Patterned Membranes for Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cells Working at Low Humidity
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methodology
2.1. Patterned Membrane Fabrication
2.2. Membrane Characterisation
2.2.1. Surface Morphology
2.2.2. Membrane Swelling and Water Uptake
2.2.3. Ion Exchange Capacity
2.3. MEA Fabrication and In Situ Testing
2.4. ECSA Calculation
3. Results
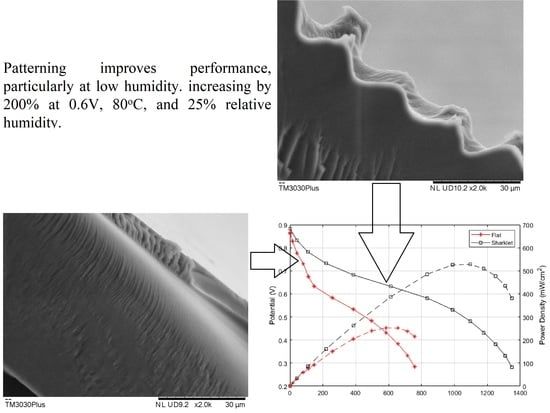
3.1. Patterned Membrane
3.2. Ion Exchange Capacity, Water Uptake, and Membrane Swelling
3.3. Membrane Electrode Assembly Test
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Nomenclature
| DOE | department of energy |
| ECSA | electrochemically active surface area |
| EIS | electrochemical impedance spectroscopy |
| GDL | gas diffusion layer |
| HFR | high frequency resistance |
| IEC | ion exchange capacity |
| LIPSS | laser-imposed periodic surface structures |
| MEA | membrane electrode assembly |
| NSTF | nano structured thin film |
| PDMS | polydimethylsiloxane |
| PEMFC | proton exchange membrane fuel cell |
| RH | relative humidity |
| TPB | triple phase boundary |
References
- Kirsch, D. The Electric Vehicle and the Budern of History; Rutgers University Press: New Brunswick, NJ, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Pollet, B.G.; Kocha, S.S.; Staffell, I. Current status of automotive fuel cells for sustainable transport. Curr. Opin. Electrochem. 2019, 16, 90–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno, N.G.; Molina, M.C.; Gervasio, D.; Robles, J.F.P. Approaches to polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cells (PEMFCs) and their cost. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2015, 52, 897–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Multi-Year Research, Development, and Demonstration Plan. 3.4 Fuel Cells; Department of Energy: Washington, DC, USA, 2016.
- Liang, Z.; Chen, W.; Liu, J.; Wang, S.; Zhou, Z.; Li, W.; Sun, G.; Xin, Q. FT-IR study of the microstructure of Nafion® membrane. J. Membr. Sci. 2004, 233, 39–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burke, K.A. Fuel Cells for Space Applications; NASA: Cleveland, OH, USA, 2003.
- Faulkner, A.J.B.L.R. Fundamentals and Applications. Annu. Rev. Mater. Sci. 2000, 30, 30–100. [Google Scholar]
- Schalenbach, M.; Hoefner, T.; Paciok, P.; Carmo, M.; Lueke, W.; Stolten, D. Gas Permeation through Nafion. Part 1: Measurements. J. Phys. Chem. C 2015, 119, 25145–25155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elliott, J.A.; Paddison, S.J. Modelling of morphology and proton transport in PFSA membranes. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2007, 9, 2602–2618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zawodzinski, T.A.; DeRouin, C.; Radzinski, S.; Sherman, R.J.; Smith, V.T.; Springer, T.E.; Gottesfeld, S. Water Uptake by and Transport Through Nafion® 117 Membranes. J. Electrochem. Soc. 1993, 140, 1041–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raistrick, I.D. Electrode Assembly for Use in a Solid Polymer Electrolyte Fuel Cell. U.S. Patent 4,876,155, 24 October 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Dhar, H.P. Near Ambient, Unhumidified Solid Polymer Fuel Cell. U.S. Patent 5,242,764, 7 September 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Sinha, P.K.; Gu, W.; Kongkanand, A.; Thompson, E. Performance of Nano Structured Thin Film (NSTF) Electrodes under Partially-Humidified Conditions. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2011, 158, B831–B840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Dominey, R.N.; Rolland, J.P.; Maynor, B.W.; Pandya, A.A.; DeSimone, J.M. Molded, High Surface Area Polymer Electrolyte Membranes from Cured Liquid Precursors. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 12963–12972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeon, Y.; Kim, D.J.; Koh, J.K.; Ji, Y.; Kim, J.H.; Shul, Y.-G. Interface-designed Membranes with Shape-controlled Patterns for High-performance Polymer Electrolyte Membrane Fuel Cells. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 16394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bae, J.W.; Cho, Y.-H.; Sung, Y.-E.; Shin, K.; Jho, J.Y. Performance enhancement of polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cell by employing line-patterned Nafion membrane. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2012, 18, 876–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omosebi, A.; Besser, R.S. Electron beam patterned Nafion membranes for DMFC applications. J. Power Sources 2013, 228, 151–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yildirim, M.H.; Braake, J.T.; Aran, H.C.; Stamatialis, D.; Wessling, M. Micro-patterned Nafion membranes for direct methanol fuel cell applications. J. Membr. Sci. 2010, 349, 231–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.M.; Kang, Y.S.; Ahn, C.-Y.; Jang, S.; Kim, M.; Sung, Y.-E.; Yoo, S.J.; Choi, M. Prism-patterned Nafion membrane for enhanced water transport in polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cell. J. Power Sources 2016, 317, 19–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romano, J.-M.; Garcia-Giron, A.; Penchev, P.; Dimov, S. Triangular laser-induced submicron textures for functionalising stainless steel surfaces. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 440, 162–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ding, X.; Fuller, T.F.; Harris, T.A.L. Effects of annealing conditions on the performance of solution cast Nafion membranes. ECS Trans. 2011, 41, 1537–1544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Branco, C.M. Multilayer Membranes for Intermediate Temperature Polymer Electrolyte Fuel Cells; University of Birmingham: Birmingham, UK, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, P.; Bharti, R.P.; Kumar, V.; Kundu, P.P. Progress and Recent Trends in Microbial Fuel Cells; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; pp. 47–72. [Google Scholar]
- Tsotridis, G.; Pilenga, A.; De Marco, G.; Malkow, T. EU Harmonised Test Protocols for PEMFC MEA Testing in Single Cell Configuration for Automotive Applications; JRC Science for Policy Report; Publications Office of the European Union: Luxembourg, 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, J.; Kim, J. Membrane electrode assembly degradation by dry/wet gas on a PEM fuel cell. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2010, 35, 13125–13130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Canut, J.-M.; Abouatallah, R.M.; Harrington, D.A. Detection of Membrane Drying, Fuel Cell Flooding, and Anode Catalyst Poisoning on PEMFC Stacks by Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2006, 153, A857–A864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kocha, S.S.; Yang, J.D.; Yi, J.S. Characterization of gas crossover and its implications in PEM fuel cells. AIChE J. 2006, 52, 1916–1925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baik, K.D.; Hong, B.K.; Kim, M.S. Effects of operating parameters on hydrogen crossover rate through Nafion® membranes in polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cells. Renew. Energy 2013, 57, 234–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, P.; Wu, Z.; Li, Y.; Jia, X.; Chen, D.; Huang, S. Improved methods to measure hydrogen crossover current in proton exchange membrane fuel cell. Appl. Energy 2018, 215, 338–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Parameters | Anode | Cathode |
|---|---|---|
| Fuel | Hydrogen | Air |
| Temperature (°C) | 80 | 80 |
| Flow rate (mL min−1) | 150 | 300 |
| Stoichiometry | 1.3 | 1.5 |
| Relative humidity (%) | 25/50/75/100 | 25/50/75/100 |
| Back pressure (bar) | 1.5 | 1.3 |
| Pattern | Lotus | Lines | Sharklet |
|---|---|---|---|
| Length (μm) | 25 | 25 | 25 |
| Diagonal (μm) | 5.1 | n/a | 18.08 |
| Depth (max/average) (μm) | 3.5/3.2 | 28.1 | 16/4.6 |
| Dry Thickness μm | Hydrated Thickness μm | |
|---|---|---|
| Flat | 52.33 ± 0.58 | 62.00 ± 1.00 |
| Lotus | 45.00 ± 1.73 | 48.67 ± 0.58 |
| Lines | 53.67 ± 8.96 | 61.33 ± 11.93 |
| Sharklet | 52.00 ± 3.00 | 58.67 ± 5.69 |
| Pattern | ECSA m2 g−1 |
|---|---|
| Flat | 18.3869 |
| Lotus | 12.5417 |
| Lines | 17.4702 |
| Sharklet | 20.2024 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fernihough, O.; Cheshire, H.; Romano, J.-M.; Ibrahim, A.; El-Kharouf, A.; Du, S. Patterned Membranes for Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cells Working at Low Humidity. Polymers 2021, 13, 1976. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13121976
Fernihough O, Cheshire H, Romano J-M, Ibrahim A, El-Kharouf A, Du S. Patterned Membranes for Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cells Working at Low Humidity. Polymers. 2021; 13(12):1976. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13121976
Chicago/Turabian StyleFernihough, Oliver, Holly Cheshire, Jean-Michel Romano, Ahmed Ibrahim, Ahmad El-Kharouf, and Shangfeng Du. 2021. "Patterned Membranes for Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cells Working at Low Humidity" Polymers 13, no. 12: 1976. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13121976
APA StyleFernihough, O., Cheshire, H., Romano, J. -M., Ibrahim, A., El-Kharouf, A., & Du, S. (2021). Patterned Membranes for Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cells Working at Low Humidity. Polymers, 13(12), 1976. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13121976