Enhancement in Crystallizability of Poly(L-Lactide) Using Stereocomplex-Polylactide Powder as a Nucleating Agent
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of LMW-PLLA and scPLA Powders
2.3. Characterization of LMW-PLLA and scPLA Powders
2.4. Preparation of PLLA/LMW-PLLA Powder and PLLA/scPLA Powder Blends
2.5. Characterization of PLLA/LMW-PLLA Powder and PLLA/scPLA Powder Blends
3. Results
3.1. Characterization of LMW-PLLA and scPLA Powders
3.2. Characterization of PLLA3251D/LMW-PLLA Powder and PLLA3251D/scPLA Powder Blends
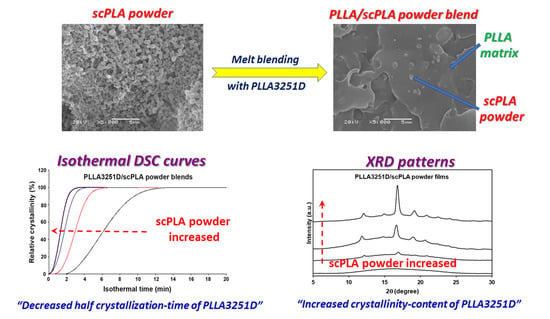
3.2.1. Phase Morphology
3.2.2. Thermal Transition Properties
3.2.3. Crystalline Structures
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, S.; Qin, S.; He, M.; Zhou, D.; Qin, Q.; Wang, H. Current applications of poly(lactic acid) composites in tissue engineering and drug delivery. Compos. B Eng. 2020, 199, 108238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daskalova, A.; Angelova, L.; Filipov, E.; Aceti, D.; Mincheva, R.; Carrete, X.; Kerdjoudj, H.; Dubus, M.; Chevrier, J.; Trifonov, A.; et al. Biomimetic hierarchical structuring of PLA by ultra-short laser pulses for processing of tissue engineered matrices: Study of cellular and antibacterial behavior. Polymers 2021, 13, 2577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmad Ruzaidi, D.A.; Mahat, M.M.; Shafiee, S.A.; Mohamed Sofian, Z.; Mohmad Sabere, A.S.; Ramli, R.; Osman, H.; Hamzah, H.H.; Zainal Ariffin, Z.; Sadasivuni, K.K. Advocating electrically conductive scaffolds with low immunogenicity for biomedical applications: A review. Polymers 2021, 13, 3395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamarudin, S.H.; Rayung, M.; Abu, F.; Ahmad, S.; Fadil, F.; Karim, A.A.; Norizan, M.N.; Sarifuddin, N.; Mat Desa, M.S.Z.; Mohd Basri, M.S.; et al. A review on antimicrobial packaging from biodegradable polymer composites. Polymers 2022, 14, 174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Da Silva, D.; Kaduri, M.; Poley, M.; Adir, O.; Krinsky, N.; Shainsky-Rotiman, J.; Schroeder, A. Biocompatibility, biodegradation and excretion of polylactic acid (PLA) in medical implants and theranostic systems. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 340, 9–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rihayat, T.; Hadi, A.E.; Aidy, N.; Safitri, A.; Siregar, J.P.; Cionita, T.; Irawan, A.P.; Hamdan, M.H.M.; Fitriyana, D.F. Biodegradation of polylactic acid-based bio-composites reinforced with chitosan and essential oils as anti-microbial material for food packaging. Polymers 2021, 13, 4019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilyas, R.A.; Sapuan, S.M.; Harussani, M.M.; Hakimi, M.Y.A.Y.; Haziq, M.Z.M.; Atikah, M.S.N.; Asyraf, M.R.M.; Ishak, M.R.; Razman, M.R.; Nurazzi, N.M.; et al. Polylactic acid (PLA) biocomposite: Processing, additive manufacturing and advanced applications. Polymers 2021, 13, 1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeidlou, S.; Huneault, M.A.; Li, H.; Park, C.B. Poly(lactic acid) crystallization. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2012, 37, 1657–1677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Zhang, C.; Luo, C.; Chen, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Yao, B.; Dong, L.; Du, X.; Ji, J. Effect of talc and diatomite on compatible, morphological, and mechanical behavior of PLA/PBAT blends. e-Polymers 2021, 21, 234–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalali, A.; Shahbikian, S.; Huneault, M.A.; Elkoun, S. Effect of molecular weight on the shear-induced crystallization of poly(lactic acid). Polymer 2017, 112, 393–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuji, H. Poly(lactic acid) stereocomplexes: A decade of progress. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2016, 107, 97–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, F.; Fortenberry, A.; Ren, J.; Qiang, Z. Recent progress in enhancing poly(lactic acid) stereocomplex formation for material property improvement. Front. Chem. 2020, 8, 688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalali, A.; Romero-Diez, S.; Nofar, M.; Park, C.B. Entirely environment-friendly polylactide composites with outstanding heat resistance and superior mechanical performance fabricated by spunbond technology: Exploring the role of nanofibrillated stereocomplex polylactide crystals. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 193 Pt B, 2210–2220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tábi, T.; Ageyeva, T.; Kovács, J.G. Improving the ductility and heat deflection temperature of injection molded Poly(lactic acid) products: A comprehensive review. Polym. Test. 2021, 101, 107282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.-X.; Ren, Y.; Lee, D.; Choi, S.-W. Crystallization behavior and electrical properties of nanoparticle-reinforced poly(lactic acid)-based films. Polymers 2022, 14, 177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Meng, L.; Li, G.; Liang, N.; Zhang, J.; Zhu, Z.; Wang, R. Effect of nucleating agents on the crystallization behavior and heat resistance of poly(l-lactide). J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2016, 133, 42999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Jing, Z.; Zhang, G. Influence of PLA stereocomplex crystals and thermal treatment temperature on the rheology and crystallization behavior of asymmetric poly(L-Lactide)/poly(D-lactide) blends. J. Polym. Res. 2018, 25, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phattarateera, S.; Pattamaprom, C. The effect of different acrylic-based rubbers on the crystallization behavior of PLA/PDLA stereocomplex. J. Polym. Environ. 2020, 28, 1592–1600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, D.; Liu, H.; Bai, H.; Zhang, Q.; Fu, Q. Powder metallurgy inspired low-temperature fabrication of high performance stereocomplexed polylactide products with good optical transparency. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 20260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purnama, P.; Samsuri, M.; Iswaldi, I. Properties enhancement of high molecular weight polylactide using stereocomplex polylactide as a nucleating agent. Polymers 2021, 13, 1725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samsuri, M.; Iswaldi, I.; Purnama, P. The Effect of stereocomplex polylactide particles on the stereocomplexation of high molecular weight polylactide blends. Polymers 2021, 13, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baimark, Y.; Pasee, S.; Rungseesantivanon, W.; Prakymoramas, N. Flexible and high heat-resistant stereocomplex PLLA-PEG-PLLA/PDLA blends prepared by melt process: Effect of chain extension. J. Polym. Res. 2019, 26, 218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chauliac, D.; Pullammanappallil, P.C.; Ingram, L.O.; Shanmugam, K.T. A combined thermochemical and microbial process for recycling polylactic acid polymer to optically pure L-lactic acid for reuse. J. Polym. Environ. 2020, 28, 1503–1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srisuwan, Y.; Baimark, Y. Thermal, morphological and mechanical properties of flexible poly(l-lactide)-b-polyethylene glycol-b-poly(l-lactide)/thermoplastic starch blends. Carbohydr. Polym. 2022, 283, 119155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srisuwan, Y.; Baimark, Y. Improvement in thermal stability of flexible poly(L-lactide)-b-poly(ethylene glycol)-b-poly(L-lactide) bioplastic by blending with native cassava starch. Polymers 2022, 14, 3186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, Y.-L.; Li, X.-L.; Diao, X.-Y.; Bai, H.-W.; Zhang, Q.; Fu, Q. Mixing of racemic poly(L-lactide)/poly(D-lactide) blend with miscible poly(D,L-lactide): Toward all stereocomplex-type polylactide with strikingly enhanced SC crystallizability. Chin. J. Polym. Sci. 2021, 39, 1470–1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Cao, Z.-Q.; Bao, R.-Y.; Xie, B.-H.; Yang, M.-B.; Yang, W. Poly(l-lactic acid)-polyethylene glycol-poly(l-lactic acid) triblock copolymer: A novel macromolecular plasticizer to enhance the crystallization of poly(l-lactic acid). Eur. Polym. J. 2017, 97, 272–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, J.; Guo, Y.; Ye, S.; Xie, B.; Xu, Y.; Hou, H. The morphology and growth of PLA stereocomplex in PLLA/PDLA blends with low molecular weights. Polym. Sci. Ser. A 2017, 59, 116–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.-S.; Hong, C.-K. Relationship between the stereocomplex crystallization behavior and mechanical properties of PLLA/PDLA blends. Polymers 2021, 13, 1851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Huneault, M.A. Effect of nucleation and plasticization on the crystallization of poly(lactic acid). Polymer 2007, 48, 6855–6866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lorenzo, M.L.D.; Androsch, R. Accelerated crystallization of high molar mass poly(l/d-lactic acid) by blending with low molar mass poly(l-lactic acid). Eur. Polym. J. 2018, 100, 172–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shakoor, A.; Thomas, N.L. Talc as a nucleating agent and reinforcing filler in poly(lactic acid) composites. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2014, 54, 64–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, H.M.; Jeong, S.-Y.; Choi, S.-W. Analysis of the rheological property and crystallization behavior of polylactic acid (IngeoTM Biopolymer 4032D) at different process temperatures. E-Polymers 2021, 21, 702–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Han, C.; Yu, Y.; Huang, D. Morphological, thermal, rheological and mechanical properties of poly (butylene carbonate) reinforced by stereocomplex polylactide. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 137, 1169–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.; Qiu, Y.; Yan, C.; Liu, L.; Xu, M.; Xu, B.; Li, B. A novel and multifunctional flame retardant nucleating agent towards superior fire safety and crystallization properties for biodegradable poly (lactic acid). Adv. Powder Technol. 2021, 32, 4210–4221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalali, A.; Huneault, M.A.; Elkoun, S. Effect of thermal history on nucleation and crystallization of poly(lactic acid). J. Mater. Sci. 2016, 51, 7768–7779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalali, A.; Huneault, M.A.; Elkoun, S. Effect of molecular weight on the nucleation efficiency of poly(lactic acid) crystalline phases. J. Polym. Res. 2017, 24, 182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]









| LMW-PLA | L-content (%) a | Theoretical M.W. (g/mol) b | Mn (g/mol) c | Ɖd | Tg (°C) e | Tm (°C) f |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LMW-PLLA LMW-PDLA | 97.5 2.8 | 5000 5000 | 6700 6200 | 1.4 1.8 | 46 46 | 161 161 |
| Powder | Tm (°C) a | ΔHm,hc (J/g) b | ΔHm,sc (J/g) c | DSC-Xc,hc (%) d | DSC-Xc,sc (%) e |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LMW-PLLA powder scPLA powder | 161 219 | 50.8 - | - 85.1 | 54.2 - | - 59.9 |
| PLLA3251D-Based Blends | Tg (°C) a | Tcc (°C) b | ΔHcc (J/g) c | Tm (°C) d | ΔHm (J/g) e | DSC-Xc,hc (%) f |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pure PLLA3251D | 58 | 110 | 32.5 | 167 | 40.6 | 8.6 |
| PLLA/2% w/w LMW-PLLA powder | 60 | 98 | 32.4 | 167 | 40.4 | 8.7 |
| PLLA/4% w/w LMW-PLLA powder | 60 | 98 | 33.4 | 167 | 42.2 | 9.8 |
| PLLA/8% w/w LMW-PLLA powder | 60 | 97 | 32 | 166 | 39.9 | 9.2 |
| PLLA/2% w/w scPLA powder | 60 | 97 | 27.8 | 167 | 40.4 | 14 |
| PLLA/4% w/w scPLA powder | 60 | 97 | 27 | 167 | 40.4 | 15.5 |
| PLLA/8% w/w scPLA powder | 59 | 96 | 24.8 | 167 | 40 | 19.1 |
| PLLA3251D-Based Blends | Tc (°C) a | ΔHc (J/g) b |
|---|---|---|
| Pure PLLA3251D | 100 | 3.8 |
| PLLA/2% w/w LMW-PLLA powder | 100 | 3.4 |
| PLLA/4% w/w LMW-PLLA powder | 100 | 3.8 |
| PLLA/8% w/w LMW-PLLA powder | 101 | 3.5 |
| PLLA/2% w/w scPLA powder | 100 | 6.2 |
| PLLA/4% w/w scPLA powder | 101 | 14.6 |
| PLLA/8% w/w scPLA powder | 103 | 28.2 |
| PLLA3251D-Based Blends | t1/2 (min) a |
|---|---|
| Pure PLLA3251D | 6.17 |
| PLLA/2% w/w LMW-PLLA powder | 7.6 |
| PLLA/4% w/w LMW-PLLA powder | 8.02 |
| PLLA/8% w/w LMW-PLLA powder | 7.59 |
| PLLA/2% w/w scPLA powder | 2.96 |
| PLLA/4% w/w scPLA powder | 1.79 |
| PLLA/8% w/w scPLA powder | 1.32 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Baimark, Y.; Srihanam, P.; Srisuwan, Y.; Phromsopha, T. Enhancement in Crystallizability of Poly(L-Lactide) Using Stereocomplex-Polylactide Powder as a Nucleating Agent. Polymers 2022, 14, 4092. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14194092
Baimark Y, Srihanam P, Srisuwan Y, Phromsopha T. Enhancement in Crystallizability of Poly(L-Lactide) Using Stereocomplex-Polylactide Powder as a Nucleating Agent. Polymers. 2022; 14(19):4092. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14194092
Chicago/Turabian StyleBaimark, Yodthong, Prasong Srihanam, Yaowalak Srisuwan, and Theeraphol Phromsopha. 2022. "Enhancement in Crystallizability of Poly(L-Lactide) Using Stereocomplex-Polylactide Powder as a Nucleating Agent" Polymers 14, no. 19: 4092. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14194092
APA StyleBaimark, Y., Srihanam, P., Srisuwan, Y., & Phromsopha, T. (2022). Enhancement in Crystallizability of Poly(L-Lactide) Using Stereocomplex-Polylactide Powder as a Nucleating Agent. Polymers, 14(19), 4092. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14194092