The Discovery of an Iridium(III) Dimer Complex as a Potent Antibacterial Agent against Non-Replicating Mycobacterium smegmatis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Tested Compounds
2.2. Strains and Media
2.3. Compound Susceptibility Testing
2.4. Starvation Conditions
2.5. Measurement of Intracellular Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS)
2.6. Protection by Iron Chelator and Hydroxyl Radical Scavenger
2.7. Generation of Norfloxacin-Resistant Mutants
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Complex 3 Displays Selective Activity against M. smegmatis
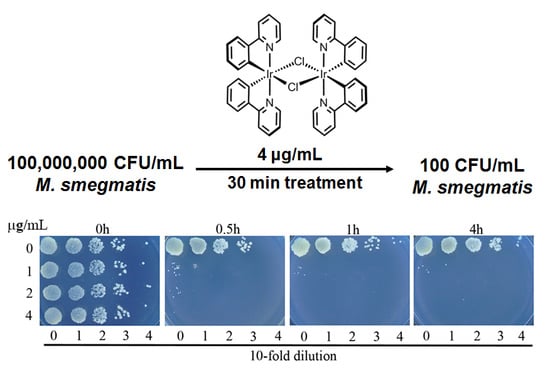
3.2. Complex 3 Displays Potent Bactericidal Activity against M. smegmatis
3.3. Complex 3 Displays Activity against Non-Replicating M. smegmatis
3.4. Complex 3 Was Active against Norfloxacin-Resistant Strains
3.5. Antibacterial Mechanism of Complex 3
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cano-Muniz, S.; Anthony, R.; Niemann, S.; Alffenaar, J.C. New approaches and therapeutic options for Mycobacterium tuberculosis in a dormant state. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2018, 31, e00060-17. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bloemberg, G.V.; Keller, P.M.; Stucki, D.; Trauner, A.; Borrell, S.; Latshang, T.; Coscolla, M.; Rothe, T.; Homke, R.; Ritter, C.; et al. Acquired resistance to bedaquiline and delamanid in therapy for tuberculosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 373, 1986–1988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manson, A.L.; Cohen, K.A.; Abeel, T.; Desjardins, C.A.; Armstrong, D.T.; Barry, C.E., 3rd; Brand, J.; TBResist Global Genome Consortium; Chapman, S.B.; Cho, S.N.; et al. Genomic analysis of globally diverse Mycobacterium tuberculosis strains provides insights into the emergence and spread of multidrug resistance. Nat. Genet. 2017, 49, 395–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoagland, D.T.; Liu, J.; Lee, R.B.; Lee, R.E. New agents for the treatment of drug-resistant Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2016, 102, 55–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zumla, A.; Maeurer, M.; Host-Directed Therapies, N.; Chakaya, J.; Hoelscher, M.; Ntoumi, F.; Rustomjee, R.; Vilaplana, C.; Yeboah-Manu, D.; Rasolof, V.; et al. Towards host-directed therapies for tuberculosis. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2015, 14, 511–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Algburi, A.; Wang, N.; Kholodovych, V.; Oh, D.O.; Chikindas, M.; Uhrich, K.E. Self-assembled cationic amphiphiles as antimicrobial peptides mimics: Role of hydrophobicity, linkage type, and assembly state. Nanomedicine 2017, 13, 343–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, G.; Ye, Z.; Liu, Y.; Fu, B.; Fu, C. Octahedral ruthenium(II) polypyridyl complexes as antimicrobial agents against mycobacterium. PeerJ 2017, 5, e3252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, L.; Liu, L.J.; Chao, W.C.; Zhong, H.J.; Wang, M.; Chen, X.P.; Lu, J.J.; Li, R.N.; Ma, D.L.; Leung, C.H. Identification of an iridium(III) complex with anti-bacterial and anti-cancer activity. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 14544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, C.; Wenzel, M.; Treutlein, E.; Harms, K.; Meggers, E. Proline as chiral auxiliary for the economical asymmetric synthesis of ruthenium(II) polypyridyl complexes. Inorg. Chem. 2012, 51, 10004–10011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frezza, M.; Hindo, S.; Chen, D.; Davenport, A.; Schmitt, S.; Tomco, D.; Dou, Q.P. Novel metals and metal complexes as platforms for cancer therapy. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2010, 16, 1813–1825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, F.F.; Collins, J.G.; Keene, F.R. Ruthenium complexes as antimicrobial agents. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2015, 44, 2529–2542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Medici, S.; Peana, M.; Nurchi, V.M.; Lachowicz, J.I.; Crisponi, G.; Zoroddu, M.A. Noble metals in medicine: Latest advances. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2015, 284, 329–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adam, A.M.A.; Refat, M.S.; Mohamed, M.A. Synthesis and spectroscopic characterizations of noble metal complexes (gold, silver, platinum) in the presence of selenium, and their biological applications as antibacterial, antifungal, and anticancer. Res. Chem. Intermed. 2015, 41, 965–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, D.L.; He, H.Z.; Leung, K.H.; Chan, D.S.H.; Leung, C.H. Bioactive luminescent transition-metal complexes for biomedical applications. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 7666–7682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leung, C.H.; Zhong, H.J.; Chan, D.S.H.; Ma, D.L. Bioactive iridium and rhodium complexes as therapeutic agents. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2013, 257, 1764–1776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karpin, G.W.; Merola, J.S.; Falkinham, J.O. Transition metal-alpha-amino acid complexes with antibiotic activity against Mycobacterium spp. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2013, 57, 3434–3436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- King, K.A.; Spellane, P.J.; Watts, R.J. Excited-state properties of a triply ortho-metalated iridium(III) complex. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1985, 107, 1431–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowry, M.S.; Hudson, W.R.; Pascal, R.A.; Bernhard, S. Accelerated luminophore discovery through combinatorial synthesis. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 14129–14135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeglis, B.M.; Pierre, V.C.; Barton, J.K. Metallo-intercalators and metallo-insertors. Chem. Commun. 2007, 4565–4579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaturvedi, V.; Dwivedi, N.; Tripathi, R.P.; Sinha, S. Evaluation of Mycobacterium smegmatis as a possible surrogate screen for selecting molecules active against multi-drug resistant Mycobacterium tuberculosis. J. Gen. Appl. Microbiol. 2007, 53, 333–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, T.S.; Mao, Z.F.; Ng, C.T.; Wang, M.D.; Wang, W.H.; Wang, C.M.; Lee, S.M.Y.; Wang, Y.T.; Leung, C.H.; Ma, D.L. Identification of an iridium(III)-based inhibitor of tumor necrosis factor-alpha. J. Med. Chem. 2016, 59, 4026–4031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shao, F.W.; Elias, B.; Lu, W.; Barton, J.K. Synthesis and characterization of iridium(III) cyclometalated complexes with oligonucleotides: Insights into redox reactions with DNA. Inorg. Chem. 2007, 46, 10187–10199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ru, J.X.; Guan, L.P.; Tang, X.L.; Dou, W.; Yao, X.; Chen, W.M.; Liu, Y.M.; Zhang, G.L.; Liu, W.S.; Meng, Y.; et al. Turn-on phosphorescent chemodosimeter for Hg2+ based on a cyclometalated ir(III) complex and its application in time-resolved luminescence assays and live cell imaging. Inorg. Chem. 2014, 53, 11498–11506. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.H.; Su, T.T.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, X.L.; Li, J.; Li, C. Liposomal co-delivery of daptomycin and clarithromycin at an optimized ratio for treatment of methicillin-resistant staphylococcus aureus infection. Drug Deliv. 2015, 22, 627–637. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nyka, W. Studies on the effect of starvation on mycobacteria. Infect. Immun. 1974, 9, 843–850. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.M.; Xie, L.X.; Long, Q.X.; Mao, J.X.; Li, H.; Zhou, M.L.; Xie, J.P. Proteasome accessory factor c (pafC) is a novel gene involved in Mycobacterium intrinsic resistance to broad-spectrum antibiotics—Fluoroquinolones. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.M.; Lian, J.M.; Hu, C.H.; Deng, C. Betahistine co-treatment ameliorates dyslipidemia induced by chronic olanzapine treatment in rats through modulation of hepatic ampkα -srebp-1 and pparα-dependent pathways. Pharmacol. Res. 2015, 100, 36–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Safi, H.; Lingaraju, S.; Amin, A.; Kim, S.; Jones, M.; Holmes, M.; McNeil, M.; Peterson, S.N.; Chatterjee, D.; Fleischmann, R.; et al. Evolution of high-level ethambutol-resistant tuberculosis through interacting mutations in decaprenylphosphoryl-β-D-arabinose biosynthetic and utilization pathway genes. Nat. Genet. 2013, 45, 1190–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





| Organism and Genotype | MIC (μg/mL) |
|---|---|
| M. smegmatis | 2 |
| S. aureus (MSSA) | 16 |
| S. aureus (MRSA) | 32 |
| P. aeruginosa | >64 |
| E. coli | >64 |
| C. albicans | >64 |
| C. neoformans | >64 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liao, G.; Peng, X.; Li, T.; Ye, Z.; Xiang, X.; Fu, C. The Discovery of an Iridium(III) Dimer Complex as a Potent Antibacterial Agent against Non-Replicating Mycobacterium smegmatis. Polymers 2018, 10, 297. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10030297
Liao G, Peng X, Li T, Ye Z, Xiang X, Fu C. The Discovery of an Iridium(III) Dimer Complex as a Potent Antibacterial Agent against Non-Replicating Mycobacterium smegmatis. Polymers. 2018; 10(3):297. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10030297
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiao, Guojian, Xixi Peng, Ting Li, Zhengyuan Ye, Xiaohong Xiang, and Chen Fu. 2018. "The Discovery of an Iridium(III) Dimer Complex as a Potent Antibacterial Agent against Non-Replicating Mycobacterium smegmatis" Polymers 10, no. 3: 297. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10030297
APA StyleLiao, G., Peng, X., Li, T., Ye, Z., Xiang, X., & Fu, C. (2018). The Discovery of an Iridium(III) Dimer Complex as a Potent Antibacterial Agent against Non-Replicating Mycobacterium smegmatis. Polymers, 10(3), 297. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10030297