Synthesis and Characterization of Silicone Contact Lenses Based on TRIS-DMA-NVP-HEMA Hydrogels
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
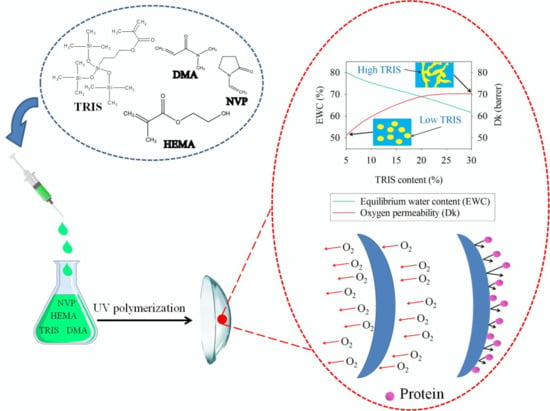
2.2. Preparation of Silicone Hydrogels
2.3. Equilibrium Water Content
2.4. Oxygen Permeability
2.5. Optical Transparency
2.6. Contact Angle [14]
2.7. Mechanical Properties
2.8. Protein Deposition [15]
2.9. Cytotoxicity [14]
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Equilibrium Water Content
3.2. Oxygen Permeability
3.3. Optical Transparency
3.4. Contact Angle
3.5. Mechanical Properties
3.6. Protein Adsorption
3.7. Cytotoxicity
3.8. Comaprison with Commercial Lenses
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhao, Z.; Xie, H.; An, S.; Jiang, Y. The relationship between oxygen permeability and phase separation morphology of the multicomponent silicone hydrogels. J. Phys. Chem. B 2014, 118, 14640–14647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fonn, D.; Dumbleton, K.; Jalbert, I.; Sivak, A. Benefits of silicone hydrogel lenses. Contact Lens Spectr. 2006, 21, 38. [Google Scholar]
- Awasthi, A.K.; Meng, F.R.; Künzler, J.F.; Linhardt, J.G.; Papagelis, P.; Oltean, G.; Myers, S.A. Ethylenically unsaturated polycarbosiloxanes for novel silicone hydrogels: Synthesis, end-group analysis, contact lens formulations, and structure–property correlations. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2013, 24, 557–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.J.; Liu, F. Simultaneous interpenetrating network silicone hydrogels prepared by free radical/cationic hybrid polymerization. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2013, 127, 2235–2242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, Y.C. Novel polyurethane–silicone hydrogels. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1995, 56, 301–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chekina, N.A.; Pavlyuchenko, V.N.; Danilichev, V.F.; Ushakov, N.A.; Novikov, S.A.; Ivanchev, S.S. A new polymeric silicone hydrogel for medical applications: Synthesis and properties. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2006, 17, 872–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tighe, B.J. A decade of silicone hydrogel development: Surface properties, mechanical properties, and ocular compatibility. Eye Contact Lens 2013, 39, 4–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Beek, M.; Weeks, A.; Jones, L.; Sheardown, H. Immobilized hyaluronic acid containing model silicone hydrogels reduce protein adsorption. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 2008, 19, 1425–1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.H.; Yeh, Y.H.; Lin, W.C.; Yang, M.C. Novel silicone hydrogel based on PDMS and PEGMA for contact lens application. Colloid. Surf. B Biointerfaces 2014, 123, 986–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, L.; Senchyna, M.; Glasier, M.A.; Schickler, J.; Forbes, I.; Louie, D.; May, C. Lysozyme and lipid deposition on silicone hydrogel contact lens materials. Eye Contact Lens 2003, 29, S75–S79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maldonado-Codina, C.; Efron, N. Hydrogel lenses-material and manufacture: A review. Optom. Pract. 2003, 4, 101–115. [Google Scholar]
- Parambil, A.M.; Puttaiahgowda, Y.M.; Shankarappa, P. Copolymerization of N-Vinyl pyrrolidone with methyl methacrylate by Ti (III)-DMG redox initiator. Turk. J. Chem. 2012, 36, 397–409. [Google Scholar]
- Luensmann, D.; Jones, L. Albumin adsorption to contact lens materials: A review. Cont. Lens Ant. Eye 2008, 31, 179–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbasi, F.; Mirzadeh, H.; Simjoo, M. Hydrophilic interpenetrating polymer networks of poly (dimethyl siloxane)(PDMS) as biomaterial for cochlear implants. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 2006, 17, 341–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishihara, K.; Fukumoto, K.; Iwasaki, Y.; Nakabayashi, N. Modification of polysulfone with phospholipid polymer for improvement of the blood compatibility. Part 1. Surface characterization. Biomaterials 1999, 20, 1545–1551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacob, J.T. Biocompatibility in the development of silicone-hydrogel lenses. Eye Contact Lens 2013, 39, 13–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, Y.C.; Valint, J.; Paul, L. Control of properties in silicone hydrogels by using a pair of hydrophilic monomers. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1996, 61, 2051–2058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Tan, G.; Zhang, S.; Guang, Y. Influence of water states in hydrogels on the transmissibility and permeability of oxygen in contact lens materials. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2008, 255, 604–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, D.; Zhou, J. Effect of water content on microstructures and oxygen permeation in PSiMA–IPN–PMPC hydrogel: A molecular simulation study. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2012, 78, 236–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pozuelo, J.; Compañ, V.; González-Méijome, J.M.; González, M.; Mollá, S. Oxygen and ionic transport in hydrogel and silicone-hydrogel contact lens materials: An experimental and theoretical study. J. Membr. Sci. 2014, 452, 62–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tranoudis, I.; Efron, N. Water properties of soft contact lens materials. Cont. Lens Ant. Eye 2004, 27, 193–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, M.; Shin, Y.H.; Kwon, Y. Synthesis and properties of siloxane-containing hybrid hydrogels: Optical transmittance, oxygen permeability and equilibrium water content. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2010, 10, 6934–6938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korogiannaki, M.; Guidi, G.; Jones, L.; Sheardown, H. Timolol maleate release from hyaluronic acid-containing model silicone hydrogel contact lens materials. J. Biomater. Appl. 2015, 30, 361–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Read, M.L.; Morgan, P.B.; Maldonado-Codina, C. Measurement errors related to contact angle analysis of hydrogel and silicone hydrogel contact lenses. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B Appl. Biomater. 2009, 91, 662–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maldonado-Codina, C.; Morgan, P.B.; Efron, N.; Canry, J.C. Characterization of the surface of conventional hydrogel and silicone hydrogel contact lenses by time-of-flight secondary ion mass spectrometry. Optom. Vis. Sci. 2004, 81, 455–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- French, K. Contact lens material properties part 1: Wettability. Optician 2005, 230, 20–28. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Z.B.; An, S.S.; Xie, H.J.; Han, X.L.; Wang, F.H.; Jiang, Y. The Relationship between the Hydrophilicity and Surface Chemical Composition Microphase Separation Structure of Multicomponent Silicone Hydrogels. J. Phys. Chem. B 2015, 119, 9780–9786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tranoudis, I.; Efron, N. Tensile properties of soft contact lens materials. Cont. Lens Anterior Eye 2004, 27, 177–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.J.; Li, X.S. Preparation and characterization of interpenetrating polymer network silicone hydrogels with high oxygen permeability. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2010, 116, 2749–2757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.B.; An, S.S.; Xie, H.J.; Jiang, Y. Copolymerization and properties of multicomponent crosslinked hydrogels. Chin. J. Polym. Sci. 2015, 33, 173–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green-Church, K.B.; Nichols, K.K.; Kleinholz, N.M.; Zhang, L.; Nichols, J.J. Investigation of the human tear film proteome using multiple proteomic approaches. Mol. Vis. 2008, 14, 456–470. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Silva, D.; Fernandes, A.; Nunes, T.; Colaço, R.; Serro, A. The effect of albumin and cholesterol on the biotribological behavior of hydrogels for contact lenses. Acta. Biomater. 2015, 26, 184–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moradi, O.; Modarress, H.; Noroozi, M. Experimental study of albumin and lysozyme adsorption onto acrylic acid (AA) and 2-hydroxyethyl methacrylate (HEMA) surfaces. J. Colloid. Interface Sci. 2004, 271, 16–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demirel, G.; Özçetin, G.; Turan, E.; Çaykara, T. pH/Temperature–Sensitive Imprinted Ionic Poly (N-tert-butylacrylamide-co-acrylamide/maleic acid) Hydrogels for Bovine Serum Albumin. Macromol. Biosci. 2005, 5, 1032–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.; Somorjai, G.A. Molecular packing of lysozyme, fibrinogen, and bovine serum albumin on hydrophilic and hydrophobic surfaces studied by infrared− visible sum frequency generation and fluorescence microscopy. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2003, 125, 3150–3158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paterson, S.M.; Liu, L.; Brook, M.A.; Sheardown, H. Poly (ethylene glycol)-or silicone-modified hyaluronan for contact lens wetting agent applications. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 2015, 103, 2602–2610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luensmann, D.; Jones, L. Protein deposition on contact lenses: The past, the present, and the future. Cont. Lens Ant. Eye 2012, 35, 53–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garrett, Q.; Laycock, B.; Garrett, R.W. Hydrogel lens monomer constituents modulate protein sorption. Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2000, 41, 1687–1695. [Google Scholar]
- Subbaraman, L.N.; Glasier, M.A.; Senchyna, M.; Sheardown, H.; Jones, L. Kinetics of in vitro lysozyme deposition on silicone hydrogel, PMMA, and FDA groups I, II, and IV contact lens materials. Curr. Eye Res. 2006, 31, 787–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Sample | Feed (wt %) | EWC (%) | Dk (barrer) | Contact Angle (°) | Modulus (MPa) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TRIS | DMA | NVP | HEMA | |||||
| TDN1 | 5 | 47.5 | 47.5 | 0 | 83.6 ± 0.4 | 58.0 | 61.4 ± 0.7 | 0.56 ± 0.20 |
| TDN2 | 10 | 45 | 45 | 0 | 75.3 ± 1.5 | 59.8 | 67.7 ± 0.2 | 0.65 ± 0.12 |
| TDN3 | 20 | 40 | 40 | 0 | 69.0 ± 0.7 | 69.0 | 70.3 ± 0.4 | 0.70 ± 0.21 |
| TDN4 | 30 | 35 | 35 | 0 | 61.7 ± 1.8 | 70.4 | 72.1 ± 0.3 | 0.84 ± 0.15 |
| TDNH1 | 20 | 24 | 48 | 8 | 60.6 ± 0.7 | 70.6 | 73.8 ± 0.2 | 0.87 ± 0.10 |
| TDNH2 | 20 | 40 | 24 | 16 | 58.1 ± 0.3 | 72.3 | 74.8 ± 0.2 | 0.94 ± 0.29 |
| TDNH3 | 30 | 21 | 42 | 7 | 55.9 ± 0.1 | 71.4 | 75.4 ± 0.3 | 1.13 ± 0.18 |
| TDNH4 | 30 | 35 | 21 | 14 | 54.8 ± 0.9 | 72.6 | 76.3 ± 0.3 | 1.09 ± 0.18 |
| TDNH5 | 40 | 18 | 36 | 6 | 49.5 ± 1.0 | 72.5 | 78.0 ± 0.7 | 1.19 ± 0.39 |
| TDNH6 | 40 | 30 | 18 | 12 | 44.5 ± 1.1 | 74.9 | 81.9 ± 0.3 | 1.29 ± 0.19 |
| Product | Manufacturer | Dk (barrers) | EWC (%) | Contact Angle (°) | Modulus (MPa) | Principle Monomers |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Biomedics 38 | CooperVision | 8.4 | 38 | 30 | 0.81 | HEMA, EGDMA |
| Acuvue 2 | Johnson & Johnson Vision Care | 19 | 58 | HEMA, MAA, EGDMA | ||
| Biomedics XC | CooperVision | 44 | 60 | HEMA, MAA, PC, TEGDMA | ||
| Acuvue Advance | Johnson & Johnson | 60 | 47 | 65.6 | 0.43 | MPDMS, DMA, HEMA, EGDMA, siloxane macromer, PVP |
| PureVision | Bausch & Lomb | 91 | 36 | 93.6 | 1.10 | TEGDMA, NVP, TPVC, NCVE, PBVC |
| Acuvue Oasys | Johnson & Johnson | 103 | 38 | 78.7 | 0.72 | MPDMS, DMA, HEMA, siloxane macromer, TEGDMA, PVP |
| Air Optix | CIBA Vision | 110 | 33 | 44.4 | 1.00 | DMA, TRIS, siloxane monomer |
| Air Optix Night & Day | CIBA Vision | 140 | 24 | 1.52 | DMA, TRIS, siloxane monomer | |
| TDN3 | This work | 69.0 | 69.0 | 70.3 | 0.70 | TRIS, DMA, NVP |
| TDN4 | 70.4 | 61.7 | 72.1 | 0.84 | ||
| TDNH4 | 72.6 | 54.8 | 76.3 | 1.09 | TRIS, DMA, NVP, HEMA | |
| TDNH6 | 74.9 | 44.5 | 81.9 | 1.29 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tran, N.-P.-D.; Yang, M.-C. Synthesis and Characterization of Silicone Contact Lenses Based on TRIS-DMA-NVP-HEMA Hydrogels. Polymers 2019, 11, 944. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11060944
Tran N-P-D, Yang M-C. Synthesis and Characterization of Silicone Contact Lenses Based on TRIS-DMA-NVP-HEMA Hydrogels. Polymers. 2019; 11(6):944. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11060944
Chicago/Turabian StyleTran, Nguyen-Phuong-Dung, and Ming-Chien Yang. 2019. "Synthesis and Characterization of Silicone Contact Lenses Based on TRIS-DMA-NVP-HEMA Hydrogels" Polymers 11, no. 6: 944. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11060944
APA StyleTran, N.-P.-D., & Yang, M.-C. (2019). Synthesis and Characterization of Silicone Contact Lenses Based on TRIS-DMA-NVP-HEMA Hydrogels. Polymers, 11(6), 944. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11060944