Cooperative Effects of Cellulose Nanocrystals and Sepiolite When Combined on Ionic Liquid Plasticised Chitosan Materials
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Sample Preparation
2.3. Characterisation
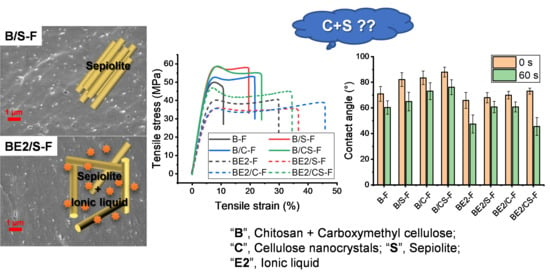
3. Results
3.1. Morphology, Molecular Interactions, and Crystalline Structure of the Chitosan-Based Composites
3.2. Properties of Chitosan-Based Composites
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Alexandridis, P.; Ghasemi, M.; Furlani, E.P.; Tsianou, M. Solvent processing of cellulose for effective bioresource utilization. Curr. Opin. Green Sustain. Chem. 2018, 14, 40–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Lu, A.; Zhang, L. Recent advances in regenerated cellulose materials. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2016, 53, 169–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muxika, A.; Etxabide, A.; Uranga, J.; Guerrero, P.; de la Caba, K. Chitosan as a bioactive polymer: Processing, properties and applications. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 105, 1358–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rinaudo, M. Chitin and chitosan: Properties and applications. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2006, 31, 603–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravi Kumar, M.N.V. A review of chitin and chitosan applications. React. Funct. Polym. 2000, 46, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsabee, M.Z.; Abdou, E.S. Chitosan based edible films and coatings: A review. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2013, 33, 1819–1841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Roman, M. Formation and Properties of Chitosan−Cellulose Nanocrystal Polyelectrolyte−Macroion Complexes for Drug Delivery Applications. Biomacromolecules 2011, 12, 1585–1593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereda, M.; Dufresne, A.; Aranguren, M.I.; Marcovich, N.E. Polyelectrolyte films based on chitosan/olive oil and reinforced with cellulose nanocrystals. Carbohydr. Polym. 2014, 101, 1018–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, F.; Biagioni, P.; Finazzi, M.; Tavazzi, S.; Piergiovanni, L. Tunable green oxygen barrier through layer-by-layer self-assembly of chitosan and cellulose nanocrystals. Carbohydr. Polym. 2013, 92, 2128–2134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karim, Z.; Mathew, A.P.; Grahn, M.; Mouzon, J.; Oksman, K. Nanoporous membranes with cellulose nanocrystals as functional entity in chitosan: Removal of dyes from water. Carbohydr. Polym. 2014, 112, 668–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marrakchi, F.; Khanday, W.A.; Asif, M.; Hameed, B.H. Cross-linked chitosan/sepiolite composite for the adsorption of methylene blue and reactive orange 16. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2016, 93, 1231–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Enescu, D.; Gardrat, C.; Cramail, H.; Le Coz, C.; Sèbe, G.; Coma, V. Bio-inspired films based on chitosan, nanoclays and cellulose nanocrystals: Structuring and properties improvement by using water-evaporation-induced self-assembly. Cellulose 2019, 26, 2389–2401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.; Xie, F.; Tang, F.; McNally, T. Thermomechanical-induced polyelectrolyte complexation between chitosan and carboxymethyl cellulose enabling unexpected hydrolytic stability. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2020, 189, 108031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basu, S.; Plucinski, A.; Catchmark, J.M. Sustainable barrier materials based on polysaccharide polyelectrolyte complexes. Green Chem. 2017, 19, 4080–4092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Ramay, H.R.; Hauch, K.D.; Xiao, D.; Zhang, M. Chitosan–alginate hybrid scaffolds for bone tissue engineering. Biomaterials 2005, 26, 3919–3928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, C.; Zhu, X.; Peng, H.; Chen, J.; Zhang, F.; Zhao, Q. Facile Preparation of Lignin-Based Underwater Adhesives with Improved Performances. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 4508–4514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, L.; Xie, F.; Zhang, B.; Wang, D.K.; Yu, L. Natural Biopolymer Alloys with Superior Mechanical Properties. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 2792–2802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Iwasaki, N.; Yamane, S.-T.; Majima, T.; Kasahara, Y.; Minami, A.; Harada, K.; Nonaka, S.; Maekawa, N.; Tamura, H.; Tokura, S.; et al. Feasibility of Polysaccharide Hybrid Materials for Scaffolds in Cartilage Tissue Engineering: Evaluation of Chondrocyte Adhesion to Polyion Complex Fibers Prepared from Alginate and Chitosan. Biomacromolecules 2004, 5, 828–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, F.; Wang, J.; Xie, F.; Zan, K.; Wang, S.; Wang, S. Applications of ionic liquids in starch chemistry: A review. Green Chem. 2020, 22, 2162–2183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, F.; Flanagan, B.M.; Li, M.; Sangwan, P.; Truss, R.W.; Halley, P.J.; Strounina, E.V.; Whittaker, A.K.; Gidley, M.J.; Dean, K.M.; et al. Characteristics of starch-based films plasticised by glycerol and by the ionic liquid 1-ethyl-3-methylimidazolium acetate: A comparative study. Carbohydr. Polym. 2014, 111, 841–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xie, F.; Flanagan, B.M.; Li, M.; Truss, R.W.; Halley, P.J.; Gidley, M.J.; McNally, T.; Shamshina, J.L.; Rogers, R.D. Characteristics of starch-based films with different amylose contents plasticised by 1-ethyl-3-methylimidazolium acetate. Carbohydr. Polym. 2015, 122, 160–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, B.; Xie, F.; Zhang, T.; Chen, L.; Li, X.; Truss, R.W.; Halley, P.J.; Shamshina, J.L.; McNally, T.; Rogers, R.D. Different characteristic effects of ageing on starch-based films plasticised by 1-ethyl-3-methylimidazolium acetate and by glycerol. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 146, 67–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, B.; Xie, F.; Shamshina, J.L.; Rogers, R.D.; McNally, T.; Wang, D.K.; Halley, P.J.; Truss, R.W.; Zhao, S.; Chen, L. Facile Preparation of Starch-Based Electroconductive Films with Ionic Liquid. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2017, 5, 5457–5467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sankri, A.; Arhaliass, A.; Dez, I.; Gaumont, A.C.; Grohens, Y.; Lourdin, D.; Pillin, I.; Rolland-Sabaté, A.; Leroy, E. Thermoplastic starch plasticized by an ionic liquid. Carbohydr. Polym. 2010, 82, 256–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leroy, E.; Jacquet, P.; Coativy, G.; Reguerre, A.L.; Lourdin, D. Compatibilization of starch–zein melt processed blends by an ionic liquid used as plasticizer. Carbohydr. Polym. 2012, 89, 955–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colomines, G.; Decaen, P.; Lourdin, D.; Leroy, E. Biofriendly ionic liquids for starch plasticization: A screening approach. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 90331–90337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Decaen, P.; Rolland-Sabaté, A.; Guilois, S.; Jury, V.; Allanic, N.; Colomines, G.; Lourdin, D.; Leroy, E. Choline chloride vs choline ionic liquids for starch thermoplasticization. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 177, 424–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.; Xie, F.; Tang, F.; McNally, T. Structure and properties of thermomechanically processed silk peptide and nanoclay filled chitosan. Nanocomposites 2020, 6, 125–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.; Xie, F.; Tang, F.; McNally, T. Ionic Liquid (1-Ethyl-3-methylimidazolium Acetate) Plasticization of Chitosan-Based Bionanocomposites. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 19070–19081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Lima, J.A.; Camilo, F.F.; Faez, R.; Cruz, S.A. A new approch to sepiolite dispersion by treatment with ionic liquids. Appl. Clay Sci. 2017, 143, 234–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chivrac, F.; Pollet, E.; Schmutz, M.; Avérous, L. Starch nano-biocomposites based on needle-like sepiolite clays. Carbohydr. Polym. 2010, 80, 145–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darder, M.; López-Blanco, M.; Aranda, P.; Aznar, A.J.; Bravo, J.; Ruiz-Hitzky, E. Microfibrous Chitosan−Sepiolite Nanocomposites. Chem. Mater. 2006, 18, 1602–1610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abitbol, T.; Kam, D.; Levi-Kalisman, Y.; Gray, D.G.; Shoseyov, O. Surface Charge Influence on the Phase Separation and Viscosity of Cellulose Nanocrystals. Langmuir 2018, 34, 3925–3933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lawrie, G.; Keen, I.; Drew, B.; Chandler-Temple, A.; Rintoul, L.; Fredericks, P.; Grøndahl, L. Interactions between Alginate and Chitosan Biopolymers Characterized Using FTIR and XPS. Biomacromolecules 2007, 8, 2533–2541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawlak, A.; Mucha, M. Thermogravimetric and FTIR studies of chitosan blends. Thermochim. Acta 2003, 396, 153–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Mo, X.; He, C.; Wang, H. Intermolecular interactions in electrospun collagen–chitosan complex nanofibers. Carbohydr. Polym. 2008, 72, 410–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quijada-Garrido, I.; Laterza, B.; Mazón-Arechederra, J.M.; Barrales-Rienda, J.M. Characteristic Features of Chitosan/Glycerol Blends Dynamics. Macromol. Chem. Phys. 2006, 207, 1742–1751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quijada-Garrido, I.; Iglesias-González, V.; Mazón-Arechederra, J.M.; Barrales-Rienda, J.M. The role played by the interactions of small molecules with chitosan and their transition temperatures. Glass-forming liquids: 1,2,3-Propantriol (glycerol). Carbohydr. Polym. 2007, 68, 173–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.; Xie, F.; Tang, F.; McNally, T. Influence of plasticiser type and nanoclay on the properties of chitosan-based materials. Eur. Polym. J. 2021, 144, 110225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Sample | Chitosan | CMC | [C2mim][OAc] | SPT | CNCs | 2M Formic Acid Solution |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A/S-F | 100 | – | – | 0.75 | – | 261 |
| A/C-F | 100 | – | – | – | 0.75 | 261 |
| A/CS-F | 100 | – | – | 0.325 | 0.325 | 261 |
| AE2/S-F | 100 | 20 | 0.75 | – | 261 | |
| AE2/C-F | 100 | – | 20 | – | 0.75 | 261 |
| AE2/CS-F | 100 | 20 | 0.325 | 0.325 | 261 | |
| B/S-F | 50 | 50 | – | 0.75 | – | 261 |
| B/C-F | 50 | 50 | – | – | 0.75 | 261 |
| B/CS-F | 50 | 50 | – | 0.325 | 0.325 | 261 |
| BE2/S-F | 50 | 50 | 20 | 0.75 | – | 261 |
| BE2/C-F | 50 | 50 | 20 | – | 0.75 | 261 |
| BE2/CS-F | 50 | 50 | 20 | 0.325 | 0.325 | 261 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, P.; Xie, F.; Tang, F.; McNally, T. Cooperative Effects of Cellulose Nanocrystals and Sepiolite When Combined on Ionic Liquid Plasticised Chitosan Materials. Polymers 2021, 13, 571. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13040571
Chen P, Xie F, Tang F, McNally T. Cooperative Effects of Cellulose Nanocrystals and Sepiolite When Combined on Ionic Liquid Plasticised Chitosan Materials. Polymers. 2021; 13(4):571. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13040571
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Pei, Fengwei Xie, Fengzai Tang, and Tony McNally. 2021. "Cooperative Effects of Cellulose Nanocrystals and Sepiolite When Combined on Ionic Liquid Plasticised Chitosan Materials" Polymers 13, no. 4: 571. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13040571
APA StyleChen, P., Xie, F., Tang, F., & McNally, T. (2021). Cooperative Effects of Cellulose Nanocrystals and Sepiolite When Combined on Ionic Liquid Plasticised Chitosan Materials. Polymers, 13(4), 571. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13040571