A Cyclic BMP-2 Peptide Upregulates BMP-2 Protein-Induced Cell Signaling in Myogenic Cells
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Synthesis of Peptide
2.2. Use of SPR for Binding Analysis of BMPRII and BMP-2 Knuckle Epitope Peptides
2.3. Cells and Cell Cultures
2.4. Measurement of ALP Activity
- B = amount of pNPP in sample well calculated from standard curve (µmol).
- T = reaction time (minutes).
- V = original sample volume added into the reaction well (mL).
- D = sample dilution factor.
2.5. ALP Staining
2.6. Western Blotting
3. Results
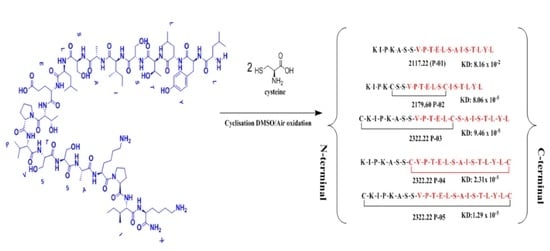
3.1. Design and Synthesis of BMP-2 Peptides
3.2. Interaction of the Peptides with BMPRII
3.3. Osteogenic Differentiation of the C2C12 Cells
3.4. Effects of the Peptides and the Combination of Peptides in Cell Signaling
3.5. Quantification of Alkaline Phosphatase (ALP)
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Barrientos, S.; Stojadinovic, O.; Golinko, M.S.; Brem, H.; Tomic-Canic, M. Growth factors and cytokines in wound healing. Wound Repair Regen. 2008, 16, 585–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ten Dijke, P.; Iwata, K.K. Growth factors for wound healing. Biol. Technol. 1989, 7, 793–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Zhao, M.; Mundy, G.R. Bone morphogenetic proteins. Growth Factors 2004, 22, 233–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katagiri, T.; Watabe, T. Bone morphogenetic proteins. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2016, 8, a021899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Miyazono, K.; Kamiya, Y.; Morikawa, M. Bone morphogenetic protein receptors and signal transduction. J. Biochem. 2010, 147, 35–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bostrom, M.P.; Lane, J.M.; Berberian, W.S.; Missri, A.A.; Tomin, E.; Weiland, A.; Doty, S.B.; Glaser, D.; Rosen, V.M. Immunolocalization and expression of bone morphogenetic proteins 2 and 4 in fracture healing. J. Orthop. Res. 1995, 13, 357–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, E.A.; Rosen, V.; D’Alessandro, J.S.; Bauduy, M.; Cordes, P.; Harada, T.; Israel, D.I.; Hewick, R.M.; Kerns, K.M.; LaPan, P. Recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein induces bone formation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1990, 87, 2220–2224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Reddi, A.H. Role of morphogenetic proteins in skeletal tissue engineering and regeneration. Nat. Biotechnol. 1998, 16, 247–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- James, A.W.; LaChaud, G.; Shen, J.; Asatrian, G.; Nguyen, V.; Zhang, X.; Ting, K.; Soo, C. A review of the clinical side effects of bone morphogenetic protein-2. Tissue Eng. Part B Rev. 2016, 22, 284–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burkus, J.K.; Transfeldt, E.E.; Kitchel, S.H.; Watkins, R.G.; Balderston, R.A. Clinical and radiographic outcomes of anterior lumbar interbody fusion using recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein-2. Spine 2002, 27, 2396–2408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Food and Drug Administration. FDA Public Health Notification: Life-threatening Complications Associated with Recombinant Human Bone Morphogenetic Protein in Cervical Spine Fusion. 2008. Available online: http://www.fda.gov/cdrh/safety/070108-rhbmp.html (accessed on 17 February 2018).
- Craik, D.J.; Fairlie, D.P.; Liras, S.; Price, D. The future of peptide-based drugs. Chem. Biol. Drug Des. 2013, 81, 136–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliver-Cervelló, L.; Martin-Gómez, H.; Mas-Moruno, C. New trends in the development of multifunctional peptides to functionalize biomaterials. J. Pept. Sci. 2021, e3335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maity, P.P.; Dutta, D.; Ganguly, S.; Kapat, K.; Dixit, K.; Chowdhury, A.R.; Samanta, R.; Das, N.C.; Datta, P.; Das, A.K. Isolation and mass spectrometry based hydroxyproline mapping of type II collagen derived from Capra hircus ear cartilage. Commun. Biol. 2019, 2, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, Y.; Tanihara, M.; Suzuki, K.; Saitou, A.; Sufan, W.; Nishimura, Y. Alginate hydrogel linked with synthetic oligopeptide derived from BMP-2 allows ectopic osteoinduction in vivo. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Off. J. Soc. Biomater. Jpn. Soc. Biomater. Aust. Soc. Biomater. Korean Soc. Biomater. 2000, 50, 405–409. [Google Scholar]
- Allendorph, G.P.; Vale, W.W.; Choe, S. Structure of the ternary signaling complex of a TGF-β superfamily member. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 7643–7648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yu, P.B.; Beppu, H.; Kawai, N.; Li, E.; Bloch, K.D. Bone morphogenetic protein (BMP) type II receptor deletion reveals BMP ligand-specific gain of signaling in pulmonary artery smooth muscle cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 24443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Saito, A.; Suzuki, Y.; Ogata, S.-i.; Ohtsuki, C.; Tanihara, M. Activation of osteo-progenitor cells by a novel synthetic peptide derived from the bone morphogenetic protein-2 knuckle epitope. Biochim. et Biophys. Acta BBA Proteins Proteom. 2003, 1651, 60–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madl, C.M.; Mehta, M.; Duda, G.N.; Heilshorn, S.C.; Mooney, D.J. Presentation of BMP-2 mimicking peptides in 3D hydrogels directs cell fate commitment in osteoblasts and mesenchymal stem cells. Biomacromolecules 2014, 15, 445–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bilem, I.; Chevallier, P.; Plawinski, L.; Sone, E.; Durrieu, M.-C.; Laroche, G. RGD and BMP-2 mimetic peptide crosstalk enhances osteogenic commitment of human bone marrow stem cells. Acta Biomater. 2016, 36, 132–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hruby, V.J. Designing peptide receptor agonists and antagonists. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2002, 1, 847–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gongora-Benitez, M.; Tulla-Puche, J.; Albericio, F. Multifaceted roles of disulfide bonds. Peptides as therapeutics. Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 901–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; Li, J.; Kang, L.; Zhang, N.; Huang, C.; He, Y.; Hu, M.; Zhou, X.; Zhang, J. Machine learning-guided design and development of multifunctional flexible Ag/poly (amic acid) composites using the differential evolution algorithm. Nanoscale 2020, 12, 3988–3996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katagiri, T.; Yamaguchi, A.; Komaki, M.; Abe, E.; Takahashi, N.; Ikeda, T.; Rosen, V.; Wozney, J.M.; Fujisawa-Sehara, A.; Suda, T. Bone morphogenetic protein-2 converts the differentiation pathway of C2C12 myoblasts into the osteoblast lineage. J. Cell Biol. 1994, 127, 1755–1766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tong, Z.; Guo, J.; Glen, R.C.; Morrell, N.W.; Li, W. A Bone Morphogenetic Protein (BMP)-derived Peptide Based on the Type I Receptor-binding Site Modifies Cell-type Dependent BMP Signalling. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, J.; Perikamana, S.K.M.; Ahmad, T.; Lee, M.S.; Yang, H.S.; Kim, D.-G.; Kim, K.; Kwon, B.; Shin, H. Controlled retention of BMP-2-derived peptide on nanofibers based on mussel-inspired adhesion for bone formation. Tissue Eng. Part A 2017, 23, 323–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.; Renner, J.N.; Liu, J.C. Incorporating the BMP-2 peptide in genetically-engineered biomaterials accelerates osteogenic differentiation. Biomater. Sci. 2014, 2, 1110–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mace, P.D.; Cutfield, J.F.; Cutfield, S.M. High resolution structures of the bone morphogenetic protein type II receptor in two crystal forms: Implications for ligand binding. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2006, 351, 831–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiyota, S.; Franzoni, L.; Nicastro, G.; Benedetti, A.; Oyama, S.; Viviani, W.; Gambarini, A.G.; Spisni, A.; Miranda, M.T.M. Introduction of a chemical constraint in a short peptide derived from human acidic fibroblast growth factor elicits mitogenic structural determinants. J. Med. Chem. 2003, 46, 2325–2333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





| Compound Name | Structure and Molecular Weight (MW) | Observed Mass [M+2H]2+ | Observed Mass [M+3H]3+ |
|---|---|---|---|
| P-01 |  | 1059.62 | 706.74 |
| P-02 |  | 1090.8 | 726.53 |
| P-03 |  | 1161.61 | 774.74 |
| P-04 |  | 1161.61 | 774.74 |
| P-05 |  | 1161.61 | 774.74 |
| Compound Name | Association Rate Constant ka (M−1s−1) | Dissociation Rate Constant kd (s−1) | Equilibrium Rate Constant KD (M) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Linear peptide (P01) | 2.7 × 10−1 | 2.21 × 10−2 | 8.16 × 10−2 |
| N-and C-terminal free peptide (P-02) | Saturation binding curve | Saturation binding curve | 8.06 × 10−5 |
| N-terminal cyclic peptide (P-03) | 3.52 × 102 | 3.33 × 10−2 | 9.46 × 10−5 |
| C-terminal cyclic peptide (P-04) | 4.60 × 102 | 1.06 × 10−2 | 2.31 × 10−5 |
| N- to C-terminal cyclic peptide (P-05) | 3.78 × 101 | 4.87 × 10−4 | 1.29 × 10−5 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gudivada, V.N.; Huang, C.-J.; Luo, Y.-H.; Dong, G.-C. A Cyclic BMP-2 Peptide Upregulates BMP-2 Protein-Induced Cell Signaling in Myogenic Cells. Polymers 2021, 13, 2549. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13152549
Gudivada VN, Huang C-J, Luo Y-H, Dong G-C. A Cyclic BMP-2 Peptide Upregulates BMP-2 Protein-Induced Cell Signaling in Myogenic Cells. Polymers. 2021; 13(15):2549. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13152549
Chicago/Turabian StyleGudivada, Vijaya Narasimha, Chen-Ji Huang, Yueh-Hsia Luo, and Guo-Chung Dong. 2021. "A Cyclic BMP-2 Peptide Upregulates BMP-2 Protein-Induced Cell Signaling in Myogenic Cells" Polymers 13, no. 15: 2549. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13152549
APA StyleGudivada, V. N., Huang, C. -J., Luo, Y. -H., & Dong, G. -C. (2021). A Cyclic BMP-2 Peptide Upregulates BMP-2 Protein-Induced Cell Signaling in Myogenic Cells. Polymers, 13(15), 2549. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13152549