New Biocompatible Polyesters Derived from α-Amino Acids: Hydrolytic Degradation Behavior
Abstract
:1. Introduction



2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Synthesis of Polymers
| Polymer | Mwa (Da) | Mna (Da) | Optical activity [α]Db (lit. value) | Solubility (g/L)c | Tg(°C)d (Lit value) | ΔH (J/gr)d | Water contact angle (θ)e | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CHCl3 | THF | ACN | ||||||||
| 1 | LPLA | 2800 | 2600 | –139(–141) [17] | 250 | 18 | <2% | 49.0(49–60) [17] | –6.3 | 37.1 |
| 2 | Poly(L)HOIle | 1000 | 800 | –10 | >600 | 150 | 60 | –10.7 | –4.1 | 53.0 |
| 3 | Poly(L)HOLeu | 2300 | 1900 | –43 | >600 | 80 | 120 | –8.8 | –3.7 | 76.2 |
| 4 | Poly(L)HOPhe | 2500 | 2200 | –37 | >600 | 37 | 47 | 32.0*(38–50) [18] | –5.9 | 85.8 |
| 5 | Poly(L)HOVal | 1000 | 700 | –32 | >600 | 122 | 65 | 16.8 | –4.3 | 73.7 |
| 6 | Poly(L)HOIle-HOLeu | 1700 | 1400 | –37 | 360 | 450 | 400 | –36.7 | –2.2 | 89.7 |
| 7 | Poly(L)HOIle-HOPhe | 1900 | 1400 | –22 | 60 | 500 | 330 | –42.0 | –2 | 86.3 |
| 8 | Poly(L)HOIle-HOVal | 800 | 800 | –12 | >600 | 520 | 280 | –45.1 | –3.7 | 37.0 |
| 9 | Poly(L)HOLeu-HOPhe | 2500 | 1900 | –31 | 110 | 400 | 400 | –36.2 | –2.3 | 89.8 |
| 10 | Poly(L)HOLeu-HOVal | 2500 | 1800 | –42 | 360 | 500 | 400 | –45.0 | –2.2 | 107.5 |
| 11 | Poly(L)HOPhe-HOVal | 1700 | 1300 | –26 | 150 | 500 | 500 | –44.1 | –2.7 | 100.5 |
| 12 | Poly(L)HOIle-LA | 1800 | 1600 | –53 | >600 | 32 | 75 | 5.4 | –3.013 | 67.4 |
| 13 | Poly(L)HOLeu-LA | 2300 | 1900 | –60 | >600 | 147 | 59 | 11.2 | –5.31 | 78.4 |
| 14 | Poly(L)HOPhe-LA | 2500 | 2300 | –55**(–66) [18] | >600 | 410 | 41 | 25.9**(38–50) [18] | –11.8 | 99.1 |
| 15 | Poly(L)HOVal-LA | 1700 | 1400 | –70 | >600 | 78 | 33 | 29.2 | –6.8 | 87.7 |
| 16 | Poly(L)HOIle-GA | 1700 | 1400 | –22 | >600 | 400 | 300 | –41.2 | –3.0 | 54.7 |
| 17 | Poly(L)HOLeu-GA | 2800 | 2100 | –46 | >600 | 400 | 400 | –43.2 | –2.8 | 95.7 |
| 18 | Poly(L)HOPhe-GA | 2400 | 1700 | –22 | 220 | 500 | 360 | –36.2 | −5.6 | 82.7 |
| 19 | Poly(L)HOVal-GA | 2200 | 1600 | –29 | >600 | 500 | 500 | –45.9 | –3.7 | 55.1 |
| 20 | Poly(L)HOIle-CA | 2500 | 2100 | –4 | 540 | 500 | 500 | –63.9 | –7.0 | 46.1 |
| 21 | PolyHOLeu-CA | 5400 | 2800 | –24 | 180 | 500 | 400 | –69.3 | –9.7 | 57.0 |
| 22 | PolyHOPhe-CA | 4100 | 2200 | –13 | 360 | 400 | 340 | –46.7 | –4.3 | 73.9 |
| 23 | PolyHOVal-CA | 2800 | 1800 | –5 | 549 | 600 | 360 | –73.2 | –6.0 | 50.4 |

| Polymer | Mn (Da,GPC) | Mn(Da,1H-NMR) |
|---|---|---|
| Poly(L)HOIle | 800 | 710 |
| Poly(L)HOLeu | 1900 | 1830 |
| Poly(L)HOPhe | 2200 | 2100 |
| Poly(L)HOVal | 700 | 650 |

2.2. Toxicity
2.3. In vitro Hydrolytic Degradation of the Polymers
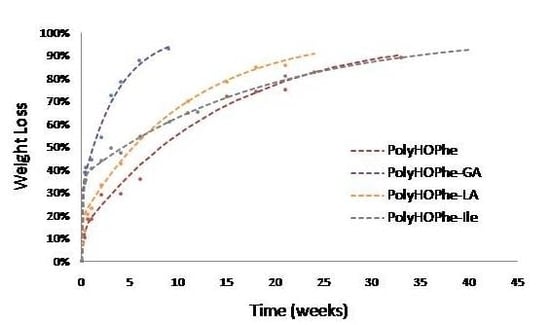
2.3.1. Weight Loss Analysis
| Polymer | k1(week−1) | P1 | k2 (week−1) | k1/k2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PolyHOPhe | 4.75 | 13.45 | 0.0669 | 71 |
| Poly-HOPhe-CA | 6.12 | 15.95 | 0.0373 | 164 |
| PolyHOPhe-GA | 17.50 | 31.60 | 0.26 | 66.79 |
| PolyHOPhe-LA | 12 | 18.83 | 0.09 | 34.83 |
| PolyHOPhe-HOVal | 9.87 | 47.6 | 0.093 | 107 |
| PolyHOPhe-HOIle | 7.10 | 37.05 | 0.053 | 134 |
| PolyHOPhe-HOLeu | 8 | 22.38 | 0.0737 | 276 |
| PolyHOLeu | 2.605 | 44.4 | 0.073 | 36.3 |
| Poly-HOLeu-CA | 3.62 | 21.96 | 0.027 | 349 |
| PolyHOLeu-GA | 10.52 | 31.6 | 0.291 | 46.5 |
| PolyHOLeu-LA | 6.46 | 23.9 | 0.0719 | 89.8 |
| PolyHOLeu-HOVal | 5.06 | 33.78 | 0.028 | 316 |
| PolyHOLeu-HOIle | 5.08 | 26.9 | 0.0587 | 87.6 |
| PolyHOIle | 5.42 | – | – | – |
| PolyHOIle-CA | 2.91 | 44.62 | 0.0328 | 88.7 |
| PolyHOIle-GA | 1.91 | – | – | – |
| PolyHOIle-LA | 5.5 | – | – | – |
| PolyHOVal | 4.48 | – | – | – |
| PolyHOVal-CA | 2.91 | 66.47 | 0.0431 | 158 |
| PolyVal-GA | 3.97 | – | – | – |
| PolyHOVal-LA | 4.67 | – | – | – |
| PolyHOVal-HOIle | 5.10 | – | – | – |


2.3.2. IR Analysis

2.3.3. GPC Analysis

| Polymer | k1(week−1) | A01 | k2(week−1) | k1/k2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PolyHOPhe | 3.03 | 11.2 | 0.027 | 105 |
| PolyHOPhe-CA | 1.87 | 27 | 0.0094 | 198 |
| PolyHOPhe-GA | 1.44 | 28.4 | 0.018 | 80 |
| PolyHOPhe-LA | 8.54 | 5.6 | 0.036 | 237 |
| PolyHOPhe-Val | 0.0738 | – | – | – |
| PolyHOPhe-Ile | 0.0176 | – | – | – |
| PolyHOPhe-Leu | 10.39 | 31 | 0.019 | 546 |
| PolyHOLeu | 8.157 | 31 | 0.059 | 138 |
| PolyHOLeu-CA | 1.26 | 39 | 0.0074 | 170.2 |
| PolyHOLeu-GA | 0.786 | 32.8 | 0.0113 | 69 |
| PolyHOLeu-LA | 8.085 | 9.4 | 0.0462 | 89.8 |
| PolyHOLeu-Val | 4.72 | 23 | 0.020 | 236 |
| PolyHOLeu-Ile | 0.0738 | – | – | – |
| PolyHOIle | 0.448 | – | – | – |
| PolyHOIle-CA | 0.045 | – | – | – |
| PolyHOIle-GA | 0.781 | – | – | – |
| PolyHOIle-LA | 1.656 | – | – | – |
| PolyHOVal | 0.395 | – | – | – |
| PolyHOVal-CA | 0.0131 | – | – | – |
| PolyHOVal-GA | 2.40 | – | – | – |
| PolyHOVal-LA | 1.145 | – | – | – |
| PolyHOVal-Ile | 0.327 | – | – | – |

| Weight Loss | MW Decrease | |
|---|---|---|
| k1 | 1.9 to 17.5 week−1 | 0.3 to 10 week−1 |
| k2 | 0.02 to 0.3 week−1 | 0.007 to 0.06 week−1 |
| t1/2(1) | 6.7 to 60 hours | 11 to 356 hours |
| t1/2(2) | 2.6 to 26 weeks | 11 to 93 weeks |
2.3.4. NMR Analysis
| Copolymer | Chemical shift of Peak A (HOPhe, ppm) | Chemical shift of Peak B (ppm) | A:B at t = 0 |
|---|---|---|---|
| PolyHOPhe-Ile | 7.26 (5 aromatic protons) | 0.92 (6 methyl protons) | 5:6 |
| PolyHOPhe-Leu | 7.26 (5 aromatic protons) | 0.93 (6 methyl protons) | 5:6 |
| PolyHOPhe-Val | 7.26 (5 aromatic protons) | 0.85 (6 methyl protons) | 5:6 |
| PolyHOPhe-LA | 3.18 (2 CH2 protons) | 1.52 (3 methyl protons) | 2:3 |
| PolyHOPhe-GA | 5.32 (1 CH proton) | 4.72 (2 CH2 protons) | 1:2 |
| PolyHOPhe-CA | 3.18 (2 CH2 protons) | 2.29 (2 CH2 protons) | 1:1 |

2.3.5. Buffer Solutions Analysis

3. Experimental
3.1. Materials
3.2. Techniques
3.3. Synthesis of α-Hydroxy Acids
3.4. Polymerization of the α-Hydroxy Acids
3.5. Toxicity
3.6. In vitro Hydrolytic Degradation of the Polymers
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
References
- Albertsson, A.C. Degradable Aliphatic Polyesters. In Advances in Polymer Science; Springer-Verlag: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2002; Volume 157. [Google Scholar]
- Li, S.M.; McCarthy, S. Further investigations on the hydrolytic degradation of poly(DL-lactide). Biomaterials 1999, 20, 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vert, M. Aliphatic polyesters: Great degradable polymers that cannot do everything. Biomacromolecules 2005, 6, 538–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, M.H.; Li, S.M.; Hutmacher, D.W.; Coudane, J.; Vert, M. Degradation characteristics of poly(epsilon-caprolactone)-based copolymers and blends. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2006, 102, 1681–1687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutmacher, D.W. Scaffold design and fabrication technologies for engineering tissues—State of the art and future perspectives. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 2001, 12, 107–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hutmacher, D.W.; Schantz, T.; Zein, I.; Ng, K.W.; Teoh, S.H.; Tan, K.C. Mechanical properties and cell cultural response of polycaprolactone scaffolds designed and fabricated via fused deposition modeling. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 2001, 55, 203–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.V.M. Biodegradation of Aliphatic Polyesters. In Degradable Polymers: Principles and Applications, 2nd ed.; Scott, G., Ed.; Kluwer Academic Publishers: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Pitt, C.G. Biodegradable Polymers as Drug Delivery Systems; Chasin, M., Langer, R., Eds.; Marcel Dekker: New York, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Vert, M.C.P.; Chabot, F.; Leray, J. Macromolecular Biomaterials; Hastings, G.W., Ducheyne, P., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Benabdillah, K.M.; Coudane, J.; Boustta, M.; Engel, R.; Vert, M. Synthesis and characterization of novel degradable polyesters derived from D-gluconic and glycolic acids. Macromolecules 1999, 32, 8774–8780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slager, J.; Domb, A.J. Biopolymer stereocomplexes. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2003, 55, 549–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deechongkit, S.; You, S.L.; Kelly, J.W. Synthesis of all nineteen appropriately protected chiral alpha-hydroxy acid equivalents of the alpha-amino acids for Boc solid-phase depsi-peptide synthesis. Org. Lett. 2004, 6, 497–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bauer, T.; Gajewiak, J. alpha-Hydroxy carboxylic acids as ligands for enantioselective diethylzinc additions to aromatic and aliphatic aldehydes. Tetrahedron 2004, 60, 9163–9170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antheunis, H.; van der Meer, J.C.; de Geus, M.; Kingma, W.; Koning, C.E. Improved Mathematical Model for the Hydrolytic Degradation of Aliphatic Polyesters. Macromolecules 2009, 42, 2462–2471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antheunis, H.; van der Meer, J.C.; de Geus, M.; Heise, A.; Koning, C.E. Autocatalytic Equation Describing the Change in Molecular Weight during Hydrolytic Degradation of Aliphatic Polyesters. Biomacromolecules 2010, 11, 1118–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albertsson, A.C.; Varma, I.K. Aliphatic polyesters: Synthesis, properties and applications. In Degradable Aliphatic Polyesters; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2002; Volume 157, pp. 1–40. [Google Scholar]
- Mark, J.E. Polymer Data Handbook; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 1999; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Fukuzaki, H.; Yoshida, M.; Asano, M.; Kumakura, M.; Imasaka, K.; Nagai, T.; Mashimo, T.; Yuasa, H.; Imai, K.; Yamanaka, H. Synthesis of Biodegradable Copoly(L-Lactic Acid/Aromatic Hydroxyacids) with Relatively Low-Molecular-Weight. Eur. Polym. J. 1990, 26, 1273–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen-Arazi, N.; Katzhendler, J.; Domb Abraham, J.; Hagag, I.; Kolitz, M.; Arien-Zakay, H.; Lazarovici, P.; Lecht, S. Biodegradable Polyester Matrixes Derived from α-Hydroxy Acids as Cell Biocompatiable Substratum. 2010; in preparation. [Google Scholar]
- Simitzis, J.; Triantou, D.; Soulis, S.; Triantou, K.; Simitzis, C.; Zoumpoulakis, L. Correlation of hydrolytic degradation with structure for copolyesters produced from glycolic and adipic acids. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2010, 21, 1069–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.W.; Gardella, J.A.; Hicks, W.; Hard, R.; Brigh, F.V. Analysis of the Initial Burst of Drug Release Coupled with Polymer Surface Degradation. Pharm. Res. 2003, 20, 149–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaikov, L.V.S. The Mechanism of Chemical Degradation of Polymers: Part I: Quantitative Prediction of Hydrolytic Stability of Polyesters. Polym. Degrad. Stabil. 1984, 9, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gopferich, A. Polymer bulk erosion. Macromolecules 1997, 30, 2598–2604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukuzaki, H.; Yoshida, M.; Asano, M.; Kumakura, M. Synthesis of Copoly(D,L-Lactic Acid) with Relatively Low Molecular Weight and in vitro Degradation. Eur. Polym. J. 1989, 25, 1019–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panyam, J.; Dali, M.M.; S.K., S.; Ma, W.; Chakravarthi, S.S.; Amidon, G.L.; Levy, R.J.; Labhasetwar, V. P olymer degradation and in vitro release of a model protein from poly(D,L-lactide-co-glycolide) nano- and microparticles. J. Control. Release 2003, 92, 173–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, Z.G.; Black, R.A.; Curran, J.M.; Hunt, J.A.; Rhodes, N.P.; Williams, D.F. Surface properties and biocompatibility of solvent-cast poly[epsilon-caprolactone] films. Biomaterials 2004, 25, 4741–4748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pitt, C.G.; Gratzl, M.M.; Kimmel, G.L.; Surles, J.; Schindler, A. Aliphatic polyestersII. The degradation of poly (DL-lactide), poly (E-caprolactone), and their copolymers in vivo. Biomaterials 1981, 2, 215–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schliecker, G.; Schmidt, C.; Fuchs, S.; Wombacher, R.; Kissel, T. Hydrolytic degradation of poly(lactide-co-glycolide) films: effect of oligomers on degradation rate and crystallinity. Int. J. Pharm. 2003, 266, 39–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, I.; Lee, M.R.; Lee, J.; Jung, M.; Lee, W.; Yoon, J. Synthesis of optically active phthaloyl D-aminooxy acids from L-amino acids or L-hydroxy acids as building blocks for the preparation of aminooxy peptides. J. Org. Chem. 2000, 65, 7667–7675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Degerbeck, F.; Fransson, B.; Grehn, L.; Ragnarsson, U. Synthesis of N-15-Labeled Chiral Boc-Amino Acids from Triflates—Enantiomers of Leucine and Phenylalanine. J. Chem. Soc. Perk. Trans. 1 1993, 1, 11–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kajiyama, T.; Kobayashi, H.; Taguchi, T.; Kataoka, K.; Tanaka, J. Improved synthesis with high yield and increased molecular weight of poly(alpha,beta-malic acid) by direct polycondensation. Biomacromolecules 2004, 5, 169–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simmons, T.L.; Baker, G.L. Poly(phenyllactide): Synthesis, characterization, and hydrolytic degradation. Biomacromolecules 2001, 2, 658–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lecht, S.; Arien-Zakay, H.; Wagenstein, Y.; Inoue, S.; Marcinkiewicz, C.; Lelkes, P.I.; Lazarovici, P. Transient signaling of Erk1/2, Akt and PLCgamma induced by nerve growth factor in brain capillary endothelial cells. Vas. Pharmacol. 2010, 53, 107–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2010 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Cohen-Arazi, N.; Domb, A.J.; Katzhendler, J. New Biocompatible Polyesters Derived from α-Amino Acids: Hydrolytic Degradation Behavior. Polymers 2010, 2, 418-439. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym2040418
Cohen-Arazi N, Domb AJ, Katzhendler J. New Biocompatible Polyesters Derived from α-Amino Acids: Hydrolytic Degradation Behavior. Polymers. 2010; 2(4):418-439. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym2040418
Chicago/Turabian StyleCohen-Arazi, Naomi, Abraham J. Domb, and Jeoshua Katzhendler. 2010. "New Biocompatible Polyesters Derived from α-Amino Acids: Hydrolytic Degradation Behavior" Polymers 2, no. 4: 418-439. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym2040418
APA StyleCohen-Arazi, N., Domb, A. J., & Katzhendler, J. (2010). New Biocompatible Polyesters Derived from α-Amino Acids: Hydrolytic Degradation Behavior. Polymers, 2(4), 418-439. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym2040418