Terbium-Tetracarboxylate Framework as a Luminescent Probe for the Selective Detection of Nitrofurazone
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental
2.1. Materials and Methods
2.2. Synthesis of ZTU-5
2.3. Crystal Structure Determination
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Synthesis and Structure Description of the Crystal Structures
3.2. Hirshfeld Surface Analysis
3.3. XRD Patterns and Thermogravimetric Analyzer Data
3.4. Magnetic Property
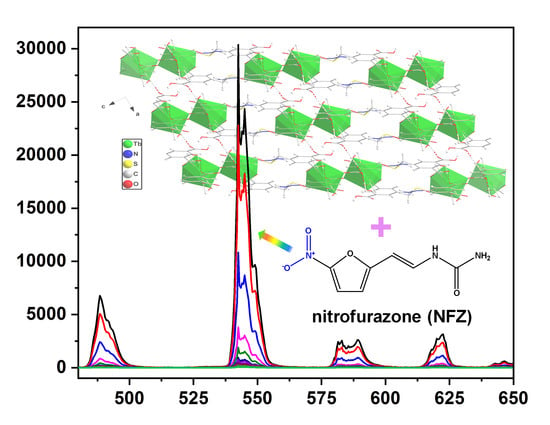
3.5. Luminescence Property
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kümmerer, K. Antibiotics in the aquatic environment—A review. Chemosphere 2009, 75, 417–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Homem, V.; Santos, L. Degradation and removal methods of antibiotics from aqueous matrices-A review. J. Environ. Manag. 2011, 92, 2304–2347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, W.F.; Xiao, Y.; Yan, W.D.; Ding, R.; Wang, S.H.; Zhao, F. The effect of bioelectrochemical systems on antibiotics removal and antibiotic resistance genes: A review. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 358, 1421–1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oberoi, A.S.; Jia, Y.Y.; Zhang, H.Q.; Khanal, S.K.; Lu, H. Insights into the Fate and Removal of Antibiotics in Engineered Biological Treatment Systems: A Critical Review. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 7234–7264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghirardinia, A.; Grillinia, V.; Verlicchi, P. A review of the occurrence of selected micro pollutants and microorganisms in different raw and treated manure—Environmental risk due to antibiotics after application to soil. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 707, 13118. [Google Scholar]
- Blasco, C.; Corcia, A.D.; Picó, Y. Determination of tetracyclines in multi-specie animal tissues by pressurized liquid extraction and liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Food Chem. 2009, 116, 1005–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno-González, D.; Lara, F.J.; Jurgovská, N.; Gámiz-Gracia, L.; García-Campana, A.M. Determination of amino glycosides in honey by capillary electrophoresis tandem mass spectrometry and extraction with molecularly imprinted polymers. Anal. Chim. Acta. 2015, 891, 321–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hakansson, K.; Coorey, R.V.; Zubarev, R.A.; Talrose, V.L.; Hakansson, P.J. Low-mass ions observed in plasma desorption mass spectrometry of high explosives. Mass Spectrom. 2000, 35, 337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moros, J.; Laserna, J.J. New Raman–laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy identity of explosives using parametric data fusion on an integrated sensing platform. Anal. Chem. 2011, 83, 6275–6285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabrizchi, M.; ILbeigi, V. Detection of explosives by positive corona discharge ion mobility spectrometry. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 176, 692–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.L.; Xie, L.H.; Joseph, E.A.; Li, J.R.; Su, X.O.; Zhou, H.C. Metal–Organic Frameworks for Food Safety. Chem. Rev. 2019, 119, 10638–10690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Lv, X.L.; Feng, D.W.; Xie, L.H.; Zhang, J.; Li, M.; Xie, Y.B.; Li, J.R.; Zhou, H.C. Highly stable Zr (IV)-based metal–organic frameworks for the detection and removal of antibiotics and organic explosives in water. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138, 6204–6216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, M.K.; Xie, Y.; Wang, X.Y.; Li, Y.X.; Li, G.M. Highly Water-Stable Dye@Ln-MOFs for Sensitive and Selective Detection toward Antibiotics in Water. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 21201–21210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, S.L.; Dong, J.; Jiang, X.L.; Jiao, Z.H.; Wang, C.M.; Zhao, B. Interpenetration-Dependent Luminescent Probe in Indium-Organic Frameworks for Selectively Detecting Nitrofurazone in Water. Anal. Chem. 2018, 90, 1516–1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Joseph, L.; Jun, B.M.; Jiang, M.; Park, C.M.; Munoz-Senmache, J.C.; Hernández-Maldonado, A.J.; Heyden, A.; Yu, M.; Yoon, Y. Removal of contaminants of emerging concern by metal-organic framework nanoadsorbents: A review. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 369, 928–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolomanov, O.-V.; Bourhis, L.-J.; Gildea, R.-J.; Howard, J.A.-K.; Puschmann, H. OLEX2: A Complete Structure Solution, Refinement and Analysis Program. J. Appl. Cryst. 2009, 42, 339–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheldrick, M. Crystal structure refinement with SHELXL. Acta Cryst. 2015, C71, 3–8. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Q.P.; Du, S.W. Two novel 3D lanthanide supramolecular coordination polymers constructed from paddle wheel SBUs and hydrogen bonding: Synthesis, structures and properties. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 30963–30967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, M.J.; McKinnon, J.J.; Wolff, S.K.; Grimwood, D.J.; Spackman, P.R.; Jayatilaka, D.; Spackman, M.A. CrystalExplorer17. Available online: https://crystalexplorer.scb.uwa.edu.au (accessed on 27 February 2020).
- McKinnon, J.J.; Spackman, M.A.; Mitchell, A.S. Novel tools for visualizing and exploring intermolecular interactions in molecular crystals. Acta Cryst. B. 2004, 60, 627–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spackman, M.A.; McKinnon, J.J. Fingerprinting Intermolecular Interactions in Molecular Crystals. CrystEngComm 2002, 4, 378–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.P.; Shen, Y.Q.; Wang, Y.; Ye, P.; Li, L.; Zhang, Z.J. Magnetic and Luminescence Properties of Two Dinuclear Lanthanide Complexes with Butterfly-like Arrangement. Z. Anorg. Allg. Chem. 2019, 645, 101–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Zhang, L.; Wang, C.; Xue, S.F.; Lin, S.Y.; Tang, J.K. Equatorially coordinated lanthanide single ion magnets. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 4484–4487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.P.; Peng, Y.; Qian, J.J.; Yan, T.; Du, L.; Zhao, Q.H. A family of planar hexanuclear CoIII4LnIII2 clusters with lucanidae-like arrangement and single-molecule magnet behavior. Dalton Trans. 2019, 48, 12880–12887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.P.; Du, S.W. A family of 3D lanthanide organic frameworks with tunable luminescence and slow magnetic relaxation. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 9898–9903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Compounds | ZTU-5 |
|---|---|
| CCDC | 1950505 |
| Formula | C18H17N2O11STb |
| Mr | 628.33 |
| Space group | P |
| a (Å) | 7.7450(2) |
| b (Å) | 11.224(3) |
| c (Å) | 12.051(3) |
| α (deg) | 78.901(6) |
| β (deg) | 82.678(7) |
| γ (deg) | 85.359(6) |
| V (Å3) | 1017.9(4) |
| Z | 2 |
| Dc (g cm−3) | 2.050 |
| Μ (mm−1) | 3.644 |
| F(000) | 616.0 |
| GOF | 1.062 |
| R1a | 0.0175 |
| wR2a | 0.0432 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, Q.; Shen, Y.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, Z.; Qian, J. Terbium-Tetracarboxylate Framework as a Luminescent Probe for the Selective Detection of Nitrofurazone. Crystals 2020, 10, 222. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst10030222
Li Q, Shen Y, Zhao J, Zhang Z, Qian J. Terbium-Tetracarboxylate Framework as a Luminescent Probe for the Selective Detection of Nitrofurazone. Crystals. 2020; 10(3):222. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst10030222
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Qipeng, Yanqiong Shen, Junsong Zhao, Zejun Zhang, and Jinjie Qian. 2020. "Terbium-Tetracarboxylate Framework as a Luminescent Probe for the Selective Detection of Nitrofurazone" Crystals 10, no. 3: 222. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst10030222
APA StyleLi, Q., Shen, Y., Zhao, J., Zhang, Z., & Qian, J. (2020). Terbium-Tetracarboxylate Framework as a Luminescent Probe for the Selective Detection of Nitrofurazone. Crystals, 10(3), 222. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst10030222