PLA-Based Hybrid Biocomposites: Effects of Fiber Type, Fiber Content, and Annealing on Thermal and Mechanical Properties
Abstract
:1. Introduction
| Sample | Coir | Bamboo | Bamboo Leaf | Sisal |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Density (g/m3) | 1.25–1.5 | 0.9 | - | 1.26–1.33 |
| Diameter (µm) | 100–450 | - | - | 100–300 |
| Cellulose (%) | 36–43 | 26–43 | 19.5–26.3 | 74–75.2 |
| Hemicellulose (%) | 0.2 | 30 | 11.3–13.5 | 10–13.9 |
| Lignin (%) | 41–45 | 21–30 | 8.7–11.6 | 8–12 |
| Microfibrillar angle (°) | 30–45 | - | - | 10–20 |
| Tensile strength (MPa) | 105–175 | - | - | 600–700 |
| Young’s modulus (GPa) | 4–6 | - | - | 38 |
| Elongation at break (%) | 17–47 | - | - | 3.64–5.12 |
| Moisture absorption (%) | 10 | - | - | 11 |
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
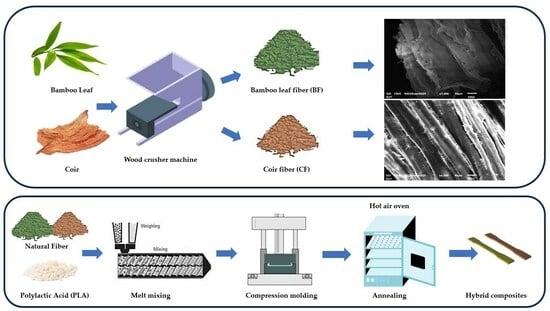
2.1.1. Fiber Preparation
2.1.2. Preparation of PLA-Based Composites
2.2. Characterization and Test
2.2.1. Tensile Test
2.2.2. Morphological Study
2.2.3. Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC)
2.3. Heat Deflection Temperature (HDT)
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Effect of Fiber Type and Content on Tensile Properties of PLA-Based Composites
3.2. Effect of Fiber Ratio and Annealing on Tensile Properties of PLA-Based Composites
3.3. Morphology of PLA-Based Composites
3.4. Thermal and Crystallinity of PLA-Based Composites
3.5. Heat Deflection Temperature (HDT)
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mohanty, A.K.; Misra, M.; Drzal, L.T. Sustainable Bio-Composites from Renewable Resources: Opportunities and Challenges in the Green Materials World. J. Polym. Environ. 2002, 10, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siracusa, V.; Rocculi, P.; Romani, S.; Rosa, M.D. Biodegradable polymers for food packaging: A review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2008, 19, 634–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pongtanayut, K.; Thongpin, C.; Santawitee, O. The Effect of Rubber on Morphology, Thermal Properties and Mechanical Properties of PLA/NR and PLA/ENR Blends. Energy Procedia 2013, 34, 888–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Xiong, Z.; Tang, Z.; Zhang, R.; Zhu, J. Research progress in the heat resistance, toughening and filling modification of PLA. Sci. China Chem. 2016, 59, 1355–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trifol, J.; Plackett, D.; Sillard, C.; Szabo, P.; Bras, J.; Daugaard, A.E. Hybrid poly(lactic acid)/nanocellulose/nanoclay composites with synergistically enhanced barrier properties and improved thermomechanical resistance. Polym. Int. 2016, 65, 988–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coskun, K.; Mutlu, A.; Dogan, M.; Bozacı, E. Effect of various enzymatic treatments on the mechanical properties of coir fiber/poly(lactic acid) biocomposites. J. Thermoplast. Compos. Mater. 2019, 34, 1066–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Ghataura, A.; Takagi, H.; Haroosh, H.J.; Nakagaito, A.N.; Lau, K.-T. Polylactic acid (PLA) biocomposites reinforced with coir fibres: Evaluation of mechanical performance and multifunctional properties. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2014, 63, 76–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Zhang, L.; Liang, D.; Xiao, W.; Lin, J. Mechanical and Thermal Properties of PLA Biocomposites Reinforced by Coir Fibers. Int. J. Polym. Sci. 2017, 2017, 2178329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yusoff, R.B.; Takagi, H.; Nakagaito, A.N. Tensile and flexural properties of polylactic acid-based hybrid green composites reinforced by kenaf, bamboo and coir fibers. Ind. Crops Prod. 2016, 94, 562–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Sun, Z.; Liang, D.; Lin, J.; Xiao, W. Preparation and performance evaluation of PLA/coir fibre biocomposites. BioResources 2017, 12, 7349–7362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adeniyi, A.G.; Onifade, D.V.; Ighalo, J.O.; Adeoye, A.S. A review of coir fiber reinforced polymer composites. Compos. Part B Eng. 2019, 176, 107305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathura, N.; Cree, D. Characterization and mechanical property of Trinidad coir fibers. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2016, 133, 43692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nam, T.H.; Ogihara, S.; Tung, N.H.; Kobayashi, S. Effect of alkali treatment on interfacial and mechanical properties of coir fiber reinforced poly(butylene succinate) biodegradable composites. Compos. Part B Eng. 2011, 42, 1648–1656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geethamma, V.G.; Kalaprasad, G.; Groeninckx, G.; Thomas, S. Dynamic mechanical behavior of short coir fiber reinforced natural rubber composites. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2005, 36, 1499–1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zainudin, E.S.; Yan, L.H.; Haniffah, W.H.; Jawaid, M.; Alothman, O.Y. Effect of coir fiber loading on mechanical and morphological properties of oil palm fibers reinforced polypropylene composites. Polym. Compos. 2014, 35, 1418–1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arrakhiz, F.Z.; El Achaby, M.; Malha, M.; Bensalah, M.; Fassi-Fehri, O.; Bouhfid, R.; Benmoussa, K.; Qaiss, A. Mechanical and thermal properties of natural fibers reinforced polymer composites: Doum/low density polyethylene. Mater. Des. 2013, 43, 200–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Essabir, H.; Bensalah, M.O.; Rodrigue, D.; Bouhfid, R.; Qaiss, A. Structural, mechanical and thermal properties of bio-based hybrid composites from waste coir residues: Fibers and shell particles. Mech. Mater. 2016, 93, 134–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morandim-Giannetti, A.A.; Agnelli, J.A.M.; Lanças, B.Z.; Magnabosco, R.; Casarin, S.A.; Bettini, S.H.P. Lignin as additive in polypropylene/coir composites: Thermal, mechanical and morphological properties. Carbohydr. Polym. 2012, 87, 2563–2568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosa, M.F.; Chiou, B.-S.; Medeiros, E.S.; Wood, D.F.; Williams, T.G.; Mattoso, L.H.C.; Orts, W.J.; Imam, S.H. Effect of fiber treatments on tensile and thermal properties of starch/ethylene vinyl alcohol copolymers/coir biocomposites. Bioresour. Technol. 2009, 100, 5196–5202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.N.; Haque, M.M.; Huque, M.M. Mechanical and Morphological Properties of Chemically Treated Coir-Filled Polypropylene Composites. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2009, 48, 10491–10497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peltola, H.; Pääkkönen, E.; Jetsu, P.; Heinemann, S. Wood based PLA and PP composites: Effect of fibre type and matrix polymer on fibre morphology, dispersion and composite properties. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2014, 61, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suardana, N.; Lokantara, I.P.; Lim, J.K. Influence of water absorption on mechanical properties of coconut coir Fiber/Poly-Lactic acid biocomposites. Mater. Phys. Mech. 2011, 12, 113–125. [Google Scholar]
- Saw, S.K.; Sarkhel, G.; Choudhury, A. Surface modification of coir fibre involving oxidation of lignins followed by reaction with furfuryl alcohol: Characterization and stability. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2011, 257, 3763–3769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irina, M.M.W.; Azmi, A.I.; Tan, C.L.; Lee, C.C.; Khalil, A.N.M. Evaluation of Mechanical Properties of Hybrid Fiber Reinforced Polymer Composites and their Architecture. Procedia Manuf. 2015, 2, 236–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanjay, M.R.; Yogesha, B. Studies on Natural/Glass Fiber Reinforced Polymer Hybrid Composites: An Evolution. Mater. Today Proc. 2017, 4, 2739–2747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, W.; Zhu, B.; Su, F.; Wang, Z.; Shao, C.; Wang, Y.; Liu, C.; Shen, C. Melting temperature, concentration and cooling rate-dependent nucleating ability of a self-assembly aryl amide nucleator on poly(lactic acid) crystallization. Polymer 2019, 168, 77–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tábi, T.; Sajó, I.E.; Szabó, F.; Luyt, A.S.; Kovacs, J.G. Crystalline structure of annealed polylactic acid and its relation to processing. Express Polym. Lett. 2010, 4, 659–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Kazemi, Y.; Wang, S.; Hamidinejad, M.; Mahmud, M.B.; Pötschke, P.; Park, C.B. Enhancing the electrical conductivity of PP/CNT nanocomposites through crystal-induced volume exclusion effect with a slow cooling rate. Compos. Part B Eng. 2020, 183, 107663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouzouita, A.; Notta-Cuvier, D.; Raquez, J.-M.; Lauro, F.; Dubois, P. Poly(lactic acid)-Based Materials for Automotive Applications. In Industrial Applications of Poly(Lactic Acid); Di Lorenzo, M., Androsch, R., Eds.; Advances in Polymer Science; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 1–43. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, Q.F.; Mou, H.Y.; Li, Q.Y.; Wang, J.K.; Guo, W.H. Influence of heat treatment on the heat distortion temperature of poly(lactic acid)/bamboo fiber/talc hybrid biocomposites. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2012, 123, 2828–2836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nam, T.H.; Ogihara, S.; Kobayashi, S. Interfacial, Mechanical and Thermal Properties of Coir Fiber-Reinforced Poly(Lactic Acid) Biodegradable Composites. Adv. Compos. Mater. 2012, 21, 103–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM D638-22; Standard Test Method for Tensile Properties of Plastics. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2022. [CrossRef]
- Choi, H.-J.; Kim, M.S.; Ahn, D.; Yeo, S.Y.; Lee, S. Electrical percolation threshold of carbon black in a polymer matrix and its application to antistatic fibre. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 6338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davachi, S.M.; Kaffashi, B. Preparation and Characterization of Poly L-Lactide/Triclosan Nanoparticles for Specific Antibacterial and Medical Applications. Int. J. Polym. Mater. Polym. Biomater. 2015, 64, 497–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM D648-18; Standard Test Method for Deflection Temperature of Plastics Under Flexural Load in the Edgewise Position. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2018. [CrossRef]
- Oksman, K.; Skrifvars, M.; Selin, J.-F. Natural fibres as reinforcement in polylactic acid (PLA) composites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2003, 63, 1317–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sitticharoen, W.; Uthiyoung, C.; Passadee, N.; Wongprom, C. Surface treated bagasse fiber ash on rheological, mechanical properties of PLA/BFA biocomposites. Polímeros 2018, 28, 187–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agunsoye, J.O.; Aigbodion, V.S. Bagasse filled recycled polyethylene bio-composites: Morphological and mechanical properties study. Results Phys. 2013, 3, 187–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chun, K.S.; Husseinsyah, S.; Osman, H. Mechanical and thermal properties of coconut shell powder filled polylactic acid biocomposites: Effects of the filler content and silane coupling agent. J. Polym. Res. 2012, 19, 9859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, J.; Wu, H.; Fu, W.; Hao, M. Mechanical properties of hybrid sisal/coir fibers reinforced polylactide biocomposites. Polym. Compos. 2018, 39, E188–E199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Z.; Wu, H.; Liu, R.; Wu, C. Preparation of Long Sisal Fiber-Reinforced Polylactic Acid Biocomposites with Highly Improved Mechanical Performance. Polymers 2021, 13, 1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petinakis, E.; Liu, X.; Yu, L.; Way, C.; Sangwan, P.; Dean, K.; Bateman, S.; Edward, G. Biodegradation and thermal decomposition of poly(lactic acid)-based materials reinforced by hydrophilic fillers. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2010, 95, 1704–1707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Shen, T.; Xu, P.; Zhao, X.; Li, X.; Dong, W.; Ma, P.; Chen, M. Crystallization modification of poly(lactide) by using nucleating agents and stereocomplexation. e-Polymers 2016, 16, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suryanegara, L.; Nakagaito, A.N.; Yano, H. Thermo-mechanical properties of microfibrillated cellulose-reinforced partially crystallized PLA composites. Cellulose 2010, 17, 771–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shih, Y.-F.; Huang, C.-C. Polylactic acid (PLA)/banana fiber (BF) biodegradable green composites. J. Polym. Res. 2011, 18, 2335–2340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aliotta, L.; Sciara, L.M.; Cinelli, P.; Canesi, I.; Lazzeri, A. Improvement of the PLA Crystallinity and Heat Distortion Temperature Optimizing the Content of Nucleating Agents and the Injection Molding Cycle Time. Polymers 2022, 14, 977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]










| Sample | PLA (wt%) | BF (wt%) | CF (wt%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Neat PLA | 100 | - | - |
| 5BF/PLA | 95 | 5 | - |
| 10BF/PLA | 90 | 10 | - |
| 20BF/PLA | 80 | 20 | - |
| 5CF/PLA | 95 | - | 5 |
| 10CF/PLA | 90 | - | 10 |
| 20CF/PLA | 80 | - | 20 |
| 1BF:2CF | 90 | 3.33 | 6.67 |
| 1BF:1BF | 90 | 5 | 5 |
| 2BF:1CF | 90 | 6.67 | 3.33 |
| Sample | Non-Annealed | Annealed | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tg (°C) | Tcc (°C) | Tm (°C) | (%) | Tg (°C) | Tcc (°C) | Tm (°C) | (%) | |
| PLA | 61.18 | 112.43 | 149.84 | 6.10 | - | - | 151.82 | 38.90 |
| 10CF | 61.28 | 115.22 | 150.30 | 2.85 | - | - | 151.32 | 36.73 |
| 1BF:2CF | 59.99 | 114.20 | 150.45 | 4.68 | - | - | 151.62 | 37.38 |
| 1BF:1CF | 59.63 | 114.53 | 150.62 | 3.63 | - | - | 150.29 | 36.36 |
| 2BF:1CF | 59.59 | 114.04 | 150.12 | 2.08 | - | - | 150.76 | 36.23 |
| 10BF | 59.75 | 116.25 | 150.47 | 2.44 | - | - | 150.47 | 35.72 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yaisun, S.; Trongsatitkul, T. PLA-Based Hybrid Biocomposites: Effects of Fiber Type, Fiber Content, and Annealing on Thermal and Mechanical Properties. Polymers 2023, 15, 4106. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15204106
Yaisun S, Trongsatitkul T. PLA-Based Hybrid Biocomposites: Effects of Fiber Type, Fiber Content, and Annealing on Thermal and Mechanical Properties. Polymers. 2023; 15(20):4106. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15204106
Chicago/Turabian StyleYaisun, Supitcha, and Tatiya Trongsatitkul. 2023. "PLA-Based Hybrid Biocomposites: Effects of Fiber Type, Fiber Content, and Annealing on Thermal and Mechanical Properties" Polymers 15, no. 20: 4106. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15204106
APA StyleYaisun, S., & Trongsatitkul, T. (2023). PLA-Based Hybrid Biocomposites: Effects of Fiber Type, Fiber Content, and Annealing on Thermal and Mechanical Properties. Polymers, 15(20), 4106. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15204106