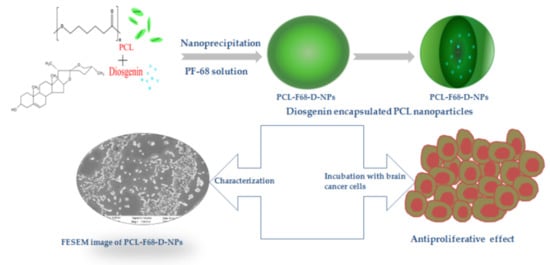
Synthesis and Characterization of Diosgenin Encapsulated Poly-ε-Caprolactone-Pluronic Nanoparticles and Its Effect on Brain Cancer Cells
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Nanoparticle Preparation
2.3. DLS, PDI, and Zeta Potential
2.4. FTIR
2.5. XRD
2.6. FESEM
2.7. TEM
2.8. Diosgenin Loading, Encapsulation Efficiency, and Yield of Production
2.9. In Vitro Drug Release Assay and Release Kinetics
2.10. In Vitro Cytotoxicity Study of Diosgenin-Loaded Nanoparticles
2.11. Cell Morphology of Diosgenin-Loaded Nanoparticles
2.12. Live/Dead Assay
2.13. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. DLS, PDI, and Zeta Potential
3.2. FTIR
3.3. X-ray Diffraction
3.4. FESEM
3.5. TEM
3.6. Encapsulation Efficiency, Diosgenin Loading, Yield of Production
3.7. In Vitro Drug Release Studies
3.8. In Vitro Cytotoxicity Assay
3.9. Cell Morphology Assessment
3.10. Live/Dead Assay
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bray, F.; Ferlay, J.; Soerjomataram, I.; Siegel, R.L.; Torre, L.A.; Jemal, A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2018, 68, 394–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Costa, D.; Valente, A.J.M.; Queiroz, J.A.; Sousa, Â. Finding the ideal polyethylenimine-plasmid DNA system for co-delivery of payloads in cancer therapy. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2018, 170, 627–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bidram, E.; Esmaeili, Y.; Ranji-Burachaloo, H.; Al-Zaubai, N.; Zarrabi, A.; Stewart, A.; Dunstan, D.E. A concise review on cancer treatment methods and delivery systems. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2019, 54, 101350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mentlein, R.; Forstreuter, F.; Mehdorn, H.M.; Held-Feindt, J. Functional significance of vascular endothelial growth factor receptor expression on human glioma cells. J. Neurooncol. 2004, 67, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, L.; Eckley, M.; Wargo, K. A review of glioblastomamultiforme. Oncology 2010, 35, 3–10. [Google Scholar]
- Ostrom, Q.T.; Gittleman, H.; Xu, J.; Kromer, C.; Wolinsky, Y.; Kruchko, C.; Barnholtz-Sloan, J.S. CBTRUS Statistical Report: Primary Brain and Other Central Nervous System Tumors Diagnosed in the United States in 2009–2013. Neuro. Oncol. 2016, 18, v1–v75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Adamson, C.; Kanu, O.O.; Mehta, A.I.; Di, C.; Lin, N.; Mattox, A.K.; Bigner, D.D. Glioblastomamultiforme: A review of where we have been and where we are going. Expert Opin. Investig. Drugs 2009, 18, 1061–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, B.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Xu, D.; Jia, Y.; Guan, Y.; Liao, A.; Liu, G.; Chun, C.; Li, J. Therapeutic Potential of Diosgenin and Its Major Derivatives against Neurological Diseases: Recent Advances. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2020, 2020, 3153082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mazumder, A.; Cerella, C.; Diederich, M. Natural scaffolds in anticancer therapy and precision medicine. Biotechnol. Adv. 2018, 36, 1563–1585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selim, S.; Al Jaouni, S. Anticancer and apoptotic effects on cell proliferation of diosgenin isolated from Costusspeciosus (Koen.) Sm. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2015, 15, 301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yuan, B.; Byrnes, D.R.; Dinssa, F.F.; Simon, J.E.; Wu, Q. Identification of Polyphenols, Glycoalkaloids, and Saponins in Solanumscabrum Berries Using HPLC-UV/Vis-MS. J. Food Sci. 2019, 84, 235–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Narula, A.; Kumar, S.; Srivastava, P.S. Genetic fidelity of in vitro regenerants, encapsulation of shoot tips and high diosgenin content in Dioscoreabulbifera L., a potential alternative source of diosgenin. Biotechnol. Lett. 2007, 29, 623–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sethi, G.; Shanmugam, M.K.; Warrier, S.; Merarchi, M.; Arfuso, F.; Kumar, A.P.; Bishayee, A. Pro-Apoptotic and Anti-Cancer Properties of Diosgenin: A Comprehensive and Critical Review. Nutrients 2018, 10, 645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hajizadeh, M.R.; Parvaz, N.; Barani, M.; Khoshdel, A.; Fahmidehkar, M.A.; Mahmoodi, M.; Torkzadeh-Mahani, M. Diosgenin-loaded niosome as an effective phytochemical nanocarrier: Physicochemical characterization, loading efficiency, and cytotoxicity assay. DARU J. Pharm. Sci. 2019, 27, 329–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, S.; Dey, K.K.; Dey, G.; Pal, I.; Majumder, A.; MaitiChoudhury, S.; Kundu, S.C.; Mandal, M. Antineoplastic and apoptotic potential of traditional medicines thymoquinone and diosgenin in squamous cell carcinoma. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e46641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Srinivasan, S.; Koduru, S.; Kumar, R.; Venguswamy, G.; Kyprianou, N.; Damodaran, C. Diosgenin targets Akt-mediated prosurvival signaling in human breast cancer cells. Int. J. Cancer 2009, 125, 961–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, S.; Fan, J.; Wang, Q.; Ju, D.; Feng, M.; Li, J.; Guan, Z.-B.; An, D.; Wang, X.; Ye, L. Diosgenin induces ROS-dependent autophagy and cytotoxicity via mTOR signaling pathway in chronic myeloid leukemia cells. Phytomedicine 2016, 23, 243–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khathayer, F.; Ray, S.K. Diosgenin as a Novel Alternative Therapy for Inhibition of Growth, Invasion, and Angiogenesis Abilities of Different Glioblastoma Cell Lines. Neurochem. Res. 2020, 45, 2336–2351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Binesh, A.; Devaraj, S.N.; Halagowder, D. Atherogenic diet induced lipid accumulation induced NFκB level in heart, liver and brain of Wistar rat and diosgenin as an anti-inflammatory agent. Life Sci. 2018, 196, 28–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uchegbu, I.F.; Vyas, S.P. Non-ionic surfactant based vesicles (niosomes) in drug delivery. Int. J. Pharm. 1998, 172, 33–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jesus, M.; Martins, A.P.J.; Gallardo, E.; Silvestre, S. Diosgenin: Recent Highlights on Pharmacology and Analytical Methodology. J. Anal. Methods Chem. 2016, 2016, 4156293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Ho, W.; Zhang, X.; Bertrand, N.; Farokhzad, O. Cancer nanomedicine: From targeted delivery to combination therapy. Trends Mol. Med. 2015, 21, 223–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ebrahimi, A.K.; Barani, M.; Sheikhshoaie, I. Fabrication of a new superparamagnetic metal-organic framework with core-shell nanocomposite structures: Characterization, biocompatibility, and drug release study. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2018, 92, 349–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.; Zheng, H.; Xu, J.; Shi, X.; Li, F.; Wang, X. Sustained-release study on Exenatide loaded into mesoporous silica nanoparticles: In vitro characterization and in vivo evaluation. DARU J. Pharm. Sci. 2017, 25, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williford, J.-M.; Archang, M.M.; Minn, I.; Ren, Y.; Wo, M.; Vandermark, J.; Fisher, P.B.; Pomper, M.G.; Mao, H.-Q. Critical Length of PEG Grafts on lPEI/DNA Nanoparticles for Efficient in Vivo Delivery. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2016, 2, 567–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moser, B.A.; Steinhardt, R.C.; Esser-Kahn, A.P. Surface Coating of Nanoparticles Reduces Background Inflammatory Activity while Increasing Particle Uptake and Delivery. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2017, 3, 206–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lancina, M.G.; Singh, S.; Kompella, U.B.; Husain, S.; Yang, H. Fast Dissolving DendrimerNanofiber Mats as Alternative to Eye Drops for More Efficient Antiglaucoma Drug Delivery. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2017, 3, 1861–1868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grottkau, B.E.; Cai, X.; Wang, J.; Yang, X.; Lin, Y. Polymeric nanoparticles for a drug delivery system. Curr. Drug Metab. 2013, 14, 840–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rao, J.P.; Geckeler, K.E. Polymer nanoparticles: Preparation techniques and size-control parameters. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2011, 36, 887–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schroeder, U.; Sommerfeld, P.; Ulrich, S.; Sabel, B.A. Nanoparticle technology for delivery of drugs across the blood-brain barrier. J. Pharm. Sci. 1998, 87, 1305–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shenoy, D.B.; Amiji, M.M. Poly(ethylene oxide)-modified poly(epsilon-caprolactone) nanoparticles for targeted delivery of tamoxifen in breast cancer. Int. J. Pharm. 2005, 293, 261–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Budhian, A.; Siegel, S.J.; Winey, K.I. Production of haloperidol-loaded PLGA nanoparticles for extended controlled drug release of haloperidol. J. Microencapsul. 2005, 22, 773–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gómez-Gaete, C.; Tsapis, N.; Besnard, M.; Bochot, A.; Fattal, E. Encapsulation of dexamethasone into biodegradable polymeric nanoparticles. Int. J. Pharm. 2007, 331, 153–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mei, L.; Zhang, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Tian, G.; Song, C.; Yangqing, Z.; Chen, H.; Sun, H.; Tian, Y.; Liu, K.; et al. A Novel Docetaxel-Loaded Poly (ε-Caprolactone)/Pluronic F68 Nanoparticle Overcoming Multidrug Resistance for Breast Cancer Treatment. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2009, 4, 1530–1539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Daraba, O.M.; Cadinoiu, A.N.; Rata, D.M.; Atanase, L.I.; Vochita, G. Antitumoral Drug-Loaded Biocompatible Polymeric Nanoparticles Obtained by Non-Aqueous Emulsion Polymerization. Polymers 2020, 12, 1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qhattal, H.S.S.; Hye, T.; Alali, A.; Liu, X. Hyaluronan polymer length, grafting density, and surface poly(ethylene glycol) coating influence in vivo circulation and tumor targeting of hyaluronan-grafted liposomes. ACS Nano 2014, 8, 5423–5440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, A.; Fauzia, E.; Kumar, M.; Mishra, R.K.; Kumar, A.; Khan, M.A.; Raza, S.S.; Khan, R. Gelatin-Coated Polycaprolactone Nanoparticle-Mediated Naringenin Delivery Rescue Human Mesenchymal Stem Cells from Oxygen Glucose Deprivation-Induced Inflammatory Stress. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2019, 5, 683–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, H.; Qian, J.; Yang, Z.; Pang, Z.; Xi, Z.; Cao, S.; Wang, Y.; Pan, S.; Zhang, S.; Wang, W.; et al. Whole-cell SELEX aptamer-functionalised poly(ethyleneglycol)-poly(ε-caprolactone) nanoparticles for enhanced targeted glioblastoma therapy. Biomaterials 2012, 33, 6264–6272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanna, V.; Chamcheu, J.C.; Pala, N.; Mukhtar, H.; Sechi, M.; Siddiqui, I.A. Nanoencapsulation of natural triterpenoidcelastrol for prostate cancer treatment. Int. J. Nanomed. 2015, 10, 6835–6846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pati, S.; Chatterji, A.; Dash, B.P.; Nelson, B.R.; Sarkar, T.; Shahimi, S.; Edinur, H.A.; AbdManan, T.S.B.; Jena, P.; Mohanta, Y.K.; et al. Structural characterization and antioxidant potential of chitosan by γ-irradiation from the carapace of horseshoe crab. Polymers 2020, 12, 2361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pati, S.; Jena, P.; Shahimi, S.; Nelson, B.R.; Acharya, D.; Dash, B.P.; Chatterji, A. Characterization dataset for pre- and post-irradiated shrimp waste chitosan. Data Br. 2020, 32, 106081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, T.; Salauddin, M.; Kumar Hazra, S.; Chakraborty, R. A novel data science application approach for classification of nutritional composition, instrumental colour, texture and sensory analysis of bael fruit (Aeglemarmelos (L) correa). Int. J. Intell. Networks 2020, 1, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, N.; Singhal, M.; Kumari, R.M.; Gupta, N.; Manchanda, R.; Syed, A.; Bahkali, A.H.; Nimesh, S. Diosgenin Loaded Polymeric Nanoparticles with Potential Anticancer Efficacy. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 1679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghosh, P.; Bag, S.; Singha Roy, A.; Subramani, E.; Chaudhury, K.; Dasgupta, S. Solubility enhancement of morin and epicatechin through encapsulation in an albumin based nanoparticulate system and their anticancer activity against the MDA-MB-468 breast cancer cell line. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 101415–101429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desai, M.P.; Labhasetwar, V.; Walter, E.; Levy, R.J.; Amidon, G.L. The Mechanism of Uptake of Biodegradable Microparticles in Caco-2 Cells Is Size Dependent. Pharm. Res. 1997, 14, 1568–1573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zauner, W.; Farrow, N.A.; Haines, A.M. In vitro uptake of polystyrene microspheres: Effect of particle size, cell line and cell density. J. Control. Release 2001, 71, 39–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benita, S.; Levy, M.Y. Submicron emulsions as colloidal drug carriers for intravenous administration: Comprehensive physicochemical characterization. J. Pharm. Sci. 1993, 82, 1069–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parashar, P.; Rathor, M.; Dwivedi, M.; Saraf, S.A. Hyaluronic Acid Decorated Naringenin Nanoparticles: Appraisal of Chemopreventive and Curative Potential for Lung Cancer. Pharmaceutics 2018, 10, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ferraris, S.; Cazzola, M.; Peretti, V.; Stella, B.; Spriano, S. Zeta Potential Measurements on Solid Surfaces for in Vitro Biomaterials Testing: Surface Charge, Reactivity Upon Contact with Fluids and Protein Absorption. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2018, 6, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, S.; More, P.; Derle, A.; Kitture, R.; Kale, T.; Gorain, M.; Avasthi, A.; Markad, P.; Kundu, G.C.; Kale, S.; et al. Diosgenin Functionalized Iron Oxide Nanoparticles as Novel Nanomaterial Against Breast Cancer. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2015, 15, 9464–9472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Zhang, J. Enhanced oral bioavailability of EGCG using pH-sensitive polymeric nanoparticles: Characterization and in vivo investigation on nephrotic syndrome rats. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2018, 12, 2509–2518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chaurasia, S.; Patel, R.R.; Vure, P.; Mishra, B. Oral naringeninnanocarriers: Fabrication, optimization, pharmacokinetic and chemotherapeutic efficacy assessments. Nanomedicine 2017, 12, 1243–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agarwal, M.; Sahoo, A.K.; Bose, B. Receptor-Mediated Enhanced Cellular Delivery of Nanoparticles Using Recombinant Receptor-Binding Domain of Diphtheria Toxin. Mol. Pharm. 2017, 14, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fazio, E.; Scala, A.; Grimato, S.; Ridolfo, A.; Grassi, G.; Neri, F. Laser light triggered smart release of silibinin from a PEGylated–PLGA gold nanocomposite. J. Mater. Chem. B 2015, 3, 9023–9032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yadav, K.S.; Chuttani, K.; Mishra, A.K.; Sawant, K.K. Effect of Size on the Biodistribution and Blood Clearance of Etoposide-Loaded PLGA Nanoparticles. PDA J. Pharm. Sci. Technol. 2011, 65, 131–139. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Muralidharan, S.; Shanmugam, K. Synthesis and Characterization of Naringenin-Loaded Chitosan-Dextran Sulfate Nanocarrier. J. Pharm. Innov. 2020, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IlkarErdagi, S.; Yildiz, U. Diosgenin-conjugated PCL–MPEG polymeric nanoparticles for the co-delivery of anticancer drugs: Design, optimization, in vitro drug release and evaluation of anticancer activity. New J. Chem. 2019, 43, 6622–6635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wang, B.M.; Schwendeman, S.P. Characterization of the initial burst release of a model peptide from poly(D,L-lactide-co-glycolide) microspheres. J. Control. Release 2002, 82, 289–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaikh, H.K.; Kshirsagar, R.; Patil, S. Mathematical models for drug release characterization: A review. World J. Pharm. Sci. 2015, 4, 324–338. [Google Scholar]
- Budiasih, S.; Jiyauddin, K.; Logavinod, N.; Kaleemullah, M.; Jawad, A.; Samer, A.; Fadli, A.; Eddy, Y. Optimization of polymer concentration for designing of oral matrix-controlled release dosage form. Pharm. Biosci. J. 2014, 2, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jagadeesan, J.; Nandakumar, N.; Rengarajan, T.; Balasubramanian, M.P. Diosgenin, a steroidal saponin, exhibits anticancer activity by attenuating lipid peroxidation via enhancing antioxidant defense system during NMU-induced breast carcinoma. J. Environ. Pathol. Toxicol. Oncol. 2012, 31, 121–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fonseca, C.; Simões, S.; Gaspar, R. Paclitaxel-loaded PLGA nanoparticles: Preparation, physicochemical characterization and in vitro anti-tumoral activity. J. Control. Release 2002, 83, 273–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ćurčić, M.G.; Stanković, M.S.; Mrkalić, E.M.; Matović, Z.D.; Banković, D.D.; Cvetković, D.M.; Đačić, D.S.; Marković, S.D. Antiproliferative and proapoptotic activities of methanolic extracts from Ligustrumvulgare L. as an individual treatment and in combination with palladium complex. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2012, 13, 2521–2534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hajrezaie, M.; Paydar, M.; Looi, C.Y.; Moghadamtousi, S.Z.; Hassandarvish, P.; Salga, M.S.; Karimian, H.; Shams, K.; Zahedifard, M.; Majid, N.A.; et al. Apoptotic effect of novel Schiff based CdCl₂(C₁₄H₂₁N₃O₂) complex is mediated via activation of the mitochondrial pathway in colon cancer cells. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 9097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hashim, F.; Shawkat, M.; Aljewari, H. Anti-cancer effect of curcuma longa on leukemic cell lines evaluated by apoptosis and comet assay. Int. J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 2013, 5, 671–674. [Google Scholar]
- RahbarSaadat, Y.; Saeidi, N.; ZununiVahed, S.; Barzegari, A.; Barar, J. An update to DNA ladder assay for apoptosis detection. Bioimpacts 2015, 5, 25–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]








| Batch | Particle Size (nm) | PDI | Zeta Potential (mV) |
|---|---|---|---|
| PCL-F68 NPs | 193.7 | 0.463 | −22.3 |
| PCL-F68 D NPs | 245.1 | 0.367 | −11.5 |
| Polymer NPs | % DL | % EE | % YP |
|---|---|---|---|
| PCL-F68-D NP | 10.3 ± 0.31% | 80.8 ± 0.26% | 68.02 ± 0.1 |
| Dissolution Condition | Zero Order (R2) | First Order (R2) | Higuchi Model (R2) | Korsmeyer–Peppas Model (R2) | Release Exponent Value (n) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH 6.5 | 0.779 | 0.605 | 0.915 | 0.947 | 0.42 |
| pH 7.4 | 0.776 | 0.645 | 0.894 | 0.951 | 0.37 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rabha, B.; Bharadwaj, K.K.; Baishya, D.; Sarkar, T.; Edinur, H.A.; Pati, S. Synthesis and Characterization of Diosgenin Encapsulated Poly-ε-Caprolactone-Pluronic Nanoparticles and Its Effect on Brain Cancer Cells. Polymers 2021, 13, 1322. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13081322
Rabha B, Bharadwaj KK, Baishya D, Sarkar T, Edinur HA, Pati S. Synthesis and Characterization of Diosgenin Encapsulated Poly-ε-Caprolactone-Pluronic Nanoparticles and Its Effect on Brain Cancer Cells. Polymers. 2021; 13(8):1322. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13081322
Chicago/Turabian StyleRabha, Bijuli, Kaushik Kumar Bharadwaj, Debabrat Baishya, Tanmay Sarkar, Hisham Atan Edinur, and Siddhartha Pati. 2021. "Synthesis and Characterization of Diosgenin Encapsulated Poly-ε-Caprolactone-Pluronic Nanoparticles and Its Effect on Brain Cancer Cells" Polymers 13, no. 8: 1322. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13081322
APA StyleRabha, B., Bharadwaj, K. K., Baishya, D., Sarkar, T., Edinur, H. A., & Pati, S. (2021). Synthesis and Characterization of Diosgenin Encapsulated Poly-ε-Caprolactone-Pluronic Nanoparticles and Its Effect on Brain Cancer Cells. Polymers, 13(8), 1322. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13081322