A Novel Approach to Increase the Oxygen Permeability of Soft Contact Lenses by Incorporating Silica Sol
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of Silica Nanoparticles and Hydrogels
2.3. Characterization of SNPs and Hydrogel Lenses
2.3.1. Size of Particles and Chemical Structure
2.3.2. Fourier-Transform Infrared Spectrometer
2.3.3. Equilibrium Water Content
2.3.4. Oxygen Permeability
2.3.5. Contact Angle
2.3.6. Optical Transparency
2.3.7. Mechanical Properties
2.3.8. Protein Deposition
2.3.9. Cytotoxicity Test
3. Results
3.1. Dynamic Light Scattering and Raman
3.2. Fourier-Transform Infrared Spectrometer
3.3. Equilibrium Water Content
3.4. Contact Angle
3.5. Optical Transparency
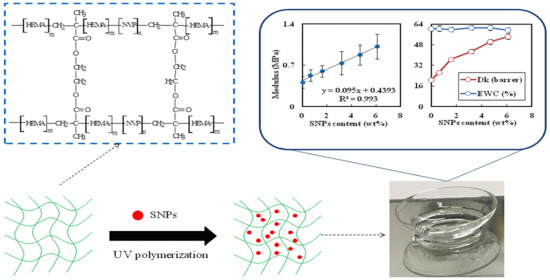
3.6. Oxygen Permeability
3.7. Mechanical Properties
3.8. Protein Deposition
3.9. Cytotoxicity Test
3.10. Comparison with Commercial Contact Lenses
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Alvord, L.; Davis, T.; Morgan, C.F.; Schindhelm, K.; Vogt, J.; Winterton, L. Oxygen permeability of a new type of high Dk soft contact lens material. Optom. Vis. Sci. 1998, 75, 30–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maldonado, C.; Efron, N. Hydrogel lenses–Materials and manufacture: A review. Optom. Pract. 2003, 4, 101–115. [Google Scholar]
- Tran, N.P.D.; Yang, M.C. Synthesis and characterization of silicone contact lenses based on TRIS-DMA-NVP-HEMA hydrogels. Polymers 2019, 11, 944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lin, C.H.; Cho, H.L.; Yeh, Y.H.; Yang, M.C. Improvement of the surface wettability of silicone hydrogel contact lenses via layer-by-layer self-assembly technique. Colloids Surf. B 2015, 136, 735–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Efron, N.; Morgan, P.B.; Cameron, I.D.; Brennan, N.A.; Goodwin, M. Oxygen permeability and water content of silicone hydrogel contact lens materials. Optom. Vis. Sci. 2007, 84, E328–E337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.H.; Yeh, Y.H.; Lin, W.C.; Yang, M.C. Novel silicone hydrogel based on PDMS and PEGMA for contact lens application. Colloids Surf. B 2014, 123, 986–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, M.; Shin, Y.H.; Kwon, Y. Synthesis and properties of siloxane-containing hybrid hydrogels: Optical transmittance, oxygen permeability and equilibrium water content. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2010, 10, 6934–6938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Xie, H.; An, S.; Jiang, Y. The relationship between oxygen permeability and phase separation morphology of the multicomponent silicone hydrogels. J. Phys. Chem. B 2014, 118, 14640–14647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.B.; An, S.S.; Xie, H.J.; Han, X.L.; Wang, F.H.; Jiang, Y. The relationship between the hydrophilicity and surface chemical composition microphase separation structure of multicomponent silicone hydrogels. J. Phys. Chem. B 2015, 119, 9780–9786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garrett, Q.; Laycock, B.; Garrett, R.W. Hydrogel lens monomer constituents modulate protein sorption. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2000, 41, 1687–1695. [Google Scholar]
- Paterson, S.M.; Liu, L.; Brook, M.A.; Sheardown, H. Poly (ethylene glycol)-or silicone-modified hyaluronan for contact lens wetting agent applications. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 2015, 103, 2602–2610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.; Somorjai, G.A. Molecular packing of lysozyme, fibrinogen, and bovine serum albumin on hydrophilic and hydrophobic surfaces studied by infrared− visible sum frequency generation and fluorescence microscopy. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2003, 125, 3150–3158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahn, J.; Chung, W.-J.; Pinnau, I.; Guiver, M.D. Polysulfone/silica nanoparticle mixed-matrix membranes for gas separation. J. Membr. Sci. 2008, 314, 123–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ahn, J.; Chung, W.-J.; Pinnau, I.; Song, J.; Du, N.; Robertson, G.P.; Guiver, M.D. Gas transport behavior of mixed-matrix membranes composed of silica nanoparticles in a polymer of intrinsic microporosity (PIM-1). J. Membr. Sci. 2010, 346, 280–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tran, N.P.D.; Yang, M.C. The ophthalmic performance of hydrogel contact lenses loaded with silicone nanoparticles. Polymers 2020, 12, 1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Li, X. Preparation and characterization of interpenetrating polymer network silicone hydrogels with high oxygen permeability. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2010, 116, 2749–2757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, N.P.D.; Yang, M.C. Synthesis and characterization of soft contact lens based on the combination of silicone nanoparticles with hydrophobic and hydrophilic monomers. J. Polym. Res. 2019, 26, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fonn, D.; Dumbleton, K.; Jalbert, I.; Sivak, A. Benefits of silicone hydrogel lenses. Contact Lens Spectr. 2006, 21, 38. [Google Scholar]
- Awasthi, A.; Meng, F.; Künzler, J.; Linhardt, J.; Papagelis, P.; Oltean, G.; Myers, S. Ethylenically unsaturated polycarbosiloxanes for novel silicone hydrogels: Synthesis, end-group analysis, contact lens formulations, and structure–property correlations. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2013, 24, 557–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghoreishi, S.; Abbasi, F.; Jalili, K. Hydrophilicity improvement of silicone rubber by interpenetrating polymer network formation in the proximal layer of polymer surface. J. Polym. Res. 2016, 23, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korogiannaki, M.; Guidi, G.; Jones, L.; Sheardown, H. Timolol maleate release from hyaluronic acid-containing model silicone hydrogel contact lens materials. J. Biomater. Appl. 2015, 30, 361–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicolson, P.C.; Vogt, J. Soft contact lens polymers: An evolution. Biomaterials 2001, 22, 3273–3283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luensmann, D.; Jones, L. Protein deposition on contact lenses: The past, the present, and the future. Cont. Lens Anterior Eye 2012, 35, 53–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, D.; Fernandes, A.; Nunes, T.; Colaço, R.; Serro, A. The effect of albumin and cholesterol on the biotribological behavior of hydrogels for contact lenses. Acta Biomater. 2015, 26, 184–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Subbaraman, L.N.; Glasier, M.-A.; Senchyna, M.; Sheardown, H.; Jones, L. Kinetics of in vitro lysozyme deposition on silicone hydrogel, PMMA, and FDA groups I, II, and IV contact lens materials. Curr. Eye Res. 2006, 31, 787–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- French, K.; Jones, L. A decade with silicone hydrogels: Part 1. Optom. Today 2008, 48, 42–46. [Google Scholar]








| Sample | SNP Content (wt%) | EWC (%) | Dk (barrer) | Dk/t (barrer/mm) | Contact Angle (°) | Protein Deposition (nmol/cm2) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HSA | Lysozyme | ||||||
| S0 | 0 | 52.5 ± 1.6 | 20.6 ± 1.0 | 198 ± 9 | 60.5 ± 2.3 | 0.76 ± 0.01 | 3.10 ± 0.05 |
| S1 | 0.18 | 51.5 ± 2.1 | 26.6 ± 1.2 | 257 ± 11 | 60.1 ± 3.1 | 0.78 ± 0.01 | 3.21 ± 0.05 |
| S2 | 0.46 | 53.5 ± 1.7 | 36.7 ± 1.5 | 355 ± 19 | 61.1 ± 2.9 | 0.75 ± 0.01 | 3.27 ± 0.04 |
| S3 | 0.92 | 52.9 ± 1.9 | 42.8 ± 1.7 | 414 ± 11 | 59.5 ± 4.1 | 0.76 ± 0.01 | 3.16 ± 0.05 |
| S4 | 1.37 | 51.9 ± 2.0 | 50.3 ± 1.9 | 494 ± 13 | 60.1 ± 3.3 | 0.75 ± 0.01 | 3.23 ± 0.06 |
| S5 | 1.82 | 53.1 ± 1.8 | 54.3 ± 2.2 | 534 ± 15 | 61.2 ± 4.5 | 0.76 ± 0.01 | 3.29 ± 0.05 |
| Product | Manufacturer | Dk (barrer) | EWC (%) | Contact angle (°) | Modulus (MPa) | Principle Monomers |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Air Optix Night & Day | CIBA Vision | 140 | 24 | 1.52 | DMA, TRIS, siloxane monomer | |
| Air Optix | 110 | 33 | 44.4 | 1.00 | DMA, TRIS, siloxane monomer | |
| Acuvue Oasys | Johnson & Johnson Vision Care | 103 | 38 | 78.7 | 0.72 | MPDMS, DMA, HEMA, siloxane macromer, TEGDMA, PVP |
| Acuvue Advance | 60 | 47 | 65.6 | 0.43 | MPDMS, DMA, HEMA, EGDMA, siloxane macromer, PVP | |
| Acuvue 2 | 19 | 58 | HEMA, MAA, EGDMA | |||
| Pure Vision | Bausch & Lomb | 91 | 36 | 93.6 | 1.10 | TEGDMA, NVP, TPVC, NCVE, PBVC |
| Biomedics XC | CooperVision | 44 | 60 | HEMA, MAA, PC, TEGDMA | ||
| Biomedics 38 | 8.4 | 38 | 30 | 0.81 | HEMA, EGDMA | |
| S4 | This work | 50.3 | 51.9 | 60.1 | 0.88 | HEMA, NVP, SNPs |
| S5 | 54.3 | 53.1 | 61.2 | 1.02 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tran, N.-P.-D.; Ting, C.-C.; Lin, C.-H.; Yang, M.-C. A Novel Approach to Increase the Oxygen Permeability of Soft Contact Lenses by Incorporating Silica Sol. Polymers 2020, 12, 2087. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12092087
Tran N-P-D, Ting C-C, Lin C-H, Yang M-C. A Novel Approach to Increase the Oxygen Permeability of Soft Contact Lenses by Incorporating Silica Sol. Polymers. 2020; 12(9):2087. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12092087
Chicago/Turabian StyleTran, Nguyen-Phuong-Dung, Chuan-Cheng Ting, Chien-Hong Lin, and Ming-Chien Yang. 2020. "A Novel Approach to Increase the Oxygen Permeability of Soft Contact Lenses by Incorporating Silica Sol" Polymers 12, no. 9: 2087. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12092087
APA StyleTran, N. -P. -D., Ting, C. -C., Lin, C. -H., & Yang, M. -C. (2020). A Novel Approach to Increase the Oxygen Permeability of Soft Contact Lenses by Incorporating Silica Sol. Polymers, 12(9), 2087. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12092087