In Vitro Characterizations of Post-Crosslinked Gelatin-Based Microspheres Modified by Phosphatidylcholine or Diammonium Phosphate as Antibiotic Delivery Vehicles
Abstract
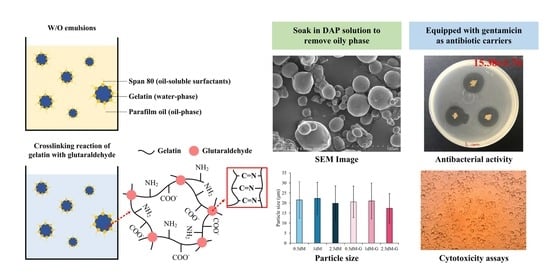
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Microsphere Preparations
2.3. Microsphere Modification
2.3.1. Solutions for Microsphere Modification
2.3.2. DAP-Modified Microspheres as Antibiotic Carriers
2.4. Characterization of Modified Microspheres
2.4.1. Analysis of Infrared Spectroscopy and Morphologies
2.4.2. Crosslinking Index Changes
2.4.3. Degradation of Microspheres In Vitro
2.5. Antibiotic Release
2.6. Antibacterial Activity
2.7. Cytotoxicity In Vitro
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Evaluation of Modified Microspheres by Cytotoxicity Assay
3.2. Characterization of DAP-Modified Microspheres
FTIR Analysis
3.3. Fixation of Free Amine
3.4. Degradation of DAP-Modified Microspheres
3.5. Observation of Gelatin-Based Microspheres via DAP Modification
3.6. Antibiotic Release
3.7. Antibacterial Abilities
3.8. Biocompatibility of Microspheres Impregnated with Antibiotic
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Coelho, J.F.; Ferreira, P.C.; Alves, P.; Cordeiro, R.; Fonseca, A.C.; Góis, J.R.; Gil, M.H. Drug delivery systems: Advanced technologies potentially applicable in personalized treatments. EPMA J. 2010, 1, 164–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ranote, S.; Musioł, M.; Kowalczuk, M.; Joshi, V.; Chauhan, G.S.; Kumar, R.; Chauhan, S.; Kumar, K. Functionalized Moringa oleifera Gum as pH-Responsive Nanogel for Doxorubicin Delivery: Synthesis, Kinetic Modelling and In Vitro Cytotoxicity Study. Polymers 2022, 14, 4697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jain, K.K. Drug Delivery Systems; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2008; Volume 251. [Google Scholar]
- Khafagy, E.-S.; Almutairy, B.K.; Abu Lila, A.S. Tailoring of Novel Bile Salt Stabilized Vesicles for Enhanced Transdermal Delivery of Simvastatin: A New Therapeutic Approach against Inflammation. Polymers 2023, 15, 677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lysik, M.A.; Wu-Pong, S. Innovations in Oligonucleotide Drug Delivery. J. Pharm. Sci. 2003, 92, 1559–1573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Persson, E.M.; Gustafsson, A.-S.; Carlsson, A.S.; Nilsson, R.G.; Knutson, L.; Forsell, P.; Hanisch, G.; Lennernäs, H.; Abrahamsson, B. The effects of food on the dissolution of poorly soluble drugs in human and in model small intestinal fluids. Pharm. Res. 2005, 22, 2141–2151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.-M.; Chen, W.-C.; Huang, S.-M.; Chen, J.-C.; Lin, C.-L. Characterization of electrospun fibers and electrospray vancomycin-containing beads through the interstitial or lamellar separation of bead composite fiber membranes to evaluate their biomedical application in vitro. J. Ind. Text. 2022, 52, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinto Reis, C.; Neufeld, R.J.; Ribeiro, A.J.; Veiga, F. Nanoencapsulation, I. Methods for preparation of drug-loaded polymeric nanoparticles. Nanomedicine, 2006; 2, 8–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, L.Y.; Wang, C.H.; Smith, K.A. Supercritical antisolvent production of biodegradable micro- and nanoparticles for controlled delivery of paclitaxel. J. Control. Release 2008, 125, 96–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lovell, P.A.; Schork, F.J. Fundamentals of emulsion polymerization. Biomacromolecules 2020, 21, 4396–4441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Su, Y.; He, C.; Wang, H.; Fong, H.; Mo, X. Sorbitan monooleate and poly (l-lactide-co-ε-caprolactone) electrospun nanofibers for endothelial cell interactions. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 2009, 91, 878–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Kim, K.; Lee, H.-R.; Jo, H.; Jeong, D.-W.; Ryu, J.; Gweon, D.-G.; Choi, S.Q. Formation of stable adhesive water-in-oil emulsions using a phospholipid and cosurfactants. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2017, 55, 198–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, M.; Wu, X.; Zhang, F.; Zhang, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, Q. Paraffin oil emulsions for the absorption of toluene gas. Chem. Eng. Technol. 2016, 39, 1438–1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandelli, M.A.; Rivasi, F.; Guerra, P.; Forni, F.; Arletti, R. Gelatin microspheres crosslinked with d,l-glyceraldehyde as a potential drug delivery system: Preparation, characterisation, in vitro and in vivo studies. Int. J. Pharm. 2001, 215, 175–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elzoghby, A.O. Gelatin-based nanoparticles as drug and gene delivery systems: Reviewing three decades of research. J. Control. Release 2013, 172, 1075–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, Z.; Li, Z.; Shen, Y. Influence of chemical cross-linking on properties of gelatin/chitosan microspheres. Polym. Plast. Technol. Eng. 2012, 51, 381–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.A.; Firdous, J.; Choi, Y.-J.; Yun, C.-H.; Cho, C.-S. Design and application of chitosan microspheres as oral and nasal vaccine carriers: An updated review. Int. J. Nanomed. 2012, 2012, 6077–6093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lindén, M.V.; Wiedmer, S.K.; Hakala, R.M.S.; Riekkola, M.-L. Stabilization of phosphatidylcholine coatings in capillary electrophoresis by increase in membrane rigidity. J. Chromatogr. A 2004, 1051, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcilla, A.; Beltran, M.I.; Gómez-Siurana, A.; Martinez-Castellanos, I.; Berenguer, D.; Pastor, V.; García, A.N. TGA/FTIR study of the pyrolysis of diammonium hydrogen phosphate–tobacco mixtures. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2015, 112, 48–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sung, H.-W.; Chang, Y.; Chiu, Y.-T.; Hsu, H.-L.; Shih, C.-C.; Lu, J.-H.; Yang, P.-C. Evaluation of an epoxy-fixed biological patch with ionically bound heparin as a pericardial substitute. Biomaterials 1996, 17, 1693–1701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zolfagharzadeh, V.; Ai, J.; Soltani, H.; Hassanzadeh, S.; Khanmohammadi, M. Sustain release of loaded insulin within biomimetic hydrogel microsphere for sciatic tissue engineering in vivo. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 225, 687–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naveed, S.; Shah, S.N.; Qamar, F.; Waheed, N.; Nazeer, S. Simple UV spectrophotometric assay of new formulation gentamycin. J. Appl. Pharm. 2014, 6, 407–410. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, S.-M.; Liu, S.-M.; Chen, W.-C.; Ko, C.-L.; Shih, C.-J.; Chen, J.-C. Morphological Changes, Antibacterial Activity, and Cytotoxicity Characterization of Hydrothermally Synthesized Metal Ions-Incorporated Nanoapatites for Biomedical Application. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, M.-H.; Chu, P.-Y.; Huang, S.-M.; Shih, B.-S.; Ko, C.-L.; Hu, J.-J.; Chen, W.-C. Injectability, processability, drug loading, and antibacterial activity of gentamicin-impregnated mesoporous bioactive glass composite calcium phosphate bone cement in vitro. Biomimetics 2022, 7, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adewunmi, A.A.; Solling, T.; Sultan, A.S.; Saikia, T. Emulsified acid systems for oil well stimulation: A review. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2022, 208, 109569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chacon, O.G.; Pournik, M. Matrix Acidizing in Carbonate Formations. Processes 2022, 10, 174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nosheen, A.; Naz, R.; Tahir, A.T.; Yasmin, H.; Keyani, R.; Mitrevski, B.; Bano, A.; Tong Chin, S.; Marriott, P.J.; Hussain, I. Improvement of safflower oil quality for biodiesel production by integrated application of PGPR under reduced amount of NP fertilizers. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0201738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sadecka, E.; Szeląg, H. One-Step Synthesis of W/O and O/W Emulsifiers in the Presence of Surface Active Agents. J. Surfactants Deterg. 2013, 16, 305–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chaiyana, W.; Leelapornpisid, P.; Phongpradist, R.; Kiattisin, K. Enhancement of antioxidant and skin moisturizing effects of olive oil by incorporation into microemulsions. Nanomater. Nanotechnol. 2016, 6, 1847980416669488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fu, P.-S.; Wang, J.-C.; Lai, P.-L.; Liu, S.-M.; Chen, Y.-S.; Chen, W.-C.; Hung, C.-C. Effects of gamma radiation on the sterility assurance, antibacterial ability, and biocompatibility of impregnated hydrogel macrosphere protein and drug release. Polymers 2021, 13, 938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, C.-H.; Chen, Y.-S.; Chang, H.-T.; Chang, K.-C.; Huang, S.-M.; Liu, S.-M.; Chen, W.-C. In vitro evaluation of antibacterial activity and biocompatibility of synergistically cross-linked gelatin-alginate hydrogel beads as gentamicin carriers. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2023, 79, 104078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haung, S.-M.; Lin, Y.-T.; Liu, S.-M.; Chen, J.-C.; Chen, W.-C. In vitro evaluation of a composite gelatin–hyaluronic acid–alginate porous scaffold with different pore distributions for cartilage regeneration. Gels 2021, 7, 165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gruber, S.; Vorhauer-Huget, N.; Foerst, P. In situ micro-computed tomography to study microstructure and sublimation front during freeze-drying. Food Struct. 2021, 29, 100213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.-H.; Hou, R.-X.; Zhan, D.-X.; Cong, Y.; Cheng, Y.-J.; Fu, J. Fabrication of hollow porous PLGA microspheres for controlled protein release and promotion of cell compatibility. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2013, 24, 710–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Chang, B.; Dong, H.; Liu, X. Functional microspheres for tissue regeneration. Bioact. Mater. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, F.; Li, Y.; Cui, W. Injectable hydrogel microspheres in cartilage repair. Biomed. Technol. 2023, 1, 18–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, M.H.; Blanco, A.; Stealey, S.; Duan, X.; Case, N.; Sell, S.A.; Rai, M.F.; Zustiak, S.P. Micro-clotting of platelet-rich plasma upon loading in hydrogel microspheres leads to prolonged protein release and slower microsphere degradation. Polymers 2020, 12, 1712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hossain, K.M.Z.; Patel, U.; Ahmed, I. Development of microspheres for biomedical applications: A review. Prog. Biomater. 2015, 4, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, Z.; Meng, X.; Yang, W.; Zhang, J.; Sun, P.; Zhang, H.; Fang, X.; Wang, D.-A.; Fan, C. Progress of gelatin-based microspheres (GMSs) as delivery vehicles of drug and cell. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2021, 122, 111949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsawy, M.A.; Wychowaniec, J.K.; Castillo Díaz, L.A.; Smith, A.M.; Miller, A.F.; Saiani, A. Controlling doxorubicin release from a peptide hydrogel through fine-tuning of drug–peptide fiber interactions. Biomacromolecules 2022, 23, 2624–2634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, S.; Siddiqui, L.; Bhattacharya, S.S.; Kaity, S.; Ghosh, A.; Chattopadhyay, P.; Pandey, A.; Singh, L. Interpenetrating polymer network (IPN) hydrogel microspheres for oral controlled release application. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2012, 50, 198–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soppimath, K.S.; Kulkarni, A.R.; Aminabhavi, T.M. Controlled release of antihypertensive drug from the interpenetrating network poly (vinyl alcohol)–guar gum hydrogel microspheres. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 2000, 11, 27–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, T.; Tan, W.; Tian, X.; Tang, Z.; Hu, K.; Ge, L.; Mu, C.; Li, X.; Xu, Y.; Zhao, L.; et al. Gelatin/alginate-based mi-crospheres with sphere-in-capsule structure for spatiotemporal manipulative drug release in gastrointestinal tract. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 226, 485–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Ahmed, A.M.Q.; Deng, Y.; Cao, D.; Du, H.; Cui, J.; Lee, B.-J.; Cao, Q. Novel triptorelin acetate-loaded microspheres prepared by a liquid/oil/oil method with high encapsulation efficiency and low initial burst release. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2019, 54, 101390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruan, L.; Su, M.; Qin, X.; Ruan, Q.; Lang, W.; Wu, M.; Chen, Y.; Lv, Q. Progress in the application of sustained-release drug microspheres in tissue engineering. Mater. Today Bio 2022, 16, 100394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sulaiman, S.B.; Idrus, R.B.H.; Hwei, N.M. Gelatin microsphere for cartilage tissue engineering: Current and future strategies. Polymers 2020, 12, 2404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Wang, M.; Ran, Y.; Wu, Y.; Wang, J.; Gao, F.; Liu, Z.; Xi, J.; Ye, L.; Feng, Z. Design and fabrication of polymeric hydrogel carrier for nerve repair. Polymers 2022, 14, 1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanungo, M.; Wang, Y.; Hutchinson, N.; Kroll, E.; DeBruine, A.; Kumpaty, S.; Ren, L.; Wu, Y.; Hua, X.; Zhang, W. Development of Gelatin-Coated Microspheres for Novel Bioink Design. Polymers 2021, 13, 3339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lei, L.; Wang, X.; Zhu, Y.; Su, W.; Lv, Q.; Li, D. Antimicrobial hydrogel micospheres for protein capture and wound healing. Mater. Des. 2022, 215, 110478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ressler, A. Chitosan-Based Biomaterials for Bone Tissue Engineering Applications: A Short Review. Polymers 2022, 14, 3430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]














Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chang, K.-C.; Chang, P.-J.; Chen, J.-C.; Huang, S.-M.; Liu, S.-M.; Shih, C.-J.; Chen, W.-C. In Vitro Characterizations of Post-Crosslinked Gelatin-Based Microspheres Modified by Phosphatidylcholine or Diammonium Phosphate as Antibiotic Delivery Vehicles. Polymers 2023, 15, 1504. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15061504
Chang K-C, Chang P-J, Chen J-C, Huang S-M, Liu S-M, Shih C-J, Chen W-C. In Vitro Characterizations of Post-Crosslinked Gelatin-Based Microspheres Modified by Phosphatidylcholine or Diammonium Phosphate as Antibiotic Delivery Vehicles. Polymers. 2023; 15(6):1504. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15061504
Chicago/Turabian StyleChang, Kai-Chi, Pei-Jheng Chang, Jian-Chih Chen, Ssu-Meng Huang, Shih-Ming Liu, Chi-Jen Shih, and Wen-Cheng Chen. 2023. "In Vitro Characterizations of Post-Crosslinked Gelatin-Based Microspheres Modified by Phosphatidylcholine or Diammonium Phosphate as Antibiotic Delivery Vehicles" Polymers 15, no. 6: 1504. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15061504
APA StyleChang, K. -C., Chang, P. -J., Chen, J. -C., Huang, S. -M., Liu, S. -M., Shih, C. -J., & Chen, W. -C. (2023). In Vitro Characterizations of Post-Crosslinked Gelatin-Based Microspheres Modified by Phosphatidylcholine or Diammonium Phosphate as Antibiotic Delivery Vehicles. Polymers, 15(6), 1504. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15061504