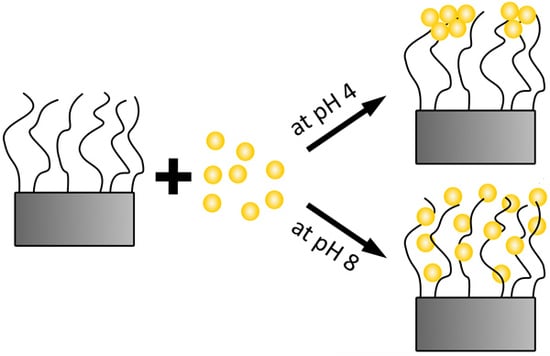
Uptake of pH-Sensitive Gold Nanoparticles in Strong Polyelectrolyte Brushes
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Materials
2.2. Synthesis
2.2.1. Preparation of Buffer Solutions with Different pH
2.2.2. Synthesis of the Initiator
2.2.3. Immobilization of the Initiator BTPAm onto the Surface by Building a SAM
2.2.4. Synthesis of Poly-2-(methacryloyloxy)ethyltrimethylammonium Chloride (PMETAC) by Si-ATRP
2.2.5. Synthesis of AuNPs
2.2.6. Preparation of PMETAC/AuNP Brush Composites
2.3. Instruments and Measurement Procedure
2.3.1. Ellipsometry Measurements
2.3.2. Atomic-Force Microscopy (AFM) Measurements
2.3.3. TEM Measurements
2.3.4. Gravimetric Analysis
2.3.5. UV-Vis Spectroscopy
3. Results
3.1. PMETAC Brush
3.1.1. Tuning of the Brush Thickness
3.1.2. Neat PMETAC Brush in Ambient Conditions and Water
3.2. Effect of pH on AuNP Dispersion
3.2.1. Particle Shape and Size at Different pH
3.2.2. UV/Vis Spectroscopy Characterization
3.2.3. Gravimetric Analysis of AuNP Concentration
3.3. Composite Material of PMETAC/AuNP
3.3.1. Characterization of PMETAC/AuNP Composites by AFM
3.3.2. UV/Vis Characterization
3.3.3. The Amount of AuNPs within PMETAC Brushes
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mizutani, A.; Kikuchi, A.; Yamato, M.; Kanazawa, H.; Okano, T. Preparation of thermoresponsive polymer brush surfaces and their interaction with cells. Biomaterials 2008, 29, 2073–2081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lian, C.; Wang, L.; Chen, X.; Han, X.; Thao, S.; Liu, H.; Hu, Y. Modelling swelling behavior of thermoresponsive polymer brush with lattice density functional theory. Langmuir 2014, 30, 4040–4048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Louquet, S.; Rousseau, B.; Epherre, R.; Guidolin, N.; Goglio, G.; Mornet, S.; Duguet, E.; Lecommandoux, S.; Schatz, C. Thermoresponsive polymer brush-functionalized magnetic manganite nanoparticles for remotely triggered drug release. Poly. Chem. 2012, 3, 1408–1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, M.; Kanaev, A.; Sun, X.; Lacaze, E.; Lau-Truong, S.; Lamouri, A.; Aubard, J.; Felidj, N.; Mangeney, C. Tunable electromagnetic coupling in plasmonic nanostructures mediated by thermoresponsive polymer brushes. Langmuir 2015, 31, 12830–12837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, H.; Wildes, A.; Titmuss, S. Structure of pH-responsive polymer brushes grown at the gold-water interface: Dependence on grafting density and temperature. Macromolecules 2012, 45, 305–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sudre, G.; Hourdet, D.; Creton, C.; Cousin, F.; Tran, Y. Probing pH-responsive interactions between polymer brushes and hydrogels by neutron reflectivity. Langmuir 2014, 30, 9700–9706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Groot, G.W.; Santonicola, M.G.; Sugihara, K.; Zambelli, T.; Reimhult, E.; Reimhult, E.; Vörös, J.; Vancso, G.J. Switching transport through nanopores with pH-responsive polymer brushes for controlled ion permeability. ACS Appl. Mater. Inter. 2013, 5, 1400–1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fielding, L.A.; Edmondson, S.; Armes, S.P. Synthesis of pH-responsive tertiary amine methacrylate polymer brushes and their response to acidic vapour. J. Mater. Chem. 2011, 21, 11773–11780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheesman, B.T.; Smith, E.G.; Murdoch, T.J.; Guibert, C.; Webber, G.B.; Edmondson, S.; Wanless, E.J. Polyelectrolyte brush pH-response at silica-aqueous solution interface: A kinetic and equilibrium investigation. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2013, 15, 14502–14510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delcroix, M.F.; Demoustier-Champagne, S.; Dupont-Gillain, C.C. Quartz crystal microbalance study of ionic strength and pH-dependent polymer conformation and protein adsorption/desorption on PAA, PEO, and mixed PEO/PAA brushes. Langmuir 2014, 30, 268–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, B.; Gon, S.; Park, M.; Kuman, K.-N.; Rotello, V.M.; Nusslein, K.; Santore, M.M. Bacterial adhesion on hybrid cationic nanoparticle-polymer brush surfaces: Ionic strength tunes capture from monovalent to multivalent binding. Colloids Surf. B 2011, 87, 109–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, P.; Wu, T.; Genuer, J.; Szleifer, I. Behavior of surface-anchored poly(acrylic acid) brushes with grafting density gradients on solid substrates: 2. Theory. Macromolecules 2007, 40, 8765–8773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhulina, E.B.; Leermakers, F.A.M. Effect of the ionic strength and pH on the equilibrium structure of a neurofilament brush. Biophys. J. 2007, 93, 1452–1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Willot, J.D.; Murdoch, T.J.; Humphreys, B.A.; Edmondson, S.; Webber, G.B.; Wanless, E.J. Critical salt effects in the swelling behavior of a weak polybasic brush. Langmuir 2014, 30, 1827–1836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Beer, S.; Kutnyanszky, E.; Schön, P.M.; Vancso, G.J.; Müser, M.H. Solvent-induced immiscibility of polymer brushes eliminates dissipation channels. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lappala, A.; Mendiratta, S.; Terentjev, E.M. Arrested spinodal decomposition in polymer brush collapsing in poor solvent. Macromolecules 2015, 48, 1894–1900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marko, J.F. Polymer brush in contact with a mixture of solvents. Macromolecules 1993, 26, 313–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karim, A.; Satija, S.K.; Douglas, J.F.; Ankner, J.F.; Fetters, L.J. Neutron reflectivity study of the density profile of a model end-grafted polymer brush: Influence of solvent quality. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1994, 73, 3407–3410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Higaki, Y.; Kobayashi, M.; Murakami, D.; Takahara, A. Anti-fouling behavior of polymer brush immobilizied surfaces. Polym. J. 2016, 85. [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi, M.; Terayama, Y.; Yamaguchi, H.; Terada, M.; Murakami, D.; Ishihara, K.; Takahara, A. Wettability and antifouling behavior on the surface of superhydrophilic polymer brushes. Langmuir 2012, 28, 7212–7222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, S.; Janczewski, D.; Zhu, X.; Quintana, R.; He, T.; Neoh, K.G. Surface charge control for zwitterionic polymer brushes: Tailoring surface properties to antifouling applications. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2015, 452, 43–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lau, K.H.A.; Sileika, T.S.; Park, S.H.; Sousa, A.M.L.; Burch, P.; Szleifer, I.; Messersmith, P.B. Molecular design of antifouling polymer brushes using sequence-specific peptoids. Adv. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 2, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diamanti, S.; Arifuzzaman, S.; Genzer, J.; Vaia, R.A. Tuning gold nanoparticle - poly(2-hydroxyethyl methacrylate) brush interactions: From reversible swelling to capture and release. ACSNano 2009, 3, 807–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Motornov, M.; Tam, T.K.; Pita, M.; Tokarev, I.; Katz, E.; Minko, S. Switchable selectivity for gating ion transport with mixed polyelectrolyte brushes: Approaching ‘smart’ drug delivery systems. Nanotechnology 2009, 20, 434006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bajpai, A.K.; Shukla, S.K.; Bhanu, S.; Kankane, S. Responsive polymers in controlled drug delivery. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2008, 33, 1088–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kost, J.; Langer, R. Responsive polymeric delivery systems. Adv. Drug Delivery Rev. 2001, 46, 125–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmaljohann, D. Thermo- and pH-responsive polymers in drug delivery. Adv. Drug Delivery Rev. 2006, 58, 1655–1670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferhan, A.R.; Guo, L.; Zhou, X.; Chen, P.; Hong, S.; Kim, D.-H. Solid-phase colorimetric sensor based on gold nanoparticle-loaded polymer brushes: Lead detection as a case study. Anal. Chem. 2013, 85, 4094–4099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeh, Y.-C.; Creran, B.; Rotello, V.M. Gold nanoparticles: Preparation, properties, and applications in bionanotechnology. Nanoscale 2012, 4, 187–1880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Templeton, A.C.; Pietron, J.J.; Murray, R.W.; Mulvaney, P. Solvent refractive index and core charge influences on the surface plasmon absorbance of alkanethiolate monolayer-protected gold clusters. J. Phys. Chem. B 2000, 104, 564–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rechberger, W.; Hohenau, A.; Leitner, A.; Krenn, J.R.; Lamprecht, B.; Aussenegg, F.R. Optical properties of two interacting gold nanoparticles. Opt. Commun. 2003, 220, 137–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christau, S.; Thurandt, S.; Zuleyha, Y.; von Klitzing, R. Stimuli-responsive polyelectrolyte brushes as a matrix for the attachment of gold nanoparticles: The effect of brush thickness on particle distribution. Polymers 2014, 6, 1877–1896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christau, S.; Möller, T.; Zuleyha, Y.; Genzer, J.; von Klitzing, R. Brush/Gold nanoparticle hybrids: Effect of grafting density on the particle uptake and distribution within weak polyelectrolyte brushes. Langmuir 2014, 30, 13033–13041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pileni, M.P. Self-assemblies of nanocrystals: fabrication and collective properties. Appl. Sur. Sci. 2001, 171, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paczesny, J.; Wojcik, M.; Sozanski, K.; Nikiforov, K.; Tschierske, C.; Lehmann, A.; Gorecka, E.; Mieczkowski, J.; Holyst, R. Self-assembly of Gold nanoparticles into 2D arrays induced by bolaamphiphilic ligands. J. Phys. Chem. C 2013, 117, 24056–24062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhat, R.R.; Genzer, J. Combinatorial study of nanoparticle dispersion in surface-grafted macromolecular gradients. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2006, 252, 2549–2554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sperling, R.A.; Parak, W.J. Surface modification, functionalization and bioconjugation of colloidal inorganic nanoparticles. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. A 2010, 368, 1333–1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patten, T.E.; Xia, J.; Abernathy, T.; Matyjaszweski, K. Polymers with very low polydispersities from atom transfer radical polymerization. Science 1996, 272, 866–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matyjaszewski, K.; Hongchen, D.; Jakubowski, W.; Pietrasik, J.; Kusumo, A. Grafting from surfaces for ‘everyone’: ARGET ATRP in the presence of air. Langmuir 2007, 23, 4528–4531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laurent, P.; Souharce, G.; Duchet-Rumeau, J.; Portinha, D.; Charlot, A. ‘Pancake’ vs. brush-like regime of quarternizable polymer grafts: An efficient tool for nano-templating polyelectrolyte self-assembly. Soft Matter 2012, 8, 715–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moya, S.E.; Azzaroni, O.; Kelby, T.; Donath, E.; Huck, W.T.S. Explanation for the apparent absence of collapse of polyelectrolyte brushes in the presence of bulky ions. J. Phys. Chem. B 2007, 111, 7034–7040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ivanov, M.R.; Bednar, H.R.; Haes, A.J. Investigations of the mechanism of Gold nanoparticle stability and surface functionalization in capillary electrophoresis. ACS Nano 2009, 3, 386–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reincke, F.; Kegel, W.K.; Zhang, H.; Nolte, M.; Wang, D.; Vanmaekelbergh, D.; Ohwald, H.M.; Möhwald, H. Understanding the self-assembly of charged nanoparticles at the water/oil interface. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2006, 8, 3828–3835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Üzüm, C.; Hellwig, J.; Madaboosi, N.; Volodkin, D.; von Klitzing, R. Growth behaviour and mechanical properties of PLL/HA multilayer films studied by AFM. Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2012, 3, 778–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yenice, Z.; Schön, S.; Bildirir, H.; Genzer, J.; von Klitzing, R. Thermoresponsive PDMAEMA brushes: Effect of Gold nanoparticle deposition. J. Phys. Chem. B 2015, 119, 10348–10358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghosh, S.K.; Pal, T. Interparticle coupling effect on the surface plasmon resonance of Gold nanoparticles: from theory to applications. Chem. Rev. 2007, 107, 4797–4862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Atwater, M.; Wang, J.; Huo, Q. Extinction coefficient of gold nanoparticles with different sizes and different capping ligands. Colloids Surf. B 2007, 58, 3–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhat, R.R.; Tmlinson, M.R.; Wu, T.; Genzer, J. Surface-grafted polymer gradients: Formation, characterization, and applications. Adv. Polym. Sci. 2006, 198, 51–124. [Google Scholar]
- Reinhard, M.B.; Siu, M.; Agarwal, H.; Alivisatos, A.P.; Liphardt, J. Calibration of dynamic molecular rulers based on plasmon coupling between Gold nanoparticles. Nano Lett. 2005, 5, 2246–2252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kizhakkedathu, J.N.; Janzen, J.; Le, Y.; Kainthan, R.K.; Brooks, D.E. Poly(oligo(ethylene glycol)acrylamide) brushes by surface initiated polymerization: Effect of macromonomer chain length on brush growth and protein adsorption from blood plasma. Langmuir 2009, 25, 3794–3801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bain, E.D.; Dawes, K.; Özcam, A.E.; Hu, X.; Gorman, C.B.; Srogl, J.; Genzer, J. Surface-initiated polymerization by means of novel, stable, non-ester-based radical initiator. Macromolecules 2012, 45, 3802–3815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klok, H.-A.; Genzer, J. Expanding the polymer mechanochemistry toolbox through surface-initiated polymerization. ACS Macro Lett. 2015, 4, 636–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, P.; Genzer, J.; Szleifer, I. Phase behavior and charge regulation of weak polyelectrolyte grafted layers. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2007, 98, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, M.; Chen, J.; Li, Z.-Y.; Au, L.; Hartland, G.V.; Li, X.; Marquez, M.; Xia, Y. Gold nanostructures: Engineering their plasmonic properties for biomedical applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2006, 35, 1084–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, I.-I.S.; Pan, Yi.; Mott, D.; Ouyang, J.; Njoki, P.N.; Luo, J.; Zhou, S.; Zhong, C.-J. Assembly of gold nanoparticles mediated by multifunctional fullerenes. Langmuir 2007, 23, 10715–10724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hinterwirth, H.; Kappel, S.; Waitz, T.; Prohaska, T.; Lindner, W.; Lämmerhofer, M. Quantifying thiol ligand Density of self-assembled monolayers on Gold nanoparticles by inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry. ACS Nano 2013, 7, 1129–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]










| Layer | n | k | Thickness (nm) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| continuum | air/water | 1/1.332 | 0 | |
| 1. layer | brush | fit | 0 | fit |
| 2. layer | SiOx | 1.500 | 0 | 1.5 |
| continuum | Si | 3.885 | −0.020 |
| Sample | Thickness (nm) |
|---|---|
| 1 | 28.04 ± 0.57 |
| 2 | 29.24 ± 0.32 |
| 3 | 27.11 ± 0.80 |
| 4 | 27.84 ± 0.77 |
| Method | Thickness |
|---|---|
| Ellipsometry | 148.12 ± 6.42 |
| AFM full-indentation | 156.43 ± 9.44 |
| Neat PMETAC brush thickness (nm) | Composite at pH 4 thickness (nm) | Composite at pH 6 thickness (nm) | Composite at pH 8 thickness (nm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 156.43 ± 9.44 | 162.97 ± 6.03 | 170.68 ± 9.27 | 178.35 ± 11.77 |
| Incubation medium | Absorbance before incubation | c before incubation (nmol/mL) | Absorbance after incubation | c after incubation (nmol/mL) | Δc (nmol/mL) | ΔNtotal (Particles) | Particle number density (Particles/nm3) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| at pH 4 | 0.574 ± 0.018 | 0.234 | 0.011 | 6.62 × 1013 | 0.0011 | ||
| at pH 6 | 0.602 ± 0.006 | 0.245 | 0.455 ± 0.019 | 0.185 | 0.059 | 3.55 × 1014 | 0.0059 |
| at pH 8 | 0.399 ± 0.021 | 0.162 | 0.083 | 4.98 × 1014 | 0.0083 |
© 2016 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons by Attribution (CC-BY) license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kesal, D.; Christau, S.; Krause, P.; Möller, T.; Von Klitzing, R. Uptake of pH-Sensitive Gold Nanoparticles in Strong Polyelectrolyte Brushes. Polymers 2016, 8, 134. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym8040134
Kesal D, Christau S, Krause P, Möller T, Von Klitzing R. Uptake of pH-Sensitive Gold Nanoparticles in Strong Polyelectrolyte Brushes. Polymers. 2016; 8(4):134. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym8040134
Chicago/Turabian StyleKesal, Dikran, Stephanie Christau, Patrick Krause, Tim Möller, and Regine Von Klitzing. 2016. "Uptake of pH-Sensitive Gold Nanoparticles in Strong Polyelectrolyte Brushes" Polymers 8, no. 4: 134. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym8040134
APA StyleKesal, D., Christau, S., Krause, P., Möller, T., & Von Klitzing, R. (2016). Uptake of pH-Sensitive Gold Nanoparticles in Strong Polyelectrolyte Brushes. Polymers, 8(4), 134. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym8040134