Preparation and Physicochemical Characterization of a Diclofenac Sodium-Dual Layer Polyvinyl Alcohol Patch
Abstract
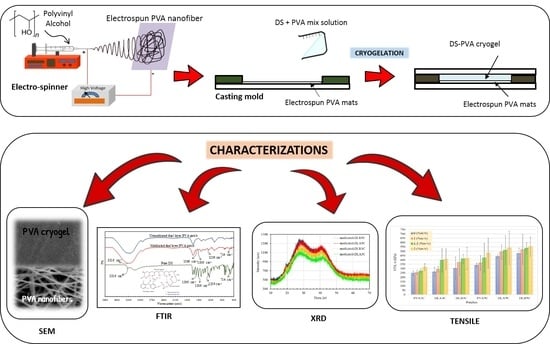
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Production of Electrospun PVA Nanofiber
2.2.2. Preparation of PVA Cryogel (Unmedicated and Medicated)
2.2.3. Preparation of Dual Layer PVA Patch
2.3. Characterization
2.3.1. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) of Electrospun PVA Nanofiber
2.3.2. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) of Unmedicated and DS Medicated Dual Layer PVA Patch
2.3.3. X-ray Diffraction (XRD)
2.3.4. Fourier Transform Infrared (FTIR)
2.3.5. Water Contact Angle
2.3.6. Tensile Test
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Morphology Characterization
3.1.1. Electrospun PVA Nanofibers
3.1.2. Prepared Dual Layer PVA Patch
3.2. Effect of Nanofiber Thickness and Freeze-Thaw Cycle on Physico-Chemical Properties of Prepared Dual Layer PVA Patches
3.3. Wetting Properties of Prepared Dual Layer PVA Patch
3.4. Tensile Properties of Unmedicated and DS Medicated-Dual Layer PVA Patches
Effect of Nanofiber Thickness, Freeze–Thaw Cycles and Percentage DS Loading on Tensile Strength
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mohammad, N.S.; Rabiee, N.; Hajebi, S.; Ahmadi, S.; Fatahi, Y.; Hosseini, M.; Bagherzadeh, M.; Ghadiri, A.M.; Rabiee, M.; Jajarmi, V.; et al. Biodegradable nanopolymers in cardiac tissue engineering: From concept towards nanomedicine. Int. J. Nanomed. 2020, 15, 4205–4224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rafieian, S.; Mirzadeh, H.; Mahdavi, H.; Masoumi, M. A review on nanocomposite hydrogels and their biomedical applications. Sci. Eng. Compos. Mater. 2019, 26, 154–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muppalaneni, S.; Omidian, H. Polyvinyl alcohol in medicine and pharmacy: A perspective. J. Dev. Drugs 2013, 2, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Croitoru, C.; Pop, M.A.; Bedo, T.; Cosnita, M.; Roata, I.C.; Hulka, I. Physically crosslinked poly (vinyl alcohol)/kappa-carrageenan hydrogels: Structure and applications. Polymers 2020, 12, 560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hassan, C.M.; Peppas, N.A. Structure and morphology of freeze/thawed PVA hydrogels. Macromolecules 2000, 33, 2472–2479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Tang, W.; Wang, X.; Zhao, X.; Chen, C.; Zhu, Z. Applications of hydrogels with special physical properties in biomedicine. Polymers 2019, 11, 1420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lotfipour, F.; Alami-Milani, M.; Salatin, S.; Hadavi, A.; Jelvehgari, M. Freeze-thaw-induced cross-linked PVA/chitosan for oxytetracycline-loaded wound dressing: The experimental design and optimization. Res. Pharm. Sci. 2019, 14, 175–189. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, T.; Gan, J.; Zhou, L.; Chen, H. Physically crosslinked hydrogels based on poly (vinyl alcohol) and fish gelatin for wound dressing application: Fabrication and characterization. Polymers 2020, 12, 1729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kartsonakis, I.A.; Goulis, P.; Charitidis, C.A. Triggerable super absorbent polymers for coating debonding applications. Polymers 2021, 13, 1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Tian, L.; Zhu, T. Electrospun aspirin/eudragit/lipid hybrid nanofibers for colon-targeted delivery using an energy-saving process. Chem. Res. Chin. Univ. 2021, 37, 443–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mousa, H.M.; Alfadhel, H.; Abouel Nasr, E. Engineering and characterization of antibacterial coaxial nanofiber membranes for oil/water separation. Polymers 2020, 12, 2597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponnamma, D.; Chamakh, M.M.; Alahzm, A.M.; Salim, N.; Hameed, N.; AlMaadeed, M.A.A. Core-shell nanofibers of polyvinylidene fluoride-based nanocomposites as piezoelectric nanogenerators. Polymers 2020, 12, 2344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, A.; Arshad, S.; Nazir, A.; Ahmad, S.; Khan, M.; Shahzad, A.; Satti, A.; Qadir, M.B.; Khaliq, Z. Development of optimized triaxially electrospun titania nanofiber-in-nanotube core-shell structure. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2021, 138, 50562. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, Y.; Dou, C.; Chang, S.; Xie, Z.; Yu, D.-G.; Liu, Y.; Shao, J. Core–shell eudragit s100 nanofibers prepared via triaxial electrospinning to provide a colon-targeted extended drug release. Polymers 2020, 12, 2034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Wang, M.; Song, W.-L.; Yu, D.-G.; Bligh, S.W.A. Electrospun janus beads-on-a-string structures for different types of controlled release profiles of double drugs. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, H.; Yu, D.; Wang, M.; Ning, T. Nanofabrication of janus fibers through side-by-side electrospinning—A mini review. Mater. Highlights 2021, 2, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aidana, Y.; Wang, Y.; Li, J.; Chang, S.; Wang, K.; Yu, D.G. Fast dissolution electrospun medicated nanofibers for effective delivery of poorly water-soluble drugs. Curr. Drug Deliv. 2021, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, K.; Kang, S.-X.; Yang, Y.-Y.; Yu, D.-G. Electrospun functional nanofiber membrane for antibiotic removal in water: Review. Polymers 2021, 13, 226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, S.; Piao, H.; Rejinold, N.S.; Jin, G.; Choi, G.; Choy, J.-H. Niclosamide–clay intercalate coated with nonionic polymer for enhanced bioavailability toward covid-19 treatment. Polymers 2021, 13, 1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Newehy, M.; Elnaggar, M.; Alotaiby, S.; El-Hamshary, H.; Moydeen, M.; Al-Deyab, S. Preparation of biocompatible system based on electrospun CMC/PVA nanofibers as controlled release carrier of diclofenac sodium. J. Macromol. Sci. A 2016, 53, 566–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madhukiran, D.R.; Abhishek, J.; Manish, K.; Gufran, A.; Gunjan, V.B.; Brahmeshwar, M. Electrospun nanofiber-based drug delivery platform: Advances in diabetic foot ulcer management. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2021, 18, 25–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.T.; Zhang, J.; Gao, Y.; Liu, X.F.; Liu, J.J.; Wang, X.X.; Long, Y.Z. Self-powered portable melt electrospinning for in situ wound dressing. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2020, 18, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shao, Z.; Jiang, J.; Wang, X.; Li, W.; Fang, L.; Zheng, G. Self-powered electrospun composite nanofiber membrane for highly efficient air filtration. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 1706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wehlage, D.; Blattner, H.; Mamun, A.; Kutzli, I.; Diestelhorst, E.; Rattenholl, A.; Gudermann, F.; Lütkemeyer, D.; Ehrmann, A. Cell growth on electrospun nanofiber mats from polyacrylonitrile (PAN) blends. J. AIMS Bioeng. 2020, 7, 43–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niemczyk-Soczynska, B.; Gradys, A.; Sajkiewicz, P. Hydrophilic surface functionalization of electrospun nanofibrous scaffolds in tissue engineering. Polymers 2020, 12, 2636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.M.; Yang, J.H.; Tsou, S.C.; Ding, C.H.; Hsu, C.C.; Yang, K.C.; Yang, C.C.; Chen, K.S.; Chen, S.W.; Wang, J.S. Cell proliferation on PVA/sodium alginate and PVA/poly (γ-glutamic acid) electrospun fiber. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2016, 66, 170–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, X.; Huo, P.; Ding, Z.; Kumar, P.; Liu, B. Preparation of Lutein-loaded pva/sodium alginate nanofibers and investigation of its release behavior. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, 449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cui, Z.; Zheng, Z.; Lin, L. Electrospinning and crosslinking of polyvinyl alcohol/chitosan composite nanofiber for transdermal drug delivery. Adv. Polym. Technol. 2018, 37, 1917–1928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponrasu, T.; Chen, B.-H.; Chou, T.-H.; Wu, J.-J.; Cheng, Y.-S. Fast dissolving electrospun nanofibers fabricated from jelly fig polysaccharide/pullulan for drug delivery applications. Polymers 2021, 13, 241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saudi, S.; Bhattarai, S.R.; Adhikari, U.; Khanal, S.; Sankar, J.; Aravamudhan, S.; Bhattarai, N. Nanonet-nano fiber electrospun mesh of PCL–chitosan for controlled and extended release of diclofenac sodium. Nanoscale 2020, 12, 23556–23569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altman, R.; Bosch, B.; Brune, K.; Patrignani, P.; Young, C. Advances in NSAID development: Evolution of diclofenac products using pharmaceutical technology. Drugs 2015, 75, 859–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Salvo, F.; Fourrier-Reglat, A.; Bazin, F.; Robinson, P.; Riera-Guardia, N.; Haag, M. Cardiovascular and gastrointestinal safety of NSAIDs: A systematic review of meta-analyses of randomized clinical trials. Clin. Pharm. Ther. 2011, 89, 855–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGettigan, P.; Henry, D. Cardiovascular risk with non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs: Systematic review of population-based controlled observational studies. PLoS Med. 2011, 8, e1001098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Haltner-Ukomadu, E.; Sacha, M.; Richter, A.; Hussein, K. Hydrogel increases diclofenac skin permeation and absorption. Biopharm. Drug Dispos. 2019, 40, 217–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qiao, Z.; Tran, L.; Parks, J.; Zhou, Y.; Hai, N.; Zhong, Y.; Ji, H.F. Highly stretchable gelatin-polyacrylamide hydrogel for potential transdermal drug release. Nano Select. 2021, 2, 107–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Wang, W.; Wang, A. A pH sensitive carboxymethyl cellulose-g-poly (acrylic acid)/polyvinylpyrrolidone/sodium alginate composite hydrogel bead for the controlled release of diclofenac. J. Control Release 2015, 213, e91–e92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saidi, L.; Vilela, C.; Oliveira, H.; Silvestre, A.J.D.; Freire, C.S.R. Poly (N-methacryloyl glycine)/nanocellulose composites as pH-sensitive systems for controlled release of diclofenac. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 169, 357–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Păduraru, O.M.; Ciolacu, D.; Darie, R.N.; Vasile, C. Synthesis and characterization of polyvinyl alcohol/cellulose cryogels and their testing as carriers for a bioactive component. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2012, 32, 2508–2515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahadoran, M.; Shamloo, A.; Nokoorani, Y.D. Development of a polyvinyl alcohol/sodium alginate hydrogel-based scaffold incorporating bFGF-encapsulated microspheres for accelerated wound healing. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 7342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mastrangelo, R.; Chelazzi, D.; Poggi, G.; Fratini, E.; Pensabene Buemi, L.; Petruzzellis, M.L.; Baglioni, P. Twin-chain polymer hydrogels based on poly (vinyl alcohol) as new advanced tool for the cleaning of modern and contemporary art. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 7011–7020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Peppas, N.A.; Stauffer, S.R. Reinforced uncrosslinked poly (vinyl alcohol) gels produced by cyclic freezing-thawing processes: A short review. J. Control Release 1991, 16, 305–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonakdar, S.; Emami, S.H.; Shokrgozar, M.A.; Farhadi, A.; Ahmadi, S.A.H.; Amanzadeh, A. Preparation and characterization of polyvinyl alcohol hydrogels crosslinked by biodegradable polyurethane for tissue engineering of cartilage. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2010, 30, 636–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, D.; Jat, S.K.; Khanna, P.K.; Vijayan, N.; Banerjee, S. Synthesis, characterization, and studies of PVA/co-doped ZnO nanocomposite films. Int. J. Green Nanotechnol. 2012, 4, 408–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peppas, N.A. Infrared spectroscopy of semicrystalline poly (vinyl alcohol) networks. Die Makromol. Chem. 1977, 178, 595–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, S.; Lan, W.; Qin, W. Fabrication and testing of pva/chitosan bilayer films for strawberry packaging. Coatings 2017, 7, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zainuddin, Z.; Hill, D.J.T.; Le, T.T. An ESR study on gamma-irradiated poly (vinyl alcohol). Radiat. Phys. Chem. 2001, 62, 283–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaidukov, S.; Danilenko, I.; Gaidukova, G. Characterization of strong and crystalline polyvinyl alcohol/montmorillonite films prepared by layer-by-layer deposition method. Int. J. Polym. Sci. 2015, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wong, R.S.H.; Dodou, K. Effect of drug loading method and drug physicochemical properties on the material and drug release properties of poly (ethylene oxide) hydrogels for transdermal delivery. Polymers 2017, 9, 286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva, T.L.; Martins, J.M.; da Silva Junior, A.C.; Gimenes, M.L.; Vieira, M.G.A.; da Silva, M.G.C. Evaluation of incorporation of diclofenac sodium in dried sericin-alginate particles prepared by ionic gelation technique. Chem. Eng. Trans. 2015, 43, 829–834. [Google Scholar]
- Younes, H.A.; Khaled, R.; Mahmoud, H.M.; Nassar, H.F.; Abdelrahman, M.M.; Abo El-Ela, F.I.; Taha, M. Computational and experimental studies on the efficient removal of diclofenac from water using ZnFe-layered double hydroxide as an environmentally benign absorbent. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2019, 102, 297–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Liu, F.; Qin, X. Adsorption of diclofenac onto goethite: Adsorption kinetics and effects of pH. Chemosphere 2017, 180, 373–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maver, T.; Gradišnik, L.; Smrke, D.M. Systematic evaluation of a diclofenac-loaded carboxymethyl cellulose-based wound dressing and its release performance with changing pH and temperature. AAPS Pharm. Sci. Tech. 2019, 20, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Zhang, Z.; Li, J.; Sun, S.; Weng, Y.; Chen, H. Diclofenac/biodegradable polymer micelles for ocular applications. Nanoscale 2012, 4, 4667–4673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Ye, L.; Cui, M.; Yang, B.; Li, J.; Sun, H.; Yao, F. Physically crosslinked poly (vinyl alcohol)-carrageenan composite hydrogels: Pore structure stability and cell adhesive ability. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 78180–78191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singhal, A.; Kaur, M.; Dubey, K.A.; Bhardwaj, Y.K.; Jain, D.; Pillai, C.G.S.; Tyagi, A.K. Polyvinyl alcohol–In2O3 nanocomposite films: Synthesis, characterization and gas sensing properties. RSC Adv. 2012, 2, 7180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricciardi, R.; Auriemma, F.; De Rosa, C.; Lauprêtre, F. X-ray diffraction analysis of poly (vinyl alcohol) hydrogels, obtained by freezing and thawing techniques. Macromolecules 2004, 37, 1921–1927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Chen, N.; Li, L.; Wang, Q.; Duan, W. Ionic liquid modified poly (vinyl alcohol) with improved thermal processability and excellent electrical conductivity. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2018, 57, 5472–5481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assender, H.E.; Windle, A.H. Crystallinity in poly (vinyl alcohol) 2. Computer modelling of crystal structure over a range of tacticities. Polymer 1998, 39, 4303–4312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Yamaguchi, K.; Nagaishi, T.; Murai, M.; Kim, M.; Wei, K.; Kim, I.S. Enhancement of mechanical properties of polymeric nanofibers by controlling crystallization behavior using a simple freezing/thawing process. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 43994–44000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tang, C.M.; Tian, Y.H.; Hsu, S.H. Poly (vinyl alcohol) nanocomposites reinforced with bamboo charcoal nanoparticles: Mineralization behavior and characterization. Materials 2015, 8, 4895–4911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hyun, J.; Hyeung, J.; Kyo, I.; Woo, I. Electrospinning fabrication and characterization of water-soluble polymer/montmorillonite/silver nanocomposite nanofibers out of aqueous solution. Adv. Nanocompos. -Synth. Charact. Ind. Appl. 2011, 20, 483–502. [Google Scholar]
- Aielo, P.B.; Borges, F.A.; Romeira, K.M.; Miranda, M.C.R.; de Arruda, L.B.; L Filho, P.N.; Drago, B.D.C.; Herculano, R.D. Evaluation of sodium diclofenac release using natural rubber latex as carrier. Mater. Res. 2014, 17, 146–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maneewattanapinyo, P.; Yeesamun, A.; Watthana, F.; Panrat, K.; Pichayakorn, W.; Suksaeree, J. Controlled release of lidocaine–diclofenac ionic liquid drug from freeze-thawed gelatin/poly (vinyl alcohol) transdermal patches. AAPS Pharm. Sci. Tech. 2019, 20, 322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Gao, J.; Feng, D.; Zhao, J.; Guo, Y.; Zhao, J.; Li, W.; Yan, W. Modification of structural and physicochemical properties of repeated freeze-thawed cycle maize starch. Int. J. Food Prop. 2020, 23, 1597–1610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stauffer, S.R.; Peppas, N.A. Poly (vinyl alcohol) hydrogels prepared by freezing-thawing cyclic processing. Polymer 1992, 33, 3932–3936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]













| Patches | Concentration of PVA (% w/v) | DS Loading (% w/v) | No. of Freeze-Thaw Cycles |
|---|---|---|---|
| * 2 mL-volume of electrospinning | |||
| DLA3C | 10 | - | 3 |
| 1%DLA3C | 1.0 | 3 | |
| 1.5%DLA3C | 1.5 | 3 | |
| 2%DLA3C | 2.0 | 3 | |
| DLA5C | - | 5 | |
| 1%DLA5C | 1.0 | 5 | |
| 1.5%DLA5C | 1.5 | 5 | |
| 2%DLA5C | 2.0 | 5 | |
| * 3 mL-volume of electrospinning | |||
| DLB3C | 10 | - | 3 |
| 1%DLB3C | 1.0 | 3 | |
| 1.5%DLB3C | 1.5 | 3 | |
| 2%DLB3C | 2.0 | 3 | |
| DLB5C | - | 5 | |
| 1%DLB5C | 1.0 | 5 | |
| 1.5%DLB5C | 1.5 | 5 | |
| 2%DLB5C | 2.0 | 5 | |
| Electrospun PVA Nanofiber Mats | |
|---|---|
| A-Batch (mm) | B-Batch (mm) |
| 0.059 | 0.085 |
| 0.042 | 0.086 |
| 0.069 | 0.093 |
| 0.064 | 0.080 |
| 0.061 | 0.086 |
| 0.059 ± 0.009 | 0.086 ± 0.004 |
| FTIR Interpretation of Diclofenac Sodium | ||
|---|---|---|
| Sr. No. | Frequency (cm−1) | Characteristics |
| 1 | 3316 | N–H stretching of a secondary amine |
| 2 | 1566 | C=O stretching of carboxyl ion |
| 3 | 1506 | C=C stretching of an aromatic ring |
| 4 | 1256 | C–N stretching of aromatic amine |
| 5 | 714 | C–Cl stretching |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sa’adon, S.; Ansari, M.N.M.; Razak, S.I.A.; Anand, J.S.; Nayan, N.H.M.; Ismail, A.E.; Khan, M.U.A.; Haider, A. Preparation and Physicochemical Characterization of a Diclofenac Sodium-Dual Layer Polyvinyl Alcohol Patch. Polymers 2021, 13, 2459. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13152459
Sa’adon S, Ansari MNM, Razak SIA, Anand JS, Nayan NHM, Ismail AE, Khan MUA, Haider A. Preparation and Physicochemical Characterization of a Diclofenac Sodium-Dual Layer Polyvinyl Alcohol Patch. Polymers. 2021; 13(15):2459. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13152459
Chicago/Turabian StyleSa’adon, Shafizah, Mohamed Nainar Mohamed Ansari, Saiful Izwan Abd Razak, Joseph Sahaya Anand, Nadirul Hasraf Mat Nayan, Al Emran Ismail, Muhammad Umar Aslam Khan, and Adnan Haider. 2021. "Preparation and Physicochemical Characterization of a Diclofenac Sodium-Dual Layer Polyvinyl Alcohol Patch" Polymers 13, no. 15: 2459. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13152459
APA StyleSa’adon, S., Ansari, M. N. M., Razak, S. I. A., Anand, J. S., Nayan, N. H. M., Ismail, A. E., Khan, M. U. A., & Haider, A. (2021). Preparation and Physicochemical Characterization of a Diclofenac Sodium-Dual Layer Polyvinyl Alcohol Patch. Polymers, 13(15), 2459. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13152459