Agarose/Spherical Activated Carbon Composite Gels for Recyclable and Shape-Configurable Electrodes
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
3.1. Preparation of the Homogeneous Agar/SAC Mixture
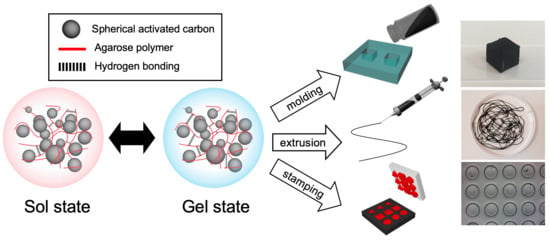
3.2. Reversible Shape Configuration of Agar/SAC Composite Gels using Various Engineering Processes
3.3. Long-Term Stability of Agar/SAC Composite Gels
3.4. Conducting Property of Agar/SAC Composite Gels
3.4.1. Effects of the Gel Composition, Recycling Process, and Mechanical Bending
3.4.2. Recovery of Conducting Properties after Mechanical Damage of Agar/SAC Composite Gels
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hecht, D.S.; Hu, L.; Irvin, G. Emerging Transparent Electrodes Based on Thin Films of Carbon Nanotubes, Graphene, and Metallic Nanostructures. Adv. Mater. 2011, 23, 1482–1513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, B.; Glavas, L.; Albertsson, A.-C. Biodegradable and electrically conducting polymers for biomedical applications. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2013, 38, 1263–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benight, S.J.; Wang, C.; Tok, J.B.H.; Bao, Z. Stretchable and self-healing polymers and devices for electronic skin. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2013, 38, 1961–1977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, C.; Lee, C.; Suh, K.-Y. Recent advances in flexible sensors for wearable and implantable devices. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2013, 130, 1429–1441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Clemente, A.; Panero, S.; Spila, E.; Scrosati, B. Solid-state, polymer-based, redox capacitors. Solid State Ionics 1996, 85, 273–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, K.S.; Kim, K.M.; Park, N.G.; Park, Y.J.; Chang, S.H. Symmetric redox supercapacitor with conducting polyaniline electrodes. J. Power Sources 2002, 103, 305–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laforgue, A.; Simon, P.; Sarrazin, C.; Fauvarque, J.F. Polythiophene-based supercapacitors. J. Power Sources 1999, 80, 142–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, I.-H.; Kim, K.-B. Electrochemical Characterization of Hydrous Ruthenium Oxide Thin-Film Electrodes for Electrochemical Capacitor Applications. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2006, 153, A383–A389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toupin, M.; Brousse, T.; Bélanger, D. Influence of Microstucture on the Charge Storage Properties of Chemically Synthesized Manganese Dioxide. Chem. Mater. 2002, 14, 3946–3952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Zhang, J.; Pan, L.; Shi, Y.; Yu, G. Energy gels: A bio-inspired material platform for advanced energy applications. Nano Today 2016, 11, 738–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koo, H.-J.; Kim, S.-K.; Braun, P.V. Facile fabrication of graphene composite microwires via drying-induced size reduction of hydrogel filaments. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 20927–20931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.-K.; Koo, H.-J.; Liu, J.; Braun, P.V. Flexible and Wearable Fiber Microsupercapacitors Based on Carbon Nanotube–Agarose Gel Composite Electrodes. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 9, 19925–19933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roy, S.; David-Pur, M.; Hanein, Y. Carbon Nanotube-Based Ion Selective Sensors for Wearable Applications. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 35169–35177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hur, J.; Im, K.; Kim, S.W.; Kim, J.; Chung, D.-Y.; Kim, T.-H.; Jo, K.H.; Hahn, J.H.; Bao, Z.; Hwang, S.; Park, N. Polypyrrole/Agarose-Based Electronically Conductive and Reversibly Restorable Hydrogel. ACS Nano 2014, 8, 10066–10076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, M.; Lee, S.; Yoon, I.; Kook, G.; Jung, Y.; Bawazir, S.; Stefanini, C.; Lee, H. Polypyrrole/Agarose Hydrogel-Based Bladder Volume Sensor with a Resistor Ladder Structure. Sensors 2018, 18, 2288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekine, S.; Ido, Y.; Miyake, T.; Nagamine, K.; Nishizawa, M. Conducting Polymer Electrodes Printed on Hydrogel. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 13174–13175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaghela, C.; Kulkarni, M.; Karve, M.; Aiyer, R.; Haram, S. Agarose–guar gum assisted synthesis of processable polyaniline composite: Morphology and electro-responsive characteristics. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 59716–59725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarrintaj, P.; Rezaeian, I.; Bakhshandeh, B.; Heshmatian, B.; Ganjali, M.R. Bio-Conductive Scaffold Based on Agarose-Polyaniline for Tissue Engineering. J. Skin Stem Cell 2017, 4, e67394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, W.G.; Kim, G.-P.; Lee, M.; Song, H.D.; Yi, J. A Biodegradable Gel Electrolyte for Use in High-Performance Flexible Supercapacitors. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 3503–3511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhim, J.W.; Wang, L.F.; Hong, S.I. Preparation and characterization of agar/silver nanoparticles composite films with antimicrobial activity. Food Hydrocolloids 2013, 33, 327–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raphael, E.; Avellaneda, C.O.; Manzolli, B.; Pawlicka, A. Agar-based films for application as polymer electrolytes. Electrochim. Acta 2010, 55, 1455–1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tako, M.; Nakamura, S. Gelation mechanism of agarose. Carbohydr. Res. 1988, 180, 277–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, F.; Chen, D. Aligned carbon nanostructures based 3D electrodes for energy storage. J. Energy Chem. 2015, 24, 559–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, M.; Qiu, W.; Wang, F.; Zhai, T.; Fang, P.; Lu, X.; Tong, Y. Three dimensional architectures: Design, assembly and application in electrochemical capacitors. J. Mater. Chem. A 2015, 3, 15792–15823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.H.; Park, O.O.; Shin, K.H.; Jin, C.S.; Kim, J.H. An electrochemical capacitor based on a Ni(OH)2/activated carbon composite electrode. Electrochem. Solid-State Lett. 2002, 5, H7–H10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabzi, M.; Samadi, N.; Abbasi, F.; Mahdavinia, G.R.; Babaahmadi, M. Bioinspired fully physically cross-linked double network hydrogels with a robust, tough and self-healing structure. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2017, 74, 374–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.-Y.; Zhao, X.; Illeperuma, W.R.K.; Chaudhuri, O.; Oh, K.H.; Mooney, D.J.; Vlassak, J.J.; Suo, Z. Highly stretchable and tough hydrogels. Nature 2012, 489, 133–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]





| Sample | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Agar10 | - | 9.36% | - |
| Agar10/SAC5 | 8.83% | 10.2% | 6.17% |
| Agar10/SAC10 | 8.41% | 10.7% | 9.27% |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, J.S.; Kim, J.-H.; Cho, Y.; Shim, T.S. Agarose/Spherical Activated Carbon Composite Gels for Recyclable and Shape-Configurable Electrodes. Polymers 2019, 11, 875. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11050875
Kim JS, Kim J-H, Cho Y, Shim TS. Agarose/Spherical Activated Carbon Composite Gels for Recyclable and Shape-Configurable Electrodes. Polymers. 2019; 11(5):875. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11050875
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Jong Sik, Ju-Hyung Kim, Younghyun Cho, and Tae Soup Shim. 2019. "Agarose/Spherical Activated Carbon Composite Gels for Recyclable and Shape-Configurable Electrodes" Polymers 11, no. 5: 875. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11050875
APA StyleKim, J. S., Kim, J. -H., Cho, Y., & Shim, T. S. (2019). Agarose/Spherical Activated Carbon Composite Gels for Recyclable and Shape-Configurable Electrodes. Polymers, 11(5), 875. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11050875