A Comparison of Different Reagents Applicable for Destroying Halogenated Anionic Textile Dye Mordant Blue 9 in Polluted Aqueous Streams
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
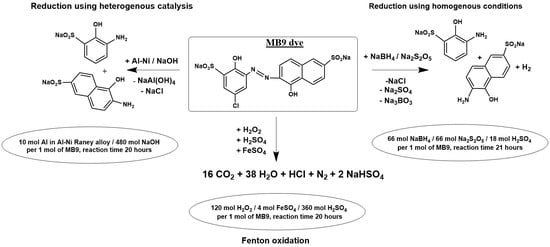
2.1. Chemical Oxidation of MB9 Using H2O2
2.2. The Chemical Reduction of MB9
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Reagents and Materials
3.2. Oxidative and Reductive Degradation of MB9 Procedures
3.3. Chemical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Varjani, S.; Rakholiya, P.; Shindhal, T.; Shah, A.V.; Ngo, H.H. Trends in dye industry effluent treatment and recovery of valueadded products. J. Water Process Eng. 2021, 39, 101734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sen, S.K.; Raut, S.; Bandyopadhyay, P.; Raut, S. Fungal decolouration and degradation of azo dyes: A review. Fungal Biol. Rev. 2016, 30, 112–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selvaraj, V.; Karthika, T.S.; Mansiya, C.; Alagar, M. An over review on recently developed techniques, mechanisms and intermediate involved in the advanced azo dye degradation for industrial applications. J. Mol. Struct. 2021, 1224, 129195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, R.; Li, M.; Yang, C.; Sun, Y.; Chen, J. Removal of cationic dyes from aqueous solution by adsorption on peanut hull. J. Hazard. Mater. 2005, 121, 247–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.; David, S.; Pailthorpe, M. Dyeing of jute and jute/cotton blend fabrics with 2:1 pre-metallised dyes. Dye. Pigment. 2000, 45, 161–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Freeman, H.S. Mordant dye application on cotton: Optimisation and combination with natural dyes. Color. Technol. 2017, 133, 369–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheikh, M.; Karim, R.; Farouqui, A.N.; Yahya, R.; Hassan, A. Effect of Acid Modification on Dyeing Properties of Rajshahi Silk Fabric with Different Dye Classes. Fibers Polym. 2011, 12, 642–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheikh, R.K.; Faruqui, A.N. A Comparative Study on Dyeing Behavior of Modified Rajshahi Silk Fabric with Reactive Orange 14, Direct Yellow 29 and Mordant Blue 9 Dyes. Man-Made Text. India 2010, 53, 10. [Google Scholar]
- Edwards, L.C.; Freeman, H.S. Synthetic dyes based on environmental considerations. Part 3: Aquatic toxicity of iron-complexed azo dyes. Color. Technol. 2005, 121, 265–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, H.W.; Lin, J.; Li, W.Y.; Hu, Z.J.; Zhang, Y.L. Formation of shaped barium sulfate-dye hybrids: Waste dye utilization for eco-friendly treatment of wastewater. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2010, 17, 78–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angelakis, A.; Snyder, S. Wastewater treatment and reuse: Past, present, and future. Water 2015, 7, 4887–4895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ran, J.H.; Shushina, I.; Priazhnikova, V.; Telegin, F. Inhibition of Mordant Dyes Destruction in Fenton Reaction. Adv. Mater. Res. 2013, 821, 493–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šimek, M.; Mikulášek, P.; Kalenda, P.; Weidlich, T. Possibilities for removal of chlorinated dye Mordant Blue 9 from model wastewater. Chem. Pap. 2016, 70, 470–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, G.; Tripathy, M. A critical review of the treatments for decolourization of textile effluent. Colourage 1993, 40, 35–38. [Google Scholar]
- Xavier, S.; Gandhimathi, R.; Nidheesh, P.V.; Ramesh, S.T. Comparison of homogeneous and heterogeneous Fenton processes for the removal of reactive dye Magenta MB from aqueous solution. Desalin. Water Treat. 2015, 53, 109–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nidheesh, P.V.; Gandhimathi, R.; Ramesh, S.T. Degradation of dyes from aqueous solution by Fenton processes: A review. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2013, 20, 2099–2132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nidheesh, P.V.; Gandhimathi, R. Trends in electro-Fenton process for water and wastewater treatment: An overview. Desalination 2012, 299, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pervez, M.N.; Telegin, F.Y.; Cai, Y.; Xia, D.; Zarra, T.; Naddeo, V. Efficient Degradation of Mordant Blue 9 Using the Fenton-Activated Persulfate System. Water 2019, 11, 2532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gulkaya, I.; Surucu, G.A.; Dilek, F.B. Importance of H2O2/Fe2+ ratio in Fenton’s treatment of a carpet dyeing wastewater. J. Hazard. Mater. 2006, 136, 763–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olmez-Hanci, T.; Arslan-Alaton, I. Comparison of sulfate and hydroxyl radical based advanced oxidation of phenol. Chem. Eng. J. 2013, 224, 10–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rastogi, A.; Al-Abed, S.R.; Dionysiou, D.D. Sulfate radical-based ferrous–peroxymonosulfate oxidative system for PCBs degradation in aqueous and sediment systems. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2009, 85, 171–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, Y.; Qu, L.; Yang, H.; Chu, W. Degradation of carbamazepine by Fe (II)-activated persulfate process. J. Hazard. Mater. 2014, 268, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Wu, J.; Lu, X.; Xu, W.; Gong, Q.; Ding, J.; Dan, B.; Xie, P. Removal of acetaminophen in the Fe2+/persulfate system: Kinetic model and degradation pathways. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 358, 1091–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, W.; Dong, Z.; Li, M.; Song, X.; Zhang, M.; Jiang, C.; Feiyun, S. Degradation of diatrizoate in water by Fe (II)-activated persulfate oxidation. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 361, 1333–1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.-P.; Lin, Y.-L.; Zhang, T.-Y.; Cao, T.-C.; Xu, B.; Pan, Y.; Zhang, X.-T.; Gao, N.-Y. Modelling of iohexol degradation in a Fe (II)-activated persulfate system. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 367, 86–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kusic, H.; Peternel, I.; Ukic, S.; Koprivanac, N.; Bolanca, T.; Papic, S.; Bozic, A.L. Modeling of iron activated persulfate oxidation treating reactive azo dye in water matrix. Chem. Eng. J. 2011, 172, 109–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, S.; Vasquez, L.; Costa, D.; Romero, A.; Santos, A. Oxidation of Orange G by persulfate activated by Fe (II), Fe (III) and zero valent iron (ZVI). Chemosphere 2014, 101, 86–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Made in China, Persulphate Price. Available online: https://www.made-in-china.com/products-search/hot-china-products/Persulphate_Price.html#:~:text=Sodium%20Persulfate%20Na2s2o8%20Factory%20Supply%20Plant%207775-27-1,PriceSodium%20Persulphate%20FOB%20Price%3A%20US%20%24%20900-1160%2F%20T (accessed on 11 November 2022).
- Procurement Resource, Hydrogen Peroxide Price Trends. Available online: https://www.procurementresource.com/resource-center/hydrogen-peroxide-price-trends (accessed on 11 November 2022).
- Weidlich, T.; Kamenická, B.; Melánová, K.; Čičmancová, V.; Komersová, A.; Čermák, J. Hydrodechlorination of different chloroaromatic compounds at room temperature and ambient pressure—Differences in reactivity of Cu-and Ni-Based Al alloys in an alkaline aqueous solution. Catalysts 2021, 10, 994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bendová, H.; Kamenická, B.; Weidlich, T.; Beneš, L.; Vlček, M.; Lacina, P.; Švec, P. Application of Raney Al-Ni alloy for simple hydrodehalogenation of Diclofenac and other halogenated biocidal contaminants in alkaline aqueous solution under ambient conditions. Materials 2022, 15, 3939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.T.; Weng, C.H.; Chen, F.Y. Effective removal of AB24 dye by nano/micro-size zero-valent iron. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2008, 64, 26–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raman, C.D.; Kanmani, S. Textile dye degradation using nano zero valent iron: A review. J. Environ. Manag. 2016, 177, 341–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, J.; Guo, Y.; Wang, J.; Fan, M. Rapid decolorization of azo dye methyl orange in aqueous solution by nanoscale zerovalent iron particles. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 166, 904–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nidheesh, P.V.; Khatri, J.; Singh, T.A.; Gandhimathi, R.; Ramesh, S.T. Review of zero-valent aluminium based water and wastewater treatment methods. Chemosphere 2018, 200, 621–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Zhang, F.; Deng, S.; Yu, G.; Zhang, H.; Xiao, J.; Shen, J. A facile method for the highly efficient hydrodechlorination of 2-chlorophenol using Al-Ni alloy in the presence of fluorine ion. J. Chem. Eng. 2012, 209, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reife, A.; Freeman, H.S. Environmental Chemistry of Dyes and Pigments, 1st ed.; John Wiley & Sons:: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1996; p. 352. ISBN 978-0-471-58927-3. [Google Scholar]
- Martins, A.; Nelson, N. Adsorption of a textile dye on commercial activated carbon: A simple experiment to explore the role of surface chemistry and ionic strength. J. Chem. Educ. 2015, 92, 143–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomic, N.M.; Dohcevic-Mitrovic, Z.D.; Paunović, N.M.; Mijin, D.Z.; Radić, N.D.; Grbic, B.V.; Bajuk-Bogdanovic, D.V. Nanocrystalline CeO2− δ as effective adsorbent of azo dyes. Langmuir 2014, 30, 11582–11590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kumar, M.; Venugopal, A.K.P.; Pakshirajan, K. Novel biologically synthesized metal nanopowder from wastewater for dye removal application. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 38478–38492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Pakshirajan, K.; Daverey, A. Screening and optimization of media constituents for decolourization of Mordant Blue-9 dye by Phanerochaete chrysosporium. Clean Technol. Environ. Policy 2010, 12, 313–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yassen, D.A.; Scholz, M. Textile dye wastewater characteristics and constituents of synthetic effluents: A critical review. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 16, 1193–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kremer, M.L. The Fenton reaction. Dependence of the rate on pH. J. Phys. Chem. A. 2003, 107, 1734–1741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Igbinosa, E.O.; Odjadjare, E.E.; Chigor, V.N.; Igbinosa, I.H.; Emoghene, A.O.; Ekhaise, F.O.; Igiehon, N.O.; Idemudia, O.G. Toxicological profile of chlorophenols and their derivatives in the environment: The public health perspective. Sci. World J. 2013, 11, 460215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Weidlich, T.; Prokes, L.; Pospisilova, D. Debromination of 2,4,6-tribromophenol coupled with biodegradation. Cent. Eur. J. Chem. 2013, 11, 979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bousalah, D.; Zazoua, H.; Boudjemaa, A.; Benmounah, A.; Bachari, K. Degradation of Indigotine food dye by Fenton and photo-Fenton processes. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 2020, 102, 4609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, S.F.; Liao, C.H.; Chen, M.C. Pre-oxidation and coagulation of textile wastewater by the Fenton process. Chemosphere 2002, 46, 923–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.X. Nanoscale iron particles for environmental remediation: An overview. J. Nanoparticle Res. 2003, 5, 323–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weidlich, T.; Kamenicka, B. Recycling of Spent Hydrodehalogenation Catalysts–Problems Dealing with Separation of Aluminium. Inz. Miner. 2019, 21, 177–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weidlich, T.; Krejcova, A.; Prokes, L. Hydrodebromination of 2,4,6-tribromophenol in aqueous solution using Devarda’s alloy. Monatsh. Chem. 2013, 144, 155–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bendova, H.; Weidlich, T. Application of diffusion dialysis in hydrometallurgical separation of nickel from spent Raney Ni catalyst. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2018, 53, 1218–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weidlich, T.; Oprsal, J.; Krejcova, A.; Jasurek, B. Effect of glucose on lowering Al-Ni alloy consumption in dehalogenation of halogenoanilines. Monatsh. Chem. 2015, 146, 613–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Made in China. H2SO4 Price. Available online: https://kunyabiological.en.made-in-china.com/product/kZMtfiCTMFWw/China-Sulfuric-Acid-with-Competitive-Price-and-CAS-No-7664-93-9.html (accessed on 23 January 2023).
- Sigma Aldrich. H2O2 Price. Available online: https://www.sigmaaldrich.com/CZ/en/substance/hydrogenperoxide34017722841 (accessed on 23 January 2023).
- Sigma Aldrich. FeSO4 Price. Available online: https://www.sigmaaldrich.com/CZ/en/substance/ironiisulfateheptahydrate278017782630 (accessed on 23 January 2023).
- AliExpress. Fe0 Price. Available online: https://www.aliexpress.com/item/1005003952039242.html?spm=a2g0o.productlist.main.1.666b1ebeXVNzaz&algo_pvid=567a960c-734e-414b-979d-f5ea646666da&algo_exp_id=567a960c-734e-414b-979d-f5ea646666da-0&pdp_ext_f=%7B%22sku_id%22%3A%2212000030178526057%22%7D&pdp_npi=2%40dis%21CZK%21367.31%21367.31%21%21%21%21%21%40214528be16744809367621410d06b6%2112000030178526057%21sea&curPageLogUid=hPMiO1R1R4b7 (accessed on 23 January 2023).
- Amazon. Al0 Price. Available online: https://www.amazon.com/Aluminum-Powder-Pound-MS-MetalShipper/dp/B0849WHSTY/ref=sr_1_1?crid=32BXCVP7ZHZH1&keywords=aluminum+powder&qid=1674482314&sprefix=%2Caps%2C1251&sr=8-1 (accessed on 23 January 2023).
- Made in China. NaOH Price. Available online: https://highmountainchem.en.made-in-china.com/product/HElUSyYxsrhD/China-Sodium-Hydroxide-Caustic-Soda-Flakes-Alkali-99-Naoh-CAS-1310-73-2.html (accessed on 23 January 2023).
- AliExpress. Ni0 Price. Available online: https://www.aliexpress.com/item/1005004187537341.html?spm=a2g0o.productlist.main.1.6f4ePBR5PBR5j9&algo_pvid=bab4e3ef-19f2-475e-b186-02000b20af84&algo_exp_id=bab4e3ef-19f2-475e-b186-02000b20af84-0&pdp_ext_f=%7B%22sku_id%22%3A%2212000028321382122%22%7D&pdp_npi=2%40dis%21CZK%21457.29%21251.53%21%21%21%21%21%402145288516744811272258567d0761%2112000028321382122%21sea&curPageLogUid=sc5TkfWdj7Qm (accessed on 23 January 2023).
- Fisher Scientific. Al-Ni Alloy Price. Available online: https://www.fishersci.fi/shop/products/aluminum-nickel-raney-type-alloy-powder-al-ni-50-50-thermo-scientific/11946951 (accessed on 23 January 2023).
- SRL CHEM. NaBH4 Price. Available online: https://srlchem.com/products/product_details/productId/1132 (accessed on 23 January 2023).
- India Global Mart. Na2S2O5 Price. Available online: https://dir.indiamart.com/impcat/sodium-metabisulfite.html (accessed on 23 January 2023).



















| Applied Degradation Method | Quantity of Used Reagents per mol of MB9 | Efficiency of MB9 Discoloration | Other Removal Efficiencies (%) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Persulfate-based AOP at pH = 4.88 | 16 mol of Na2S2O8 + 14 mol of FeSO4 | 97% (after 30 min) | 60% of TOC (after 30 min) | [18] |
| Fenton oxidation at pH = 4.88 | 16 mol of H2O2 + 14 mol of FeSO4 | 48% of MB9 (after 30 min) | 38% of TOC (after 30 min) | [18] |
| Fenton oxidation at pH = 2–2.5 | 28 mol of H2SO4 120 mol of H2O2 + 4 mol of FeSO4 | 86.1% of MB9 (after 3 h) | 37.6% of COD (after 3 h) | This work |
| Fenton oxidation at pH = 2–2.5 | 28 mol of H2SO4 120 mol of H2O2 + 4 mol of FeSO4 | >99% of MB9 (after 20 h) | 98.3% of AOX and 93.7% of COD (after 20 h) | This work |
| Chemical reduction ZVI | 150 mol of Fe0 800 mol of H2SO4 | 99.5% of MB9 (after 3 h) | 35.2% of AOX (after 3 h) | This work |
| Chemical reduction Al0 powder | 370 mol of Al0 800 mol of H2SO4 | 97.5% of MB9 (after 20 h) | 30.5% of AOX (after 20 h) | This work |
| Chemical reduction Al0 powder | 200 mol of Al0 100 mol of NaOH | 96.5% of MB9 (after 3 h) | 41.4% of AOX (after 3 h) | This work |
| Chemical reduction Al0 powder + Ni0 powder | 200 mol of Al0 50 mol of Ni0 100 mol of NaOH | 96.7% of MB9 | 56.4% of AOX (after 3 h) | This work |
| Chemical reduction Raney Al-Ni | 100 mol of Al0 used in Al-Ni 100 mol of NaOH | 96.9% of MB9 (after 3 h) | 94.5% of AOX (after 3 h) | This work |
| Chemical reduction Al0 powder + Raney Al-Ni | 120 mol of Al0 480 mol of NaOH 44 mol of Al0 (in Al-Ni) 480 mol of NaOH | 99% of MB9 (after 3 + 20 h) | 91.7% of AOX (after 3 + 20 h) | This work |
| Chemical reduction NaBH4 | 132 mol of NaBH4 | 99.4% of MB9 (after 20 h) | 68.7% of AOX (after 20 h) | This work |
| Chemical reduction NaBH4/Na2S2O5 | 66 mol of NaBH4 + 66 mol of Na2S2O5 + 18 mol of H2SO4 | 99.5% of MB9 (after 30 min) | 95.9% of AOX (after 20 h) | This work |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kamenická, B.; Weidlich, T. A Comparison of Different Reagents Applicable for Destroying Halogenated Anionic Textile Dye Mordant Blue 9 in Polluted Aqueous Streams. Catalysts 2023, 13, 460. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal13030460
Kamenická B, Weidlich T. A Comparison of Different Reagents Applicable for Destroying Halogenated Anionic Textile Dye Mordant Blue 9 in Polluted Aqueous Streams. Catalysts. 2023; 13(3):460. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal13030460
Chicago/Turabian StyleKamenická, Barbora, and Tomáš Weidlich. 2023. "A Comparison of Different Reagents Applicable for Destroying Halogenated Anionic Textile Dye Mordant Blue 9 in Polluted Aqueous Streams" Catalysts 13, no. 3: 460. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal13030460
APA StyleKamenická, B., & Weidlich, T. (2023). A Comparison of Different Reagents Applicable for Destroying Halogenated Anionic Textile Dye Mordant Blue 9 in Polluted Aqueous Streams. Catalysts, 13(3), 460. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal13030460