Towards A Deeper Understanding of the Interfacial Adsorption of Enzyme Molecules in Gigaporous Polymeric Microspheres
Abstract
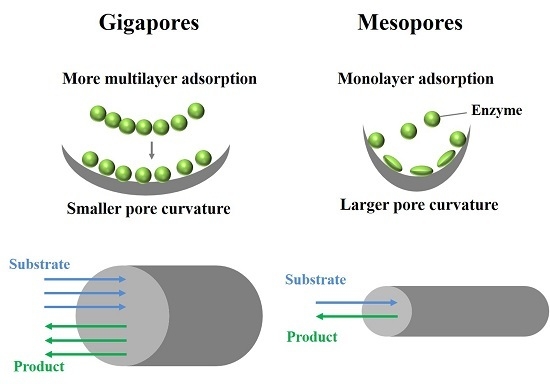
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Adsorption of Lipase in PST Microspheres
2.3. Assay of Adsorption Mass and Activity of Lipase in PST Microspheres
2.4. CLSM Analysis of Lipase Adsorbed in Microspheres
2.5. QCM-D Measurement
2.6. Assay of Adsorption Mass and Activity of Lipase on PST Chip
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Analysis of Lipase Adsorption in PST Microspheres
3.2. Comparison of the Adsorption in Microsphere with the Adsorption on Flat Surface
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| PST | polystyrene |
| CALB | lipase B from Candida antarctica |
| CLSM | confocal laser scanning microscopy |
| QCM-D | quartz crystal microbalance with dissipation monitoring |
References
- Pinto, M.C.C.; Freire, D.M.G.; Pinto, J.C. Influence of the morphology of core-shell supports on the immobilization of lipase B from Candida antarctica. Molecules 2014, 19, 12509–12530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Luo, S.; Chen, W. Activity of catalase adsorbed to carbon nanotubes: Effects of carbon nanotube surface properties. Talanta 2013, 113, 142–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gustafsson, H.; Johansson, E.M.; Barrabino, A.; Odén, M.; Holmberg, K. Immobilization of lipase from Mucor miehei and Rhizopus oryzae into mesoporous silica—The effect of varied particle size and morphology. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2012, 100, 22–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sabbani, S.; Hedenström, E.; Nordin, O. The enantioselectivity of Candida rugosa lipase is influenced by the particle size of the immobilising support material Accurel. J. Mol. Catal. B Enzym. 2006, 42, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; Wang, Y.; Diao, X.; Luo, G.; Dai, Y. Effect of pore diameter and cross-linking method on the immobilization efficiency of Candida rugosa lipase in SBA-15. Bioresource Technol. 2010, 101, 3830–3837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaijitrsakool, T.; Tonanon, N.; Tanthapanichakoon, W.; Tamon, H.; Prichanont, S. Effects of pore characters of mesoporous resorcinol–formaldehyde carbon gels on enzyme immobilization. J. Mol. Catal. B Enzym. 2008, 55, 137–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Liu, Y.; Wang, X.; Li, Q.; Wang, J.; Yan, Y. Improving catalytic performance of Burkholderia cepacia lipase immobilized on macroporous resin NKA. J. Mol. Catal. B Enzym. 2011, 71, 45–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Y.; He, J.; Guo, X.; Guo, X.; Song, Z. Influence of pore diameters on the immobilization of lipase in SBA-15. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2007, 46, 4474–4479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Hartmann, M. Progress in enzyme immobilization in ordered mesoporous materials and related applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 3894–3912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hartmann, M.; Kostrov, X. Immobilization of enzymes on porous silicas–benefits and challenges. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 6277–6289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bayne, L.; Ulijn, R.V.; Halling, P.J. Effect of pore size on the performance of immobilised enzymes. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 9000–9010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fried, D.I.; Brieler, F.J.; Froeba, M. Designing inorganic porous materials for enzyme adsorption and applications in biocatalysis. ChemCatChem 2013, 5, 862–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlipf, D.M.; Rankin, S.E.; Knutson, B.L. Pore-size dependent protein adsorption and protection from proteolytic hydrolysis in tailored mesoporous silica particles. Acs. Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2013, 5, 10111–10117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vijayaraj, M.; Gadiou, R.; Anselme, K.; Ghimbeu, C.; Vix-Guterl, C.; Orikasa, H.; Kyotani, T.; Ittisanronnachai, S. The influence of surface chemistry and pore size on the adsorption of proteins on nanostructured carbon materials. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2010, 20, 2489–2499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, H.; Li, B.; Sasaki, T.; Miyazaki, C.; Kajino, T.; Inagaki, S. Catalytic activity in organic solvents and stability of immobilized enzymes depend on the pore size and surface characteristics of mesoporous silica. Chem. Mater. 2000, 12, 3301–3305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, E.; Sirim, D.; Schreiber, T.; Thomas, B.; Pleiss, J.; Hunger, M.; Gläser, R.; Urlacher, V.B. Immobilization of P450 BM-3 monooxygenase on mesoporous molecular sieves with different pore diameters. J. Mol. Catal. B Enzym. 2010, 64, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Gao, F.; Wei, W.; Qu, J.B.; Ma, G.H.; Zhou, W.Q. Pore size of macroporous polystyrene microspheres affects lipase immobilization. J. Mol. Catal. B Enzym. 2010, 66, 182–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, Y.; Miller, L.; Gao, W.; Gross, R.A. Imaging the distribution and secondary structure of immobilized enzymes using infrared microspectroscopy. Biomacromolecules 2003, 4, 70–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loos, K.; Kennedy, S.B.; Eidelman, N.; Tai, Y.; Zharnikov, M.; Amis, E.J.; Ulman, A.; Gross, R.A. Combinatorial approach to study enzyme/surface interactions. Langmuir 2005, 21, 5237–5241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, B.; Miller, E.M.; Miller, L.; Maikner, J.J.; Gross, R.A. Effects of macroporous resin size on Candida antarctica lipase B adsorption, fraction of active molecules, and catalytic activity for polyester synthesis. Langmuir 2007, 23, 1381–1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, B.; Miller, E.M.; Gross, R.A. Effects of porous polystyrene resin parameters on Candida antarctica lipase B adsorption, distribution, and polyester synthesis activity. Langmuir 2007, 23, 6467–6474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miletić, N.; Vuković, Z.; Nastasović, A.; Loos, K. Macroporous poly(glycidyl methacrylate-co-ethylene glycol dimethacrylate) resins—Versatile immobilization supports for biocatalysts. J. Mol. Catal. B Enzym. 2009, 56, 196–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nihira, T.; Mori, T.; Asakura, M.; Okahata, Y. Kinetic studies of dextransucrase enzyme reactions on a substrate- or enzyme-immobilized 27 MHz quartz crystal microbalance. Langmuir 2011, 27, 2107–2111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, P.; Krohn, R.I.; Hermanson, G.; Mallia, A.; Gartner, F.; Provenzano, M.; Fujimoto, E.; Goeke, N.; Olson, B.; Klenk, D. Measurement of protein using bicinchoninic acid. Anal. Biochem. 1985, 150, 76–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, X.; Zong, Y.; Richter, R.; Knoll, W. Enzyme immobilization on poly(ethylene-co-acrylic acid) films studied by quartz crystal microbalance with dissipation monitoring. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2005, 287, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodahl, M.; Kasemo, B. On the measurement of thin liquid overlayers with the quartz-crystal microbalance. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 1996, 54, 448–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, D.-X.; Sandström, C.; Huang, Y.-D.; Kenne, L.; Janson, J.-C.; Ma, G.-H.; Su, Z.-G. Residue-level elucidation of the ligand-induced protein binding on phenyl-argarose microspheres by NMR hydrogen/deuterium exchange technique. Soft Matter 2012, 8, 6248–6255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, L. Carrier-Bound Immobilized Enzymes: Principles, Application and Design, 1st ed.; Wiley-VCH: New York, NY, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Geitmann, M.; Danielson, U.H. Studies of substrate-induced conformational changes in human cytomegalovirus protease using optical biosensor technology. Anal. Biochem. 2004, 332, 203–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]






| Microspheres | Average Pore Size (nm) | Total Pore Surface Area (m2/g) | Total Pore Volume (cm3/g) | Porosity (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PST-300 | 340.3 | 14.7 | 1.9 | 70.4 |
| PST-14 | 14.5 | 738.4 | 2.7 | 78.7 |
© 2016 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons by Attribution (CC-BY) license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, W.; Zhou, W.; Wei, W.; Li, J.; Hao, D.; Su, Z.; Ma, G. Towards A Deeper Understanding of the Interfacial Adsorption of Enzyme Molecules in Gigaporous Polymeric Microspheres. Polymers 2016, 8, 116. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym8040116
Wang W, Zhou W, Wei W, Li J, Hao D, Su Z, Ma G. Towards A Deeper Understanding of the Interfacial Adsorption of Enzyme Molecules in Gigaporous Polymeric Microspheres. Polymers. 2016; 8(4):116. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym8040116
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Weichen, Weiqing Zhou, Wei Wei, Juan Li, Dongxia Hao, Zhiguo Su, and Guanghui Ma. 2016. "Towards A Deeper Understanding of the Interfacial Adsorption of Enzyme Molecules in Gigaporous Polymeric Microspheres" Polymers 8, no. 4: 116. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym8040116
APA StyleWang, W., Zhou, W., Wei, W., Li, J., Hao, D., Su, Z., & Ma, G. (2016). Towards A Deeper Understanding of the Interfacial Adsorption of Enzyme Molecules in Gigaporous Polymeric Microspheres. Polymers, 8(4), 116. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym8040116