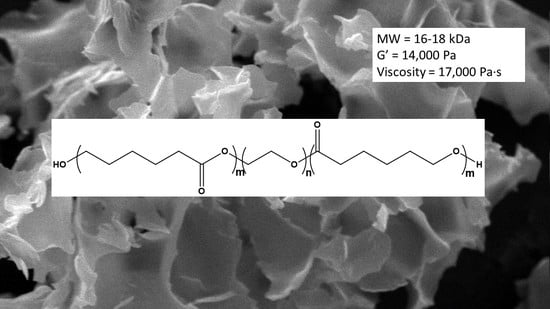
Effect of Molecular Weight on Gelling and Viscoelastic Properties of Poly(caprolactone)–b-Poly(ethylene glycol)–b-Poly(caprolactone) (PCL–PEG–PCL) Hydrogels
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. General Methods
2.3. Synthesis
2.4. Gel Studies
2.5. Rheological Studies
3. Results
3.1. Synthesis
3.2. Characterization
3.3. Molecular Weight Determination
3.4. Gelling Properties
3.5. Rheology Studies
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Srivastava, A.; Yadav, T.; Sharma, S.; Nayak, A.; Kumari, A.A.; Mishra, N. Polymers in drug delivery. J. Biosci. Med. 2015, 4, 69–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zada, M.H.; Kumar, A.; Elmalak, O.; Markovitz, E.; Icekson, R.; Machlev, E.; Mechrez, G.; Domb, A.J. Biodegradable implantable balloons: Mechanical stability under physiological conditions. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2019, 100, 103404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teo, A.J.; Mishra, A.; Park, I.; Kim, Y.-J.; Park, W.-T.; Yoon, Y.-J. Polymeric biomaterials for medical implants and devices. Acs Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2016, 2, 454–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doppalapudi, S.; Katiyar, S.; Domb, A.J.; Khan, W. Biodegradable Natural Polymers. In Advanced Polymers in Medicine; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015; pp. 33–66. [Google Scholar]
- Doppalapudi, S.; Jain, A.; Khan, W.; Domb, A.J. Biodegradable polymers—An overview. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2014, 25, 427–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- George, A.; Sanjay, M.; Sriusk, R.; Parameswaranpillai, J.; Siengchin, S. A comprehensive review on chemical properties and applications of biopolymers and their composites. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 154, 329–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghasemiyeh, P.; Mohammadi-Samani, S. Hydrogels as Drug Delivery Systems; Pros and Cons. Trends Pharm. Sci. 2019, 5, 7–24. [Google Scholar]
- Bray, D.; Hopkins, C.; Roberts, D.N. A review of dermal fillers in facial plastic surgery. Curr. Opin. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2010, 18, 295–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mathew, A.P.; Uthaman, S.; Cho, K.-H.; Cho, C.-S.; Park, I.-K. Injectable hydrogels for delivering biotherapeutic molecules. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 110, 17–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Homicz, M.R.; Watson, D. Review of injectable materials for soft tissue augmentation. Facial Plast. Surg. 2004, 20, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Deng, H.; Dong, A.; Song, J.; Chen, X. Injectable thermosensitive hydrogel systems based on functional PEG/PCL block polymer for local drug delivery. J. Control. Release 2019, 297, 60–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.B.; Gong, C.Y.; Huang, M.J.; Wang, J.W.; Pan, Y.F.; Zhang, Y.D.; Li, G.Z.; Gou, M.L.; Wang, K.; Tu, M.J.; et al. Thermoreversible gel–sol behavior of biodegradable PCL-PEG-PCL triblock copolymer in aqueous solutions. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part B Appl. Biomater. 2008, 84B, 165–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, H.; Mei, L.; Song, C.; Cui, X.; Wang, P. The in vivo degradation, absorption and excretion of PCL-based implant. Biomaterials 2006, 27, 1735–1740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, M.K.; Lee, D.S. Injectable Biodegradable Hydrogels. Macromol. Biosci. 2010, 10, 563–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinman, N.Y.; Haim-Zada, M.; Goldstein, I.A.; Goldberg, A.H.; Haber, T.; Berlin, J.M.; Domb, A.J. Effect of PLGA block molecular weight on gelling temperature of PLGA-PEG-PLGA thermoresponsive copolymers. J. Polym. Sci. Part A: Polym. Chem. 2019, 57, 35–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, W.; Chang, L.; Li, X.; Wu, Y.; Xing, J.; Deng, L.; Dong, A. Controlled thermal gelation of poly(ε-caprolactone)/poly(ethylene glycol) block copolymers by modifying cyclic ether pendant groups on poly(ε-caprolactone). Soft Matter 2012, 8, 1575–1583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, C.; Shi, S.; Dong, P.; Kan, B.; Gou, M.; Wang, X.; Li, X.; Luo, F.; Zhao, X.; Wei, Y. Synthesis and characterization of PEG-PCL-PEG thermosensitive hydrogel. Int. J. Pharm. 2009, 365, 89–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.; Deng, X.; Hao, J. Thermogelling hydrogels of poly (ε-caprolactone-co-D, L-lactide)–poly (ethylene glycol)–poly (ε-caprolactone-co-D, L-lactide) and poly (ε-caprolactone-co-L-lactide)–poly (ethylene glycol)–poly (ε-caprolactone-co-L-lactide) aqueous solutions. J. Polym. Sci. Part A Polym. Chem. 2007, 45, 4091–4099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalarickal, N.C.; Rimmer, S.; Sarker, P.; Leroux, J.-C. Thiol-Functionalized Poly(ethylene glycol)-b-polyesters: Synthesis and Characterization. Macromolecules 2007, 40, 1874–1880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.; You, Y.; Deng, X.; Hao, J. Injectable hydrogels of poly(ɛ-caprolactone-co-glycolide)–poly(ethylene glycol)–poly(ɛ-caprolactone-co-glycolide) triblock copolymer aqueous solutions. Polymer 2007, 48, 4786–4792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huynh, D.P.; Nguyen, M.K.; Kim, B.S.; Lee, D.S. Molecular design of novel pH/temperature-sensitive hydrogels. Polymer 2009, 50, 2565–2571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.H.; Choi, B.G.; Joo, M.K.; Han, D.K.; Sohn, Y.S.; Jeong, B. Temperature-Sensitive Poly(caprolactone-co-trimethylene carbonate)−Poly(ethylene glycol)−Poly(caprolactone-co-trimethylene carbonate) as in Situ Gel-Forming Biomaterial. Macromolecules 2008, 41, 6486–6492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shim, M.S.; Lee, H.T.; Shim, W.S.; Park, I.; Lee, H.; Chang, T.; Kim, S.W.; Lee, D.S. Poly(d,l-lactic acid-co-glycolic acid)-b-poly(ethylene glycol)-b-poly (d,l-lactic acid-co-glycolic acid) triblock copolymer and thermoreversible phase transition in water. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 2002, 61, 188–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bae, Y.H.; Huh, K.M.; Kim, Y.; Park, K.-H. Biodegradable amphiphilic multiblock copolymers and their implications for biomedical applications. J. Control. Release 2000, 64, 3–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, G.H. Electrospun PCL nanofibers with anisotropic mechanical properties as a biomedical scaffold. Biomed. Mater. 2008, 3, 025010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shakiba, E.; Khazaei, S.; Hajialyani, M.; Astinchap, B.; Fattahi, A. Preparation and in vitro characterization of retinoic acid-loaded poly(ε-caprolactone)-poly(ethylene glycol)-poly(ε-caprolactone) micelles. Res. Pharm. Sci. 2017, 12, 465–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steinman, N.Y.; Domb, A.J. Injectable Pasty Biodegradable Polyesters Derived from Castor Oil and Hydroxyl-Acid Lactones. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2019, 370, 736–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitagawa, M.; Maeda, T.; Hotta, A. PEG-based nanocomposite hydrogel: Thermo-responsive sol-gel transition and degradation behavior controlled by the LA/GA ratio of PLGA-PEG-PLGA. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2018, 147, 222–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondal, D.; Griffith, M.; Venkatraman, S.S. Polycaprolactone-based biomaterials for tissue engineering and drug delivery: Current scenario and challenges. Int. J. Polym. Mater. Polym. Biomater. 2016, 65, 255–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, C.; Shi, S.; Wu, L.; Gou, M.; Yin, Q.; Guo, Q.; Dong, P.; Zhang, F.; Luo, F.; Zhao, X.; et al. Biodegradable in situ gel-forming controlled drug delivery system based on thermosensitive PCL–PEG–PCL hydrogel. Part 2: Sol–gel–sol transition and drug delivery behavior. Acta Biomater. 2009, 5, 3358–3370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, S.J.; Suh, J.M.; Sohn, Y.S.; Bae, Y.H.; Kim, S.W.; Jeong, B. Thermogelling poly (caprolactone-b-ethylene glycol-b-caprolactone) aqueous solutions. Macromolecules 2005, 38, 5260–5265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunes, R.W.; Martin, J.R.; Johnson, J.F. Influence of molecular weight and molecular weight distribution on mechanical properties of polymers. Polym. Eng. Sci. 1982, 22, 205–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, S.J.; Joo, M.K.; Jeong, Y.; Kim, S.W.; Lee, W.-K.; Sohn, Y.S.; Jeong, B. Gelation Behavior of Poly(ethylene glycol) and Polycaprolactone Triblock and Multiblock Copolymer Aqueous Solutions. Macromolecules 2006, 39, 4873–4879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Sample | PEG MW (kDa) 1 | Expected Copolymer MW (kDa) 2 | Mn (1H NMR, kDa) 3 | Mn (GPC, kDa) 4 | MW (GPC, kDa) 4 | PDI 4 | Solubility 5 | Gelling Temperature |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| I | 2 | 3.0 | 3.0 | 4.1 | 4.8 | 1.2 | Soluble | - |
| II | 2 | 3.3 | 3.2 | 4.4 | 4.9 | 1.1 | Insoluble | - |
| III | 4 | 6.6 | 6.2 | 8.3 | 10.9 | 1.3 | Soluble | - |
| IV | 4 | 9.2 | 9.0 | 7.2 | 11.0 | 1.5 | Soluble | 50 °C |
| V | 4 | 9.6 | 9.5 | 9.1 | 13.5 | 1.5 | Soluble | 50 °C |
| VI | 4 | 10.0 | 9.7 | 10.2 | 15.0 | 1.5 | Insoluble | - |
| VII | 8 | 10.3 | 10.1 | 12.2 | 14.3 | 1.2 | Soluble | - |
| VIII | 8 | 16.8 | 16.8 | 9.1 | 16.3 | 1.8 | Soluble | 25 °C |
| IX | 8 | 18.4 | 17.8 | 10.0 | 17.7 | 1.1 | Soluble | 25 °C |
| X | 8 | 19.9 | 40.1 | 10.3 | 19.1 | 1.8 | Insoluble | - |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Steinman, N.Y.; Bentolila, N.Y.; Domb, A.J. Effect of Molecular Weight on Gelling and Viscoelastic Properties of Poly(caprolactone)–b-Poly(ethylene glycol)–b-Poly(caprolactone) (PCL–PEG–PCL) Hydrogels. Polymers 2020, 12, 2372. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12102372
Steinman NY, Bentolila NY, Domb AJ. Effect of Molecular Weight on Gelling and Viscoelastic Properties of Poly(caprolactone)–b-Poly(ethylene glycol)–b-Poly(caprolactone) (PCL–PEG–PCL) Hydrogels. Polymers. 2020; 12(10):2372. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12102372
Chicago/Turabian StyleSteinman, Noam Y., Noam Y. Bentolila, and Abraham J. Domb. 2020. "Effect of Molecular Weight on Gelling and Viscoelastic Properties of Poly(caprolactone)–b-Poly(ethylene glycol)–b-Poly(caprolactone) (PCL–PEG–PCL) Hydrogels" Polymers 12, no. 10: 2372. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12102372
APA StyleSteinman, N. Y., Bentolila, N. Y., & Domb, A. J. (2020). Effect of Molecular Weight on Gelling and Viscoelastic Properties of Poly(caprolactone)–b-Poly(ethylene glycol)–b-Poly(caprolactone) (PCL–PEG–PCL) Hydrogels. Polymers, 12(10), 2372. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12102372