Effect of Small Molecular Organic Acids on the Structure and Catalytic Performance of Sol–Gel Prepared Cobalt Cerium Oxides towards Toluene Combustion
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. TG–DSC Results
2.2. XRD Results
2.3. N2–Adsorption and Desorption Results
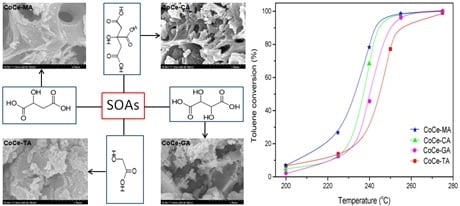
2.4. SEM–EDS Results
2.5. XPS Results
2.6. H2–TPR Results
2.7. Catalytic Performance
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Catalyst Preparation
4.2. Catalyst Characterization
4.3. Catalyst Evaluation
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, Y.; Fan, Z.; Shi, J.; Liu, Z.; Zhou, J.; Shangguan, W. Removal of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) at room temperature using dielectric Bbarrier discharge and plasma–catalysis. Plasma Chem. Plasma P. 2014, 34, 801–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, S.F.; Huang, Q.Q.; Li, J.; Zhou, R.X. Promoting effect of Ce added to metal oxide supported on Al pillared clays for deep benzene oxidation. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2009, 91, 204–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Xu, Y.; Feng, Q.; Leung, D.Y.C. Low temperature catalytic oxidation of volatile organic compounds: a review. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2015, 5, 2649–2669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Jiang, Z.; Shangguan, W. Low–temperature catalysis for VOCs removal in technology and application: A state–of–the–art review. Catal. Today 2016, 264, 270–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.C.; Nahm, S.W.; Shim, W.G.; Lee, J.W.; Moon, H. Influence of physicochemical treatments on spent palladium based catalyst for catalytic oxidation of VOCs. J. Hazard. Mater. 2007, 141, 305–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonelli, R.; Lucarelli, C.; Pasini, T.; Liotta, L.F.; Zacchini, S.; Albonetti, S. Total oxidation of volatile organic compounds on Au/FeOx catalysts supported on mesoporous SBA–15 silica. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2011, 400, 54–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Zhang, H.; Yan, Y. Fabrication of porous copper/manganese binary oxides modified ZSM–5 membrane catalyst and potential application in the removal of VOCs. Chem. Eng. J. 2014, 254, 133–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Y.; Zhang, X.; Peng, R.; Zhao, M.; Ye, D. Catalytic properties of manganese oxide polyhedra with hollow and solid morphologies in toluene removal. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2017, 405, 20–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carabineiro, S.A.C.; Chen, X.; Konsolakis, M.; Psarras, A.C.; Tavares, P.B.; Orfao, J.J.M.; Pereira, M.F.R.; Figueiredo, J.L. Catalytic oxidation of toluene on Ce–Co and La–Co mixed oxides synthesized by exotemplating and evaporation methods. Catal. Today 2015, 244, 161–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barakat, T.; Rooke, J.C.; Tidahy, H.L.; Hosseini, M.; Cousin, R.; Lamonier, J.F.; Giraudon, J.M.; De Weireld, G.; Su, B.L.; Siffert, S. Noble–metal–based catalysts supported on zeolites and macro–mesoporous metal oxide supports for the total oxidation of volatile organic compounds. ChemSusChem 2011, 4, 1420–1430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Shi, W.; Zhang, X.; Arandiyan, H.; Li, D.; Li, J. Roles of Li+ and Zr4+ cations in the catalytic performances of Co1–xMxCr2O4 (M = Li, Zr; x=0–0.2) for methane combustion. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 8491–8497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.B.; Wang, J.X.; Gong, H. Catalytic combustion of VOCs on non–noble metal catalysts. Catal. Today 2009, 148, 81–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, W.; Liu, G.; Li, D.; Liu, H.; Wu, X.; Han, N.; Chen, Y. Design and synthesis of porous non–noble metal oxides for catalytic removal of VOCs. Sci. China Chem. 2015, 58, 1359–1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zabihi, M.; Khorasheh, F.; Shayegan, J. Supported copper and cobalt oxides on activated carbon for simultaneous oxidation of toluene and cyclohexane in air. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 5107–5122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Deng, J.; Xie, S.; Wang, Z.; Dai, H. Catalytic removal of volatile organic compounds using ordered porous transition metal oxide and supported noble metal catalysts. Chin. J. Catal. 2016, 37, 1193–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.; Guo, J.; Wen, X.; Xu, M.; Chu, Y.; Yuan, S. Enhancing performance of Co/CeO2 catalyst by Sr doping for catalytic combustion of toluene. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 445. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, C.F.; Chen, H.; Hu, R.R.; Huang, S.; Luo, W.; Guo, C.; Li, M.; Li, W. Synthesis of mesoporous Co–Ce oxides catalysts by glycine–nitrate combustion approach for CO preferential oxidation reaction in excess H2. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2014, 39, 18695–18701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Q.; Wang, X.; Lu, G. Low–temperature catalytic combustion of trichloroethylene over cerium oxide and catalyst deactivation. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2008, 81, 192–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liotta, L.F.; Di Carlo, G.; Pantaleo, G.; Venezia, A.M.; Deganello, G. Co3O4/CeO2 composite oxides for methane emissions abatement: relationship between Co3O4–CeO2 interaction and catalytic activity. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2006, 66, 217–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konsolakis, M.; Sgourakis, M.; Carabineiro, S.A.C. Surface and redox properties of cobalt–ceria binary oxides: on the effect of Co content and pretreatment conditions. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2015, 341, 48–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Lu, G.; Qiao, D.; Wang, Y.; Guo, Y.; Guo, Y. Catalytic methane combustion over Co3O4/CeO2 composite oxides prepared by modified citrate sol–gel method. Catal. Lett. 2011, 141, 452–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liotta, L.F.; Ousmane, M.; Di Carlo, G.; Pantaleo, G.; Deganello, G.; Marci, G.; Retailleau, L.; Giroir-Fendler, A. Total oxidation of propene at low temperature over Co3O4–CeO2 mixed oxides: role of surface oxygen vacancies and bulk oxygen mobility in the catalytic activity. Applied Catalysis A Gen. 2008, 347, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, J.; Ke, Y.; Yu, Z.; Hu, X.; Qu, Z.; Yan, N. Morphology–dependent properties of Co3O4/CeO2 catalysts for low temperature dibromomethane (CH2Br2) oxidation. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 320, 124–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, W.; Dai, Q.; Lao, Y.; Shi, B.; Wang, X. Low temperature catalytic combustion of 1,2–dichlorobenzene over CeO2–TiO2 mixed oxide catalysts. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2016, 181, 848–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Pei, Z.; Wu, T.; Lu, H.; Huang, H. A mechanistic study of the sulfur tolerance of Cu–V mixed oxides in toluene catalytic combustion. React. Kinet. Mech. Catal. 2015, 116, 467–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.; Kong, X.; Huang, H.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, Y. Cu–Mn–Ce ternary mixed–oxide catalysts for catalytic combustion of toluene. J. Environ. Sci. 2015, 32, 102–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Luo, L.; Lu, X. Preparation of mesoporous Ce1–xFexO2 mixed oxides and their catalytic properties in methane combustion. Kinet. Catal. 2008, 49, 676–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, L.; Li, C.; Zhang, J.; Du, X.; Li, S.; Zeng, J.; Yi, Y.; Zeng, G. Simultaneous removal of NO and Hg0 from simulated flue gas over CoOx–CeO2 loaded biomass activated carbon derived from maize straw at low temperatures. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 342. [Google Scholar]
- Sanpo, N.; Wang, J.; Ang, A.S.M.; Berndt, C.C. Influence of the different organic chelating agents on the topography, physical properties and phase of SPPS–deposited spinel ferrite splats. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2013, 284, 171–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Cao, L.; Huang, J.; Wu, J. Effects of different chelating agents on the composition, morphology and electrochemical properties of LiV3O8 crystallites synthesized via sol–gel method. Ceram. Int. 2013, 39, 3759–3764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hessien, M.M.; Mostafa, N.Y.; Abd-Elkader, O.H. Influence of carboxylic acid type on microstructure and magnetic properties of polymeric complex sol–gel driven NiFe2O4. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2016, 398, 109–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Lee, J. Microwave–assisted sol–gel synthesis and photoluminescence characterization of LaPO4: Eu3+, Li+ nanophosphors. J. Phys. Chem. C 2008, 112, 11679–11684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinaykumar, R.; Mazumder, R.; Bera, J. Characterization of SrCo1.5Ti1.5Fe9O19 hexagonal ferrite synthesized by solgel combustion and solid state route. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2017, 429, 359–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.Y.; Meng, M.; Li, X.; Li, X.G.; Zha, Y.Q.; Hu, T.D.; Xie, Y.N.; Zhang, J. Mesoporous Co3O4–CeO2 and Pd/Co3O4–CeO2 catalysts: Synthesis, characterization and mechanistic study of their catalytic properties for low–temperature CO oxidation. J. Catal. 2008, 254, 310–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Cao, F.; Qu, R.; Gao, X.; Cen, K. Bimetallic cerium–copper nanoparticles embedded in ordered mesoporous carbons as effective catalysts for the selective catalytic reduction of NO with NH3. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2015, 456, 66–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Fu, H.; Fu, L.; Hao, J. Complete combustion of methane over indium tin oxides catalysts. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2006, 40, 6455–6459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, T.; Huang, H.; Deng, W.; Dai, Q.; Liu, W.; Wang, X. Catalytic combustion of 1,2–dichlorobenzene at low temperature over Mn–modified Co3O4 catalysts. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2015, 166, 393–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solsona, B.; Davies, T.E.; Garcia, T.; Vazquez, I.; Dejoz, A.; Taylor, S.H. Total oxidation of propane using nanocrystalline cobalt oxide and supported cobalt oxide catalysts. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2008, 84, 176–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Prior, J.; Lopez-Fonseca, R.; Gutierrez-Ortiz, J.I.; de Rivas, B. Catalytic removal of chlorinated compounds over ordered mesoporous cobalt oxides synthesised by hard–templating. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2018, 222, 9–17. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, L.; Li, C.; Li, S.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Wang, T.; Zeng, G. Simultaneous removal of elemental mercury and NO in simulated flue gas over V2O5/ZrO2–CeO2 catalyst. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2016, 198, 420–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Li, C.; Li, S.; Lu, P.; Gao, L.; Du, X.; Yi, Y. Simultaneous removal of HCHO and elemental mercury from flue gas over Co–Ce oxides supported on activated coke impregnated by sulfuric acid. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 338, 358–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, N.; Furfori, S.; Fino, D.; Saracco, G.; Specchia, V. Lanthanum cobaltite catalysts for diesel soot combustion. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2008, 83, 85–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liotta, L.F.; Di Carlo, G.; Pantaleo, G.; Deganello, G. Co3O4/CeO2 and Co3O4/CeO2–ZrO2 composite catalysts for methane combustion: Correlation between morphology reduction properties and catalytic activity. Catal. Commun. 2005, 6, 329–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konsolakis, M.; Ioakeimidis, Z. Surface/structure functionalization of copper–based catalysts by metal–support and/or metal–metal interactions. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2014, 320, 244–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, H.; Yuan, W.; Scott, K.; Browning, D.J.; Lakeman, J.B. The catalytic activity and methanol tolerance of transition metal modified–ruthenium–selenium catalysts. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2007, 75, 221–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baccile, N.; Babonneau, F.; Thomas, B.; Coradin, T. Introducing ecodesign in silica sol–gel materials. J. Mater. Chem. 2009, 19, 8537–8559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danks, A.E.; Hall, S.R.; Schnepp, Z. The evolution of ‘sol–gel’ chemistry as a technique for materials synthesis. Mater. Horiz. 2016, 3, 91–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonio Aguilera, D.; Perez, A.; Molina, R.; Moreno, S. Cu–Mn and Co–Mn catalysts synthesized from hydrotalcites and their use in the oxidation of VOCs. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2011, 104, 144–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, Z.; Gao, K.; Fu, Q.; Qin, Y. Low–temperature catalytic oxidation of toluene over nanocrystal–like Mn–Co oxides prepared by two–step hydrothermal method. Catal. Commun. 2014, 52, 31–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bialas, A.; Mazur, M.; Natkanski, P.; Dudek, B.; Kozak, M.; Wach, A.; Kustrowski, P. Hydrotalcite–derived cobalt–aluminum mixed oxide catalysts for toluene combustion. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2016, 362, 297–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Li, W.B.; Liu, R.F. Highly efficient copper–doped manganese oxide nanorod catalysts derived from CuMnO hierarchical nanowire for catalytic combustion of VOCs. Catal. Today 2018, 314, 147–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Zuo, J.; Feng, X.; Wang, X.; Zhang, T.; Zhang, K.; Jiang, L. Insights into the high performance of Mn–Co oxides derived from metal organic frameworks for total toluene oxidation. J. Hazard. Mater. 2018, 349, 119–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Zhang, C.; Hua, W.; Guo, Y.; Lu, G.; Gil, S.; Giroir-Fendler, A. Catalytic oxidation of vinyl chloride emissions over Co–Ce composite oxide catalysts. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 315, 392–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]










| Organic Acid | Abbreviation | Chemical Formula | Structure | Molecular Mass (g/mol) | Boiling Points (°C) | ΔcHmθ (kJ/mol) a |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Malic acid | MA | C4H6O5 |  | 134.1 | 140 | −1326.5 |
| Citric acid | CA | C6H8O7 |  | 192.1 | 175 | −1952.8 |
| Glycolic acid | GA | C2H4O3 |  | 76.1 | 100 | −695.3 |
| Tartaric acid | TA | C4H6O6 |  | 150.1 | 170 | −1141.1 |
| Sample | Crystallite Size of CeO2 (nm) a | Crystallite Size of Co3O4 (nm) b | BET Surface Area (m2/g) | Average Pore Volume (cm3/g) | Average Pore Diameter (nm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CoCe–MA | 9.6 | 19.8 | 40.3 | 0.153 | 11.7 |
| CoCe–CA | 10.0 | 25.8 | 21.1 | 0.071 | 10.8 |
| CoCe–GA | 11.5 | 30.2 | 14.5 | 0.069 | 12.3 |
| CoCe–TA | 12.8 | 38.2 | 14.3 | 0.041 | 9.2 |
| Sample | Elemental Content (wt.%) a | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| O | Co | Ce | |
| CoCe–MA | 10.76 | 39.95 | 49.29 |
| CoCe–CA | 10.65 | 40.21 | 49.14 |
| CoCe–GA | 10.92 | 39.82 | 49.26 |
| CoCe–TA | 11.05 | 41.06 | 47.89 |
| Sample | Binding Energy (eV) | Atomic Ratio | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| O 1s | Co 2p3/2 | Ce 3d5/2 | Oads/Olat | Co2+/Co3+ | Ce3+/Ce4+ | ||||
| Olat | Oads | Co2+ | Co3+ | Ce3+ | Ce4+ | ||||
| CoCe–MA | 529.9 | 531.4 | 782.2 | 779.8 | 885.8 | 882.6 | 0.40 | 0.35 | 0.22 |
| CoCe–CA | 529.9 | 531.4 | 782.9 | 779.9 | 885.7 | 882.4 | 0.36 | 0.33 | 0.20 |
| CoCe–GA | 529.9 | 531.5 | 782.5 | 779.9 | 886.0 | 882.5 | 0.35 | 0.30 | 0.19 |
| CoCe–TA | 529.9 | 531.4 | 782.7 | 779.9 | 885.6 | 882.6 | 0.33 | 0.28 | 0.17 |
| Sample | H2 Consumption (mmol/gcat) | Catalytic Activity | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PH2–I | PH2–II | PH2–III | Total | Ratio of PH2–II /PH2–I | T50 (°C) | T90 (°C) | |
| CoCe–MA | 1.84 | 5.33 | 1.41 | 8.58 | 2.90 | 232 | 242 |
| CoCe–CA | 1.91 | 5.71 | 1.10 | 8.72 | 2.99 | 237 | 245 |
| CoCe–GA | 1.89 | 5.80 | 0.60 | 8.29 | 3.07 | 240 | 250 |
| CoCe–TA | 2.19 | 6.55 | 0.05 | 8.74 | 2.99 | 245 | 256 |
| Sample | Atomic Ratio | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Oads/Olat | Co2+/Co3+ | Ce3+/Ce4+ | |
| CoCe–MA | 0.40 | 0.35 | 0.22 |
| CoCe–MA–used | 0.27 | 0.24 | 0.17 |
| Catalyst | GHSV (mL/(g·h)) | Concentration (ppm) | T90 (°C) | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CoCe–MA | 20,000 | 500 | 242 | this work |
| CuMn0.5 CoMn0.5 | 60,000 60,000 | 1200 1200 | 273 258 | [48] [48] |
| Mn1Co1 | 30,000 | 1000 | 249 | [49] |
| CoAl5–70 CoAl3–70 | 60,000 60,000 | 1000 1000 | 298 281 | [50] [50] |
| Cu1Mn1O–600 | 20,000 | 1000 | 243 | [51] |
| MOF a–Mn1Co2 | 96,000 | 500 | 270 | [52] |
| Cu1Mn6 Cu1Ce6 | 24,000 24,000 | 500 500 | 255 259 | [26] [26] |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, J.; Lin, J.; Chen, J.; Wang, J. Effect of Small Molecular Organic Acids on the Structure and Catalytic Performance of Sol–Gel Prepared Cobalt Cerium Oxides towards Toluene Combustion. Catalysts 2019, 9, 483. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal9050483
Chen J, Lin J, Chen J, Wang J. Effect of Small Molecular Organic Acids on the Structure and Catalytic Performance of Sol–Gel Prepared Cobalt Cerium Oxides towards Toluene Combustion. Catalysts. 2019; 9(5):483. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal9050483
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Jianmeng, Junhong Lin, Jinghuan Chen, and Jiade Wang. 2019. "Effect of Small Molecular Organic Acids on the Structure and Catalytic Performance of Sol–Gel Prepared Cobalt Cerium Oxides towards Toluene Combustion" Catalysts 9, no. 5: 483. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal9050483
APA StyleChen, J., Lin, J., Chen, J., & Wang, J. (2019). Effect of Small Molecular Organic Acids on the Structure and Catalytic Performance of Sol–Gel Prepared Cobalt Cerium Oxides towards Toluene Combustion. Catalysts, 9(5), 483. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal9050483