1. Introduction
Flory investigated that the physical properties of polymers and, accordingly, their practical applications would be related to their macromolecular topologies [
1,
2]. After the first reported syntheses of dendrimers, intense research efforts were dedicated toward finding new and simpler approaches for the formation of highly branched macromolecules [
3,
4]. Both convergent and divergent methods have been used to synthesize numerous examples of dendrimers with compositionally and functionally tunable inner and outer region and unique globular shapes [
5,
6,
7]. In addition, approximations to the regular structures of dendrimers have been accomplished through the synthesis of hyperbranched polymers. Although the structures of hyperbranched polymers are less regular than those of dendrimers, they may be more conducive to industrial applications because of their simpler syntheses. In early syntheses of hyperbranched polymers, reactions of monomers AB
x (
x ≥ 2) where the A and B groups can condense with each other exclusively resulted in step-growth polymerization becoming a predominant method. Thus, an enormous numbers of different types of hyperbranched polymers have been synthesized, including polyphenylenes [
8,
9], polyesters [
10,
11,
12], polyether [
13,
14], polysiloxysilanes [
15], and polybenzamides [
16,
17], a variety of which have been reviewed [
18,
19]. Through conventional step-growth mechanisms, hyperbranched polymers can be synthesized in one-pot, avoiding the need for multiple reactions with protection, deprotection, and purification steps typically required for constructing perfect dendrimers, but with the drawback of large polydispersities in molecular weight and structure. Recent developments in chain-growth condensation polymerization (CGCP, an analogue to living condensation polymerization), have allowed the syntheses of hyperbranched aromatic polyamides having high degrees of polymerization and very narrow molecular weight distributions (
Đ ≤ 1.13) through simple condensation polymerization of special AB
2 monomers [
20,
21,
22].
The enormous efforts aimed at developing living chain-growth polymerizations on developments of branched structures (e.g., cationic [
23]/anionic [
24,
25] polymerization, nitroxide-mediated radical polymerization (NMRP) [
26,
27], atom transfer radical polymerization (ATRP) [
28,
29,
30,
31], group transfer polymerization (GTP) [
32,
33], UV-initiated RAFT (reversible addition-fragmentation chain-transfer) polymerization [
34,
35], and ring-opening (metathesis) polymerization (RO(M)P) [
36,
37]), have led to many novel systems being amenable to the syntheses of hyperbranched polymers. One of the most promising approaches is the synthesis of hyperbranched polymers through atom transfer radical self-condensing vinyl polymerization (AT-SCVP) of AB* inimers [
28,
29,
38].
Scheme 1 presents a typical mechanism for AT-SCVP used to prepare hyperbranched polymers. The AB*-type inimer, featuring both initiation and propagation sites, can be activated externally (e.g., using Cu(I)/L (L: ligand)). Because the initiation and the propagation sites have similar reactivities, chain propagation and re-initiation proceed simultaneously, leading to a polymer topology having a hyperbranched structure. As mentioned above, SCVP approaches with AB*-type inimers have been applied widely to NMRP, GTP, RO(M)P, and cationic/anionic polymerizations.
Scheme 1.
General mechanism of atom transfer self-condensing vinyl polymerization (AT-SCVP) of an AB*-type inimer.
Scheme 1.
General mechanism of atom transfer self-condensing vinyl polymerization (AT-SCVP) of an AB*-type inimer.
Specifically, the concept of “active site transfer” has attracted interests for the synthesis of hyperbranched structures; it involves switching the active site within intra-propagating chains or among inter-propagating chains during the periods of initiation and propagation to control the polymer topology. One approach is to use “iniferter” monomers containing a chain-transfer group (e.g., methacrylate and styrene derivatives with a dithioester [
39] or thiocarbamate [
35,
40] groups). Another approach uses an azomethylmalonodinitrile-substituted styrene derivative for the preparation of highly branched polymers through a radical process [
41]. These dithioester, dithiocarbamate, and malonodinitrile approaches based on reversible termination/transfer agents are all effective at avoiding crosslinking reactions, even in nonliving systems under UV radiation or thermal decomposition. Grubbs
et al. applied acyclic diene metathesis polymerization (ADMET) to a variety of AB
2 monomers under mild reaction conditions. Using imidazolinylidene-based catalysts, electron-poor olefins did not homodimerize but switched to attack the more reactive olefins to perform a secondary metathesis reaction, leading to hyperbranched poly(ester ene)s without any gelation [
36]. A few studies based on the concept of “active site transfer” have demonstrated the distinctive benefits of directly polymerizing existing commodity monomers or catalysts. One is related to the use of a styrene derivative containing a chlorodimethylsilyl substituent that undergoes quantitative S
N2 reactions during anionic polymerization. This system requires slow addition of the monomer to avoid gelation [
42]. The “active site transfer” mechanism can also be designed to yield soluble products through free radical copolymerizations of monomers and crosslinkers. Sherrington
et al. investigated the effect of adding large amounts of thiol-based chain transfer agents to avoid gelation to obtain branched methacrylic copolymers [
43]. The specific concept of “active site transfer” has also been investigated in the RAFT polymerization of methyl methacrylate (MMA) and ethylene glycol dimethacrylate (EGDMA) [
44]; anionic SCVP of divinylbenzene (DVB) and 1,3-isopropenylenebenzene [
45]; AT-SCVP of DVB and (1-bromoethyl)benzene [
46]; AT-SCVP of EGDMA and bisphenol A dimethacrylate [
47]; and deactivation-enhanced AT-SCVP of commercially available multifunctional vinyl monomers [
48]. A remarkable approach using Pd(II) and Ni(II) catalysts and very bulky chelating diimine ligands [
49,
50,
51], has been reported for the formation of hyperbranched polyethylene at low pressure (a so-called “chain walking” process). The mechanism of active site transfer occurring predominantly among intra-chain provides a facile approach for controlling the topology of polyethylene. Hence, developing new synthetic routes with control over polymer topology is of great interest, as is the preparation of dendritic materials with controlled architectures. Accordingly, using commodity monomers and catalysts, we wished to combine the concept of “active site transfer” with AT-SCVP, by manipulating catalyst solubility during polymerization to synthesize hyperbranched polymers in a simple, one-pot procedure.
Some literatures have illustrated one-pot procedure to control over polymer topologies with different single solvents, different thermostated temperatures or adding specific reagents [
52,
53,
54,
55]. Besides, cupric complexes (
i.e., Cu(I)/ligand or Cu(II)/ligand) have significantly different solubilities in various solvents at various temperatures [
56]. To the best of our knowledge, there have been no previous reports of manipulating differences in solubility to control polymer topologies through variations in temperature or solvent in a one-pot procedure. In this paper, we report a facile and simple methodology for controlling polymer topologies. As displayed in
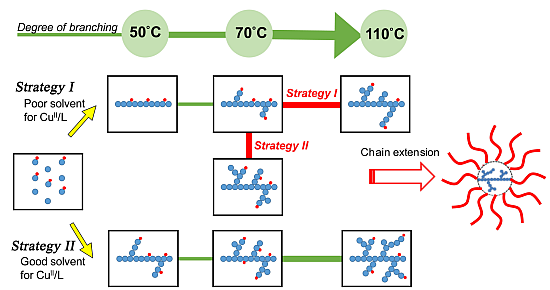
Scheme 2I, poor solubility conditions for a cupric complex allowed atom transfer radical reactions to occur initially in the presence of an initiator with a more-active initiating site, a Cu(I) complex (
i.e., activator), a monomer, and an inimer with less-active initiating site. After initiating the more-active site through atom transfer reaction and producing a higher-oxidation-state Cu(II) complex (
i.e., deactivator), the heterogeneity/precipitation of the deactivator leads the polymerization to a conventional free radical mechanism. This approach provides a linear copolymer with pendent groups of the less-active initiating site. Subsequently, we employed two strategies increasing the temperature or the solvent polarity to re-dissolve the deactivator into the reaction medium. The pendent group with the less-active initiating site could be re-initiated to undergo a typical atom transfer radical self-condensing vinyl polymerization. The copper complexes’ solubility differences are influenced by relative solvent polarity; consequently, we could control the polymer topologies by tuning the timing of the transformation of the poor-to-good solubility conditions. Based on the adjustable solubility properties of the copper complex, we developed a facile route, through atom transfer radical polymerizations, to control the polymer topology in one-pot. To prepare more-complex architectures, we investigated the preparation of star polymers having a hyperbranched core. Chain extensions of the resulting hyperbranched macroinitiator with styrene or acrylate monomers provided hyperbranched core star polymers (hb-core stars) exhibiting functionality on the peripheral segments.
Scheme 2.
Proposed strategies for controlling polymer topology through a one-pot procedure and preparations of hyper-branched core star polymers.
Scheme 2.
Proposed strategies for controlling polymer topology through a one-pot procedure and preparations of hyper-branched core star polymers.
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Characterization
1H NMR (nuclear magnetic resonance) spectroscopy was performed using a Varian Inova 600 NMR (Palo Alto, CA, USA) and CDCl3 or deuterated dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO-d6) as solvents, with calibrating to the chemical shift of CDCl3 at 7.26 ppm or DMSO-d6 at 2.49 ppm (s: singlet; m: multiplet; br: broad). FT-IR (Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy) spectroscopy was performed using a Nicolet Avatar 320 FT-IR spectrometer (Nicolet, Madsion, WI, USA) and a KBr disk; 32 scans were collected at a resolution of 1 cm−1. A THF (tetrahydrofuran) solution containing the sample was cast onto a KBr disk and dried under conditions similar to those used for bulk preparation. The sample chamber was purged with N2 to maintain film dryness. Gel permeation chromatography (GPC) was performed in tetrahydrofuran (THF; flow rate: 1 mL/min) at 40 °C using a system equipped with a Waters 515 pump (Milford, MA, USA), a Waters 410 differential refractometer (RI), a Waters 486 absorbance detector (UV), a Viscotek SEC-MALS 20 multi-angle light (LS) scattering detector (Malvern, Worcestshire, UK) and two PSS SDV columns (Linear S and 100 Å pore size). Monodisperse polystyrene standards were used for calibrations. Conversions of monomers were monitored using a HP 5890 series II (Hewlett Packard, Palo Alto, CA, USA) gas chromatograph (GC), equipped with a flame ionization detector (FID), and employing a CNW CD-5 column (30 m) featuring a proper internal standard. Concentrations of copper were determined through atomic absorption (AA) spectroscopy using a PerkinElmer (Waltham, MA, USA) Analyst 400 apparatus. Three analyses were performed for each sample and averaged. The measured intensities were converted to copper concentrations using a six-point calibration curve derived from aqueous Cu(NO3)2 solutions at concentrations ranging from 0 to 5 ppm (slope: 0.0844; R2: 0.9997).
2.2. Materials
Styrene (St, 99%) was purchased from Aldrich (St. Louis, MO, USA) and purified by passing through a column filled with basic alumina to remove the inhibitors or antioxidants. Cu(I) bromide (CuBr, 98%, Acros, (Geel, Belgium) and Cu(I) chloride (CuCl, 98%, Acros) were washed with glacial AcOH (to remove any soluble oxidized species), filtered, washed with EtOH, and dried under vacuum. 4-Vinylbenzyl chloride (VBC, 90%), ethyl 2-bromoisobutyrate (EBiB, 98%), benzyl chloride (BzCl, 99%), 2,2,6,6-tetramethylpiperidine-1-oxyl (TEMPO, 98%), 2,2'-bipyridyne (Bpy, 99%), N,N,N',N'',N''-pentamethyldiethylenetriamine (PMDETA), Cu(II) bromide (CuBr2, 99%), and Cu(II) chloride (CuCl2, 99%) were purchased from Aldrich. All other solvents were purified through distillation prior to use.
2.3. Solubility Examinations
A single solvent or co-solvent was loaded into a 10-mL Schlenk flask. A desired amount of a copper complex (CuBr/Bpy or CuBr2/Bpy) and a stirrer bar were loaded into a second 10-mL Schlenk flask. Each flask was sealed with a glass cap and glass stopcocks equipped with a latex septum. The flasks were subjected to five freeze-pump-thaw cycles. A degassed (co)solvent was added to the second flask (containing the copper complex), via the septum, using a N2-purged syringe. For CuBr, the solution remained transparent and light-brownish when air was excluded from the flask. The presence of air, however, caused the solution to turn green upon oxidation of Cu(I) to Cu(II). The flask was placed in a thermostatted oil bath and the sample stirred for a desired period of time. The flask was then opened to the air; its contents became heterogeneous with the formation of a greenish precipitate. The solvent was concentrated under vacuum to obtain a greenish solid. Concentrated HCl (1 mL) was added to completely dissolve the precipitate. The sample was diluted with deionized water; its total copper content was determined using a flame AA spectrophotometer to calculate the soluble copper concentration in the organic media.
2.4. Model Reactions of Mixed Initiators
Reactions of mixed initiators in various single solvents at various temperatures and ratios of copper/ligands were performed based on previous literature [
56,
57,
58,
59,
60]. The Cu(I) complexes were prepared in situ under a N
2 atmosphere by adding deoxygenated solvent (2 mL) to Bpy (0.2 mmol), TEMPO (1.0 mmol), and CuBr (0.1 mmol) in a Schlenk flask. After three freeze-pump-thaw cycles and stirring for 30 min at 35 °C, a deoxygenated stock solution (0.5 mL) of EBiB (0.5 mmol) and BzCl (8.0 mmol) mixed in the same solvent (
i.e., toluene (T) or anisole (A)) was added to the Schlenk flask via a degassed syringe. A sample was removed immediately for use as the reference; other samples were removed at timed intervals ([EBiB]
0 = 0.25 M). The degrees of consumption of the alkyl halides were determined using gas chromatography.
2.5. Procedures of Typical AT-SCVP
A general polymerization is described: St, VBC, EBiB, Bpy, and A (e.g., St/VBC/EBiB/Bpy = 160/80/5/2; [St]0 = 3.5 M) were added to a Schlenk flask. The mixture was deoxygenated through three freeze-pump-thaw cycles and then the flask was backfilled with N2. CuBr was added to the frozen solution. The flask was closed, evacuated, and deoxygenated through two additional freeze-pump-thaw cycles. An initial sample was removed via syringe and then the flask was immersed in thermostatted oil bath. Aliquots were withdrawn at intervals during the polymerization process to allow monitoring of the monomer conversion through GC with A as an internal standard. The polymerization was stopped by placing the flask in an ice bath and exposing the contents to air. The resulting mixture was diluted with THF. The mixture was precipitated into cold MeOH, collected, and dried under vacuum (Mn = 1500; Đ (i.e., Mw/Mn) = 1.35; conversion = 46.7%; yield = 32%). 1H NMR (600 MHz, CDCl3, ppm from TMS): 7.4–6.4 (br, aromatic), 5.69 and 5.19 (br, initial moiety of double bond), 4.5 (s, Ph–CH2–Cl), 2.85 (s, Ph–CH2–alkyl), 2.50–1.45 (br, alkyl).
2.6. Procedures of Catalyst Phase Switching Atom Transfer Radical Self-Condensing Vinyl Copolymerization in One-Pot
A typical polymerization, through temperature control, is described. St, VBC, EBiB, Bpy, and T (e.g., St/VBC/EBiB/Bpy = 160/80/5/2; [St]0 = 3.5 M) were added to a Schlenk flask. Procedures similar to those described above were performed, except that the starting temperature was fixed at 70 °C. After performing the reaction for a desired period of time, the reaction mixture was transferred to a thermostatted oil bath at 110 °C. The polymerization was stopped by placing the flask in an ice bath and exposing the contents to air. The resulting mixture was diluted with THF and precipitated into cold MeOH; the precipitate was collected and dried under vacuum (Mn = 2100; Đ = 1.39; conversion = 42.5%; yield = 31%).
A typical polymerization, through solvent polarity control, is also described. Procedures similar to those described above were performed, except that DMF (
N,
N-dimethylformamide) was used as an internal standard. After performing the reaction for a desired period of time at 70 °C, degassed A was charged into the reaction mixture rapidly. After an additional few hours, the polymerization was stopped by placing the flask in an ice bath and exposing the contents to air. The resulting mixture was diluted with THF and precipitated into cold MeOH; the precipitate was collected and dried under vacuum (
Mn = 2200;
Đ = 1.42; conversion = 47.6%; yield = 31%). The fraction of branching (FB), from NMR spectroscopic analysis, and the branching index (BI), from GPC-RI and GPC-LS measurements, were estimated using Equations (1) [
19] and (2) [
61], respectively:
2.7. Synthesis of Hyperbranched Core Star Polymers through ATRP
A resulting hyperbranched P(St-co-VBC) macroinitiator (named herein as hbPSt MI) was subjected to chain extension through ATRP using St or tBA. For example, St/hbPSt/CuCl/CuCl2/PMDETA reagents were reacted in a ratio of 200:1:0.9:0.1:1 in A (Mn,hbPSt = 1700; Đ = 1.31; [St]0 = 4.3 M). St, PMDETA, hbPSt, and A were added to a Schlenk flask. The mixture was deoxygenated through three freeze-pump-thaw cycles and then the flask was backfilled with N2. CuCl and CuCl2 were added to the frozen solution. The flask was sealed, evacuated, and deoxygenated through two additional freeze-pump-thaw cycles. An initial sample was removed via syringe and then the flask was immersed in an oil bath preheated at 100 °C to begin the polymerization. Aliquots were withdrawn at intervals during the polymerization procedure for monitoring of the conversion through GC using A as an internal standard. The polymerization was stopped by placing the flask in an ice bath and exposing the contents to air. The resulting mixture was diluted with THF and passed through a neutral aluminum oxide column to remove the copper catalyst. With sampling, the initiation efficiency was estimated by Mn,th/Mn,GPC. The mixture was precipitated in MeOH, filtered, and dried under vacuum (Mn = 25,000; Đ = 1.77; conversion = 55.5%; yield = 40%).
2.8. Hydrolysis
NaOH (equal to polymer weight) in THF/MeOH (2:1, v/v) was added to a solution of the polymer dissolved in a 10-fold weight of dioxane. The mixture was heated under reflux for approximately 4 h. The polymer was precipitated into Et2O, dried under vacuum, and characterized using 1H NMR and FT-IR spectroscopy (yield = 86%).
3. Results and Discussion
Scheme 3 displays our proposed mechanism for two-step, one-pot switching of the polymer topology from linear to branched via tuning of the solubility of the copper complex. At the beginning of this process, we mixed a more-active initiator (EBiB), Cu(I)/L, a monomer (St), and an inimer (VBC). Condition under which the copper complex retained poor solubility were employed to perform irreversible initiation of the atom transfer radical reaction from EBiB; the initiating site of the VBC monomer or P(St-
co-VBC) copolymer could not be activated efficiently as a result of precipitation of the deactivators. This atom transfer reaction induced a conventional free radical polymerization process (named herein as AT-FRP) and resulted in a linear structure. During the AT-FRP procedure, the reaction medium contained mainly the propagating linear polymer with a pendent initiating site (
i.e., benzyl chloride), poorly dispersed Cu(II)/L deactivator, and the rest of the monomers and inimers. In the second step, the conditions were changed to increase the solubility of the deactivator (
i.e., increasing the temperature or the solvent polarity). The propagating chains and re-dissolved deactivators guided the recovery of the balance between activation and deactivation. Namely, the linear polymer with a pendent initiating site, Cu(I)/Cu(II) species, the monomer, and the inimer could undergo a typical SCVP procedure, resulting in a branched polymer.
Scheme 3.
Control over polymer topology through one-pot AT-SCVP with catalyst phase transfer.
Scheme 3.
Control over polymer topology through one-pot AT-SCVP with catalyst phase transfer.
To examine this proposed concept, we selected a poorly soluble and less-effective copper complex. We first examined the solubilities of CuBr/Bpy and CuBr
2/Bpy in toluene (T) and anisole (A), prior to performing the catalyst-phase-switchable AT-SCVP. We performed the solubility tests using the (co)solvents at a thermostatted temperature. As displayed in
Figure 1a, the solubilities of CuBr/Bpy in T were approximately an order of magnitude lower than those of CuBr/Bpy in A at the various temperatures. Compared to the case in T alone, the solubility of CuBr/Bpy in the cosolvent [
i.e., T/A, 1:1 (
v/
v)] was approximately five times greater at 50 or 70 °C. CuBr
2/Bpy (
Figure 1b) exhibited very limited solubilities in T, even at 110 °C (
ca. 40 ppm). The solubilities of CuBr
2/Bpy in the higher-polarity solvent (A) were over an order of magnitude greater than those in T. The solubility of CuBr
2/Bpy in the cosolvent also increased by over five times at 50 or 70 °C. These results indicated that both the temperature and the solvent polarity could tune the solubility of these copper complexes, with increased solvent polarity providing significant improvements.
Table 1 summarizes the results.
Figure 1.
Solubility tests of (a) CuBr/Bpy and (b) CuBr2/Bpy catalysts at various temperatures and solvent polarities.
Figure 1.
Solubility tests of (a) CuBr/Bpy and (b) CuBr2/Bpy catalysts at various temperatures and solvent polarities.
Table 1.
Solubilities of CuBr/Bpy (a) and CuBr2/Bpy (b) (units: ppm).
Table 1.
Solubilities of CuBr/Bpy (a) and CuBr2/Bpy (b) (units: ppm).
| | Solvents | T | T/A (1:1, v/v) | A |
|---|
| Temp. (°C) | |
|---|
| 50 | (a) 14.2 | (a) 46.7 | (a) 165.1 |
| (b) 1.0 | (b) 6.8 | (b) 10.7 |
| 70 | (a) 34.7 | (a) 103.8 | (a) 340.2 |
| (b) 2.3 | (b) 13.2 | (b) 37.9 |
| 110 | (a) 168 | (a) 388.5 | (a) 1500 |
| (b) 44 | (b) 70.2 | (b) 260.6 |
The radicals generated through C–X bond homolysis of the alkyl halides (RX) activated by Cu(I)/L species were trapped irreversibly by the stable nitroxide radical to yield the corresponding alkoxyamines (
i.e., R
y-TEMPO in
Scheme S1). This method has been used frequently to measure the activation rate constants (
kact) during ATRP [
62]. Previous studies have indicated that TEMPO functions only as a radical trap; the measured rate constants were nonrelated to the concentration of excess TEMPO. To further understand the related activation rate constants (
kact), we examined the effect of a high molar ratio difference between the initiators EBiB and BzCl (herein, EBiB/BzCl = 1:16), which have similar initiating moieties to the reagents in
Scheme 3. We employed systematic model conditions for the trapping reactions of the atom transfer radical with TEMPO (AT-TEMPO). We monitored (GC) the reactions by following the consumptions of the initiators.
Figure 2 displays the kinetic results obtained using various temperatures (50, 70, and 110 °C) and solvents [T (hollow symbols in
Figure 2a–c) and A (solid symbols in
Figure 2d–f)]. By fitting plots of ln[1 − (
C0/
I0) ×
X] − ln(1 −
X) with respect to time (
t), we could obtain the activation rate constants of each mixing system (
i.e.,
kEBiB and
kBzCl). We performed the kinetic experiments under pseudo-first-order conditions, using a large excess of the alkyl halide and nitroxide. In all cases, the activation rate constants of EBiB were higher than those of BzCl. The ratios of the activation rate constants (
i.e.,
kEBiB/
kBzCl) were approximately greater than 35, implying significant differences in reactivity for the copper complex with the two initiators. Notably, activation rate constants in
Figure 2a,d even reached a difference of about an order of magnitude. These results indicate that the reaction temperature and solvent polarity retained their significant influence over the reactivity even at such a high difference in molar ratio of the tertiary bromoester and benzyl chloride co-initiator system. According to the related reactivity and activation rate constants, the radicals could be generated initially from the EBiB initiator with consumption of the Cu(I)/L complex under conditions of a lower temperature and a less polar solvent.
Table 2 summarizes the results of the model reactions.
Figure 2.
Model reactions of atom transfer radical with TEMPO (AT-TEMPO) with EBiB and BzCl mixed initiators (EBiB/BzCl/CuBr/Bpy/TEMPO = 5/80/1/2/10, [EBiB]0 = 0.25 M; C0: initial activator concentration (conc.); I0: initial initiator conc.; (a–c): reactions in T and (d–f): reactions in A.
Figure 2.
Model reactions of atom transfer radical with TEMPO (AT-TEMPO) with EBiB and BzCl mixed initiators (EBiB/BzCl/CuBr/Bpy/TEMPO = 5/80/1/2/10, [EBiB]0 = 0.25 M; C0: initial activator concentration (conc.); I0: initial initiator conc.; (a–c): reactions in T and (d–f): reactions in A.
Table 2.
Activation rate constants (kact) for EBiB (kEBiB) and BzCl (kBzCl) mixed systems under various conditions.
Table 2.
Activation rate constants (kact) for EBiB (kEBiB) and BzCl (kBzCl) mixed systems under various conditions.
| kact (M–1·min–1) | 50 °C | 70 °C | 110 °C |
|---|
| T | A | T | A | T | A |
|---|
| EBiB | 1.44 × 10−2 | 2.87 × 10−2 | 4.77 × 10−2 | 6.20 × 10−2 | 5.89 × 10−2 | 8.07 × 10−2 |
| BzCl | 1.50 × 10−4 | 3.00 × 10–4 | 6.00 × 10−4 | 1.25 × 10−3 | 1.20 × 10−3 | 2.44 × 10−3 |
| kEBiB/kBzCl | 96.1 | 95.2 | 79.5 | 49.5 | 49.1 | 35.1 |
Next, we examined AT-SCVP in a single solvent.
Figure 3 displays the results of our investigations of the AT-SCVP of St and VBC in T and A at various temperatures (50, 70, and 110 °C). When considering the same solvent (
Figure 3a,b for T;
Figure 3c,d for A), VBC underwent both faster polymerization and higher conversion than did St at each temperature, consistent with that the reactivity of VBC being slightly higher than that of St (
rVBC/
rSt ≈ 2.0) [
63,
64]. When considering the same monomer (
Figure 3a,c for St;
Figure 3b,d for VBC), the polymerizations in A were faster and occurred with higher conversions at the various temperatures than did those in T, due to the higher-polarity solvent accelerating the reaction rate. Comparison of the reactions performed at 70 °C (
Figure 3b,d) revealed that polymerization in A (opened asterisk) occurred with a significant improvement in conversion relative to that in T (closed asterisk), presumably as a result of consumption of both the vinyl and benzyl chloride moieties on the VBC inimer. These findings suggest that the AT-SCVP proceeded in A at 70 °C.
Figure 3.
AT-SCVP kinetic plots of comonomers (St, VBC) in a single solvent (a,b) T and (c,d) A at various temperatures (50, 70, and 110 °C).
Figure 3.
AT-SCVP kinetic plots of comonomers (St, VBC) in a single solvent (a,b) T and (c,d) A at various temperatures (50, 70, and 110 °C).
Figure 4 displays the
1H NMR spectra of the products of SCVP performed in T and A at 50, 70, and 110 °C. The peak near 4.5 ppm represents both the un-reacted and chain-ending benzyl chloride moieties (
i.e., linear and terminal units), while that near 2.8 ppm represents the reacted ones (
i.e., branched units). In the case of the poor solvent for Cu (II)/Bpy (
Figure 4a), we obtained a polymer with un-reacted and terminal benzyl chloride moieties, but nearly no branched points, at low temperature. This result indicates that P(St-
co-VBC) with a predominantly linear structure formed through AT-FRP. In the good solvent for Cu (II)/Bpy (
Figure 4b), a typical SCVP process occurred readily; we observed signals for linear, terminal, and branched units, indicating a branched polymer structure.
Figure S1 presents
1H NMR spectra of linear PVBC and hyperbranched PVBC polymers. The broad signals of the protons of the aromatic rings (7.4–6.4 ppm) and benzyl chloride moieties (
ca. 4.5 ppm) provided additional evidence for the non-linear structure, suggesting a complicated mixture of different chemical environments for the benzyl chloride moieties. These results are consistent with the trends in
Figure 3 and illustrated that control over different polymer topologies can be achieved merely by tuning the catalyst solubility through changes in temperature or solvent polarity. Thus, we further examined the switching from AT-FRP to SCVP in a one-pot procedure.
Figure 4.
1H NMR (600 MHz, CDCl3) spectra of the polymerization products formed in a single solvent at various temperatures (St/VBC/EBiB/CuBr/Bpy = 160/80/5/1/2; [St]0 = 3.5 M). (a) In T (less-polar solvent); (b) In A (higher-polar solvent).
Figure 4.
1H NMR (600 MHz, CDCl3) spectra of the polymerization products formed in a single solvent at various temperatures (St/VBC/EBiB/CuBr/Bpy = 160/80/5/1/2; [St]0 = 3.5 M). (a) In T (less-polar solvent); (b) In A (higher-polar solvent).
Figure 5 displays the kinetic plot for the manipulation of the polymer topology through an increase in temperature. The consumptions of St and VBC were determined through GC analysis. After reacting for 5 h in T at 70 °C, the mixture was heated to 110 °C rapidly and then heated at that temperature for another 19 h.
Figure 5a reveals ramped increases in the conversions of St and VBC upon increasing the temperature, reaching approximately 18% and 36%, respectively.
Figure 5b reveals the progress in the molecular evolutions and broad molecular weight distributions (
Đ = 1.43–1.65) for samples (1)–(3) in
Figure 5a.
Figure S2 displays the results of two one-pot reactions in which manipulations of polymer the topology were performed through increases in temperature.
Figure S2a (from 70 °C/1 h to 110 °C/+23 h) reveals that the conversions of St and VBC reached approximately 40% and 66% after the additional reaction time. In contrast,
Figure S2b (from 70 °C/24 h to 110 °C/+24 h) reveals almost unchanged conversions of St (
ca. 30%) and VBC (
ca. 55%). These results indicate that a suitable temperature and period of time are required to maintain the presence of propagating radicals in the reaction medium to allow the catalyst phase transfer AT-SCVP procedure to occur. We used
1H NMR spectroscopy to analyze the microstructures of the resulting branched polymers in
Figure 5 and
Figure S2.
Figure 6A–C reveals that the catalyst-phase-transfer AT-SCVP procedures can be distinguished. According to the signals of linear (A
4.5), terminal (A
4.4), and branched units (A
2.8), we estimated the FB through Equation (1) and the BI through Equation (2). We found that the FBs and BIs followed the same order: 6C > 6B > 6A. A higher FB resulted from greater consumption of the VBC inimer. The trends are consistent with the GC results in
Figure 5 and
Figure S2.
Table S1 summarizes the results of our BI analyses.
Figure 5.
(a) Kinetic plot of conversion vs. time and (b) gel permeation chromatography (GPC) traces (eluent: THF) of one-pot reaction performed at various temperatures (St/VBC/EBiB/CuBr/Bpy = 160/80/5/1/2; [St]0 = 3.5 M).
Figure 5.
(a) Kinetic plot of conversion vs. time and (b) gel permeation chromatography (GPC) traces (eluent: THF) of one-pot reaction performed at various temperatures (St/VBC/EBiB/CuBr/Bpy = 160/80/5/1/2; [St]0 = 3.5 M).
Figure 6.
1H NMR spectra (600 MHz, CDCl3) of branched polymers obtained at various reaction temperatures in one-pot (St/VBC/EBiB/CuBr/Bpy = 160/80/5/1/2; [St]0 = 3.5 M).
Figure 6.
1H NMR spectra (600 MHz, CDCl3) of branched polymers obtained at various reaction temperatures in one-pot (St/VBC/EBiB/CuBr/Bpy = 160/80/5/1/2; [St]0 = 3.5 M).
Figure 7 presents the kinetic plot for the manipulations of the polymer topology as a result of increasing the solvent polarity. Again, we monitored the consumptions of St and VBC through GC analysis. After a 5-h reaction in T at 70 °C, we added an equal volume of A and continued the reaction for another 19 h.
Figure 7a reveals ramped increases in the conversions of St and VBC upon increasing the solvent polarity, to approximately 35% and 66%, respectively.
Figure 7b displays the progress in the molecular evolution and broad molecular weight distributions (
Đ = 1.43–1.60) of samples (1)–(3) in
Figure 7a.
Figure S3 displays the conversions in two sets of one-pot reactions for the manipulation of the polymer topology.
Figure S3a (from T/1 h to 50T50A/+23 h) reveals conversions of St and VBC of approximately 43% and 66%, respectively, after the additional reaction time; in contrast,
Figure S3b (from T/24 h to 50T50A/+24 h) reveals almost no changes in the conversions of St (
ca. 35%) and VBC (
ca. 62%). These results also suggest that the first stage of the reaction should proceed for a suitable period of time such that propagating radicals remain in the reaction medium to perform the catalyst phase transfer AT-SCVP procedure through the polarity change. We used
1H NMR spectroscopy to analyze the microstructures of the resulting branched polymers in
Figure 8 and
Figure S3. As revealed in
Figure 8A–C, the FBs and BIs followed the order 8C > 8B > 8A, the same as that in the case of varying the temperature; nevertheless, here we obtained a higher FBs.
Figure 7.
(a) Kinetic plot of conversion vs. time and (b) GPC traces (eluent: THF) of an one-pot reaction after increasing the solvent polarity (St/VBC/EBiB/CuBr/Bpy = 160/80/5/1/2; [St]0 = 3.5 M).
Figure 7.
(a) Kinetic plot of conversion vs. time and (b) GPC traces (eluent: THF) of an one-pot reaction after increasing the solvent polarity (St/VBC/EBiB/CuBr/Bpy = 160/80/5/1/2; [St]0 = 3.5 M).
Figure 8.
1H NMR spectra (600 MHz, CDCl3) of branched polymers via tuning solvent polarity (St/VBC/EBiB/CuBr/Bpy = 160/80/5/1/2, [St]0 = 3.5 M; *: solvent peak).
Figure 8.
1H NMR spectra (600 MHz, CDCl3) of branched polymers via tuning solvent polarity (St/VBC/EBiB/CuBr/Bpy = 160/80/5/1/2, [St]0 = 3.5 M; *: solvent peak).
Concerning the composition of the branched polymer, herein we classify poly(St-
co-VBC) as an analogue of the hyperbranched polystyrene macroinitiator (hbPSt MI) ended with initiating sites. Thus, we employed the resulting hbPSt MI (
Mn = 1700;
Đ = 1.31) to synthesize hyperbranched core star polymers through typical chain extension procedures using ATRP.
Figure 9a displays a pseudo-first-order kinetic plot for the chain extension of hbPSt MI using St in A at 100 °C (St/hbPSt/CuCl/CuCl
2/PMDETA = 200/1/0.9/0.1/1; [St]
0 = 4.3 M). The apparent rate constant had a moderate value (
kapp = 1.17 ° 10
−5 s
−1). In
Figure 9b, we observe an evolution of the molecular weight (MW) in the GPC traces during chain extension. However, the initiation efficiency was 0.71 based on the molecular weight at 20 h. The GPC traces reveal tailing toward low-MW presumably because of the occurrence of side reactions (e.g., radical termination or Mayo thermal reaction) that result in losing the integrity of the chain end. The products with low-MW were readily removed through further precipitation in MeOH/H
2O. Using the approach, we obtained an hbPSt-
g-PSt hyperbranched core star polymer (
Mn = 25,000;
Đ = 1.77).
We also examined chain extension of hbPSt MI using
tBA. Again, we observed a pseudo-first-order kinetic plot (
Figure 10a) for the chain extension of hbPSt MI with
tBA in A at 100 °C (
tBA/hbPSt/CuCl/CuCl
2/PMDETA = 200/1/1/0.1/1.1; [
tBA]
0 = 3.5 M). Relative to the chain extension with St, the apparent rate constant in the case had increased by over an order of magnitude (
kapp = 1.42 ° 10
−4 s
−1), with a gradual evolution of the MW in the GPC traces (
Figure 10b). The initiation efficiency was 0.98 based on the molecular weight at 7 h. These results illustrate our ability to perform a controlled/living polymerization to form an hbPSt-
g-P
tBA hyperbranched core star polymer (
Mn: 27,000;
Đ: 1.98).
Figure 9.
(a) Kinetic plot of Ln(M0/M) vs. time for the chain extension of hbPSt MI with St in A at 100 °C and (b) GPC traces (eluent: THF; St/hbPSt/CuCl/CuCl2/PMDETA = 200/1/0.9/0.1/1; [St]0 = 4.3 M).
Figure 9.
(a) Kinetic plot of Ln(M0/M) vs. time for the chain extension of hbPSt MI with St in A at 100 °C and (b) GPC traces (eluent: THF; St/hbPSt/CuCl/CuCl2/PMDETA = 200/1/0.9/0.1/1; [St]0 = 4.3 M).
Figure 10.
(a) Kinetic plot of Ln(M0/M) vs. time for the chain extension of hbPSt MI with tBA in A at 100 °C and (b) GPC traces (eluent: THF; tBA/hbPSt/CuCl/CuCl2/PMDETA = 200/1/1/0.1/1.1; [tBA]0 = 3.5 M).
Figure 10.
(a) Kinetic plot of Ln(M0/M) vs. time for the chain extension of hbPSt MI with tBA in A at 100 °C and (b) GPC traces (eluent: THF; tBA/hbPSt/CuCl/CuCl2/PMDETA = 200/1/1/0.1/1.1; [tBA]0 = 3.5 M).
We performed the hydrolysis of hbPSt-
g-P
tBA under basic conditions to obtain an hbPSt-
g-PAA amphiphilic star polymer, transforming the outer segment from hydrophobic to hydrophilic (
Scheme S2).
Figure 11 presents the
1H NMR spectra of the hbPSt-
g-PtBA (in CDCl
3) and the hbPSt-
g-PAA (in D
2O). Most significantly, we observe the disappearance of the signal for the
tert-butyl groups (
i.e., peak c). FT-IR spectra revealed (
Figure S4) that the signals for the ester linkage (
ca. 1725 cm
−1) and ether linkage (
ca. 1250 cm
−1) had vanished, with the appearance of a broad signal (
ca. 3380 cm
−1) for carboxylic acid moieties. Together, these spectra confirmed the hydrolysis of hbPSt-
g-P
tBA to form hbPSt-
g-PAA. The hydrolyzed star polymer hbPSt-
g-PAA, with hydrophobic inner and hydrophilic outer regions, readily dissolved in MeOH with high transparency. Thus, performing polymerizations at a suitable concentration can provide amphiphilic star polymers, with nanoscale dimensions, that can be dispersed well in highly polar solvents—an attractive property for the applications of such polymers as nanocarriers and nanoreactors and for drug delivery. Hence, our facile catalyst-phase-switching mechanism, from AT-FRP to AT-SCVP, in one-pot can be performed successfully to obtain branched polymer topologies. Indeed, we have demonstrated the synthesis of hyperbranched core star polymers, as well as the ability to transform the chemical structure of the outer compartment.
Figure 11.
1H NMR (600 MHz) spectra of (A) hbPSt-g-PtBA in CDCl3 and (B) hbPSt-g-PAA in D2O (*, solvent peaks).
Figure 11.
1H NMR (600 MHz) spectra of (A) hbPSt-g-PtBA in CDCl3 and (B) hbPSt-g-PAA in D2O (*, solvent peaks).