Synthesis of Xanthan Gum Anchored α-Fe2O3 Bionanocomposite Material for Remediation of Pb (II) Contaminated Aquatic System
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
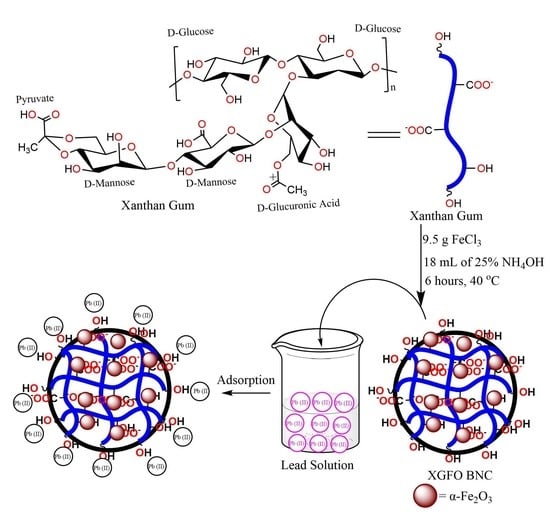
2.1. Synthesis of XG Capsuling α-Fe2O3 (XGFO) BNC
2.2. Analytical Techniques Used for Nanoparticle Characterization
2.3. Adsorption Experiments and Design
2.4. Statistical Verification of Data
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Adsorbent Characterization
3.2. Optimization of Variables and Contour Plots
3.3. Adsorption Isotherm
3.4. Adsorption Kinetics
3.5. Thermodynamic Aspect of Adsorption Reaction
3.6. Adsorption Mechanism
3.7. Desorption and Regeneration
3.8. Comparison with Literature
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yang, X.; Chen, L.; Ren, D.; Wang, S.; Ren, Z. Adsorption of Pb(II) from Water by Treatment with an O-Hydroxyphenyl Thiourea-Modified Chitosan. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 220, 280–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; He, R.; Yang, T.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, N.; Yang, C. Three-Dimensional Mesoporous Calcium Carbonate-Silica Frameworks Thermally Activated from Porous Fossil Bryophyte: Adsorption Studies for Heavy Metal Uptake. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 25754–25766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Huang, Y.; Kong, Q.; Zhang, X.; Peng, H. DMSA-Incorporated Silsesquioxane-Based Hybrid Polymer for Selective Adsorption of Pb(II) from Wastewater. J. Mol. Liq. 2022, 368, 120723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, F.; Lu, Y.; Li, L. Synthesis, Adsorption Kinetics and Thermodynamics of Ureido-Functionalized Pb(Ii) Surface Imprinted Polymers for Selective Removal of Pb(Ii) in Wastewater. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 111120–111128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, M.; Wang, R.; Xue, Y.; Ren, L.; Chen, S.; Liu, J.; Mei, M.; Wang, T.; Li, J. Eco-Friendly Ceramsite from Dredged Sediment/Biomass for Pb(II) Removal: Process Optimization and Adsorption Mechanistic Insights. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 108939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Z.; Gao, H.; Hu, L. Removal of Pb(II) by Nano-Titanium Oxide Investigated by Batch, XPS and Model Techniques. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 88520–88528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, M.; Chen, Y.; Chen, S.; Liu, J.; Mei, M.; Wang, T.; Li, J. Potentiality of the Porous Geopolymer Sphere in Adsorption of Pb (II) from Aqueous Solutions: Behaviors and Mechanisms. Ceram. Int. 2022, 49, 698–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turan, K.; Kalfa, O.M. Removal of Lead from Aqueous Solution Using Electrospun Nanofibers: Preparation, Characterization, Adsorption Isotherm, and Kinetic Study. Anal. Methods 2022, 14, 3382–3396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Wang, H.; Wang, S.; Fu, L.; Zhang, L. Novel Magnetic Covalent Organic Framework for the Selective and Effective Removal of Hazardous Metal Pb(II) from Solution: Synthesis and Adsorption Characteristics. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2023, 307, 122783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, T.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, J.; Aggarwal, S. Pb(II) Adsorption from Aqueous Solution by an Aluminum-Based Metal Organic Framework-Graphene Oxide Nanocomposite. Mater. Adv. 2021, 2, 3051–3059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Xiong, Y.; Liu, Y.; Han, J.; Duan, G.; Chen, Y.; He, S.; Mei, C.; Jiang, S.; Zhang, K. When MOFs Meet Wood: From Opportunities toward Applications. Chem 2022, 8, 2342–2361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obey, G.; Adelaide, M.; Ramaraj, R. Biochar Derived from Non-Customized Matamba Fruit Shell as an Adsorbent for Wastewater Treatment. J. Bioresour. Bioprod. 2022, 7, 109–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jjagwe, J.; Olupot, P.W.; Menya, E.; Kalibbala, H.M. Synthesis and Application of Granular Activated Carbon from Biomass Waste Materials for Water Treatment: A Review. J. Bioresour. Bioprod. 2021, 6, 292–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy Choudhury, P.; Majumdar, S.; Sahoo, G.C.; Saha, S.; Mondal, P. High Pressure Ultrafiltration CuO/Hydroxyethyl Cellulose Composite Ceramic Membrane for Separation of Cr (VI) and Pb (II) from Contaminated Water. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 336, 570–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Conceição, F.T.; da Silva, M.S.G.; Menegário, A.A.; Antunes, M.L.P.; Navarro, G.R.B.; Fernandes, A.M.; Dorea, C.; Moruzzi, R.B. Precipitation as the Main Mechanism for Cd(II), Pb(II) and Zn(II) Removal from Aqueous Solutions Using Natural and Activated Forms of Red Mud. Environ. Adv. 2021, 4, 100056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, K.; Wu, Y.; Wang, B.; Liu, Y.; Xu, W.; Wang, A.; Niu, Y. Adsorption Behavior and Mechanism for Pb(II) and Cd(II) by Silica Anchored Salicylaldehyde Modified Polyamidoamine Dendrimers. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2022, 139, 104525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, M.; Chen, J.; Zhang, L.; Cheng, Y.; Lu, C.; Liu, Y.; Singh, A.; Trivedi, M.; Kumar, A.; Liu, J. Metal Organic Frameworks as Efficient Adsorbents for Drugs from Wastewater. Mater. Today Commun. 2022, 31, 103514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, L.; Liang, F.; Li, Y.; Wu, J.; Guan, S.; Wu, M.; Xie, S.; Luo, M.; Ma, D. A 2D Porous Zinc-Organic Framework Platform for Loading of 5-Fluorouracil. Inorganics 2022, 10, 202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, M.; Kaur, M.; Singh, D.; Oliveira, A.C.; Garg, V.K.; Sharma, V.K. Synthesis of Cafe2o4-Ngo Nanocomposite for Effective Removal of Heavy Metal Ion and Photocatalytic Degradation of Organic Pollutants. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 1471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdullah, N.H.; Shameli, K.; Abdullah, E.C.; Abdullah, L.C. Solid Matrices for Fabrication of Magnetic Iron Oxide Nanocomposites: Synthesis, Properties, and Application for the Adsorption of Heavy Metal Ions and Dyes. Compos. B Eng. 2019, 162, 538–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vesali-Naseh, M.; Vesali Naseh, M.R.; Ameri, P. Adsorption of Pb (II) Ions from Aqueous Solutions Using Carbon Nanotubes: A Systematic Review. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 291, 125917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Tian, S.; Zhu, Y.; Zhong, W.; Qiu, R.; Han, L. Insight into the Adsorption Isotherms and Kinetics of Pb (II) on Pellet Biochar via in-Situ Non-Destructive 3D Visualization Using Micro-Computed Tomography. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 358, 127406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasan, I.; Khan, R.A.; Alharbi, W.; Alharbi, K.H.; Alsalme, A. In Situ Copolymerized Polyacrylamide Cellulose Supported Fe3O4 Magnetic Nanocomposites for Adsorptive Removal of Pb(II): Artificial Neural Network Modeling and Experimental Studies. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 1687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, L.; Zou, J.; Han, Y.; Liao, Z.; Lu, P.; Nezamzadeh-Ejhieh, A.; Liu, J.; Peng, Y. Recent Advances in Al(III)/In(III)-Based MOFs for the Detection of Pollutants. New J. Chem. 2022, 46, 19577–19592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rathore, B.S.; Chauhan, N.P.S.; Panneerselvam, P.; Jadoun, S.; Barani, M.; Ameta, S.C.; Ameta, R. Synthesis and Characterization of Ch-PANI-Fe2O3 Nanocomposite and Its Water Remediation Applications. Water 2022, 14, 3615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prajapati, A.K.; Mondal, M.K. Development of CTAB Modified Ternary Phase α-Fe2O3-Mn2O3-Mn3O4 Nanocomposite as Innovative Super-Adsorbent for Congo Red Dye Adsorption. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 104827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babu Poudel, M.; Shin, M.; Joo Kim, H. Interface Engineering of MIL-88 Derived MnFe-LDH and MnFe2O3 on Three-Dimensional Carbon Nanofibers for the Efficient Adsorption of Cr(VI), Pb(II), and As(III) Ions. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 287, 120463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Li, T.; Zhang, L.; Wang, R.; Jiang, F.; Chen, J. Pb(II) Adsorption on Magnetic γ-Fe2O3/Titanate Nanotubes Composite. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2015, 3, 2022–2030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- del Orta, M.M.; Martín, J.; Santos, J.L.; Aparicio, I.; Medina-Carrasco, S.; Alonso, E. Biopolymer-Clay Nanocomposites as Novel and Ecofriendly Adsorbents for Environmental Remediation. Appl. Clay Sci. 2020, 198, 105838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foroughnia, A.; Khalaji, A.D.; Kolvari, E.; Koukabi, N. Synthesis of New Chitosan Schiff Base and Its Fe2O3 Nanocomposite: Evaluation of Methyl Orange Removal and Antibacterial Activity. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 177, 83–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, D.; Pal, S. Modified Biopolymer-Dextrin Based Crosslinked Hydrogels: Application in Controlled Drug Delivery. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 25014–25050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Njuguna, D.G.; Schönherr, H. Smart and Regeneratable Xanthan Gum Hydrogel Adsorbents for Selective Removal of Cationic Dyes. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 107620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sulaiman, H.; Taha, M.R.; Abd Rahman, N.; Mohd Taib, A. Performance of Soil Stabilized with Biopolymer Materials—Xanthan Gum and Guar Gum. Phys. Chem. Earth Parts A B C 2022, 128, 103276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazachenko, A.S.; Vasilieva, N.Y.; Borovkova, V.S.; Fetisova, O.Y.; Issaoui, N.; Malyar, Y.N.; Elsuf’ev, E.V.; Karacharov, A.A.; Skripnikov, A.M.; Miroshnikova, A.V.; et al. Food Xanthan Polysaccharide Sulfation Process with Sulfamic Acid. Foods 2021, 10, 2571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmad, R.; Mirza, A. Application of Xanthan Gum/n-Acetyl Cysteine Modified Mica Bionanocomposite as an Adsorbent for the Removal of Toxic Heavy Metals. Groundw. Sustain. Dev. 2018, 7, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jana, S.; Mondal, A. Fabrication of SnO2/α-Fe2O3, SnO2/α-Fe2O3-PB Heterostructure Thin Films: Enhanced Photodegradation and Peroxide Sensing. ACS. Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 15832–15840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hidayat, A.R.P.; Sulistiono, D.O.; Murwani, I.K.; Endrawati, B.F.; Fansuri, H.; Zulfa, L.L.; Ediati, R. Linear and Nonlinear Isotherm, Kinetic and Thermodynamic Behavior of Methyl Orange Adsorption Using Modulated Al2O3@UiO-66 via Acetic Acid. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 106675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, T.; Wei, Y.; Jin, X.; Jiu, H.; Zhang, L.; Sun, Y.; Tian, J.; Shang, R.; Hang, D.; Zhao, R. Hydrothermal Self-Assembly of α-Fe2O3 Nanorings@graphene Aerogel Composites for Enhanced Li Storage Performance. J. Mater. Sci. 2019, 54, 7119–7130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sethi, S.; Saruchi; Kaith, B.S.; Kaur, M.; Sharma, N.; Kumar, V. Cross-Linked Xanthan Gum–Starch Hydrogels as Promising Materials for Controlled Drug Delivery. Cellulose 2020, 27, 4565–4589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fauzi, N.I.M.; Fen, Y.W.; Omar, N.A.S.; Saleviter, S.; Daniyal, W.M.E.M.M.; Hashim, H.S.; Nasrullah, M. Nanostructured Chitosan/Maghemite Composites Thin Film for Potential Optical Detection of Mercury Ion by Surface Plasmon Resonance Investigation. Polymers 2020, 12, 1497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saberi, D.; Mansourinejhad, S.; Shadi, A.; Habibi, H. One-Pot Synthesis of a Highly Disperse Core–Shell CuO–Alginate Nanocomposite and the Investigation of Its Antibacterial and Catalytic Properties. New J. Chem. 2021, 46, 199–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scherrer, P. Bestimmung Der Größe Und Der Inneren Struktur von Kolloidteilchen Mittels Röntgenstrahlen. Nachr. Ges. Wiss. Göttingen Math. Phys. Kl. 1918, 26, 98–100. [Google Scholar]
- Maji, S.K.; Mukherjee, N.; Mondal, A.; Adhikary, B. Synthesis, Characterization and Photocatalytic Activity of α-Fe2O3 Nanoparticles. Polyhedron 2012, 33, 145–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, B.; Pan, Z.; Shen, L.; Zhao, D.; Teng, J.; Hong, H.; Lin, H. Effects of Polysaccharides’ Molecular Structure on Membrane Fouling and the Related Mechanisms. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 836, 155579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sephra, P.J.; Baraneedharan, P.; Sivakumar, M.; Thangadurai, T.D.; Nehru, K. In Situ Growth of Hexagonal-Shaped α-Fe2O3 Nanostructures over Few Layered Graphene by Hydrothermal Method and Their Electrochemical Performance. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2018, 29, 6898–6908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalatbary, M.; Sayadi, M.H.; Hajiani, M.; Nowrouzi, M. Adsorption Studies on the Removal of Malachite Green by γ-Fe2O3/MWCNTs/Cellulose as an Eco-Friendly Nanoadsorbent. Biomass Convers. Biorefin. 2022, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manzoor, K.; Ahmad, M.; Ahmad, S.; Ikram, S. Removal of Pb(Ii) and Cd(Ii) from Wastewater Using Arginine Cross-Linked Chitosan–Carboxymethyl Cellulose Beads as Green Adsorbent. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 7890–7902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mustapha, S.; Shuaib, D.T.; Ndamitso, M.M.; Etsuyankpa, M.B.; Sumaila, A.; Mohammed, U.M.; Nasirudeen, M.B. Adsorption Isotherm, Kinetic and Thermodynamic Studies for the Removal of Pb(II), Cd(II), Zn(II) and Cu(II) Ions from Aqueous Solutions Using Albizia Lebbeck Pods. Appl. Water Sci. 2019, 9, 142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Langmuir, I. The Adsorption of Gases on Plane Surfaces of Glass, Mica and Platinum. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1918, 40, 1361–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Freundlich, H. Über Die Adsorption in Lösungen. Z. Phys. Chem. 1907, 57U, 385–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutson, N.D.; Yang, R.T. Theoretical Basis for the Dubinin-Radushkevitch (D-R) Adsorption Isotherm Equation. Adsorption 1997, 3, 189–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Temkin, M.I.; Pyzhev, V. Kinetics of Ammonia Synthesis on Promoted Iron Catalysts. Acta Physiochim. URSS 1940, 12, 327–356. [Google Scholar]
- Lagergren, S.; Svenska, B.K. On the Theory of So-Called Adsorption of Materials. R. Swed. Acad. Sci. Doc Band 1898, 24, 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Ho, Y.S.; McKay, G. Pseudo-Second Order Model for Sorption Processes. Process Biochem. 1999, 34, 451–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aharoni, C.; Ungarish, M. Kinetics of Activated Chemisorption. Part 1.—The Non-Elovichian Part of the Isotherm. J. Chem. Soc. Faraday Trans. 1 Phys. Chem. Condens. Phases 1976, 72, 400–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, W.J., Jr.; Morris, J.C. Kinetics of Adsorption on Carbon from Solution. J. Sanit. Eng. Div. 1963, 89, 31–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, S.; Tang, R.; Xue, Z.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, J.; Wang, B.; Zeng, S.; Sun, D. Effective Removal of Pb(II) Using Magnetic Co0.6Fe2.4O4 Micro-Particles as the Adsorbent: Synthesis and Study on the Kinetic and Thermodynamic Behaviors for Its Adsorption. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2015, 469, 211–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsuhybani, M.; Alshahrani, A.; Algamdi, M.; Al-Kahtani, A.A.; Alqadami, A.A. Highly Efficient Removal of Pb(II) from Aqueous Systems Using a New Nanocomposite: Adsorption, Isotherm, Kinetic and Mechanism Studies. J. Mol. Liq. 2020, 301, 112393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, A.; Si, Y.; Yin, H.; Chen, J.; Huo, J. Synthesis of Na-, Fe-, and Mg-Containing Titanate Nanocomposites Starting from Ilmenite and NaOH and Adsorption Kinetics, Isotherms, and Thermodynamics of Cu(II), Cd(II), and Pb(II) Cations. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 2019, 249, 114411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varadwaj, G.B.B.; Oyetade, O.A.; Rana, S.; Martincigh, B.S.; Jonnalagadda, S.B.; Nyamori, V.O. Facile Synthesis of Three-Dimensional Mg-Al Layered Double Hydroxide/Partially Reduced Graphene Oxide Nanocomposites for the Effective Removal of Pb2+ from Aqueous Solution. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 17290–17305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarei, F.; Marjani, A.; Soltani, R. Novel and Green Nanocomposite-Based Adsorbents from Functionalised Mesoporous KCC-1 and Chitosan-Oleic Acid for Adsorption of Pb(II). Eur. Polym. J. 2019, 119, 400–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadinezhad, A.; Marandi, G.B.; Farsadrooh, M.; Javadian, H. Synthesis of Poly(Acrylamide-Co-Itaconic Acid)/MWCNTs Superabsorbent Hydrogel Nanocomposite by Ultrasound-Assisted Technique: Swelling Behavior and Pb (II) Adsorption Capacity. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2018, 49, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, W.; Wu, H.; Chen, Y.; Zhong, K.; Feng, L. Application of New Chitosan 2,4-Dihydroxyacetophenone Schiff Base @SrFe12O19 Nanocomposite for Remove of Pb(II) Ion from Aqueous Solution. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 226, 336–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Najaflou, S.; Rad, M.F.; Baghdadi, M.; Nabi Bidhendi, G.R. Removal of Pb(II) from Contaminated Waters Using Cellulose Sulfate/Chitosan Aerogel: Equilibrium, Kinetics, and Thermodynamic Studies. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 286, 112167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]














| Model | Parameters | 303 K | 313 K | 323 K | 333 K |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Langmuir | Qm (mg g−1) | 117.45 | 126.23 | 145.12 | 191.27 |
| KL (L mg−1) | 0.074 | 0.085 | 0.089 | 0.095 | |
| R2 | 0.99 | 0.99 | 0.99 | 0.99 | |
| RMSE | 0.018 | 0.015 | 0.013 | 0.010 | |
| Freundlich | KF (mg g−1) | 24.13 | 24.42 | 24.87 | 28.67 |
| n | 2.05 | 2.37 | 2.58 | 2.84 | |
| R2 | 0.85 | 0.94 | 0.96 | 0.92 | |
| RMSE | 0.062 | 0.057 | 0.048 | 0.069 | |
| D–R | qm (mg g−1) | 232.45 | 235.78 | 251.73 | 273.69 |
| KD–R (mol2 J−2) | 3.78 × 10−7 | 4.69 × 10−7 | 5.54 × 10−7 | 6.86 × 10−7 | |
| E (J mol−1) | 1112.19 | 1279.47 | 1304.35 | 1422.87 | |
| R2 | 0.96 | 0.82 | 0.97 | 0.91 | |
| RMSE | 0.21 | 0.92 | 0.72 | 0.79 | |
| Temkin | A (L mg−1) | 0.624 | 0.859 | 1.342 | 1.521 |
| B (J mol−1) | 105.45 | 98.49 | 107.23 | 92.85 | |
| R2 | 0.91 | 0.97 | 0.99 | 0.97 | |
| RMSE | 2.13 | 1.75 | 1.89 | 1.05 |
| Parameters | Kinetic Models | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pseudo-First-Order | Pseudo-Second-Order | Elovich | Intraparticle Diffusion | |
| qe (mg g−1) | 6.76 | 166.66 | 0.602 | 6.579 |
| k1/k2/kp/kint | 0.011 | 111.102 | 171.23 | 0.566 |
| R2 | 0.95 | 0.99 | 0.955 | 0.88 |
| RMSE | 0.039 | 0.019 | 0.053 | 0.25 |
| Thermodynamics Study | ∆H (KJ mol−1) | ∆S (KJ mol K−1) | ∆G (KJ mol−1) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 303 K | 313 K | 323 K | 333 K | |||
| 29.72 | 0.112 | −4.22 | −5.34 | −6.45 | −7.57 | |
| S.N. | Adsorbent Material | Adsorption Capacity (mg g−1) | Optimum Time (min) | Adsorbent Dose (mg) | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Fe3O4@BDC@AGPA | 157 | 180 | 20 | [58] |
| 2 | NaxFeyMgiTiOz | 20.3 | 400 | 10 | [59] |
| 3 | Mg–Al LDH/rGO | 116.2 | 180 | 100 | [60] |
| 4 | TA-KCC-1/Chi-OLA NC | 168 | 100 | 20 | [61] |
| 5 | P(AAm-co-IA)/MWCNTs | 101.01 | 90 | 50 | [62] |
| 6. | Cs-SB@SrFe12O19 | 132 | 120 | 20 | [63] |
| 7 | Cellulose sulfate/chitosan | 137.8 | 40 | 100 | [64] |
| 8 | CS-ag-CM | 182.5 | 40 | 50 | [47] |
| 9 | XGFO | 191.27 | 120 | 15 | Present Study |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alharthi, F.A.; Alshammari, R.H.; Hasan, I. Synthesis of Xanthan Gum Anchored α-Fe2O3 Bionanocomposite Material for Remediation of Pb (II) Contaminated Aquatic System. Polymers 2023, 15, 1134. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15051134
Alharthi FA, Alshammari RH, Hasan I. Synthesis of Xanthan Gum Anchored α-Fe2O3 Bionanocomposite Material for Remediation of Pb (II) Contaminated Aquatic System. Polymers. 2023; 15(5):1134. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15051134
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlharthi, Fahad A., Riyadh H. Alshammari, and Imran Hasan. 2023. "Synthesis of Xanthan Gum Anchored α-Fe2O3 Bionanocomposite Material for Remediation of Pb (II) Contaminated Aquatic System" Polymers 15, no. 5: 1134. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15051134
APA StyleAlharthi, F. A., Alshammari, R. H., & Hasan, I. (2023). Synthesis of Xanthan Gum Anchored α-Fe2O3 Bionanocomposite Material for Remediation of Pb (II) Contaminated Aquatic System. Polymers, 15(5), 1134. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15051134