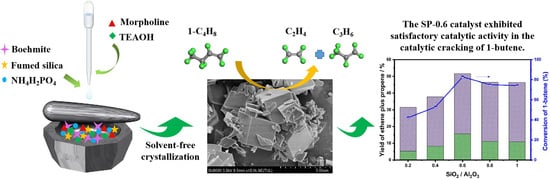
Solvent-Free Synthesis of SAPO-34 Zeolite with Tunable SiO2/Al2O3 Ratios for Efficient Catalytic Cracking of 1-Butene
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Catalyst Characterization
2.1.1. The Structural and Chemical Compositions of SAPO-34 Zeolite
2.1.2. The Morphology of SAPO-34 Zeolite
2.1.3. The Textural Properties of SAPO-34 Zeolite
2.1.4. The Acid Properties of SAPO-34 Zeolite
2.1.5. The 27Al, 29Si, and 31P MAS NMR Spectra of SAPO-34 Zeolite
2.2. Catalytic Performance of As-Synthesized SAPO-34 Zeolite
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Chemicals
3.2. Synthesis of SAPO-34 Zeolite
3.3. Catalyst Characterization
3.4. Catalytic Activity Evaluation
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sun, Q.; Xie, Z.; Yu, J. The state-of-the-art synthetic strategies for SAPO-34 zeolite catalysts in methanol-to-olefin conversion. Natl. Sci. Rev. 2018, 5, 542–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Peng, S.C.; Gao, M.B.; Li, H.; Yang, M.; Ye, M.; Liu, Z.M. Control of Surface Barriers in Mass Transfer to Modulate Methanol-to-Olefins Reaction over SAPO-34 Zeolites. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 21945–21948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, M.B.; Li, H.; Liu, W.J.; Xu, Z.C.; Peng, S.C.; Yang, M.; Ye, M.; Liu, Z.M. Imaging spatiotemporal evolution of molecules and active sites in zeolite catalyst during methanol-to-olefins reaction. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 3641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dusselier, M.; Davis, M.E. Small-Pore Zeolites: Synthesis and Catalysis. Chem. Rev. 2018, 118, 5265–5329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moliner, M.; Martinez, C.; Corma, A. Synthesis Strategies for Preparing Useful Small Pore Zeolites and Zeotypes for Gas Separations and Catalysis. Chem. Mater. 2014, 26, 246–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Wang, L.; Song, Z.N.; Li, S.G.; Yu, M. Growth of High-Quality, Thickness-Reduced Zeolite Membranes towards N2/CH4 Separation Using High-Aspect-Ratio Seeds. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2015, 54, 10843–10847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, L.F.; Qiu, C.F.; Zhuo, Z.X.; Zhang, D.W.; Zhao, S.F.; Wu, H.H.; Liu, Y.M.; He, M.Y. Acid strength controlled reaction pathways for the catalytic cracking of 1-butene to propene over ZSM-5. J. Catal. 2014, 309, 136–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zang, Y.H.; Dong, X.F.; Ping, D.; Geng, J.M.; Dang, H.F. Green routes for the synthesis of hierarchical HZSM-5 zeolites with low SiO2/Al2O3 ratios for enhanced catalytic performance. Catal. Commun. 2018, 113, 51–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minova, I.B.; Barrow, N.S.; Sauerwein, A.C.; Naden, A.B.; Cordes, D.B.; Slawin, A.M.Z.; Schuyten, S.J.; Wright, P.A. Silicon redistribution, acid site loss and the formation of a core–shell texture upon steaming SAPO-34 and their impact on catalytic performance in the Methanol-to-Olefins (MTO) reaction. J. Catal. 2021, 395, 425–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pimerzin, A.; Savinov, A.; Vutolkina, A.; Makova, A.; Glotov, A.; Vinokurov, V.; Pimerzin, A. Transition Metal Sulfides- and Noble Metal-Based Catalysts for N-Hexadecane Hydroisomerization: A Study of Poisons Tolerance. Catalysts 2020, 10, 594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, J.; Liu, Z.M.; Bao, X.H.; Liu, X.C.; Han, X.W.; He, C.Q.; Zhai, R.S. Crystallization and Si incorporation mechanisms of SAPO-34. Micropor. Mesopor. Mater. 2002, 53, 97–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sena, F.C.; de Souza, B.F.; de Almeida, N.C.; Cardoso, J.S.; Fernandes, L.D. Influence of framework composition over SAPO-34 and MeAPSO-34 acidity. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2011, 406, 59–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Du, A.P.; Wei, Y.X.; Wang, Y.L.; Yu, Z.X.; He, Y.L.; Zhang, X.Z.; Liu, Z.M. Synthesis of SAPO-34 with only Si(4Al) species: Effect of Si contents on Si incorporation mechanism and Si coordination environment of SAPO-34. Micropor. Mesopor. Mater. 2008, 115, 332–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, B.B.; Yang, M.; Qiao, Y.Y.; Li, J.Z.; Xiang, X.; Wu, P.F.; Wei, Y.X.; Xu, S.T.; Tian, P.; Liu, Z.M. A low-temperature approach to synthesize low-silica SAPO-34 nanocrystals and their application in the methanol-to-olefins (MTO) reaction. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2016, 6, 7569–7578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izadbakhsh, A.; Farhadi, F.; Khorasheh, F.; Sahebdelfar, S.; Asadi, M.; Yan, Z.F. Key parameters in hydrothermal synthesis and characterization of low silicon content SAPO-34 molecular sieve. Micropor. Mesopor. Mater. 2009, 126, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Meng, X.; Gao, X.; Xiao, F.S. Solvent-Free Synthesis of Zeolites: Mechanism and Utility. Acc. Chem. Res. 2018, 51, 1396–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Q.; Wang, Y.; Wang, L.; Yang, Z.; Wang, L.; Meng, X.; Xiao, F.-S. Solvent-free crystallization of ZSM-5 zeolite on SiC foam as a monolith catalyst for biofuel upgrading. Chin. J. Catal. 2020, 41, 1118–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.; Sun, Q.; Qi, G.; Yang, C.; Xu, J.; Chen, F.; Meng, X.; Deng, F.; Xiao, F.-S. Solvent-Free Synthesis of Silicoaluminophosphate Zeolites. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 9172–9175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, Y.; Chen, X.; Sun, Q.; Sheng, N.; Liu, Y.; Bian, C.; Chen, F.; Meng, X.; Xiao, F.-S. Solvent-Free Syntheses of Hierarchically Porous Aluminophosphate-Based Zeolites with AEL and AFI Structures. Chem. Eur. J. 2014, 20, 17616–17623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.J.; Xiao, F.S. Green Routes for Synthesis of Zeolites. Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 1521–1543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Yang, C.; Li, S.; Yu, G.; Liu, Z.; Wang, H.; Gao, P.; Sun, Y. Solvent-Free Synthesis of Mg-Incorporated Nanocrystalline SAPO-34 Zeolites via Natural Clay for Chloromethane-to-Olefin Conversion. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 4185–4193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Ren, S.; Yu, X.; Chen, X.; Wang, G.; Wu, X.; Yu, G.; Qiu, M.; Yang, C.; Sun, Y. Melting-assisted solvent-free synthesis of hierarchical SAPO-34 with enhanced methanol to olefins (MTO) performance. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2018, 8, 423–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, B.; Mao, G.L.; Wang, D.K.; Fu, Y.D.; Wang, B.H.; Luo, M.J. Conversion and coking of olefins on SAPO-34. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2017, 7, 5785–5794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blay, V.; Louis, B.; Miravalles, R.; Yokoi, T.; Peccatiello, K.A.; Clough, M.; Yilmaz, B. Engineering Zeolites for Catalytic Cracking to Light Olefins. ACS Catal. 2017, 7, 6542–6566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sattler, J.J.H.B.; Ruiz-Martinez, J.; Santillan-Jimenez, E.; Weckhuysen, B.M. Catalytic dehydrogenation of light alkanes on metals and metal oxides. Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 10613–10653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheng, J.; Yan, B.; Lu, W.D.; Qiu, B.; Gao, X.Q.; Wang, D.; Lu, A.H. Oxidative dehydrogenation of light alkanes to olefins on metal-free catalysts. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2021, 50, 1438–1468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, L.S.; Yu, F.; An, Y.L.; Zhao, Y.H.; Sun, Y.H.; Li, Z.J.; Lin, T.J.; Lin, Y.J.; Qi, X.Z.; Dai, Y.Y.; et al. Cobalt carbide nanoprisms for direct production of lower olefins from syngas. Nature 2016, 538, 84–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, F.; Li, J.J.; Pan, X.L.; Xiao, J.P.; Li, H.B.; Ma, H.; Wei, M.M.; Pan, Y.; Zhou, Z.Y.; Li, M.R.; et al. Selective conversion of syngas to light olefins. Science 2016, 351, 1065–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, Y.; Koiwai, A.; Takeuchi, H.; Hyodo, S.A.; Noda, S. Multinuclear NMR Studies on the Thermal Stability of SAPO-34. J. Catal. 1993, 143, 430–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Martínez-Triguero, J.; Concepción, P.; Yu, J.; Corma, A. Methanol to olefins: Activity and stability of nanosized SAPO-34 molecular sieves and control of selectivity by silicon distribution. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2013, 15, 14670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Blackwell, C.S.; Patton, R.L. Aluminum-27 and Phosphorus-31 Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Studies of Aluminophosphate Molecular Sieves. J. Phys. Chem. 1984, 88, 6135–6139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Epelde, E.; Ibanez, M.; Aguayo, A.T.; Gayubo, A.G.; Bilbao, J.; Castano, P. Differences among the deactivation pathway of HZSM-5 zeolite and SAPO-34 in the transformation of ethylene or 1-butene to propylene. Micropor. Mesopor. Mater. 2014, 195, 284–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Epelde, E.; Ibáñez, M.; Valecillos, J.; Aguayo, A.T.; Gayubo, A.G.; Bilbao, J.; Castaño, P. SAPO-18 and SAPO-34 catalysts for propylene production from the oligomerization-cracking of ethylene or 1-butene. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2017, 547, 176–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| Samples | x(SiO2) | Molar Composition 1 | Si/(Si + Al + P) |
|---|---|---|---|
| SP-0.2 | 0.2 | Al0.338Si0.042P0.620O2 | 0.042 |
| SP-0.4 | 0.4 | Al0.290Si0.053P0.657O2 | 0.053 |
| SP-0.6 | 0.6 | Al0.284Si0.074P0.642O2 | 0.074 |
| SP-0.8 | 0.8 | Al0.290Si0.095P0.615O2 | 0.095 |
| SP-1.0 | 1.0 | Al0.246Si0.127P0.627O2 | 0.127 |
| Samples | SBET 1 | Smicro 2 | Sext 3 | Vmicro 4 | Vmeso 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (m2/g) | (m2/g) | (m2/g) | (cm3/g) | (cm3/g) | |
| SP-0.2 | 224 | 204 | 20 | 0.11 | 0.02 |
| SP-0.4 | 326 | 299 | 27 | 0.16 | 0.03 |
| SP-0.6 | 425 | 410 | 15 | 0.21 | 0.02 |
| SP-0.8 | 395 | 363 | 32 | 0.19 | 0.06 |
| SP-1.0 | 358 | 329 | 29 | 0.17 | 0.09 |
| Samples | Acid Amount (mmol/g) | Desorption Temperature (°C) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total Acid Amount | Weak Acid Amount | Strong Acid Amount | Low Temperature | High Temperature | |
| SP-0.2 | 1.51 | 0.77 | 0.74 | 184 | 435 |
| SP-0.4 | 1.54 | 0.78 | 0.76 | 187 | 441 |
| SP-0.6 | 1.82 | 0.89 | 0.93 | 188 | 452 |
| SP-0.8 | 1.76 | 0.87 | 0.89 | 186 | 457 |
| SP-1.0 | 1.75 | 0.87 | 0.88 | 188 | 465 |
| Catalysts | Conversion (wt%) | Selectivity (wt%) | HTC 1 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CH4 + C2H6 | H2 | C2H4 | C3H6 | C3H8 + C4H10 | C5+ | |||
| SP-0.2 | 42.2 | 0.5 | 0.2 | 12.6 | 62.1 | 9.9 | 14.6 | 0.16 |
| SP-0.4 | 52.7 | 0.9 | 0.2 | 15.6 | 56.2 | 14.8 | 12.2 | 0.26 |
| SP-0.6 | 82.8 | 2.1 | 0.5 | 18.9 | 43.3 | 28.2 | 7.0 | 0.65 |
| SP-0.8 | 75.0 | 1.1 | 0.4 | 14.8 | 47.2 | 19.1 | 16.9 | 0.40 |
| SP-1.0 | 74.1 | 0.9 | 0.4 | 14.7 | 47.8 | 18.2 | 16.7 | 0.38 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xiao, X.; Xu, Z.; Wang, P.; Liu, X.; Fan, X.; Kong, L.; Xie, Z.; Zhao, Z. Solvent-Free Synthesis of SAPO-34 Zeolite with Tunable SiO2/Al2O3 Ratios for Efficient Catalytic Cracking of 1-Butene. Catalysts 2021, 11, 835. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal11070835
Xiao X, Xu Z, Wang P, Liu X, Fan X, Kong L, Xie Z, Zhao Z. Solvent-Free Synthesis of SAPO-34 Zeolite with Tunable SiO2/Al2O3 Ratios for Efficient Catalytic Cracking of 1-Butene. Catalysts. 2021; 11(7):835. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal11070835
Chicago/Turabian StyleXiao, Xia, Zhongliang Xu, Peng Wang, Xinfei Liu, Xiaoqiang Fan, Lian Kong, Zean Xie, and Zhen Zhao. 2021. "Solvent-Free Synthesis of SAPO-34 Zeolite with Tunable SiO2/Al2O3 Ratios for Efficient Catalytic Cracking of 1-Butene" Catalysts 11, no. 7: 835. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal11070835
APA StyleXiao, X., Xu, Z., Wang, P., Liu, X., Fan, X., Kong, L., Xie, Z., & Zhao, Z. (2021). Solvent-Free Synthesis of SAPO-34 Zeolite with Tunable SiO2/Al2O3 Ratios for Efficient Catalytic Cracking of 1-Butene. Catalysts, 11(7), 835. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal11070835