Tuning the Latency by Anionic Ligand Exchange in Ruthenium Benzylidene Phosphite Complexes
Abstract
:1. Introduction
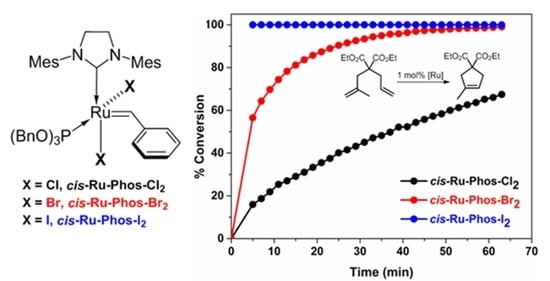
2. Results and Discussion
3. Experimental Section
3.1. General
3.2. Synthetic Procedure and Data for the Complexes
3.3. General Procedures for Ring-Closing Metathesis (RCM)
3.4. General Procedures for Ring-Opening Metathesis Polymerization (ROMP)
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hoveyda, A.H.; Zhugralin, A.R. The Remarkable Metal-catalysed Olefin Metathesis Reaction. Nature 2007, 450, 243–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grela, K. (Ed.) Olefin Metathesis: Theory and Practice; Wiley & Sons, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Grubbs, R.H.; Wenzel, A.G.; O’Leary, D.J.; Khosravi, E. (Eds.) Handbook of Metathesis; Wiley-VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Nicolaou, K.C.; Bulger, P.G.; Sarlah, D. Metathesis Reactions in Total Synthesis. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2005, 44, 4490–4527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogba, O.M.; Warner, N.C.; O’Leary, D.J.; Grubbs, R.H. Recent advances in ruthenium-based olefin metathesis. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2018, 47, 4510–4544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Higman, C.S.; Lummiss, J.A.M.; Fogg, D.E. Olefin Metathesis at the Dawn of Implementation in Pharmaceutical and Specialty-Chemicals Manufacturing. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 3552–3565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, M.; Lou, S.; Gonzalez-Bobes, F. Ring-Closing Metathesis in Pharmaceutical Development: Fundamentals, Applications and Future Directions. Org. Process Res. Dev. 2018, 22, 918–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsedalu, A. A Review on Olefin Metathesis Reactions as a Green Method for the Synthesis of Organic Compounds. J. Chem. 2021, 2021, e3590613. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, P.; Ai, C. Olefin Metathesis Reaction in Rubber Chemistry and Industry and Beyond. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2018, 57, 3807–3820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gladiali, S.; Alberico, E. Asymmetric transfer hydrogenation: Chiral ligands and applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2006, 35, 226–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorin, D.J.; Sherry, B.D.; Toste, F.D. Ligand effects in homogeneous Au catalysis. Chem. Rev. 2008, 108, 3351–3378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogalski, S.; Pietraszuk, C. Application of Olefin Metathesis in the Synthesis of Carbo- and Heteroaromatic Compounds—Recent Advances. Molecules 2023, 28, 1680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guidone, S.; Songis, O.; Nahra, F.; Cazin, C.S.J. Conducting Olefin Metathesis Reactions in Air: Breaking the Paradigm. ACS Catal. 2015, 5, 2697–2701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antreil, X.; Schmid, T.E.; Randall, R.A.M.; Slawin, A.M.Z.; Cazin, C.S.J. Mixed N-heterocyclic carbene/phosphite ruthenium complexes: Towards a new generation of olefin metathesis catalysts. Chem. Commun. 2010, 46, 7115–7117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eivgi, O.; Guidone, S.; Frenklah, A.; Kozuch, S.; Goldberg, I.; Lemcoff, N.G. Photoactivation of Ruthenium Phosphite Complexes for Olefin Metathesis. ACS Catal. 2018, 8, 6413–6418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmid, T.E.; Bantreil, X.; Citadelle, C.A.; Slawin, A.M.Z.; Cazin, C.S.J. Phosphites as ligands in ruthenium-benzylidene catalysts for olefin metathesis. Chem. Commun. 2011, 47, 7060–7062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eivgi, O.; Vaisman, A.; Nechmad, N.B.; Baranov, M.; Lemcoff, N.G. Latent Ruthenium Benzylidene Phosphite Complexes for Visible Light Induced Olefin Metathesis. ACS Catal. 2020, 10, 2033–2038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemcoff, N.; Nechmad, N.B.; Eivgi, O.; Yehezkel, E.; Shelonchik, O.; Phatake, R.S.; Yesodi, D.; Vaisman, A.; Biswas, A.; Lemcoff, N.G.; et al. Plasmonic Visible–near Infrared Photothermal Activation of Olefin Metathesis Enabling Photoresponsive Materials. Nat. Chem. 2023, 15, 475–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albalawi, M.O.; Falivene, L.; Jedidi, A.; Osman, O.I.; Elroby, S.A.; Cavallo, L. Influence of the Anionic Ligands on Properties and Reactivity of Hoveyda-Grubbs Catalysts. Mol. Catal. 2021, 509, 111612. [Google Scholar]
- Buchmeiser, M.R.; Anderson, E.B. Pseudo-halide Derivatives of Grubbs- and Schrock-Type Catalysts for Olefin Metathesis. Synlett 2012, 2012, 185–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engl, P.C.; Santiago, C.B.; Gordon, C.P.; Liao, W.; Fedorov, A.; Copéret, C.; Sigman, M.S.; Togni, A. Exploiting and Understanding the Selectivity of Ru-N-Heterocyclic Carbene Metathesis Catalysts for the Ethenolysis of Cyclic Olefins to α,ω-Dienes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 13117–13125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, R.K.M.; Torke, S.; Hoveyda, A.H. Readily Accessible and Easily Modifiable Ru-Based Catalysts for Efficient and Z-Selective Ring-Opening Metathesis Polymerization and Ring-Opening/Cross-Metathesis. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 10258–10261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halbach, T.S.; Mix, S.; Fischer, D.; Maechling, S.; Krause, J.O.; Sievers, C.; Blechert, S.; Nuyken, O.; Buchmeiser, M.R. Novel Ruthenium-Based Metathesis Catalysts Containing Electron- Withdrawing Ligands: Synthesis, Immobilization, and Reactivity. J. Org. Chem. 2005, 70, 4687–4694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braddock, D.C.; Tanak, K.; Chadwick, D.; Böhm, V.P.W.; Roeper, M. Vacuum-driven anionic ligand exchange in Buchmeiser-Hoveyda-Grubbs ruthenium(II) benzylidenes. Tetrahedron Lett. 2007, 48, 5301–5303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gawin, R.; Czarnecka, P.; Grela, K. Ruthenium catalysts bearing chelating carboxylate ligands: Application to metathesis reactions in water. Tetrahedron 2010, 66, 1051–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wappel, J.; Urbina-Blanco, C.A.; Abbas, M.; Albering, J.H.; Saf, R.; Nolan, S.P.; Slugovc, C. Halide exchanged Hoveyda-type complexes in olefin metathesis. Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2010, 6, 1091–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ivry, E.; Nechmad, N.B.; Baranov, M.; Goldberg, I.; Lemcoff, N.G. Influence of Anionic Ligand Exchange in Latent Sulfur-Chelated Ruthenium Precatalysts. Inorg. Chem. 2018, 57, 15592–15599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seiders, T.J.; Ward, D.W.; Grubbs, R.H. Enantioselective Ruthenium-Catalyzed Ring-Closing Metathesis. Org. Lett. 2001, 3, 3225–3228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillingham, D.G.; Kataoka, O.; Garber, S.B.; Hoveyda, A.H. Efficient Enantioselective Synthesis of Functionalized Tetrahydropyrans by Ru-Catalyzed Asymmetric Ring-Opening Metathesis/Cross-Metathesis (AROM/CM). J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 12288–12290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berlin, J.M.; Goldberg, S.D.; Grubbs, R.H. Highly Active Chiral Ruthenium Catalysts for Asymmetric Cross- and Ring-Opening Cross-Metathesis. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2006, 45, 7591–7595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dias, E.L.; Nguyen, S.T.; Grubbs, R.H. Well-Defined Ruthenium Olefin Metathesis Catalysts: Mechanism and Activity. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1997, 119, 3887–3897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanford, M.S.; Love, J.A.; Grubbs, R.H. Mechanism and Activity of Ruthenium Olefin Metathesis Catalysts. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2001, 123, 6543–6554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nechmad, N.B.; Phatake, R.S.; Ivry, E.; Poater, A.; Lemcoff, N.G. Unprecedented Selectivity of Ruthenium Iodide Benzylidenes in Olefin Metathesis Reactions. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2020, 9, 3539–3543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bieszczad, B.; Barbasiewicz, M. The Key Role of the Nonchelating Conformation of the Benzylidene Ligand on the Formation and Initiation of Hoveyda–Grubbs Metathesis Catalysts. Chem. Eur. J. 2015, 21, 10322–10325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phatake, R.S.; Nechmad, N.B.; Reany, O.; Lemcoff, N.G. Highly Substrate-Selective Macrocyclic Ring Closing Metathesis. Adv. Synth. Cat. 2022, 364, 1465–1472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alassad, N.; Nechmad, N.B.; Phatake, R.S.; Reany, O.; Lemcoff, N.G. Steric and Electronic Effects in Latent S-Chelated Olefin Metathesis Catalysts. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2023, 13, 321–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grudzień, K.; Żukowska, K.; Malińska, M.; Woźniak, K.; Barbasiewicz, M. Mechanistic Studies of Hoveyda–Grubbs Metathesis Catalysts Bearing S-, Br-, I-, and N-coordinating Naphthalene Ligands. Chem. Eur. J. 2014, 20, 2819–2828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weitekamp, R.A.; Atwater, H.A.; Grubbs, R.H. Photolithographic Olefin Metathesis Polymerization. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 16817–16820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, S.T.; Johnson, L.K.; Grubbs, R.H.; Ziller, J.W. Ring-opening metathesis polymerization (ROMP) of norbornene by a Group VIII carbene complex in protic media. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1992, 114, 3974–3975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Abdellatif, M.M.; Nomura, K. Olefin metathesis polymerization: Some recent developments in the precise polymerizations for synthesis of advanced materials (by ROMP, ADMET). Tetrahedron 2018, 74, 619–643. [Google Scholar]







| Bond Lengths (Å) | cis-Ru-Phos-Cl2 | cis-Ru-Phos-Br2 | cis-Ru-Phos-I2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ru–P | 2.256 (3) | 2.226 (10) | 2.250 (8) |
| Ru–NHC | 2.067 (8) | 2.067 (3) | 2.043 (3) |
| Ru–Cbenzylidene | 1.818 (6) | 1.844 (3) | 1.861 (3) |
| Ru–X1 (trans to NHC) | 2.404 (2) | 2.535 (4) | 2.720 (3) |
| Ru–X2 (trans to P) | 2.401 (3) | 2.565 (5) | 2.741 (3) |
| Entry | Substrates | Catalyst (1 mol%) | Thermal (80 °C) % conv. a | Photochemical(350 nm) % conv. b |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 |  | cis-Ru-Phos-Cl2 | 4 | 62 |
| cis-Ru-Phos-Br2 | 16 | 71 | ||
| cis-Ru-Phos-I2 | 99 | 66 | ||
| 2 |  | cis-Ru-Phos-Cl2 | 5 | 57 |
| cis-Ru-Phos-Br2 | 33 | 93 | ||
| cis-Ru-Phos-I2 | 99 | 93 | ||
| 3 |  | cis-Ru-Phos-Cl2 | 15 | 92 |
| cis-Ru-Phos-Br2 | 20 | 99 | ||
| cis-Ru-Phos-I2 | 99 | 99 | ||
| 4 |  | cis-Ru-Phos-Cl2 | 17 | 70 |
| cis-Ru-Phos-Br2 | 30 | 80 | ||
| cis-Ru-Phos-I2 | 97 | 81 | ||
| 5 |  | cis-Ru-Phos-Cl2 | 29 | 80 |
| cis-Ru-Phos-Br2 | 42 | 78 | ||
| cis-Ru-Phos-I2 | 88 | 23 | ||
| 6 |  | cis-Ru-Phos-Cl2 | 17 | 41 |
| cis-Ru-Phos-Br2 | 42 | 64 | ||
| cis-Ru-Phos-I2 | 99 | 29 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alassad, N.; Phatake, R.S.; Baranov, M.; Reany, O.; Lemcoff, N.G. Tuning the Latency by Anionic Ligand Exchange in Ruthenium Benzylidene Phosphite Complexes. Catalysts 2023, 13, 1411. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal13111411
Alassad N, Phatake RS, Baranov M, Reany O, Lemcoff NG. Tuning the Latency by Anionic Ligand Exchange in Ruthenium Benzylidene Phosphite Complexes. Catalysts. 2023; 13(11):1411. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal13111411
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlassad, Nebal, Ravindra S. Phatake, Mark Baranov, Ofer Reany, and N. Gabriel Lemcoff. 2023. "Tuning the Latency by Anionic Ligand Exchange in Ruthenium Benzylidene Phosphite Complexes" Catalysts 13, no. 11: 1411. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal13111411
APA StyleAlassad, N., Phatake, R. S., Baranov, M., Reany, O., & Lemcoff, N. G. (2023). Tuning the Latency by Anionic Ligand Exchange in Ruthenium Benzylidene Phosphite Complexes. Catalysts, 13(11), 1411. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal13111411