TiO2-Doped Chitosan Microspheres Supported on Cellulose Acetate Fibers for Adsorption and Photocatalytic Degradation of Methyl Orange
Abstract
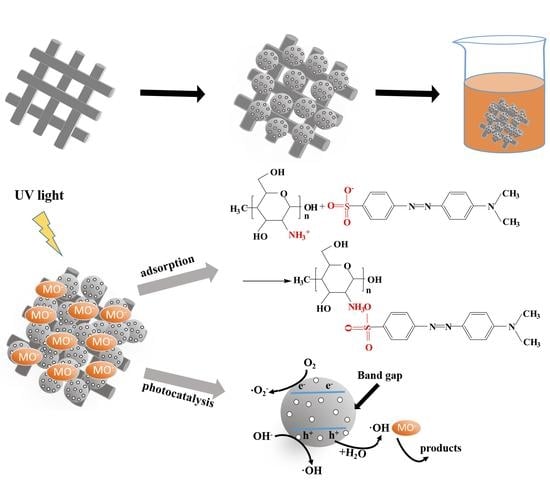
:1. Introduction
2. Experiment
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of Polymer Solutions
2.3. Fabrication of C-T/CA Fiber Membranes
2.4. Characterizations
2.5. Investigations on MO Adsorption and Photocatalysis Study
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Morphology Observation
3.2. XRD Characterization
3.3. MO Removal Analysis
3.3.1. Effect of TiO2 Content on MO Removal
3.3.2. Effect of pH Values on the MO Removal
3.3.3. Effect of Initial MO Concentration on the MO Removal
3.3.4. Effect of Contact Time and Kinetic Study
3.3.5. Isotherm Study
3.4. Removal Mechanism Analysis
3.4.1. FTIR Spectra Results
3.4.2. XPS Spectra Results
3.4.3. BET Analysis
3.4.4. Mechanism Analysis
3.5. Recycling Ability
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cantarellaa, M.; Sanza, R.; Buccheria, M.A.; Ruffinoa, F.; Rappazzoc, G.; Scalesed, S.; Impellizzeria, G.; Romanoa, L.; Privitera, V. Immobilization of nanomaterials in PMMA composites for photocatalytic removal of dyes, phenols and bacteria from water. J. Photochem. Photobiol. Chem. A 2016, 321, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.F.; Park, M.; Kim, H.Y.; Newehy, M.E.; Rhee, K.Y.; Park, S.J. Effect of TiO2 on photocatalytic activity of polyvinylpyrrolidone fabricated via electrospinning. Compos. Part B Eng. 2015, 80, 355–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pahasupanan, T.; Suwannahong, K.; Dechapanya, W.; Rangkupan, R. Fabrication and photocatalytic activity of TiO2 composite membranes via simultaneous electrospinning and electrospraying process. J. Environ. Sci. 2018, 72, 13–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doh, S.J.; Kim, C.; Lee, S.G.; Lee, S.J.; Kim, H. Development of photocatalytic TiO2 fibers by electrospinning and its application to degradation of dye pollutants. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 154, 118–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Odling, G.; Robertson, N. SILAR BiOI–Sensitized TiO2 Films for Visible–Light Photocatalytic Degradation of Rhodamine B and 4–Chlorophenol. Chem. Phys. Chem. 2017, 18, 728–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramos, P.G.; Flores, E.; Sánchez, L.A.; Candal, R.J.; Hojamberdiev, M.; Estrada, W.; Rodriguez, J. Enhanced photoelectrochemical performance and photocatalytic activity of ZnO/TiO2 nanostructures fabricated by an electrostatically modified electrospinning. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2017, 426, 844–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, P.F.; Song, L.X.; Xiong, J.; Cao, H.B. Photocatalytic degradation of Rhodamine B using electrospun TiO2 and ZnO fibers: A comparative study. J. Mater. Sci. 2013, 48, 8386–8392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; Wang, X.Q.; Yan, J.H.; Yu, J.Y.; Sun, G.; Ding, B. Soft Zr–doped TiO2 Nanofbrous Membranes with Enhanced Photocatalytic Activity for Water Purifcation. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Hou, X.B.; Pang, Z.Y.; Cai, Y.B.; Zhou, H.M.; Lv, P.F.; Wei, Q.F. Fabrication of hierarchical TiO2 fibers by microemulsion electrospinning for photocatalysis applications. Ceram. Int. 2017, 43, 15911–15917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meichtry, J.M.; Levy, I.K.; Mohamed, H.H.; Dillert, R.; Bahnemann, D.W.; Litter, M.I. Mechanistic Features of TiO2–Heterogeneous Photocatalysis of Arsenic and Uranyl Nitrate in Aqueous Suspensions Studied by the Stopped Flow Technique. Chem. Phys. Chem. 2016, 17, 885–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, R.; Wang, Y.; Li, X.; Sun, B.L.; Wang, C. Synthesisof β–Cyclodextrin–Based Electrospun Nanofiber Membranesfor Highly Efficient Adsorption and Separation of Methylene Blue. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 26649–26657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, R.M.; Shi, Y.Z.; Yang, D.Z.; Liu, Y.X.; Qu, J.; Yu, Z.Z. Graphene oxide/chitosan aerogel microspheres with honeycomb–cobweb and radially oriented microchannel structures for broad–spectrum and rapid adsorption of water contaminants. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 21809–21819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, L.J.; Zhang, H.M.; Cao, J. Electrospinning of Ag/ZnWO4/WO3 composite fibers with high visible light photocatalytic activity. Mater. Lett. 2019, 236, 171–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.H.; Shao, C.L.; Wang, L.J.; Zhang, L.N.; Li, X.H.; Liu, Y.C. Electrospinning preparation, characterization and photocatalytic properties of Bi2O3 fibers. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2009, 333, 242–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, J.H.; Liu, K.L.; Fan, W.Q.; Li, M.; Liu, Y.; Mao, B.D.; Bai, H.Y.; Shen, H.Q.; Yuan, S.L.; Shi, W.D. Electrospinning synthesis and photocatalytic property of Fe2O3/MgFe2O4 heterostructure for photocatalytic degradation of tetracycline. Mater. Lett. 2016, 176, 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Mantilaka, M.P.; De Silva, R.T.; Ratnayake, S.P.; Amaratunga, G.; de Silva, K.N. Photocatalytic activity of electrospun MgO nanofibres: Synthesis, characterization and applications. Mater. Res. Bull. 2018, 99, 204–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Yang, G.R.; Peng, S.J.; Wang, J.N.; Ji, D.X.; Yan, W.; Ramakrishna, S. Fabrication of MgTiO3 fibers by electrospinning and their photocatalytic water splitting activity. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2017, 42, 25882–25890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhao, H.; Yang, M. TiO2 nanoparticles supported on PMMA fibers for photocatalytic degradation of methyl orange. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2017, 508, 500–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, C.D.; Sun, J.X.; Chen, G.; Zhou, Y.S.; Li, D.Y.; Wang, Z.K.; Zhao, B.R. Organic salt induced electrospinning gradient effect: Achievement of BiVO4 nanotubes with promoted photocatalytic performance. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2017, 208, 14–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, M.T.; Tu, H.; Chen, J.J.; Liu, R.; Liang, Z.Y.; Jiang, L.B.; Shi, X.W.; Du, Y.M.; Deng, H.B. Chitosan–rectorite microspheres embedded aminated polyacrylonitrile fibers via shoulder–to–shoulder electrospinning and electrospraying for enhanced heavy metal removal. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 437, 294–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haider, S.; Park, S.Y. Preparation of the electrospun chitosan nanofibers and their applications to the adsorption of Cu (II) and Pb (II) ions from an aqueous solution. J. Membrane Sci. 2009, 328, 90–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, S.J.; Zeng, Z.Y.; Zhou, X.; Luo, W.J.; Shi, X.W.; Wang, Q.; Deng, H.B.; Du, Y.M. Recyclable Saccharomyces cerevisiae loaded nanofibrous mats with sandwich structure constructing via bio–electrospraying for heavy metal removal. J. Hazard. Mater. 2017, 324, 365–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.G.; Javed, H.; Zhang, D.N.; Kim, J.H.; Westerhoff, P.; Li, Q.L.; Alvarez, P.J.J. Porous electrospun fibers embedding TiO2 for adsorption and photocatalytic degradation of water pollutants. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 4285–4293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, R.; Tomer, V.K.; Joshi, N.; Dankwort, T.; Lin, L.W.; Kienle, L. Au−TiO2−Loaded Cubic g−C3N4 Nanohybrids for Photocatalytic and Volatile Organic Amine Sensing Applications. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 34087–34097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez, P.A.; Bercero, M.Á.L.; Barrientos, L.; Valenzuela, M.L.; Díaz, C. Solid State Tuning of TiO2 Morphology, Crystal Phase and Size through Metal Macromolecular Complexes and its significance in the Photocatalytic Response. ACS Appl. Energy Mater. 2018, 1, 3159–3170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasr, M.; Balme, S.; Eid, C.; Habchi, R.; Miele, P.; Bechelany, M. Enhanced Visible–Light Photocatalytic Performance of Electrospun GO/TiO2 Composite Fibers. J. Phys. Chem. C 2017, 121, 261–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, L.; Chen, W.F.; Koshy, P.; Sorrell, C.C. Effect of Ce–doping on the photocatalytic performance of TiO2 thin films. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2017, 197, 236–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seong, D.B.; Son, Y.R.; Park, S.J. A study of reduced graphene oxide/leaf–shaped TiO2, fibers for enhanced photocatalytic performance via electrospinning. J. Solid State Chem. 2018, 266, 196–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Cai, Y.B.; Hou, X.B.; Zhou, H.M.; Qiao, H.; Wei, Q.F. Preparation of TiO2 Nanofibrous Membranes with Hierarchical Porosity for Efficient Photocatalytic Degradation. J. Phys. Chem. C 2018, 122, 8946–8953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, L.G.; Taxipalati, M.; Zhang, A.; Que, F.; Wei, H.W.; Feng, F.Q.; Zhang, H. Electrospun chitosan/polyethylene oxide/lauric arginate nanofibrous film with enhanced antimicrobial activity. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 6219–6226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, T.; Yang, H.Y.; Yang, D.Z.; Yu, Z.Z. Polylactic Acid Nanofiber Scaffold Decorated with Chitosan Islandlike Topography for Bone Tissue Engineering. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 21094–21104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Wen, W.; Chen, S.T.; Zhou, C.G.; Luo, B.H. Preparation of Icariin and Deferoxamine Functionalized Poly(L–lactide)/chitosan Micro/Nanofibrous Membranes with Synergistic Enhanced Osteogenesis and Angiogenesis. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2018, 1, 389–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Severyukhina, A.N.; Parakhonskiy, B.V.; Prikhozhdenko, E.S.; Gorin, D.A.; Sukhorukov, G.B.; Möhwald, H.; Nanoplasmonic, A.M.Y. Chitosan Fibers as Effective SERS Substrate for Detection of Small Molecules. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 15466–15473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, L.D.; He, X.W.; Lei, X.F.; Qiao, M.T.; Gu, J.W.; Zhang, Q.Y. An efficient and green fabrication of porous magnetic chitosan particles based on high adhesive superhydrophobic polyimide fiber mat. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 12194–12924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.Y.; Li, T.T.; An, L.B.; Fu, P.F.; Gao, C.J.; Zhang, Z.M. Highly efficient chromium (VI) adsorption with nanofibrous filter paper prepared through electrospinning chitosan/polymethylmethacrylate composite. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 137, 119–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Li, Y.X.; Cao, L.X.; Yang, C.F. Enhanced chromium (VI) adsorption using nanosized chitosan fibers tailored by electrospinning. Carbohydr. Polym. 2015, 125, 206–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.Y.; Lou, T.; Yan, X.; Long, Y.Z.; Cui, G.P.; Wang, X.J. Fabrication of pure chitosan nanofibrous membranes as effective. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 106, 768–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, P.; Xia, D.; Kazlauciunas, A.; Thornton, P.; Lin, L.; Menzel, R. Dye–Mediated Interactions in Chitosan–Based Polyelectrolyte/Organoclay Hybrids for Enhanced Adsorption of Industrial Dyes. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 11961–11969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez, K.; Renneckar, S.; Gatenholm, P. Biomimetic Calcium Phosphate Crystal Mineralization on Electrospun Cellulose–Based Scaffolds. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2011, 3, 681–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arslan, O.; Aytac, Z.; Uyar, T. Superhydrophobic, Hybrid, Electrospun Cellulose Acetate Nanofibrous Mats for Oil/Water Separation by Tailored Surface Modification. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 19747–19754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; He, D.; Wang, G.S.; Yu, S.H. Bioinspired Crystallization of CaCO3 Coatings on Electrospun Cellulose Acetate Fiber Scaffolds and Corresponding CaCO3 Microtube Networks. Langmuir 2011, 27, 7199–7206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Sun, M.; Liu, Y.; Liu, H.J.; Qu, J.H.; Li, J.H. Ionic Liquid Assisted Electrospun Cellulose Acetate Fibers for Aqueous Removal of Triclosan. Langmuir 2015, 31, 1820–1827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.H.; Yang, H.; Hou, J.Z.; Zhang, W.X.; Xiang, C.H.; Li, L.L. Effect of the electrical conductivity of core solutions on the morphology and structure of core–shell CA–PCL/CS fibers. New J. Chem. 2017, 41, 15072–15078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salihu, G.; Goswami, P. Hybrid electrospun nonwovens from chitosan/cellulose acetate. Cellulose 2012, 19, 739–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, L.C.; Li, H.; Meng, Y.H. Layer–by–layer structured polysaccharides–based multilayers on cellulose acetate membrane: Towards better hemocompatibility, antibacterial and antioxidant activities. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2017, 401, 25–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razzaz, A.; Ghorban, S.; Hosayni, L.; Irani, M.; Aliabadi, M. Chitosan nanofibers functionalized by TiO2 nanoparticles for the removal of heavy metal ions. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2016, 58, 333–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yousefi, B.; Charehaghaji, A.A.; Jeddi, A.A.A.; Karimi, M. The Combined Effect of Wrinkles and Noncircular Shape of Fibers on Wetting Behavior of Electrospun Cellulose Acetate Membranes. J. Polym. Sci. B 2018, 56, 1012–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gebru, K.A.; Das, C. Removal of Pb (II) and Cu (II) ions from wastewater using composite electrospun cellulose acetate/titanium oxide (TiO2) adsorbent. J. Water Process Eng. 2017, 16, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranjbari, S.; Tanhaei, B.; Ayati, A.; Sillanp, M. Novel Aliquat–336 impregnated chitosan beads for the adsorptive removal of anionic azo dyes. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 125, 989–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.P.; Wang, L.H.; Dong, S.J.; Zhang, G.H.; Shi, X.J.; Xiang, C.H.; Li, L.L. Adsorption of hexavalent chromium by chitosan/poly(ethylene oxide)/permutit electrospun fibers. New J. Chem. 2018, 42, 17740–17749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahimi, K.; Mirzaei, R.; Akbari, A.; Mirghaffari, N. Preparation of nanoparticle–modified polymeric adsorbent using wastage fuzzes of mechanized carpet and its application in dye removal from aqueous solution. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 178, 373–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]














| TiO2 Content | 0% | 1% | 2% | 3% | 4% | 5% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Viscosity (mPa s) | 140.7 | 158.8 | 172.5 | 183.6 | 209.5 | 220.4 |
| Conductivity (μS cm−1) | 219.0 | 230.7 | 243.8 | 256.1 | 265.0 | 273.4 |
| Sample | qe, exp (mg/g) | Pseudo-First-Order Model | Pseudo-Second-Order Model | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| k1 | R2 | qe, cal (mg/g) | k2 | R2 | qe, cal (mg/g) | ||
| CS/CA | 19.24 | 5.44 × 10−2 | 0.9748 | 15.08 | 13.48 × 10−2 | 0.9799 | 20.80 |
| C-T-3/CA | 39.20 | 9.86 × 10−2 | 0.9878 | 30.61 | 32.33 × 10−2 | 0.9952 | 40.67 |
| Sample | Langmuir Model | Freundlich Model | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| KL | qm (mg/g) | R2 | KF | n | R2 | |
| CS/CA | 7.28 × 10−2 | 30.01 | 0.9714 | 2.30 | 1.41 | 0.9932 |
| C-T-3/CA | 62.5 × 10−2 | 76.22 | 0.9948 | 25.33 | 1.90 | 0.9997 |
| Sample | Specific Surface Area (m2/g) | Pore Volume (cc/g) | Average Pore Diameter (nm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| CS/CA | 301.30 | 0.33 | 4.39 |
| C-T-3/CA | 342.10 | 0.48 | 4.79 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shi, X.; Zhang, X.; Ma, L.; Xiang, C.; Li, L. TiO2-Doped Chitosan Microspheres Supported on Cellulose Acetate Fibers for Adsorption and Photocatalytic Degradation of Methyl Orange. Polymers 2019, 11, 1293. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11081293
Shi X, Zhang X, Ma L, Xiang C, Li L. TiO2-Doped Chitosan Microspheres Supported on Cellulose Acetate Fibers for Adsorption and Photocatalytic Degradation of Methyl Orange. Polymers. 2019; 11(8):1293. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11081293
Chicago/Turabian StyleShi, Xuejuan, Xiaoxiao Zhang, Liang Ma, Chunhui Xiang, and Lili Li. 2019. "TiO2-Doped Chitosan Microspheres Supported on Cellulose Acetate Fibers for Adsorption and Photocatalytic Degradation of Methyl Orange" Polymers 11, no. 8: 1293. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11081293
APA StyleShi, X., Zhang, X., Ma, L., Xiang, C., & Li, L. (2019). TiO2-Doped Chitosan Microspheres Supported on Cellulose Acetate Fibers for Adsorption and Photocatalytic Degradation of Methyl Orange. Polymers, 11(8), 1293. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11081293