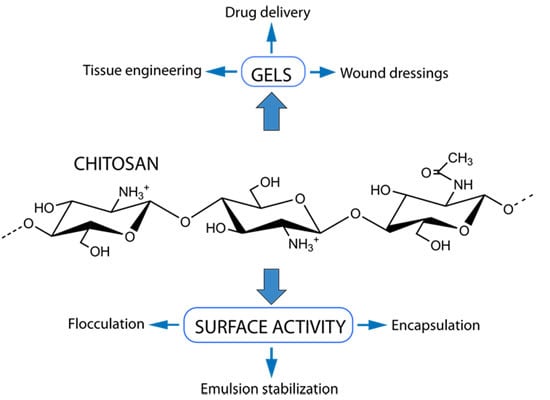
Chitosan: Gels and Interfacial Properties
Abstract
:1. Introduction

2. Chitosan Hydrogels
2.1. Chitosan Physical Gels

Polyelectrolyte Complexation

2.2. Chitosan Covalently Crosslinked Gels
2.3. Biomedical Applications of Chitosan Gels
2.3.1. Tissue Engineering
2.3.2. Drug Delivery
3. Interfacial Properties of Chitosan
3.1. Biopolymer Emulsifiers
3.2. Surface Activity of Chitosan
3.3. Emulsification Properties of Chitosan


3.4. Chitosan as Emulsion Stabilizer
Chitosan in Multilayer Emulsions
3.5. Emulsion Flocculation



3.6. Applications
4. Regulatory Status
5. Materials and Methods
5.1. Emulsion Droplet Measurements on Optical Tweezers
5.2. Flocculation of SDS Coated Emulsion Droplets by Chitosan
| Chitosan | Fraction of Acetylation (FA) | Intrinsic Viscosity ([η]) | Molecular Weight (Mw) * |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.001 | 800 mL/g | 220,000 |
| 2 | 0.18 | 800 mL/g | 220,000 |
| 3 | 0.35 | 760 mL/g | 210,000 |
| 4 | 0.49 | 900 mL/g | 260,000 |
| 5 | 0.65 | 950 mL/g | 270,000 |
6. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Peter, M.G. Chitin and chitosan from animal sources. In Polysaccharides and Polyamides in the Food Industry; Steinbüchel, A., Rhee, S.K., Eds.; Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH: Weinheim, Germany, 2005; pp. 115–208. [Google Scholar]
- Vårum, K.M.; Smidsrød, O. Structure–property relationship in chitosans. In Polysaccharides: Structural Diversity and Functional Versatility; Dimitriu, S., Ed.; Marcel Decker: New York, NY, USA, 2005; pp. 625–642. [Google Scholar]
- Strand, S.P.; Tømmeraas, K.; Vårum, K.M.; Østgaard, K. Electrophoretic light scattering studies of chitosans with different degrees of N-acetylation. Biomacromolecules 2001, 2, 1310–1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, E.; Xioung, Y.; Cheng, Y.; Wu, H.C.; Liu, Y.; Morrow, B.H.; Ben-Yoav, H.; Ghodssi, R.; Rubloff, G.W.; Shen, J.; et al. Chitosan to connect biology to electronics: Fabricating the bio-device interface and communicating across this interface. Polymers 2015, 7, 1–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vårum, K.M.; Holme, H.K.; Izume, M.; Torger Stokke, B.; Smidsrød, O. Determination of enzymatic hydrolysis specificity of partially N-acetylated chitosans. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1996, 1291, 5–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nordtveit, R.J.; Vårum, K.M.; Smidsrød, O. Degradation of partially N-acetylated chitosans with hen egg white and human lysozyme. Carbohydr. Polym. 1996, 29, 163–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ross-Murphy, S. Rheological methods. In Biophysical Methods in Food Research; Chan, H.W.-S., Ed.; Blackwell Scientific Publications: Oxford, UK, 1984; pp. 137–199. [Google Scholar]
- Strand, S.P.; Lelu, S.; Reitan, N.K.; Davies, C.D.; Artursson, P.; Varum, K.M. Molecular design of chitosan gene delivery systems with an optimized balance between polyplex stability and polyplex unpacking. Biomaterials 2010, 31, 975–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mumper, R.; Wang, J.; Claspell, J.; Rolland, A.P. Novel polymeric condensing carriers for gene delivery. Proc. Int. Symp. Control Release Bioact. Mater. 1995, 22, 178–179. [Google Scholar]
- Croisier, F.; Jerome, C. Chitosan-based biomaterials for tissue engineering. Eur. Polym. J. 2013, 49, 780–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berger, J.; Reist, M.; Mayer, J.M.; Felt, O.; Peppas, N.A.; Gurny, R. Structure and interactions in covalently and ionically crosslinked chitosan hydrogels for biomedical applications. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2004, 57, 19–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, K.D.; Yao, F.L.; Li, J.J.; Yin, Y.J.; Jarry, C.; Shive, M.S. Chitosan-based gels and hydrogels. In Smart Materials; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Ta, H.T.; Dass, C.R.; Dunstan, D.E. Injectable chitosan hydrogels for localised cancer therapy. J. Control. Release 2008, 126, 205–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaur, S.; Dhillon, G.S. The versatile biopolymer chitosan: Potential sources, evaluation of extraction methods and applications. Crit. Rev. Microbiol. 2014, 40, 155–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhattarai, N.; Gunn, J.; Zhang, M.Q. Chitosan-based hydrogels for controlled, localized drug delivery. Adv. Drug. Deliv. Rev. 2010, 62, 83–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vårum, K.M.; Ottøy, M.H.; Smidsrød, O. Water-solubility of partially N-acetylated chitosans as a function of pH: Effect of chemical composition and depolymerisation. Carbohydr. Polym. 1994, 25, 65–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vachoud, L.; Zydowicz, N.; Domard, A. Physicochemical behaviour of chitin gels. Carbohydr. Res. 2000, 326, 295–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chenite, A.; Buschmann, M.; Wang, D.; Chaput, C.; Kandani, N. Rheological characterisation of thermogelling chitosan/glycerol-phosphate solutions. Carbohydr. Polym. 2001, 46, 39–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavertu, M.; Filion, D.; Buschmann, M.D. Heat-induced transfer of protons from chitosan to glycerol phosphate produces chitosan precipitation and gelation. Biomacromolecules 2008, 9, 640–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montembault, A.; Viton, C.; Domard, A. Rheometric study of the gelation of chitosan in aqueous solution without cross-linking agent. Biomacromolecules 2005, 6, 653–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ladet, S.; David, L.; Domard, A. Multi-membrane hydrogels. Nature 2008, 452, 76–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rami, L.; Malaise, S.; Delmond, S.; Fricain, J.-C.; Siadous, R.; Schlaubitz, S.; Laurichesse, E.; Amédéé, J.; Montembault, A.; David, L.; et al. Physicochemical modulation of chitosan-based hydrogels induces different biological responses: Interest for tissue engineering. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 2014, 102, 3666–3676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shu, X.Z.; Zhu, K.J. Controlled drug release properties of ionically cross-linked chitosan beads: The influence of anion structure. Int. J. Pharm. 2002, 233, 217–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Draget, K.I.; Värum, K.M.; Moen, E.; Gynnild, H.; Smidsrød, O. Chitosan cross-linked with Mo (VI) polyoxyanions: A new gelling system. Biomaterials 1992, 13, 635–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dambies, L.; Vincent, T.; Domard, A.; Guibal, E. Preparation of chitosan gel beads by ionotropic molybdate gelation. Biomacromolecules 2001, 2, 1198–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, Y.; Wang, Q. Recent development of chitosan-based polyelectrolyte complexes with natural polysaccharides for drug delivery. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2014, 64, 353–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsuchida, E.; Abe, K. Interactions between macromolecules in solution and intermolecular complexes. Adv. Polym. Sci. 1982, 45, 1–119. [Google Scholar]
- Sæther, H.V.; Holme, H.K.; Maurstad, G.; Smidsrød, O.; Stokke, B.T. Polyelectrolyte complex formation using alginate and chitosan. Carbohydr. Polym. 2008, 74, 813–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khong, T.T.; Aarstad, O.A.; Skjåk-Bræk, G.; Draget, K.I.; Vårum, K.M. Gelling concept combining chitosan and alginate—Proof of principle. Biomacromolecules 2013, 14, 2765–2771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Draget, K.I. Associating phenomena in highly acetylated chitosan gels. Polym. Gels Netw. 1996, 4, 143–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tømmeraas, K.; Strand, S.P.; Christensen, B.E.; Smidsrød, O.; Vårum, K.M. Preparation and characterization of branched chitosans. Carbohydr. Polym. 2011, 83, 1558–1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Argüelles-Monal, W.; Goycoolea, F.M.; Peniche, C.; Higuera-Ciapara, I. Rheological study of the chitosan/glutaraldehyde chemical gel system. Polym. Gels Netw. 1998, 6, 429–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neimert-Andersson, T.; Hällgren, A.-C.; Andersson, M.; Langebäck, J.; Zettergren, L.; Nilsen-Nygaard, J.; Draget, K.I.; van Hage, M.; Lindberg, A.; Gafvelin, G.; et al. Improved immune responses in mice using the novel chitosan adjuvant ViscoGel, with a Haemophilus influenzae type b glycoconjugate vaccine. Vaccine 2011, 29, 8965–8973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rinaudo, M. New way to crosslink chitosan in aqueous solution. Eur. Polym. J. 2010, 46, 1537–1544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simi, C.K.; Abraham, T.E. Transparent xyloglucan–chitosan complex hydrogels for different applications. Food Hydrocoll. 2010, 24, 72–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, B.; Elgsaeter, A.; Stokke, B.T. Gelation kinetics of scleraldehyde–chitosan co-gels. Polym. Gels Netw. 1998, 6, 113–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christensen, B.E.; Aasprong, E.; Stokke, B.T. Gelation of periodate oxidised scleroglucan (scleraldehyde). Carbohydr. Polym. 2001, 46, 241–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hennink, W.E.; van Nostrum, C.F. Novel crosslinking methods to design hydrogels. Adv. Drug. Deliv. Rev. 2012, 64, 223–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, I.Y.; Seo, S.J.; Moon, H.S.; Yoo, M.K.; Park, I.Y.; Kim, B.C.; Cho, C.S. Chitosan and its derivatives for tissue engineering applications. Biotech. Adv. 2008, 26, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anitha, A.; Sowmya, S.; Kumar, P.T.S.; Deepthi, S.; Chennazhi, K.P.; Ehrlich, H.; Tsurkan, M.; Jayakumar, R. Chitin and chitosan in selected biomedical applications. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2014, 39, 1644–1667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chenite, A.; Chaput, C.; Wang, D.; Combes, C.; Buschmann, M.D.; Hoemann, C.D.; Leroux, J.C.; Atkinson, B.L.; Binette, F.; Selmani, A. Novel injectable neutral solutions of chitosan form biodegradable gels in situ. Biomaterials 2000, 21, 2155–2161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernkop-Schnurch, A.; Dunnhaupt, S. Chitosan-based drug delivery systems. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2012, 81, 463–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agarwal, P.; Rupenthal, I.D. Injectable implants for the sustained release of protein and peptide drugs. Drug Discov. Today 2013, 18, 337–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luppi, B.; Bigucci, F.; Cerchiara, T.; Zecchi, V. Chitosan-based hydrogels for nasal drug delivery: From inserts to nanoparticles. Exp. Opin. Drug Deliv. 2010, 7, 811–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhise, K.S.; Dhumal, R.S.; Paradkar, A.R.; Kadam, S.S. Effect of drying methods on swelling, erosion and drug release from chitosan-naproxen sodium complexes. AAPS PharmSciTech 2008, 9, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dutta, P.K.; Tripathi, S.; Mehrotra, G.K.; Dutta, J. Perspectives for chitosan based antimicrobial films in food applications. Food Chem. 2009, 114, 1173–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, W.S.; Liu, P.; Zhang, J.L.; Chen, J. Biological activities of chitosan and chitooligosaccharides. Food Hydrocoll. 2011, 25, 170–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norowski, P.A.; Bumgardner, J.D. Biomaterial and antibiotic strategies for peri-implantitis. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 2009, 88B, 530–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ong, S.Y.; Wu, J.; Moochhala, S.M.; Tan, M.H.; Lu, J. Development of a chitosan-based wound dressing with improved hemostatic and antimicrobial properties. Biomaterials 2008, 29, 4323–4332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jayakumar, R.; Prabaharan, M.; Kumar, P.T.S.; Nair, S.V.; Tamura, H. Biomaterials based on chitin and chitosan in wound dressing applications. Biotech. Adv. 2011, 29, 322–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walstra, P. Physical Chemistry of Foods; Marcel Dekker: New York, NY, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Dickinson, E. Hydrocolloids at interfaces and the influence on the properties of dispersed systems. Food Hydrocoll. 2003, 17, 25–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McClements, D.J. Food Emulsions: Principles, Practices and Techniques; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2005; p. 609. [Google Scholar]
- Norde, W. Colloids and Interfaces in Life Sciences; Marcel Dekker: New York, NY, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Del Blanco, L.F.; Rodriguez, M.S.; Schulz, P.C.; Agullo, E. Influence of the deacetylation degree on chitosan emulsification properties. Colloid Polym. Sci. 1999, 277, 1087–1092. [Google Scholar]
- Schulz, P.C.; Rodríguez, M.S.; del Blanco, L.F.; Pistonesi, M.; Agulló, E. Emulsification properties of chitosan. Colloid Polym. Sci. 1998, 276, 1159–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrı́guez, M.S.; Albertengo, L.A.; Agulló, E. Emulsification capacity of chitosan. Carbohydr. Polym. 2002, 48, 271–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.K.; Xia, W.S. Effects of concentration, degree of deacetylation and molecular weight on emulsifying properties of chitosan. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2011, 48, 768–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Wang, C.Y.; Zou, S.W.; Wei, Z.J.; Tong, Z. Simple, reversible emulsion system switched by pH on the basis of chitosan without any hydrophobic modification. Langmuir 2012, 28, 11017–11024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Payet, L.; Terentjev, E.M. Emulsification and stabilization mechanisms of O/W emulsions in the presence of chitosan. Langmuir 2008, 24, 12247–12252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pepic, I.; Filipovic-Grcic, J.; Jalsenjak, I. Interactions in a nonionic surfactant and chitosan mixtures. Colloid Surface A 2008, 327, 95–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mai-Ngam, K. Comblike poly(ethylene oxide)/hydrophobic C6 branched chitosan surfactant polymers as anti-infection surface modifying agents. Colloid Surface B 2006, 49, 117–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qun, G.; Ajun, W. Effects of molecular weight, degree of acetylation and ionic strength on surface tension of chitosan in dilute solution. Carbohydr. Polym. 2006, 64, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babak, V.; Lukina, I.; Vikhoreva, G.; Desbrières, J.; Rinaudo, M. Interfacial properties of dynamic association between chitin derivatives and surfactants. Colloid Surface A 1999, 147, 139–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, X.; Kwon, O.-H.; Jang, J. Electrospinning of chitosan dissolved in concentrated acetic acid solution. Biomaterials 2005, 26, 5427–5432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calero, N.; Munoz, J.; Ramirez, P.; Guerrero, A. Flow behaviour, linear viscoelasticity and surface properties of chitosan aqueous solutions. Food Hydrocoll. 2010, 24, 659–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nilsen-Nygaard, J.; Sletmoen, M.; Draget, K.I. Stability and interaction forces of oil-in-water emulsions as observed by optical tweezers—A proof-of-concept study. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 52220–52229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klinkesorn, U. The role of chitosan in emulsion formation and stabilization. Food Rev. Int. 2013, 29, 371–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guzey, D.; McClements, D.J. Formation, stability and properties of multilayer emulsions for application in the food industry. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2006, 128–130, 227–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guzey, D.; McClements, D.J. Influence of environmental stresses on O/W emulsions stabilized by β-lactoglobulin-pectin and β-lactoglobulin-pectin-chitosan membranes produced by the electrostatic layer-by-layer deposition technique. Food Biophys. 2006, 1, 30–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gudipati, V.; Sandra, S.; McClements, D.J.; Decker, E.A. Oxidative stability and in vitro digestibility of fish oil-in-water emulsions containing multilayered membranes. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 8093–8099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klinkesorn, U.; Sophanodora, P.; Chinachoti, P.; Decker, E.A.; McClements, D.J. Encapsulation of emulsified tuna oil in two-layered interfacial membranes prepared using electrostatic layer-by-layer deposition. Food Hydrocoll. 2005, 19, 1044–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klinkesorn, U.; Sophanodora, P.; Chinachoti, P.; Decker, E.A.; McClements, D.J. Characterization of spray-dried tuna oil emulsified in two-layered interfacial membranes prepared using electrostatic layer-by-layer deposition. Food Res. Int. 2006, 39, 449–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calvo, P.; RemunanLopez, C.; VilaJato, J.L.; Alonso, M.J. Development of positively charged colloidal drug carriers: Chitosan coated polyester nanocapsules and submicron-emulsions. Colloid Polym. Sci. 1997, 275, 46–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mun, S.; Decker, E.A.; McClements, D.J. Influence of droplet characteristics on the formation of oil-in-water emulsions stabilized by surfactant-chitosan layers. Langmuir 2005, 21, 6228–6234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mun, S.; Decker, E.A.; McClements, D.J. Effect of molecular weight and degree of deacetylation of chitosan on the formation of oil-in-water emulsions stabilized by surfactant-chitosan membranes. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2006, 296, 581–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Svensson, O.; Lindh, L.; Cardenas, M.; Arnebrant, T. Layer-by-layer assembly of mucin and chitosan—Influence of surface properties, concentration and type of mucin. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2006, 299, 608–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogawa, S.; Decker, E.A.; McClements, D.J. Production and characterization of O/W emulsions containing cationic droplets stabilized by lecithin-chitosan membranes. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2003, 51, 2806–2812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogawa, S.; Decker, E.A.; McClements, D.J. Influence of environmental conditions on the stability of oil in water emulsions containing droplets stabilized by lecithin-chitosan membranes. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2003, 51, 5522–5527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogawa, S.; Decker, E.A.; McClements, D.J. Production and characterization of O/W emulsions containing droplets stabilized by lecithin-chitosan-pectin mutilayered membranes. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2004, 52, 3595–3600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zinoviadou, K.G.; Moschakis, T.; Kiosseoglou, V.; Biliaderis, C.G. Impact of emulsifier–polysaccharide interactions on the stability and rheology of stabilised oil-in-water emulsions. Proced. Food Sci. 2011, 1, 57–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klinkesorn, U.; McClements, D.J. Influence of chitosan on stability and lipase digestibility of lecithin-stabilized tuna oil-in-water emulsions. Food Chem. 2009, 114, 1308–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Speiciene, V.; Guilmineau, F.; Kulozik, U.; Leskauskaite, D. The effect of chitosan on the properties of emulsions stabilized by whey proteins. Food Chem. 2007, 102, 1048–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laplante, S.; Turgeon, S.L.; Paquin, P. Emulsion stabilizing properties of various chitosans in the presence of whey protein isolate. Carbohydr. Polym. 2005, 59, 425–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laplante, S.; Turgeon, S.L.; Paquin, P. Effect of pH, ionic strength, and composition on emulsion stabilising properties of chitosan in a model system containing whey protein isolate. Food Hydrocoll. 2005, 19, 721–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laplante, S.; Turgeon, S.L.; Paquin, P. Emulsion-stabilizing properties of chitosan in the presence of whey protein isolate: Effect of the mixture ratio, ionic strength and pH. Carbohydr. Polym. 2006, 65, 479–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zinoviadou, K.G.; Scholten, E.; Moschakis, T.; Biliaderis, C.G. Properties of emulsions stabilised by sodium caseinate–chitosan complexes. Int. Dairy. J. 2012, 26, 94–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aoki, T.; Decker, E.A.; McClements, D.J. Influence of environmental stresses on stability of O/W emulsions containing droplets stabilized by multilayered membranes produced by a layer-by-layer electrostatic deposition technique. Food Hydrocoll. 2005, 19, 209–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strand, S.P.; Nordengen, T.; Ostgaard, K. Efficiency of chitosans applied for flocculation of different bacteria. Water Res. 2002, 36, 4745–4752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strand, S.P.; Vandvik, M.S.; Varum, K.M.; Ostgaard, K. Screening of chitosans and conditions for bacterial flocculation. Biomacromolecules 2001, 2, 126–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hughes, J.; Ramsden, D.K.; Symes, K.C. The flocculation of bacteria using cationic synthetic flocculatants and chitosan. Biotechnol. Tech. 1990, 4, 55–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Divakaran, R.; Pillai, V.N.S. Flocculation of algae using chitosan. J. Appl. Phycol. 2002, 14, 419–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashmore, M.; Hearn, J. Flocculation of model latex particles by chitosans of varying degrees of acetylation. Langmuir 2000, 16, 4906–4911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinotti, A.; Bevilacqua, A.; Zaritzky, N. Optimization of the flocculation stage in a model system of a food emulsion waste using chitosan as polyelectrolyte. J. Food Eng. 1997, 32, 69–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bratskaya, S.; Avramenko, V.; Schwarz, S.; Philippova, I. Enhanced flocculation of oil-in-water emulsions by hydrophobically modified chitosan derivatives. Colloid Surface A 2006, 275, 168–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Axberg, C.; Wennerburg, A.M.; Stenius, P. Flocculation of waste emulsion using polyelectrolytes. Progr. Water Tech. 1980, 12, 371–384. [Google Scholar]
- Israelachvili, J.N. Intermolecular and Surface Forces, 3rd ed.; Academic Press: Burlington, MA, USA, 2011; p. 674. [Google Scholar]
- Klaypradit, W.; Huang, Y.W. Fish oil encapsulation with chitosan using ultrasonic atomizer. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2008, 41, 1133–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseini, S.F.; Zandi, M.; Rezaei, M.; Farahmandghavi, F. Two-step method for encapsulation of oregano essential oil in chitosan nanoparticles: Preparation, characterization and in vitro release study. Carbohydr. Polym. 2013, 95, 50–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abreu, F.O.M.S.; Oliveira, E.F.; Paula, H.C.B.; de Paula, R.C.M. Chitosan/cashew gum nanogels for essential oil encapsulation. Carbohydr. Polym. 2012, 89, 1277–1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoksan, R.; Jirawutthiwongchai, J.; Arpo, K. Encapsulation of ascorbyl palmitate in chitosan nanoparticles by oil-in-water emulsion and ionic gelation processes. Colloid Surface B 2010, 76, 292–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helgason, T.; Gislason, J.; McClements, D.J.; Kristbergsson, K.; Weiss, J. Influence of molecular character of chitosan on the adsorption of chitosan to oil droplet interfaces in an in vitro digestion model. Food Hydrocoll. 2009, 23, 2243–2253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beysseriat, M.; Decker, E.A.; McClements, D.J. Preliminary study of the influence of dietary fiber on the properties of oil-in-water emulsions passing through an in vitro human digestion model. Food Hydrocoll. 2006, 20, 800–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fäldt, P.; Bergenståhl, B.; Claesson, P.M. Stabilization by chitosan of soybean oil emulsions coated with phospholipid and glycocholic acid. Colloid Surface A 1993, 71, 187–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, H.-T.; Huang, S.-Y.; Chiang, M.-T. A comparative study on hypoglycemic and hypocholesterolemic effects of high and low molecular weight chitosan in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2008, 46, 1525–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Liu, J.; Li, L.; Xia, W. Dietary chitosan improves hypercholesterolemia in rats fed high-fat diets. Nutr. Res. 2008, 28, 383–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, L.K.; Kimura, Y.; Okuda, H. Reduction in fat storage during chitin-chitosan treatment in mice fed a high-fat diet. Int. J. Obes. 1999, 23, 174–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renault, F.; Sancey, B.; Badot, P.M.; Crini, G. Chitosan for coagulation/flocculation processes—An eco-friendly approach. Eur. Polym. J. 2009, 45, 1337–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guibal, E.; Roussy, J. Coagulation and flocculation of dye-containing solutions using a biopolymer (chitosan). React. Funct. Polym. 2007, 67, 33–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkataraman, P.; Tang, J.J.; Frenkel, E.; McPherson, G.L.; He, J.B.; Raghavan, S.R.; Kolesnichenko, V.; Bose, A.; John, V.T. Attachment of a hydrophobically modified biopolymer at the oil-water interface in the treatment of oil spills. ACS Appl. Mater. Inter. 2013, 5, 3572–3580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, A.L.; Sumathi, S.; Hameed, B.H. Coagulation of residue oil and suspended solid in palm oil mill effluent by chitosan, alum and PAC. Chem. Eng. J. 2006, 118, 99–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, A.L.; Sumathi, S.; Hameed, B.H. Residual oil and suspended solid removal using natural adsorbents chitosan, bentonite and activated carbon: A comparative study. Chem. Eng. J. 2005, 108, 179–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khachatoorian, R.; Petrisor, I.G.; Kwan, C.C.; Yen, T.F. Biopolymer plugging effect: Laboratory-pressurized pumping flow studies. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2003, 38, 13–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dornish, M.; Kaplan, D.S.; Arepalli, S.R. Regulatory status of chitosan and derivatives. In Chitosan-Based Systems for Biopharmaceuticals: Delivery, Targeting and Polymer Therapeutics; Sarmento, B., das Neves, J., Eds.; John Wiley and Sons, Ltd.: Chichester, UK, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Vårum, K.M.; Antohonsen, M.W.; Grasdalen, H.; Smidsrød, O. Determination of the degree of N-acetylation and the distribution of N-acetyl groups in partially N-deacetylated chitins (chitosans) by high-field NMR spectroscopy. Carbohyd. Res. 1991, 211, 17–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berth, G.; Dautzenberg, H. The degree of acetylation of chitosans and its effect on the chain conformation in aqueous solution. Carbohydr. Polym. 2002, 47, 39–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nilsen-Nygaard, J.; Strand, S.P.; Vårum, K.M.; Draget, K.I.; Nordgård, C.T. Chitosan: Gels and Interfacial Properties. Polymers 2015, 7, 552-579. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym7030552
Nilsen-Nygaard J, Strand SP, Vårum KM, Draget KI, Nordgård CT. Chitosan: Gels and Interfacial Properties. Polymers. 2015; 7(3):552-579. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym7030552
Chicago/Turabian StyleNilsen-Nygaard, Julie, Sabina P. Strand, Kjell M. Vårum, Kurt I. Draget, and Catherine T. Nordgård. 2015. "Chitosan: Gels and Interfacial Properties" Polymers 7, no. 3: 552-579. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym7030552
APA StyleNilsen-Nygaard, J., Strand, S. P., Vårum, K. M., Draget, K. I., & Nordgård, C. T. (2015). Chitosan: Gels and Interfacial Properties. Polymers, 7(3), 552-579. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym7030552