Supercritical CO2 Foaming of Poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-4-hydroxybutyrate)
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental
3. Results and Discussion
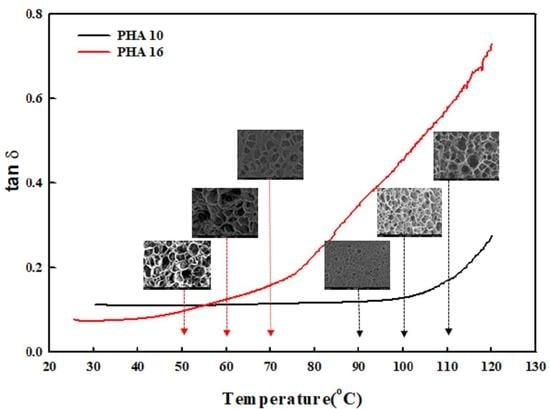
3.1. Foamability of P(3HB-co-4HB) Copolymer
3.2. Characteristics of P(3HB-co-4HB) Foams
3.3. Effect of Chain Extender on Foam Structures
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, G.Q. A microbial polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHA) based bio- and materials industry. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2009, 38, 2434–2446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ong, S.Y.; Chee, J.Y.; Sudesh, K. Degradation of Polyhydroxyalkanoate (PHA): A Review. J. Sib. Fed. Univ. Biol. 2017, 10, 211–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puppi, D.; Pecorini, G.; Chiellini, F. Biomedical Processing of Polyhydroxyalkanoates. Bioengineering 2019, 6, 0108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Thellen, C.; Coyne, M.; Froio, D.; Auerbach, M.; Wirsen, C.; Ratto, J.A. A Processing. Characterization and Marine Biodegradation Study of Melt-Extruded Polyhydroxyalkanoate (PHA) Films. J. Polym. Environ. 2008, 16, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vostrejs, P.; Adamcova, D.; Vaverkova, M.D.; Enev, V.; Kalina, M.; Machovsky, M.; Sourkov, M.; Marovaa, I.; Kovalcik, A. Active biodegradable packaging films modified with grape seeds lignin. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 29202–29213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cravo, C.; Duarte, A.R.C.; Duarte, C.M.M. Solubility of carbon dioxide in a natural biodegradable polymer: Determination of diffusion coefficients. J. Supercrit. Fluids 2007, 740, 194–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volova, T.; Goncharov, D.; Sukovatyi, A.; Shabanov, A.; Nikolaeva, E.; Shishatskaya, E. Electrospinning of polyhydroxyalkanoate fibrous scaffolds: Effects on electrospinning parameters on structure and properties. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 2013, 25, 370–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grande, D.; Ramier, J.; Versace, D.L.; Renard, E.; Langlois, V. Design of functionalized biodegradable PHA-based electrospun scaffolds meant for tissue engineering applications. New Biotechnol. 2017, 37, 129–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, S.; Shumilova, A.A.; Kiselev, E.G.; Baranovsky, S.V.; Vasiliev, A.D.; Nemtsev, I.V.; Kuzmin, A.P.; Sukovatyi, A.G.; Avinash, R.P.; Volova, T.G. Thermal, mechanical and biodegradation studies of biofiller based poly-3-hydroxybutyrate biocomposites. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 155, 1373–1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Che, X.M.; Ye, H.M.; Chen, G.Q. Effects of uracil on crystallization and rheological property of poly(R-3-hydroxybutyrate-co-4-hydroxybutyrate). Compos. A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2018, 109, 141–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.Y.; Shen, J.J.; Chen, S.K.; Cooper, M.A.; Fu, H.B.; Wu, D.M.; Yang, Z.G. Nanofiller Reinforced Biodegradable PLA/PHA Composites: Current Status and Future Trends. Polymers 2018, 10, 0505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Parulekar, Y.; Mohanty, A.K. Extruded Biodegradable Cast Films from Polyhydroxyalkanoate and Thermoplastic Starch Blends: Fabrication and Characterization. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2007, 292, 1218–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musiol, M.; Jurczyk, S.; Sobota, M.; Klim, M.; Sikorska, W.; Zieba, M.; Janeczek, H.; Rydz, J.; Kurcok, P.; Johnston, B.; et al. (Bio)Degradable Polymeric Materials for Sustainable Future—Part 3: Degradation Studies of the PHA/Wood Flour-Based Composites and Preliminary Tests of Antimicrobial Activity. Materials 2020, 13, 2200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ventura, H.; Laguna-Gutierrez, E.; Rodriguez-Perez, M.A.; Ardanuy, M. Effect of chain extender and water-quenching on the properties of poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-4-hydroxybutyrate) foams for its production by extrusion foaming. Eur. Polym. J. 2016, 85, 14–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.Y.; Dong, C.L.; Wang, S.Y.; Ye, H.M.; Chen, G.Q. Microbial production of polyhydroxyalkanoate block copolymer by recombinant Pseudomonas putida. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2010, 90, 659–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahankari, S.S.; Mohanty, A.K.; Misra, M. Mechanical behaviour of agro-residue reinforced poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyvalerate), (PHBV) green composites: A comparison with traditional polypropylene composites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2011, 71, 653–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Kaddo, K.B.; Mohamad, F.; Murugan, P.; Tan, J.S.; Sudesh, K.; Samian, M.R. Production of P(3HB-co-4HB) copolymer with high 4HB molar fraction by Burkholderia contaminans Kad1 PHA synthase. Biochem. Eng. J. 2020, 153, 107394–107400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripathi1, L.; Wu, L.P.; Chen, J.C.; Chen, G.Q. Synthesis of Diblock copolymer poly-3-hydroxybutyrate -block-poly-3-hydroxyhexanoate [PHB-b-PHHx] by a β-oxidation weakened Pseudomonas putida KT2442. Microb. Cell. Factories 2012, 11, 44–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vijayendra, S.V.N.; Shamala, T.R. Film forming microbial biopolymers for commercial applications—A review. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 2014, 34, 338–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.Q.; Kasuya, K.; Hikima, T.; Takata, M.; Takemura, A.; Lwata, T. Mechanical properties, structure analysis and enzymatic degradation of uniaxially cold-drawn films of poly[(R)-3-hydroxybutyrate-co-4-hydroxybutyrate]. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2011, 96, 2130–2138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plackett, D.; Siro, I. Polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHAs) for food packaging. Multifunct. Nanoreinforced Polym. Food Packag. 2011, 4, 498–526. [Google Scholar]
- Liao, Q.; Tsui, A.; Billington, S.; Frank, C.W. Extruded Foams from Microbial Poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyvalerate) and Its Blends with Cellulose Acetate Butyrate. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2012, 52, 1495–1508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, Z.C.; Frank, C.W. Increasing Cell Homogeneity of Semicrystalline, Biodegradable Polymer Foams with a Narrow Processing Window via Rapid Quenching. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2014, 54, 2877–2886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moigne, N.L.; Sauceau, M.; Benyakhlef, M.; Jemai, R.; Benezet, J.C.; Rodier, E.; Lopez-Cuesta, J.M.; Fages, J. Foaming of poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyvalerate)/organo-clays nano-biocomposites by a continuous supercritical CO2 assisted extrusion process. Eur. Polym. J. 2014, 61, 157–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Takahashi, S.; Hassler, J.C.; Kiran, E. Melting behavior of biodegradable polyesters in carbon dioxide at high pressures. J. Supercrit. Fluids 2012, 72, 278–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, J.; Zhang, L.; Li, D.L.; Bao, J.B.; Wang, Z.B. Foaming of Poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyvalerate) with Supercritical Carbon Dioxide: Foaming Performance and Crystallization Behavior. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 9839–9845. [Google Scholar]
- Ge, C.B.; Ren, Q.; Wang, S.P.; Zheng, W.G.; Zhai, W.T.; Park, C.B. Steam-chest molding of expanded thermoplastic polyurethane bead foams and their mechanical properties. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2017, 17, 337–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossieny, N.; Ameli, A.; Park, C.B. Characterization of Expanded Polypropylene Bead Foams with Modified Steam-Chest Molding. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2013, 52, 8236–8247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.J.; Liu, F.; Yang, X.; Xiong, Z.J.; Liu, H.W.; Xu, D.H.; Zhai, W.T. Evolution of ordered structure of TPU in high-elastic state and their influences on the autoclave foaming of TPU and inter-bead bonding of expanded TPU beads. Polymer 2021, 228, 123872–123884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, L.Q.; Zhai, W.T.; Zheng, W.G. Autoclave preparation of expanded polypropylene/poly(lactic acid) blend bead foams with a batch foaming process. J. Cell. Plast. 2011, 47, 429–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, P.J.; Zhai, S.; Lee, R.; Zhao, C.X.; Buahom, P.; Li, G.X.; Park, C.B. Environmentally Friendly Polylactic Acid-Based Thermal Insulation Foams Blown with Supercritical CO2. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2015, 57, 5464–5471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.C.; Li, X.Y.; Zhang, Q.Q.; Xia, C.H.; Chen, C.; Chen, X.H.; Yu, P. Foaming of poly(lactic acid) with supercritical CO2: The combined effect of crystallinity and crystalline morphology on cellular structure. J. Supercrit. Fluids 2019, 145122–145132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nofar, M.; Park, C.B. Poly(lactic acid)foaming. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2014, 39, 1721–1741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Standau, T.; Zhao, C.J.; Castellon, S.M.; Bonten, C.; Altstadt, V. Chemical Modification and Foam Processing of Polylactide (PLA). Polymers 2019, 11, 0306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Szegda, D.; Duangphet, S.; Song, J.; Tarverdi, K. Extrusion foaming of PHBV. J. Cell. Plast. 2014, 50, 145–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javadi, A.; Srithep, Y.; Clemons, C.C.; Turng, L.S.; Gong, S.Q. Processing of poly(hydroxybutyrate-co-hydroxyvalerate)-based bionanocomposite foams using supercritical fluids. J. Mater. Res. 2012, 27, 1506–1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frerich, S.C. Biopolymer foaming with supercritical CO2—Thermodynamics, foaming behaviour and mechanical characteristics. J. Supercrit. Fluids 2015, 96, 349–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, R.; Ray, S.S. Foamability and Special Applications of Microcellular Thermoplastic Polymers: A Review on Recent Advances and Future Direction. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2020, 305, 2000366–2000414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Lee, S.J.; Yoo, Y.H.; Park, K.H.; Kang, H.J. Compression Molding of Thermoplastic Polyurethane Foam Sheets with Beads Expanded by Supercritical CO2 Foaming. Polymers 2021, 13, 0656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]











| Sample Code [Polymer] | 4HB Content (%) | Mw (k) | Tm1(°C) | Tm2(°C) | Tc(°C) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PHA10 [P(3HB-co-10% 4HB)] | 10 | 600 | 23.97 | 129.96 | 145.92 | 75.82 |
| PHA10 with ADR(5phr) | 10 | 600 | 9.65 | 113.59 | 141.96 | 72.53 |
| PHA10 [P(3HB-co-16% 4HB)] | 16 | 1000 | 3.99 | 115.82 | 155.59 | 59.67 |
| PHA10 with ADR(5phr) | 16 | 1000 | 2.54 | 113.55 | 154.96 | 56.84 |
| PHA10 [P(3HB-co-30% 4HB)] | 30 | 687 | - | - | - | - |
| PHA10 [P(3HB-co-50% 4HB)] | 53.7 | 901 | - | - | - | - |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, T.; Jang, Y.; Lee, E.; Shin, S.; Kang, H.-J. Supercritical CO2 Foaming of Poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-4-hydroxybutyrate). Polymers 2022, 14, 2018. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14102018
Zhang T, Jang Y, Lee E, Shin S, Kang H-J. Supercritical CO2 Foaming of Poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-4-hydroxybutyrate). Polymers. 2022; 14(10):2018. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14102018
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Tao, Yunjae Jang, Eunhye Lee, Sooan Shin, and Ho-Jong Kang. 2022. "Supercritical CO2 Foaming of Poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-4-hydroxybutyrate)" Polymers 14, no. 10: 2018. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14102018
APA StyleZhang, T., Jang, Y., Lee, E., Shin, S., & Kang, H. -J. (2022). Supercritical CO2 Foaming of Poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-4-hydroxybutyrate). Polymers, 14(10), 2018. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14102018