Nanoscale Cerium Oxide: Synthesis, Biocatalytic Mechanism, and Applications
Abstract
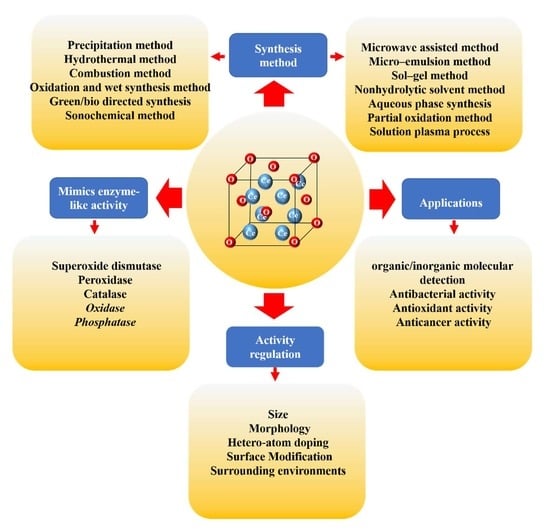
:1. Introduction
2. Synthesis Method
3. Mimics of Enzyme-Like Activity
3.1. Superoxide Dismutase
3.2. Peroxidase
3.3. Catalase
3.4. Oxidase
3.5. Phosphatase
4. Activity Regulation
4.1. Size
4.2. Morphology
4.3. Hetero-Atom Doping
4.4. Surface Modification
4.5. Surrounding Environments
5. Applications
5.1. Organic/Inorganic Molecular Detection
5.2. Antibacterial Activity
5.3. Antioxidant Activity
5.4. Anticancer Activity
6. Conclusions and Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Das, S.; Dowding, J.M.; Klump, K.E. Cerium oxide nanoparticles: Applications and prospects in nanomedicine. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2013, 8, 1483–1508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bryant, N.; Monique, J.; Marlon, W. Antioxidant Cerium Oxide Nanoparticles in Biology and Medicine. Antioxidants 2016, 5, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Karakoti, A.; Singh, S.; Dowding, J.M. Redox-active radical scavenging nanomaterials. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2010, 39, 4422–4432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukui, K.I.; Namai, Y.; Iwasawa, Y. Imaging of surface oxygen atoms and their defect structures on CeO2(1 1 1) by noncontact atomic force microscopy. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2002, 188, 252–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dowding, J.M.; Das, S.; Kumar, A. Cellular interaction and toxicity depend on physicochemical properties and surface modification of redox-active nanomaterials. ACS Nano 2013, 7, 4855–4868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yokel, R.A.; Florence, R.L.; Unrine, J.M.; Tseng, M.T.; Graham, U.M.; Wu, P.; Grulke, E.A.; Sultana, R.; Hardas, S.S.; Butterfield, D.A. Biodistribution and oxidative stress effects of a systemically-introduced commercial ceria engineered nanomaterial. Nanotoxicology 2009, 3, 234–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.Y.; Zhao, H.; Mercer, R.R. Cerium oxide nanoparticle-induced pulmonary inflammation and alveolar macrophage functional change in rats. Nanotoxicology 2011, 5, 312–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hussain, S.; Al-Nsour, F.; Rice, A.B. Cerium dioxide nanoparticles induce apoptosis and autophagy in human peripheral blood monocytes. ACS Nano 2012, 6, 5820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhou, X.; Wong, L.L.; Karakoti, A.S. Nanoceria Inhibit the Development and Promote the Regression of Pathologic Retinal Neovascularization in the Vldlr Knockout Mouse. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e16733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thill, A.; Zeyons, O.; Spalla, O. Cytotoxicity of CeO2 Nanoparticles for Escherichia coli. Physico-Chemical Insight of the Cytotoxicity Mechanism. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2006, 40, 6151–6156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, N.; Cohen, C.A.; Rzigalinski, B.A. Treatment of Neurodegenerative Disorders with Radical Nanomedicine. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2010, 1122, 219–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Babu, S.; Cho, J.H.; Dowding, J.M. Multicolored redox active upconverter cerium oxide nanoparticle for bio-imaging and therapeutics. Chem. Commun. 2010, 46, 6915–6917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Renu, G.; Rani, V.V.D.; Nair, S.V.; Subramanian, K.R.V.; Lakshmanan, V.K. Development of Cerium Oxide Nanoparticles and Its Cytotoxicity in Prostate Cancer Cell. Adv. Sci. Lett. 2012, 6, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asati, A.; Santra, S.; Kaittanis, C. Oxidase-like activity of polymer-coated cerium oxide nanoparticles. Angew. Chem. 2009, 121, 2344–2348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, S.Q. The chemical preparation method and application of nano-dioxide research. Chem. Technol. Dev. 2014, 43, 38–40. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, X.Y.; Li, L.H.; Zhang, J.S.; Yang, P. Research progress on preparation and application of nano cerium oxideApplied. Chem. Ind. 2014, 43, 1701–1704. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.C.; Zhang, Y.J.; Tan, S.L.; Zheng, H.D. Preparation and application of nano-cerium oxide. Preparation and ozonation application of cerium dioxide nano-catalyst. Mod. Chem. 2004, 17, 233–235. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, Y.M.; Wu, L.N.; He, A.Z.; Jiang, P.P. Preparation and ozonation application of cerium dioxide nano-catalyst. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 35, 212–214. [Google Scholar]
- Liao, H.; Liu, Y.; Chen, M. A colorimetric heparin assay based on the inhibition of the oxidase mimicking activity of cerium oxide nanoparticles. Microchim. Acta 2019, 186, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, R.; Wang, Y.; Yu, S.; Zhu, W.; Zheng, F.; Liu, W.; Wang, J. Dual role of hydrogen peroxide on the oxidase-like activity of nanoceria and its application for colorimetric hydrogen peroxide and glucose sensing. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 59939–59945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrei, V.; Sharpe, E.; Vasilescu, A.; Andreescu, S. A single use electrochemical sensor based on biomimetic nanoceria for the detection of wine antioxidants. Talanta 2016, 156–157, 112–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xue, T.A.; Hong, L.A.; Min, W.B. Highly sensitive chemiluminescent sensing of intracellular Al3+ based on the phosphatase mimetic activity of cerium oxide nanoparticles—ScienceDirect. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2020, 152, 112027. [Google Scholar]
- Olivera, S.; Chaitra, K.; Venkatesh, K. Cerium dioxide and composites for the removal of toxic metal ions. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2018, 16, 1233–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latif, M.M.; Amin, F.; Ajaz-Un-Nabi, M.; Khan, I.-U.; Sabir, N. Synthesis and antimicrobial activities of manganese (Mn) and iron (Fe) Co-Doped cerium dioxide (CeO2)Nanoparticles. Phys. B Condens. Matter 2020, 600, 412562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Matos Rodrigues, M.H.; Borges, K.C.M.; de Cássia Santos, M.R.; de Carvalho Barros, J.J.; de Fátima Gonçalves, R.; Motta, F.V.; Godinho, M. Synthesis, characterization and in vitro antimicrobial prospecting of silver-doped ceria. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2020, 139, 849–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakur, N.; Manna, P.; DAS, J. Synthesis and biomedical applications of nanoceria, a redox active nanoparticle. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2019, 17, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karakoti, A.S.; Monteiro-Riviere, N.A.; Aggarwal, R.; Davis, J.P.; Narayan, R.J.; Self, W.T.; Seal, S. Nanoceria as antioxidant: Synthesis and biomedical applications. JOM 2008, 60, 33–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Das, M.; Patil, S.; Bhargava, N. Auto-catalytic ceria nanoparticles offer neuroprotection to adult rat spinal cord neurons. Biomaterials 2007, 28, 1918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, S.; Hou, Y.; Cheng, G.; Zhang, C.; Wang, S.; Zhang, J. Cerium Oxide Nanoparticles Protect Endothelial Cells from Apoptosis Induced by Oxidative Stress. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2013, 154, 156–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colon, J.; Hsieh, N.; Ferguson, A. Cerium oxide nanoparticles protect gastrointestinal epithelium from radiation-induced damage by reduction of reactive oxygen species and upregulation of superoxide dismutase 2. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2010, 6, 698–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez, J.M.; Asati, A.; Nath, S.; Kaittanis, C. Synthesis of biocompatible dextran-coated nanoceria with pH-dependent antioxidant properties. Small 2010, 4, 552–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, C.; Qu, X. Cerium oxide nanoparticle: A remarkably versatile rare earth nanomaterial for biological applications. NPG Asia Mater. 2014, 6, e90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, W.; Huang, Y.W.; Zhou, X.D.; Ma, Y. Toxicity of Cerium Oxide Nanoparticles in Human Lung Cancer Cells. Int. J. Toxicol. 2006, 25, 451–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esmail, N.; Hoda, K.S.; Reza, N. Evaluation of anticancer effects of cerium oxide nanoparticles on mouse fibrosarcoma cell line. J. Cell. Physiol. 2018, 234, 4987–4996. [Google Scholar]
- Jana, S.K.; Banerjee, P.; Das, S.; Seal, S.; Chaudhury, K. Redox-active nanoceria depolarize mitochondrial membrane of human colon cancer cells. J. Nanopart. Res. 2014, 16, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.L.; Ko, H.H.; Hsu, Y.W. Growth behavior of nanosized ceria powders prepared by coprecipitation routes. Ceram. Int. 2013, 39, 6805–6811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Wang, J.; Li, Y.; Jia, P.; Lu, F.; Chen, K. Hydrothermal synthesis of monodisperse α-Fe2O3 nanocubes. Mater. Res. Innov. 2015, 19, S5-371–S5-375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinjari, D.V.; Pandit, A.B. Room temperature synthesis of crystalline CeO2 nanopowder: Advantage of sonochemical method over conventional method. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2011, 18, 1118–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Ju, X.; Wu, Z.Y.; Liu, T.; Hu, T.D.; Xie, Y.N.; Zhang, Z.L. Structural Characteristics of Cerium Oxide Nanocrystals Prepared by the Microemulsion Method. Chem. Mater. 2001, 1, 73–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tambat, S.; Umale, S.; Sontakke, S. Photocatalytic degradation of Milling Yellow dye using sol–gel synthesized CeO2. Mater. Res. Bull. 2016, 76, 466–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Huyan, Y.; Wang, J. Synthesis of CeO2 nanoparticles with different morphologies and their properties as peroxidase mimic. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2018, 102, 2218–2227. [Google Scholar]
- Hayat, A.; Andreescu, S. Nanoceria particles as catalytic amplifiers for alkaline phosphatase assays. Anal. Chem. 2013, 85, 10028–10032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, X.; Luan, Q.; Yao, X. Single-crystal CeO2 nanocubes used for the direct electron transfer and electrocatalysis of horseradish peroxidase. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2009, 24, 2447–2451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhang, Z.; Tao, L. A chemiluminescence microarray based on catalysis by CeO(2) nanoparticles and its application to determine the rate of removal of hydrogen peroxide by human erythrocytes. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2013, 171, 63–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korsvik, C.; Patil, S.; Seal, S.; Self, W.T. Superoxide dismutase mimetic properties exhibited by vacancy engineered ceria nanoparticles. Chem. Commun. 2007, 14, 1056–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.; Li, X.; Feng, Y. Morphology- and pH-dependent peroxidase mimetic activity of nanoceria. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 11764–11770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tian, Z.; Li, J.; Zhang, Z. Highly sensitive and robust peroxidase-like activity of porous nanorods of ceria and their application for breast cancer detection. Biomaterials 2015, 59, 116–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, L.; Zhuang, J.; Nie, L.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Gu, N.; Wang, T.; Feng, J.; Yang, D.; Perrett, S.; et al. Intrinsic peroxidase-like activity of ferromagnetic nanoparticles. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2007, 2, 577–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiao, X.; Song, H.; Zhao, H. Well-redispersed ceria nanoparticles: Promising peroxidase mimetics for H2O2 and glucose detection. Anal. Methods 2012, 4, 3261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attar, F.; Shahpar, M.G.; Rasti, B. Nanozymes with intrinsic peroxidase-like activities. J. Mol. Liq. 2019, 278, 130–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rzigalinski, B.A.; Carfagna, C.S.; Ehrich, M. Cerium oxide nanoparticles in neuroprotection and considerations for efficacy and safety. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Nanomed. Nanobiotechnol. 2017, 9, e1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Celardo, I.; Pedersen, J.Z.; Traversa, E.; Ghibelli, L. Pharmacological potential of cerium oxide nanoparticles. Nanoscale 2011, 3, 1411–1420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Yue, L.; Wang, J. Synthesis of CeO2 hollow microspheres with oxidase-like activity and their application in the catalytic degradation of p-nitrophenol. Environ. Technol. 2019, 42, 134–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.; Chen, X.; Yi, G.; Gao, Z. Mechanism of the oxidation of organic dyes in the presence of nanoceria. Chem. Commun. 2011, 47, 2916–2918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Monte, R.; Kašpar, J. On the Role of Oxygen Storage in Three-Way Catalysis. Top. Catal. 2004, 28, 47–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franklin, S.J. Lanthanide-mediated DNA hydrolysis. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2001, 5, 201–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chin, J. Artificial dinuclear phosphoesterases. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 1997, 1, 514–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chong, Y.; Liu, Q.; Ge, C. Advances in oxidase-mimicking nanozymes: Classification, activity regulation and biomedical applications. Nano Today 2021, 37, 101076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tinoco, M.; Fernandez-Garcia, S.; Villa, A. Selective oxidation of glycerol on morphology controlled ceria nanomaterials. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2019, 9, 2328–2334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Udayabhaskar, R.; Sahlevani, S.F.; Prabhakaran, T. Modulation of optical and photocatalytic properties by morphology and microstrain in hierarchical ceria nanostructures. Solar Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2019, 195, 106–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Ren, J.; Qu, X. Nanozymes: Classification, Catalytic Mechanisms, Activity Regulation, and Applications. Chem. Rev. 2019, 119, 4357–4412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, A.; Yu, X.; Zhou, Y.; Miao, S.; Li, Y.; Kuld, S.; Shen, W. Structure of the catalytically active copper–ceria interfacial perimeter. Nat. Catal. 2019, 2, 334–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbayrak, S.; Tonbul, Y.; Zkar, S. Ceria Supported Rhodium Nanoparticles: Superb Catalytic Activity in Hydrogen Generation from the Hydrolysis of Ammonia Borane. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2016, 198, 162–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mullen, G.M.; Evans, E.J.; Siegert, B. The interplay between ceria particle size, reducibility, and ethanol oxidation activity of ceria-supported gold catalysts. React. Chem. Eng. 2018, 3, 75–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Liu, J. Surface modification of nanozymes. Nano Res. 2017, 10, 1125–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Huang, Z.; Liu, J. Boosting the oxidase mimicking activity of nanoceria by fluoride capping: Rivaling protein enzymes and ultrasensitive F-detection. Nanoscale 2016, 8, 13562–13567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Wang, Y.; Mathur, A. Fluoride-capped nanoceria as highly efficient oxidase-mimicking nanozyme: Inhibiting product adsorption and increasing oxygen vacancy. Nanoscale 2019, 11, 17841–17850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pautler, R.; Kelly, E.Y.; Huang, P.-J.J.; Cao, J.; Liu, B.; Liu, J. Attaching DNA to Nanoceria: Regulating Oxidase Activity and Fluorescence Quenching. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2013, 5, 6820–6825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tian, Z.; Liu, H.; Guo, Z. A pH-Responsive Polymer-CeO(2) Hybrid to Catalytically Generate Oxidative Stress for Tumor Therapy. Small 2020, 16, e2004654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naqvi, S.T.R.; Shirinfar, B.; Majeed, S.; Najam-ul-Haq, M.; Hussain, D.; Iqbal, T.; Ahmed, N. Synthesis, design and sensing applications of nanostructured ceria-based materials. Analyst 2018, 143, 5610–5628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, B.; Xiao, K.; Huang, X.; Zhang, Z.; Kong, X.-Y.; Wang, Z.; Wen, L.; Jiang, L. High-Sensitivity Detection of Iron(III) by Dopamine-Modified Funnel-Shaped Nanochannels. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 22632–22639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, J.; Feng, Y.; Cheng, D. Construction of a Mesoporous Ceria Hollow Sphere/Enzyme Nanoreactor for Enhanced Cascade Catalytic Antibacterial Therapy. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 40302–40314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damle, M.A.; Jakhade, A.P.; Chikate, R.C. Modulating Pro- A nd Antioxidant Activities of Nanoengineered Cerium Dioxide Nanoparticles against Escherichia coli. ACS Omega 2019, 4, 3761–3771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, C.; Lin, Y.; Wang, J.; Wu, L.; Wei, W.; Ren, J.; Qu, X. Nanoceria-triggered synergetic drug release based on CeO(2)-capped mesoporous silica host-guest interactions and switchable enzymatic activity and cellular effects of CeO(2). Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2013, 2, 1591–1599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Shi, P.; Xu, C.; Ren, J.; Qu, X. Cerium oxide caged metal chelator: Anti-aggregation and anti-oxidation integrated H2O2-responsive controlled drug release for potential Alzheimer’s disease treatment. Chem. Sci. 2013, 4, 2536–2542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Song, G.; Cheng, N.; Zhang, J.; Huang, H.; Yuan, Y.; He, X.; Luo, Y.; Huang, K. Nanoscale Cerium Oxide: Synthesis, Biocatalytic Mechanism, and Applications. Catalysts 2021, 11, 1123. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal11091123
Song G, Cheng N, Zhang J, Huang H, Yuan Y, He X, Luo Y, Huang K. Nanoscale Cerium Oxide: Synthesis, Biocatalytic Mechanism, and Applications. Catalysts. 2021; 11(9):1123. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal11091123
Chicago/Turabian StyleSong, Guangchun, Nan Cheng, Junjie Zhang, Huixian Huang, Yanfang Yuan, Xiaoyun He, Yunbo Luo, and Kunlun Huang. 2021. "Nanoscale Cerium Oxide: Synthesis, Biocatalytic Mechanism, and Applications" Catalysts 11, no. 9: 1123. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal11091123
APA StyleSong, G., Cheng, N., Zhang, J., Huang, H., Yuan, Y., He, X., Luo, Y., & Huang, K. (2021). Nanoscale Cerium Oxide: Synthesis, Biocatalytic Mechanism, and Applications. Catalysts, 11(9), 1123. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal11091123