residual Babassu Oil (Orbignya sp.) via RSM. Catalysts, 10(4), 414. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal10040414